Transfer Learning Applied to Characteristic Prediction of Injection Molded Products
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Relevant Technical Research
2.1. Artificial Neural Networks (ANN)
2.1.1. Backpropagation Neural Network (BPNN)
2.1.2. Training and Learning Process
2.2. Transfer Learning (TL)
2.3. Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE)
2.4. The “Random Shuffle” Method
2.5. Data Normalization
2.6. The Taguchi Method
2.6.1. Quality Characteristics
2.6.2. Definition and Selection of Experimental Factors
3. Using CAE Data to Study Transfer Learning among Different Models
3.1. Network Training of the Circular Flat Model
3.1.1. Training Materials
3.1.2. Hyperparameter Settings
3.2. Transfer Learning of the Square Plate Model
3.2.1. Training Materials
3.2.2. Hyperparameter Tuning
3.3. Comparison of Transfer Learning Results among Different Products
3.3.1. Training Results of the Round Plate Model
3.3.2. Training Results for the Square Flat Model
3.3.3. Transfer Learning Results for the Square Tablet Model
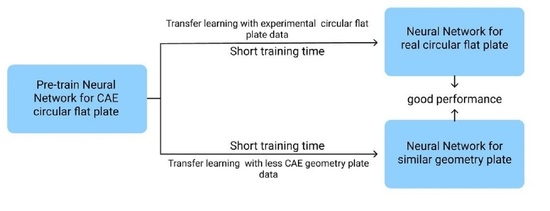
4. Prediction of Molding Using the Network Trained via CAE Data and Transferred for Actual Injection
4.1. Transfer Learning between Virtual and Actual Reality
4.2. Round Flat CAE Data Pretraining
4.2.1. Training Data
4.2.2. Hyperparameter Tuning
4.2.3. Hyperparameter Optimization
4.3. Transfer Learning for Injection Molding
4.3.1. Training Data
4.3.2. Hyperparameter Settings
4.4. Comparison of Simulation and Actual Transfer Learning Results, CAE Data Training Results for the Circular Flat Model
4.4.1. Training Results of Experimental Data of the Circular Flat Model
4.4.2. The Results of the Transfer Learning Trials Data for the Round Plate Model
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Discussion on Random Shuffle Method’s Effect
5.2. Discussion on the Effect of Transfer Learning
6. Conclusions
6.1. Artificial Neural Network Applications
- Random shuffle can reduce the error rate and standard deviation. In this study, the data volume was 80% and the learning rate was 0.1 for random shuffle pretraining.
- The Taguchi method can effectively optimize the hyperparameters of artificial neural networks, and after ANOVA analysis, optimal solutions can be achieved.
- By monitoring the loss value of the training and verification data simultaneously, it can be judged whether there is overfitting. If the loss curve of the training data continues to decline while diverging ever further from the loss curve of the verification data, it may be that the training time is too long and overfitting is caused. If the two loss curves can no longer be optimized, there are two possibilities: one is that the learning rate is not suitable, which makes it impossible to get rid of the local minimum. The other is that the content of the training data is more complex, and the number of neurons is insufficient. Optimization has bottlenecks.
6.2. Transfer Learning Applications
- Since the cost of injection data acquisition is quite high, the transfer learning can predict with less data under some specific conditions. At the same time, actual experiments can prove that transfer learning has better effects in similar work.
- From the weight and bias distributions before and after transfer learning, it can be found that retraining will not significantly change the distribution; however, a slight change is possible. Therefore, the original network selected will determine the results of transfer learning.
- If the set of training data is too small to contain enough effective content, the fluctuation range of weight and bias will be smaller. In this state, adding neurons will not improve the training error value.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosa, J.L.; Robin, A.; Silva, M.B.; Baldan, C.A.; Peres, M.P. Electrodeposition of Copper on Titanium Wires: Taguchi Experimental Design Approach. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marins, N.H.; Mello, F.B.; Silva, R.M.; Ogliari, F. Statistical Approach to Analyze the Warpage, Shrinkage and Mechanical Strength of Injection Molded Parts. Polym. Process. 2016, 31, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hifsa, P.; Mohammad, S.M.; Abdel-Hamid, I.M. Optimization of Injection Molding Parameters for HDPE/TiO2 Nanocomposites Fabrication with Multiple Performance Characteristics Using the Taguchi Method and Grey Relational Analysis. Materials 2016, 9, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, J.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, B. Optimum tooling design for resin transfer molding with virtual manufacturing and artificial intelligence. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2001, 32, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenig, S.; Ben David, A.; Omer, M.; Sadeh, A. Control of Properties in Injection Molding by Neural Networks. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2001, 14, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denni, K. An Integrated Optimization System for Plastic Injection Molding Using Taguchi Method, BPNN, GA, and Hybrid PSO-GA. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Technology Management, Chung Hua University, Hsinchu City, Taiwan, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, T.S.; Suzuki, T.; Bae, W.B.; Uehara, Y.; Ohmori, H. Application of Neural Network and Computer Simulation to Improve Surface Profile of Injection Molding Optic Lens. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2005, 70, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, C.E.; Rios, M.C.; Castro, J.M.; Lilly, B. Multiple Criteria Optimization with Variability Considerations in Injection Molding. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2007, 47, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Wang, L.; Li, Q. Optimization of Injection Molding Process Parameters Using Combination of Artificial Neural Network and Genetic Algorithm Method. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 183, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirigul, A. Reducing Shrinkage in Injection Moldings Via the Taguchi, ANOVA and Neural Network Methods. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Mao, H.; Hua, L.; Guo, W.; Shu, M. Back Propagation Neural Network Modeling for Warpage Prediction and Optimization of Plastic Products During Injection Molding. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 1844–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberto, T.; Ramón, A. Machine learning algorithms for quality control in plastic molding industry. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 18th Conference on Emerging Technologies & Factory Automation (ETFA), Cagliari, Italy, 10–13 September 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Yu, D. Deep Learning: Methods and Applications; Microsoft Research; Microsoft: Redmond, WA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jong, W.R.; Huang, Y.M.; Lin, Y.Z.; Chen, S.C.; Chen, Y.W. Integrating Taguchi method and artificial neural network to explore machine learning of computer aided engineering. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 2020, 43, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinno, J.P.; Qiang, Y. A Survey on Transfer Learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2009, 22, 1345–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, C.C.; Ueli, M.; Jürgen, S. Transfer learning for Latin and Chinese characters with Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Brisbane, Australia, 10–15 June 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.T.; Li, J.; Yu, D.; Deng, L.; Gong, Y. Cross-Language Knowledge Transfer Using Multilingual Deep Neural Network with Shared Hidden Layers. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–31 May 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiahuan, L.; Fei, G.; Huang, G.; Maoyuan, L.; Yun, Z.; Huamin, Z. Defect detection of injection molding products on small datasets using transfer learning. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 70, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yannik, L.; Christian, H. Induced network-based transfer learning in injection molding for process modelling and optimization with artificial neural networks. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 112, 3501–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.C.; Roth, H.R.; Gao, M.; Lu, L.; Xu, Z.; Nogues, I.; Yao, J.; Mollura, D.; Summer, R.M. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Computer-Aided Detection: CNN Architectures, Dataset Characteristics and Transfer Learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasan, T.; Alexandro, G.; Julian, H.; Thomas, T.; Chrisitan, H.; Tobias, M. Transfer-Learning Bridging the Gap between Real and Simulation Data for Machine Learning in Injection Molding. In Proceedings of the 51st CIRP Conference on Manufacturing Systems, Stockholm, Sweden, 16–18 May 2018; Volume 72, pp. 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, T.; Alexandro, G.; Tobias, M. Industrial Transfer Learning: Boosting Machine Learning in Production. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 17th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Helsinki, Finland, 22–25 July 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

























| Factor | Default | Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Melt Temperature (°C) | 210 | 185 | 207.5 | 230 |
| Packing Time (sec) | 4.5 | 3 | 6 | 9 |
| Packing Pressure (MPa) | 135 | 100 | 130 | 160 |
| Injection Speed (mm/sec) | 70 | 50 | 65 | 80 |
| Mold Temperature (°C) | 50 | 40 | 55 | 70 |
| Total Processed Data | 243 | |||
| No. | Melt Temp. (°C) | Packing Time (sec) | Packing Pressure (MPa) | Injection Speed (mm/sec) | Mold Temp. (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 195 | 4 | 110 | 55 | 45 |
| 2 | 195 | 5 | 120 | 60 | 50 |
| 3 | 195 | 7 | 140 | 70 | 60 |
| 4 | 195 | 8 | 150 | 75 | 65 |
| 5 | 205 | 4 | 120 | 70 | 65 |
| 6 | 205 | 5 | 110 | 75 | 60 |
| 7 | 205 | 7 | 150 | 55 | 50 |
| 8 | 205 | 8 | 140 | 60 | 45 |
| 9 | 210 | 4 | 140 | 75 | 50 |
| 10 | 210 | 5 | 150 | 70 | 45 |
| 11 | 210 | 7 | 110 | 60 | 65 |
| 12 | 210 | 8 | 120 | 55 | 60 |
| 13 | 220 | 4 | 150 | 60 | 60 |
| 14 | 220 | 5 | 140 | 55 | 65 |
| 15 | 220 | 7 | 120 | 75 | 45 |
| 16 | 220 | 8 | 110 | 70 | 50 |
| Parameters | Value | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epoch | 20,000 | Learning Rate | 0.1 |
| Hidden Layer 1 | 7 | Initial Weight | Random |
| Hidden Layer 2 | 3 | Initial Bias | Random |
| Optimized Method | SGD | Activation Function | Sigmoid |
| No. | Melt Temp(°C) | Packing Time (sec) | Packing Pressure (MPa) | Injection Speed (mm/sec) | Mold Temp. (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 185 | 3 | 100 | 50 | 40 |
| 2 | 185 | 3 | 100 | 50 | 55 |
| 3 | 185 | 3 | 100 | 50 | 70 |
| 4 | 185 | 6 | 130 | 65 | 40 |
| 5 | 185 | 6 | 130 | 65 | 55 |
| 6 | 185 | 6 | 130 | 65 | 70 |
| 7 | 185 | 9 | 160 | 80 | 40 |
| 8 | 185 | 9 | 160 | 80 | 55 |
| 9 | 185 | 9 | 160 | 80 | 70 |
| 10 | 207.5 | 3 | 130 | 80 | 40 |
| 11 | 207.5 | 3 | 130 | 80 | 55 |
| 12 | 207.5 | 3 | 130 | 80 | 70 |
| 13 | 207.5 | 6 | 160 | 50 | 40 |
| 14 | 207.5 | 6 | 160 | 50 | 55 |
| 15 | 207.5 | 6 | 160 | 50 | 70 |
| 16 | 207.5 | 9 | 100 | 65 | 40 |
| 17 | 207.5 | 9 | 100 | 65 | 55 |
| 18 | 207.5 | 9 | 100 | 65 | 70 |
| 19 | 230 | 3 | 160 | 65 | 40 |
| 20 | 230 | 3 | 160 | 65 | 55 |
| 21 | 230 | 3 | 160 | 65 | 70 |
| 22 | 230 | 6 | 100 | 80 | 40 |
| 23 | 230 | 6 | 100 | 80 | 55 |
| 24 | 230 | 6 | 100 | 80 | 70 |
| 25 | 230 | 9 | 130 | 50 | 40 |
| 26 | 230 | 9 | 130 | 50 | 55 |
| 27 | 230 | 9 | 130 | 50 | 70 |
| No. | Melt Temp. (°C) | Packing Time (sec) | Packing Pressure (MPa) | Injection Speed (mm/sec) | Mold Temp. (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 195 | 4 | 110 | 55 | 45 |
| 2 | 195 | 5 | 120 | 60 | 50 |
| 3 | 195 | 7 | 140 | 70 | 60 |
| 4 | 195 | 8 | 150 | 75 | 65 |
| 5 | 205 | 4 | 120 | 70 | 65 |
| 6 | 205 | 5 | 110 | 75 | 60 |
| 7 | 205 | 7 | 150 | 55 | 50 |
| 8 | 205 | 8 | 140 | 60 | 45 |
| 9 | 210 | 4 | 140 | 75 | 50 |
| 10 | 210 | 5 | 150 | 70 | 45 |
| 11 | 210 | 7 | 110 | 60 | 65 |
| 12 | 210 | 8 | 120 | 55 | 60 |
| 13 | 220 | 4 | 150 | 60 | 60 |
| 14 | 220 | 5 | 140 | 55 | 65 |
| 15 | 220 | 7 | 120 | 75 | 45 |
| 16 | 220 | 8 | 110 | 70 | 50 |
| Parameters | Value | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epoch | 20,000 | Learning Rate | 0.1 |
| Hidden Layer 1 | 7 | Initial Weight | Transfer |
| Hidden Layer 2 | 3 | Initial Bias | Transfer |
| Optimized Method | SGD | Activation Function | Sigmoid |
| Circle Plate Result (CAE-243) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EOF Pressure | Cooling Time | Z-Axis Warpage | X-Axis Shrinkage | Y-Axis Shrinkage | ||
| Full Data | AVG (%) | 12.67 | 8.78 | 29.84 | 14.80 | 13.36 |
| STD | 5.29 | 4.48 | 45.46 | 18.33 | 11.71 | |
| Random Shuffle | AVG (%) | 11.22 | 8.61 | 19.89 | 12.83 | 10.72 |
| STD | 5.22 | 4.42 | 26.45 | 13.91 | 7.54 | |
| Difference | AVG (%) | 1.45 | 0.16 | 9.94 | 2.06 | 2.63 |
| STD | 0.07 | 0.05 | 19.01 | 4.42 | 4.17 | |
| Square Plate Result (CAE-27) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EOF Pressure | Cooling Time | Z-Axis Warpage | X-Axis Shrinkage | Y-Axis Shrinkage | ||
| Full Data | AVG (%) | 4.85 | 10.98 | 59.61 | 17.14 | 20.64 |
| STD | 2.18 | 7.43 | 66.65 | 22.05 | 18.43 | |
| Random Shuffle | AVG (%) | 3.91 | 10.16 | 56.25 | 15.39 | 18.54 |
| STD | 1.90 | 6.40 | 60.58 | 18.66 | 17.63 | |
| Difference | AVG (%) | 0.94 | 0.82 | 3.36 | 1.75 | 2.10 |
| STD | 0.28 | 1.03 | 6.07 | 3.39 | 0.81 | |
| Square Plate with Transfer Learning Result (CAE-27) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EOF Pressure | Cooling Time | Z-Axis Warpage | X-Axis Shrinkage | Y-Axis Shrinkage | ||
| Full Data | AVG (%) | 3.44 | 8.69 | 79.96 | 15.02 | 18.15 |
| STD | 1.83 | 5.36 | 70.34 | 10.85 | 12.18 | |
| Random Shuffle | AVG (%) | 2.77 | 8.48 | 31.05 | 11.81 | 16.46 |
| STD | 1.80 | 4.94 | 17.56 | 8.97 | 11.19 | |
| Difference | AVG (%) | 0.67 | 0.22 | 48.91 | 3.22 | 1.69 |
| STD | 0.03 | 0.42 | 52.78 | 1.89 | 0.99 | |
| Factor | Default | Level | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Melt Temperature (°C) | 210 | 185 | 200 | 215 | 230 |
| Packing Time (sec) | 4.5 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 |
| Packing Pressure (MPa) | 135 | 100 | 120 | 140 | 160 |
| Injection Speed (mm/sec) | 70 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 |
| Mold Temperature (°C) | 50 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 |
| Total Process Data | 1024 | ||||
| No. | Melt Temp. (°C) | Packing Time (sec) | Packing Pressure (MPa) | Injection Speed (mm/sec) | Mold Temp. (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 194 | 4.2 | 112 | 56 | 46 |
| 2 | 194 | 5.4 | 124 | 62 | 52 |
| 3 | 194 | 6.6 | 136 | 68 | 58 |
| 4 | 194 | 7.8 | 148 | 74 | 64 |
| 5 | 203 | 4.2 | 124 | 68 | 64 |
| 6 | 203 | 5.4 | 112 | 74 | 58 |
| 7 | 203 | 6.6 | 148 | 56 | 52 |
| 8 | 203 | 7.8 | 136 | 62 | 46 |
| 9 | 212 | 4.2 | 136 | 74 | 52 |
| 10 | 212 | 5.4 | 148 | 68 | 46 |
| 11 | 212 | 6.6 | 112 | 62 | 64 |
| 12 | 212 | 7.8 | 124 | 56 | 58 |
| 13 | 221 | 4.2 | 148 | 64 | 58 |
| 14 | 221 | 5.4 | 136 | 56 | 64 |
| 15 | 221 | 6.6 | 124 | 74 | 46 |
| 16 | 221 | 7.8 | 112 | 68 | 52 |
| Factor | Parameters | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Training Cycle | 10,000 | 20,000 | 30,000 |
| B | Learning Rate | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.3 |
| C | Hidden Layer 1 | 7 | 9 | 11 |
| D | Hidden Layer 2 | 7 | 9 | 11 |
| No | A | B | C | D | Training Cycle | Learning Rate | Hidden Layer 1 | Hidden Layer 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 10,000 | 0.05 | 7 | 7 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 10,000 | 0.1 | 9 | 9 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 10,000 | 0.3 | 11 | 11 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 20,000 | 0.05 | 9 | 11 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 20,000 | 0.1 | 11 | 7 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 20,000 | 0.3 | 7 | 9 |
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 30,000 | 0.05 | 11 | 9 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 30,000 | 0.1 | 7 | 11 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 30,000 | 0.3 | 9 | 7 |
| No | A | B | C | D | EOF Pressure | Cooling Time | Z−Axis Warpage | X−Axis Radius | Y−Axis Radius | S/N Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5.04 | 3.21 | 7.10 | 2.22 | 1.99 | −17.03 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4.90 | 3.20 | 7.31 | 2.28 | 2.18 | −17.28 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4.97 | 3.55 | 8.10 | 2.28 | 2.22 | −18.17 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4.98 | 1.36 | 5.50 | 2.17 | 2.56 | −14.81 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 5.10 | 1.72 | 5.22 | 2.04 | 2.20 | −14.35 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 4.78 | 3.42 | 6.78 | 2.11 | 2.38 | −16.62 |
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 5.04 | 1.32 | 5.85 | 1.98 | 1.96 | −15.34 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 5.18 | 2.06 | 6.39 | 1.73 | 2.40 | −16.11 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 4.94 | 1.13 | 6.26 | 2.08 | 2.09 | −15.93 |
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LEVEL 1 | −17.49 | −15.73 | −16.59 | −15.77 |
| LEVEL 2 | −15.26 | −15.91 | −16.41 | −16.41 |
| LEVEL 3 | −15.79 | −16.91 | −15.95 | −16.36 |
| Training Cycle | Learning Ratio | Layer 1 | Layer 2 | Z-axis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No.5 | 20,000 | 0.1 | 11 | 7 | 5.22% |
| Op1. | 20,000 | 0.05 | 11 | 7 | 3.61% |
| Op2. | 20,000 | 0.03 | 13 | 5 | 4.88% |
| Parameters | Value | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epoch | 20,000 | Learning Rate | 0.05 |
| Hidden Layer 1 | 11 | Initial Weight | Random |
| Hidden Layer 2 | 7 | Initial Bias | Random |
| Optimized Method | SGD | Activation Function | Sigmoid |
| No. | Melt Temp. (°C) | Packing Time (sec) | Packing Pressure (MPa) | Injection Speed (mm/sec) | Mold Temp. (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 185 | 3 | 100 | 50 | 40 |
| 2 | 185 | 5 | 113 | 60 | 50 |
| 3 | 185 | 7 | 126 | 70 | 60 |
| 4 | 185 | 9 | 139 | 80 | 70 |
| 5 | 200 | 3 | 113 | 70 | 70 |
| 6 | 200 | 5 | 100 | 80 | 60 |
| 7 | 200 | 7 | 139 | 50 | 50 |
| 8 | 200 | 9 | 126 | 60 | 40 |
| 9 | 215 | 3 | 126 | 80 | 50 |
| 10 | 215 | 5 | 139 | 70 | 40 |
| 11 | 215 | 7 | 100 | 60 | 70 |
| 12 | 215 | 9 | 113 | 50 | 60 |
| 13 | 230 | 3 | 139 | 60 | 60 |
| 14 | 230 | 5 | 126 | 50 | 70 |
| 15 | 230 | 7 | 113 | 80 | 40 |
| 16 | 230 | 9 | 100 | 70 | 50 |
| No. | Melt Temp. (°C) | Packing Time (sec) | Packing Pressure (MPa) | Injection Speed (mm/sec) | Mold Temp. (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 194 | 4.2 | 109 | 56 | 46 |
| 2 | 194 | 5.4 | 118 | 62 | 52 |
| 3 | 194 | 6.6 | 127 | 68 | 58 |
| 4 | 194 | 7.8 | 136 | 74 | 64 |
| 5 | 203 | 4.2 | 118 | 68 | 64 |
| 6 | 203 | 5.4 | 109 | 74 | 58 |
| 7 | 203 | 6.6 | 136 | 56 | 52 |
| 8 | 203 | 7.8 | 127 | 62 | 46 |
| 9 | 212 | 4.2 | 127 | 74 | 52 |
| 10 | 212 | 5.4 | 136 | 68 | 46 |
| 11 | 212 | 6.6 | 109 | 62 | 64 |
| 12 | 212 | 7.8 | 118 | 56 | 58 |
| 13 | 221 | 4.2 | 136 | 62 | 58 |
| 14 | 221 | 5.4 | 127 | 56 | 64 |
| 15 | 221 | 6.6 | 118 | 74 | 46 |
| 16 | 221 | 7.8 | 109 | 68 | 52 |
| Parameters | Value | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epoch | 20,000 | Learning Rate | 0.05 |
| Hidden Layer 1 | 11 | Initial Weight | Transfer |
| Hidden Layer 2 | 7 | Initial Bias | Transfer |
| Optimized Method | SGD | Activation Function | Sigmoid |
| Circle Plate Result (CAE-1024) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EOF Pressure | Cooling Time | Z-Axis Warpage | X-Axis Shrinkage | Y-Axis Shrinkage | ||
| Full Data | AVG (%) | 4.01 | 1.84 | 8.50 | 3.48 | 2.73 |
| STD | 2.61 | 1.35 | 5.21 | 2.78 | 2.23 | |
| Random Shuffle | AVG (%) | 3.99 | 1.27 | 3.61 | 1.34 | 1.89 |
| STD | 2.01 | 0.92 | 2.87 | 1.01 | 1.10 | |
| Difference | AVG (%) | 0.02 | 0.57 | 4.9 | 2.14 | 0.84 |
| STD | 0.60 | 0.43 | 2.34 | 1.77 | 1.13 | |
| Circle Plate Result (EXP-16) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EOF Pressure | Cooling Time | Z-Axis Warpage | X-Axis Shrinkage | Y-Axis Shrinkage | ||
| Full Data | AVG (%) | 15.03 | 8.31 | 9.26 | 15.03 | 8.31 |
| STD | 8.58 | 13.34 | 15.73 | 8.58 | 13.34 | |
| Random Shuffle | AVG (%) | 13.61 | 7.36 | 7.45 | 13.61 | 7.36 |
| STD | 6.62 | 9.33 | 8.63 | 6.62 | 9.33 | |
| Difference | AVG (%) | 1.42 | 0.95 | 1.81 | 1.42 | 0.95 |
| STD | 4.96 | 4.01 | 7.10 | 4.96 | 4.01 | |
| Circle Plate Result (EXP-16) | with Transfer Learning | without Transfer Learning | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EOF Pressure | X-Axis Shrinkage | Y-Axis Shrinkage | EOF Pressure | X-Axis Shrinkage | Y-Axis Shrinkage | ||
| Full Data | AVG (%) | 5.88 | 2.56 | 3.96 | 15.03 | 8.31 | 9.26 |
| STD | 4.71 | 2.26 | 3.97 | 8.58 | 13.34 | 15.73 | |
| Random Shuffle | AVG (%) | 5.56 | 2.35 | 3.91 | 13.61 | 7.36 | 7.45 |
| STD | 4.20 | 2.19 | 3.42 | 6.62 | 9.33 | 8.63 | |
| Difference | AVG (%) | 0.32 | 0.21 | 0.05 | 1.42 | 0.95 | 1.81 |
| STD | 0.51 | 0.07 | 0.55 | 4.96 | 4.01 | 7.10 | |
| Result of Square Plate (CAE-27) & Circle Plate (EXP-16) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EOF Pressure | Cooling Time | Z-Axis Warpage | X-Axis Shrinkage | Y-Axis Shrinkage | ||
| Square Plate | AVG (%) | 3.91 | 10.16 | 56.25 | 15.39 | 18.54 |
| STD | 1.90 | 6.40 | 60.58 | 18.66 | 17.63 | |
| Circle Plate | AVG (%) | 13.61 | 7.36 | 7.45 | ||
| STD | 6.62 | 9.33 | 8.63 | |||
| Result of Square Plate (CAE-27) & Circle Plate (EXP-16) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EOF Pressure | Cooling Time | Z-Axis Warpage | X-Axis Shrinkage | Y-Axis Shrinkage | ||
| Square Plate | AVG (%) | 3.91 | 10.16 | 56.25 | 15.39 | 18.54 |
| STD | 1.90 | 6.40 | 60.58 | 18.66 | 17.63 | |
| Square Plate (TL) | AVG (%) | 2.77 | 8.48 | 31.05 | 11.81 | 16.46 |
| STD | 1.80 | 4.94 | 17.56 | 8.97 | 11.19 | |
| Circle Plate | AVG (%) | 13.61 | 7.36 | 7.45 | ||
| STD | 6.62 | 9.33 | 8.63 | |||
| Circle Plate(TL) | AVG (%) | 5.56 | 2.35 | 3.91 | ||
| STD | 4.20 | 2.19 | 3.42 | |||
| Input to Hidden Layer 1 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | H101 | H102 | H103 | H104 | H105 | H106 | H107 | H108 | H109 | H110 | H111 |
| I01 | −1.1380 | −1.3887 | −0.2855 | −1.4546 | −4.7642 | 2.0215 | 0.5312 | 2.7493 | 3.0976 | −2.0409 | 0.3560 |
| I02 | 3.7457 | 0.6322 | 1.7630 | 1.2978 | 0.0940 | 0.0474 | 0.1391 | 0.4969 | −0.0035 | 5.3307 | 1.1453 |
| I03 | −0.0767 | 0.4169 | 0.2950 | −1.4659 | 0.2065 | 0.0649 | 0.1480 | −0.0729 | −0.0716 | −1.5080 | 0.6472 |
| I04 | 0.4478 | 0.6541 | −0.3143 | 0.0424 | −1.1876 | 4.3344 | −0.0358 | 0.6161 | −1.3805 | −0.1439 | 0.2278 |
| I05 | 0.1851 | −0.0521 | −0.4043 | −1.0403 | −0.2708 | 0.3893 | 3.1411 | −1.1837 | −0.1945 | −1.4266 | 1.2472 |
| Bias | 0.4616 | −0.4964 | −0.3441 | −0.1590 | −0.4003 | 0.4831 | −4.2604 | 0.7888 | −0.8406 | 0.5141 | −0.5477 |
| Input to Hidden Layer 2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | H201 | H202 | H203 | H204 | H205 | H206 | H207 |
| H101 | 0.4846 | −0.2906 | −0.4810 | 0.0960 | 4.0143 | 0.8524 | −0.7530 |
| H102 | 0.7461 | 0.3182 | −0.0355 | −0.2350 | 0.9976 | 1.7191 | −0.8385 |
| H103 | −0.2167 | −0.7549 | 0.3227 | −1.3992 | 0.0234 | 0.5743 | −1.3188 |
| H104 | −0.2193 | 1.0535 | 1.0047 | 0.3022 | −1.0671 | −0.8595 | 1.7802 |
| H105 | 0.1245 | 0.1110 | 3.5158 | −0.6555 | 0.3523 | −0.1515 | 2.2811 |
| H106 | 0.3782 | −0.6278 | 0.1922 | −0.3553 | −0.9026 | 1.3512 | 1.7357 |
| H107 | −0.6336 | −2.0454 | −1.5661 | 2.2850 | −1.7217 | 0.4527 | −0.1687 |
| H108 | −0.6807 | 0.9787 | −2.7245 | −0.1729 | −1.7629 | 0.0099 | −0.0046 |
| H109 | −0.0665 | −0.2635 | −0.7414 | −0.0496 | −0.1540 | −1.1532 | −1.7003 |
| H110 | 0.7065 | 0.4036 | 0.5818 | 0.4633 | 3.8549 | −0.7217 | 0.6002 |
| H111 | 0.2691 | 0.0886 | −1.2342 | 0.6715 | −0.6184 | −1.4114 | 0.8704 |
| Bias | 0.0969 | −0.4892 | −0.1725 | −0.2370 | −1.9194 | −0.2119 | 0.1383 |
| Hidden Layer 2 to Output | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | O01 | O02 | O03 | O04 | O05 |
| H201 | 0.1771 | −0.9374 | 1.2355 | 1.4501 | 1.2729 |
| H202 | −0.8741 | −1.1480 | 0.7641 | 0.0267 | −0.3646 |
| H203 | 1.7557 | 0.3356 | −0.0501 | 1.3303 | 2.0018 |
| H204 | −0.6002 | 2.2428 | 1.1498 | −0.0814 | −0.5862 |
| H205 | 0.0348 | 0.0010 | −1.1131 | −0.1650 | 0.2440 |
| H206 | 0.7898 | 0.1205 | −0.8733 | 0.8862 | 1.7326 |
| H207 | 1.1126 | 0.0468 | 0.4803 | −1.3758 | −2.2127 |
| Bias | −0.4228 | 0.4861 | −0.2742 | −0.0809 | 0.2185 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.-M.; Jong, W.-R.; Chen, S.-C. Transfer Learning Applied to Characteristic Prediction of Injection Molded Products. Polymers 2021, 13, 3874. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13223874
Huang Y-M, Jong W-R, Chen S-C. Transfer Learning Applied to Characteristic Prediction of Injection Molded Products. Polymers. 2021; 13(22):3874. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13223874
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yan-Mao, Wen-Ren Jong, and Shia-Chung Chen. 2021. "Transfer Learning Applied to Characteristic Prediction of Injection Molded Products" Polymers 13, no. 22: 3874. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13223874
APA StyleHuang, Y. -M., Jong, W. -R., & Chen, S. -C. (2021). Transfer Learning Applied to Characteristic Prediction of Injection Molded Products. Polymers, 13(22), 3874. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13223874