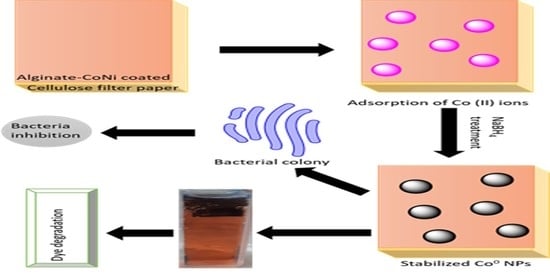
Antibacterial Films of Alginate-CoNi-Coated Cellulose Paper Stabilized Co NPs for Dyes and Nitrophenol Degradation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Catalyst
2.2.1. Synthesis of CoNi Nanocomposite
2.2.2. Preparation of Alg/FP
2.2.3. Preparation of Alg-CoNi1/FP and Alg-CoNi2/FP
2.2.4. Preparation of Alg-CoNi1/FP@Co and Alg-CoNi2/FP@Co NPs
2.3. Antibacterial Activity
2.4. Pollutants Degradation Experiment
2.5. Physiochemical Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterizations
3.1.1. FESEM
3.1.2. EDS
3.1.3. FTIR
3.1.4. XRD
3.2. Antibacterial Characteristics
3.3. Catalyst activity
3.3.1. Discoloration of CR Dye
Effect of Concentration on CR Dye Degradation
Effect of NaBH4 on the Discoloration of CR Dye
Effect of Catalyst Dosage on the Discoloration of CR Dye
3.3.2. Discoloration of MO Dye
3.3.3. Reduction of 4NP
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sapsford, K.E.; Algar, W.R.; Berti, L.; Gemmill, K.B.; Casey, B.J.; Oh, E.; Stewart, M.H.; Medintz, I.L. Functionalizing nanoparticles with biological molecules: Developing chemistries that facilitate nanotechnology. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 1904–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzato, C.; Maiti, S.; Chen, J.-Y.; Cazzolaro, A.; Gobbo, C.; Prins, L. Monolayer protected gold nanoparticles with metal-ion binding sites: Functional systems for chemosensing applications. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 9922–9931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nie, Z.; Petukhova, A.; Kumacheva, E. Properties and emerging applications of self-assembled structures made from inorganic nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, M.; Geszke-Moritz, M. The newest achievements in synthesis, immobilization and practical applications of antibacterial nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 228, 596–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Ismail, M.; Anwar, Y.; Farooq, A.; Al Johny, B.O.; Akhtar, K.; Shah, Z.A.; Nadeem, M.; Raza, M.A.; Asiri, A.M. A highly efficient and multifunctional biomass supporting Ag, Ni, and Cu nanoparticles through wetness impregnation for environmental remediation. Green Process. Synth. 2019, 8, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.A.; Khan, N.; Irum, U.; Farooq, A.; Asiri, A.M.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Khan, S.B. Cellulose acetate-Ce/Zr@ Cu0 catalyst for the degradation of organic pollutant. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figen, A.K. Improved catalytic performance of metal oxide catalysts fabricated with electrospinning in ammonia borane methanolysis for hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 28451–28462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Khan, S.B.; Asiri, A.M.; Ahmad, I. Zirconia-based catalyst for the one-pot synthesis of coumarin through Pechmann reaction. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sohni, S.; Khan, S.A.; Akhtar, K.; Khan, S.B.; Asiri, A.M.; Hashim, R.; Omar, A.M. Room temperature preparation of lignocellulosic biomass supported heterostructure (Cu+ Co@ OPF) as highly efficient multifunctional nanocatalyst using wetness co-impregnation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 549, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslamani, N.; Khan, S.B.; Danish, E.Y.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Asiri, A.M. Carboxymethyl cellulose nanocomposite beads as super-efficient catalyst for the reduction of organic and inorganic pollutants. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Asiri, A.M.; Khan, S.B. Chitosan coated NiAl layered double hydroxide microsphere templated zero-valent metal NPs for environmental remediation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 124830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Baksh, E.M.; Akhtar, K.; Khan, S.B. A template of cellulose acetate polymer-ZnAl layered double hydroxide composite fabricated with Ni NPs: Applications in the hydrogenation of nitrophenols and dyes degradation. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 241, 118671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, K.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, S.B.; Asiri, A.M. Nanomaterials and Environmental Remediation: A Fundamental Overview. Nanomater. Environ. Appl. Fascin. Attrib. 2018, 2, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, F.; Marchal, P.; Bouillard, J.; Vignes, A.; Dufaud, O.; Perrin, L. The effect of agglomeration on the emission of particles from nanopowders flow. In Proceedings of the 14th International Symposium on Loss Prevention and Safety Promotion in the Process Industry, Florence, Italy, 12–15 May 2013; pp. 811–816. [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian, V.; Ordomsky, V.V.; Legras, B.; Cheng, K.; Cordier, C.; Chernavskii, P.A.; Khodakov, A.Y. Design of iron catalysts supported on carbon–silica composites with enhanced catalytic performance in high-temperature Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 4953–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, K.R.; Wang, Z.; Yan, X.; Cao, S.; Ye, Y.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, X.; Thorne, J.E.; Jin, L. Stable iridium dinuclear heterogeneous catalysts supported on metal-oxide substrate for solar water oxidation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 2902–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.; Hao, C.; Jin, G.; Zhu, H.Y.; Guo, X.Y. Copper nanoparticles on graphene support: An efficient photocatalyst for coupling of nitroaromatics in visible light. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 1973–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, Y.S.; Shin, J.Y.; Song, C.E.; Lee, S.-g. Palladium nanoparticles supported onto ionic carbon nanotubes as robust recyclable catalysts in an ionic liquid. Chem. Commun. 2008, 8, 942–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.W.; Chen, M.Q.; Serizawa, T.; Akashi, M. In-situ formation of silver nanoparticles on poly (N-isopropylacrylamide)-coated polystyrene microspheres. Adv. Mater. 1998, 10, 1122–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, T.; Khan, S.B.; Asiri, A.M. Synthesis of zero-valent Cu nanoparticles in the chitosan coating layer on cellulose microfibers: Evaluation of azo dyes catalytic reduction. Cellulose 2016, 23, 1911–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Khan, S.B.; Farooq, A.; Asiri, A.M. A facile synthesis of CuAg nanoparticles on highly porous ZnO/carbon black-cellulose acetate sheets for nitroarene and azo dyes reduction/degradation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Pal, A.; Kundu, S.; Basu, S.; Pal, T. Photochemical green synthesis of calcium-alginate-stabilized Ag and Au nanoparticles and their catalytic application to 4-nitrophenol reduction. Langmuir 2010, 26, 2885–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, P.; Heravi, M.; Daraie, M. Ag nanoparticles immobilized on new magnetic alginate halloysite as a recoverable catalyst for reduction of nitroaromatics in aqueous media. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.B.; Ahmad, S.; Kamal, T.; Asiri, A.M.; Bakhsh, E.M. Metal nanoparticles decorated sodium alginate-carbon nitride composite beads as effective catalyst for the reduction of organic pollutants. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 1087–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ghamdi, Y.O.; Khan, S.A. Stabilization of zero-valent Au nanoparticles on carboxymethyl cellulose layer coated on chitosan-CBV 780 zeolite Y sheets: Assessment in the reduction of 4-nitrophenol and dyes. Cellulose 2020, 27, 8827–8841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uberoi, V.; Bhattacharya, S.K. Toxicity and degradability of nitrophenols in anaerobic systems. Water Environ. Res. 1997, 69, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brecken-Folse, J.A.; Mayer, F.L.; Pedigo, L.E.; Marking, L.L. Acute toxicity of 4-nitrophenol, 2,4-dinitrophenol, terbufos and trichlorfon to grass shrimp (Palaemonetes spp.) and sheepshead minnows (Cyprinodon variegatus) as affected by salinity and temperature. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 1994, 13, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.S.; Kamal, T.; Khan, S.A.; Anwar, Y.; Saeed, M.T.; Asiri, A.M.; Khan, S.B. Assessment of Anti-bacterial Ni-Al/chitosan Composite Spheres for Adsorption Assisted Photo-Degradation of Organic Pollutants. Curr. Nanosci. 2016, 12, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Khan, S.B.; Kamal, T.; Yasir, M.; Asiri, A.M. Antibacterial nanocomposites based on chitosan/Co-MCM as a selective and efficient adsorbent for organic dyes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Kamran, M.; Khan, S.A.; Shaheen, K.; Shah, Z.; Suo, H.; Khan, Q.; Shah, A.B.; Rehman, W.U.; Al-Ghamdi, Y.O. Adsorption, kinetics and thermodynamics studies of methyl orange dye sequestration through chitosan composites films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gičević, A.; Hindija, L.; Karačić, A. Toxicity of azo dyes in pharmaceutical industry. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering, Banja Luka, Bosnia, 16–18 May 2019; pp. 581–587. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.A.; De Vito, S.C. Predicting azo dye toxicity. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 23, 249–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Shah, S.A.; Khattak, I.; Ullah, H.; Khan, A.A.; Shah, R.A.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, S.B. Melia Azedarach impregnated Co and Ni zero-valent metal nanoparticles for organic pollutants degradation: Validation of experiments through statistical analysis. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 16938–16950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudzicki, J. Kirby-Bauer Disk Diffusion Susceptibility Test Protocol; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hospodarova, V.; Singovszka, E.; Stevulova, N. Characterization of cellulosic fibers by FTIR spectroscopy for their further implementation to building materials. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2018, 9, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.A.; Khan, S.B.; Khan, L.U.; Farooq, A.; Akhtar, K.; Asiri, A.M. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy: Fundamentals and Application in Functional Groups and Nanomaterials Characterization. In Handbook of Materials Characterization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 317–344. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, T.; Khan, S.B.; Haider, S.; Alghamdi, Y.G.; Asiri, A.M. Thin layer chitosan-coated cellulose filter paper as substrate for immobilization of catalytic cobalt nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Hu, G.; Zhang, J. Preparation of Sn-Cu-graphene nanocomposites with superior reversible lithium ion storage. Mater. Lett. 2016, 185, 565–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, K.; Randle, J. Toys-friend or foe? A study of infection risk in paediatric intensive care unit. Paediatr. Nurs. 2006, 18, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokoena, M.P.; Mutanda, T.; Olaniran, A.O. Perspectives on the probiotic potential of lactic acid bacteria from African traditional fermented foods and beverages. Food Nutr. Res. 2016, 60, 29630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bello, B.A.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, J.A.; Syed, F.Q.; Mirza, M.B.; Shah, L.; Khan, S.B. Anticancer, antibacterial and pollutant degradation potential of silver nanoparticles from Hyphaene thebaica. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 490, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, T.-T.; Huang, T.-H.; Chang, C.-J.; Ho, N.Y.-J.; Tseng, Y.-T.; Chen, C.-F. Antibacterial cellulose paper made with silver-coated gold nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.; Nisi, R.; Stoppa, M.; Licciulli, A. Silver-functionalized bacterial cellulose as antibacterial membrane for wound-healing applications. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 3632–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ali, H.S.H.M.; Khan, S.A. Stabilization of Various Zero-Valent Metal Nanoparticles on a Superabsorbent Polymer for the Removal of Dyes, Nitrophenol, and Pathogenic Bacteria. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 7379–7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.S.M.; Anwar, Y.; Khan, S.A. Vigna radiata Impregnated Zero-Valent CuAg NPs: Applications in Nitrophenols Reduction, Dyes Discoloration and Antibacterial Activity. J. Clust. Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunder, S.; Polzer, F.; Lu, Y.; Mei, Y.; Ballauff, M. Kinetic analysis of catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol by metallic nanoparticles immobilized in spherical polyelectrolyte brushes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 8814–8820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeswari, A.; Christy, E.J.S.; Pius, A. New insight of hybrid membrane to degrade Congo red and Reactive yellow under sunlight. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 179, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Naikoo, G.A.; Sheikh, M.U.D.; Bano, M.; Khan, F. Effective photocatalytic degradation of Congo red dye using alginate/carboxymethyl cellulose/TiO2 nanocomposite hydrogel under direct sunlight irradiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2016, 327, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchini, M.A.; Lizundia, E.; Moser, S.; Niederberger, M.; Nystrom, G. Titania-cellulose hybrid monolith for in-flow purification of water under solar illumination. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 29599–29607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.T.; Rosales, J.A.; Saenz-Arana, R.; Ghadimi, S.J.; Noveron, J.C. Rapid synthesis of ultrasmall platinum nanoparticles supported on macroporous cellulose fibers for catalysis. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 2953–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melinte, V.; Chibac-Scutaru, A.-L.; Culica, M.E.; Coseri, S. Mineralization versus photoreduction of 4-nitrophenol under the influence of surface functionalized CeO2 nanoparticles, hosted by versatile cellulose supports. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 565, 150494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizundia, E.; Jimenez, M.; Altorfer, C.; Niederberger, M.; Caseri, W. Electroless plating of platinum nanoparticles onto mesoporous cellulose films for catalytically active free-standing materials. Cellulose 2019, 26, 5513–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, Y.; Ullah, I.; Ul-Islam, M.; Alghamdi, K.M.; Khalil, A.; Kamal, T. Adopting a green method for the synthesis of gold nanoparticles on cotton cloth for antimicrobial and environmental applications. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Catalyst | Zone of Inhibition (cm) |
|---|---|
| Alg/FP | 0.3 |
| Alg/FP@Co NPs | 1.0 |
| Alg-CoNi1/FP@Co NPs | 1.7 |
| Alg-CoNi2/FP@Co NPs | 2.5 |
| Targeted Pollutants | Catalyst | kapp (min−1) | R2 | % Degradation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR | Alg/FP@Co | 1.27 × 10−1 | 0.9382 | 91.76 |
| Alg-CoNi1/FP@Co | 1.46 × 10−1 | 0.9694 | 91.65 | |
| Alg-CoNi2/FP@Co | 3.63 × 10−1 | 0.9084 | 90.41 | |
| MO | Alg/FP@Co | 2.47 × 10−1 | 0.9263 | 92.02 |
| Alg-CoNi1/FP@Co | 3.10 × 10−1 | 0.9371 | 91.55 | |
| Alg-CoNi2/FP@Co | 4.68 × 10−1 | 0.9376 | 94.22 | |
| 4NP | Alg/FP@Co | 1.71 × 10−1 | 0.9855 | 92.50 |
| Alg-CoNi1/FP@Co | 2.56 × 10−1 | 0.9636 | 91.06 | |
| Alg-CoNi2/FP@Co | 5.55 × 10−1 | 0.9740 | 94.69 |
| Reaction Condition | Various Reaction Effect | Reaction Parameters | kapp (min−1) | R2 | % Degradation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 mL NaBH4 + 30 mg catalyst | Concentration | 0.03 mM | 3.63 × 10−1 | 0.9568 | 86.8 |
| 0.05 mM | 2.57 × 10−1 | 0.9139 | 91.65 | ||
| 0.09 mM | 3.63 × 10−1 | 0.9084 | 90.41 | ||
| 3 mL of 0.09 mM CR dye solution + 30 mg catalyst | NaBH4 (1 mM) | 0.5 mL | 3.63 × 10−1 | 0.9084 | 90.42 |
| 1 mL | 3.68 × 10−1 | 0.9076 | 89.91 | ||
| 2 mL | 6.98 × 10−1 | 0.9508 | 94.85 | ||
| 3 mL of 0.09 mM CR dye solution + 0.5 mL of 1 mM NaBH4 solution | Catalyst dosage | 30 mg | 3.68 × 10−1 | 0.9084 | 90.42 |
| 60 mg | 4.28 × 10−1 | 0.8897 | 90.42 | ||
| 90 mg | 5.97 × 10−1 | 0.9074 | 93.82 |
| Catalyst | Targeted Pollutant | Concentration (mg/L) | Amount of Catalyst (g/L) | % Discoloration | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA-PS-ZnO | CR | 50.00 | __ | 95.0 | [47] |
| Ba/Alg/CMC/TiO2 | 30.00 | 1.20 | 95.0 | [48] | |
| Ba/Alg/CMC | 30.00 | 1.20 | 58.0 | [48] | |
| Alg-CoNi2/FP@Co | 48.72 | 8.44 | 90.4 | Present work | |
| cellulose/TiO2 monolith | MO | 20.00 | 0.19 | __ | [49] |
| PtNPs@KWP | 20.00 | __ | 99.0 | [50] | |
| Alg-CoNi2/FP@Co | 22.89 | 8.44 | 94.2 | Present work | |
| CelA_C2–F-5% | 4NP | 0.10 | 10.0 | 85.7 | [51] |
| Alg-CoNi2/FP@Co | 21.00 | 8.44 | 94.6 | Present work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anwar, Y.; Mohammed Ali, H.S.H.; Rehman, W.U.; Hemeg, H.A.; Khan, S.A. Antibacterial Films of Alginate-CoNi-Coated Cellulose Paper Stabilized Co NPs for Dyes and Nitrophenol Degradation. Polymers 2021, 13, 4122. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13234122
Anwar Y, Mohammed Ali HSH, Rehman WU, Hemeg HA, Khan SA. Antibacterial Films of Alginate-CoNi-Coated Cellulose Paper Stabilized Co NPs for Dyes and Nitrophenol Degradation. Polymers. 2021; 13(23):4122. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13234122
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnwar, Yasir, Hani S. H. Mohammed Ali, Waseeq Ur Rehman, Hassan A. Hemeg, and Shahid Ali Khan. 2021. "Antibacterial Films of Alginate-CoNi-Coated Cellulose Paper Stabilized Co NPs for Dyes and Nitrophenol Degradation" Polymers 13, no. 23: 4122. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13234122
APA StyleAnwar, Y., Mohammed Ali, H. S. H., Rehman, W. U., Hemeg, H. A., & Khan, S. A. (2021). Antibacterial Films of Alginate-CoNi-Coated Cellulose Paper Stabilized Co NPs for Dyes and Nitrophenol Degradation. Polymers, 13(23), 4122. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13234122