Investigation of Mechanical, Chemical, and Antibacterial Properties of Electrospun Cellulose-Based Scaffolds Containing Orange Essential Oil and Silver Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Silver and Orange Essential Oil Integrated in Cellulose Nanofibers
2.3. Characterizations
2.4. Antibacterial Assays
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Composition of the OEO
3.2. Morphology Study of Nanofiber Membranes
3.3. FT-IR Spectral Analysis
3.4. X-ray Diffraction Study
3.5. EDS Analyses
3.6. Mechanical Properties
3.7. Water Absorption and Silver Release Profile
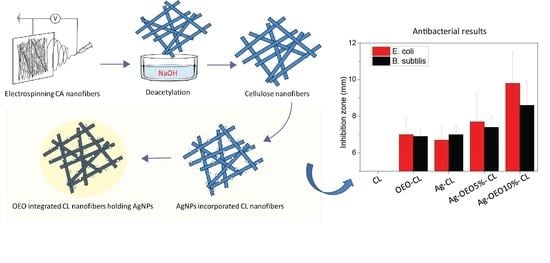
3.8. Antibacterial Activity of Composite CL Nanofibers
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leng, E.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Gong, X.; Mao, M.; Li, X.; Yu, Y. In situ structural changes of crystalline and amorphous cellulose during slow pyrolysis at low temperatures. Fuel 2018, 216, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.-N.; Lee, H.; Huang, B.; Mukai, Y.; Kim, I.-S. Fabrication of electrospun chitosan/cellulose nanofibers having adsorption.
- Ahmadzadeh, S.; Nasirpour, A.; Harchegani, M.B.; Hamdami, N.; Keramat, J. Effect of electrohydrodynamic technique as a complementary process for cellulose extraction from bagasse: Crystalline to amorphous transition. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 188, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.-N.; Khan, M.Q.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Phan, T.-T.; Ullah, A.; Khatri, M.; Kien, N.N.; Kim, I.-S. A review on the fabrication of several carbohydrate polymers into nanofibrous structures using electrospinning for removal of metal ions and dyes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 252, 117175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Chen, C.; Yang, Z.; Kuang, Y.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Kierzewski, I.; Liu, B.; He, S.; et al. Highly Compressible, Anisotropic Aerogel with Aligned Cellulose Nanofibers. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lyu, L.; Wang, Y.; Ye, F. Study on the Electrospinning of Gelatin/Pullulan Composite Nanofibers. Polymers 2019, 11, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barhoum, A.; Pal, K.; Rahier, H.; Uludag, H.; Kim, I.S.; Bechelany, M. Nanofibers as new-generation materials: From spinning and nano-spinning fabrication techniques to emerging applications. Appl. Mater. Today 2019, 17, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.-N.; Dorjjugder, N.; Saito, Y.; Taguchi, G.; Ullah, A.; Kharaghani, D.; Kim, I.-S. The synthesis of silver-nanoparticle-anchored electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers and a comparison with as-spun silver/polyacrylonitrile nanocomposite membranes upon antibacterial activity. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 4197–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, D.-N.; Dorjjugder, N.; Saito, Y.; Khan, M.Q.; Ullah, A.; Bie, X.; Taguchi, G.; Kim, I.-S. Antibacterial mechanisms of various copper species incorporated in polymeric nanofibers against bacteria. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.-N.; Rebia, R.A.; Saito, Y.; Kharaghani, D.; Khatri, M.; Tanaka, T.; Lee, H.; Kim, I.-S. Zinc oxide nanoparticles attached to polyacrylonitrile nanofibers with hinokitiol as gluing agent for synergistic antibacterial activities and effective dye removal. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 85, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaminian, H.; Montazer, M. Decorating silver nanoparticles on electrospun cellulose nanofibers through a facile method by dopamine and ultraviolet irradiation. Cellulose 2017, 24, 3179–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, I.X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, I.S.; Mei, M.L.; Li, Q.; Chu, C.H. The Antibacterial Mechanism of Silver Nanoparticles and Its Application in Dentistry. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 2555–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panáček, A.; Kvítek, L.; Smékalová, M.; Večeřová, R.; Kolář, M.; Röderová, M.; Dyčka, F.; Šebela, M.; Prucek, R.; Tomanec, O.; et al. Bacterial resistance to silver nanoparticles and how to overcome it. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdușel, A.-C.; Gherasim, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Mogoantă, L.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E. Biomedical Applications of Silver Nanoparticles: An Up-to-Date Overview. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phan, D.-N.; Dorjjugder, N.; Saito, Y.; Taguchi, G.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, I.-S. The mechanistic actions of different silver species at the surfaces of polyacrylonitrile nanofibers regarding antibacterial activities. Mater. Today Commun. 2019, 21, 100622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castangia, I.; Marongiu, F.; Manca, M.L.; Pompei, R.; Angius, F.; Ardu, A.; Fadda, A.M.; Manconi, M.; Ennas, G. Combination of grape extract-silver nanoparticles and liposomes: A totally green approach. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 97, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giunti, G.; Palermo, D.; Laudani, F.; Algeri, G.M.; Campolo, O.; Palmeri, V. Repellence and acute toxicity of a nano-emulsion of sweet orange essential oil toward two major stored grain insect pests. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 142, 111869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavahian, M.; Chu, Y.; Khaneghah, A.M. Recent advances in orange oil extraction: An opportunity for the valorisation of orange peel waste a review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 54, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelho, J.A.D.; Dannenberg, G.D.S.; Biduski, B.; el Halal, S.L.M.; Kringel, D.H.; Gularte, M.A.; Fiorentini, A.M.; Zavareze, E.D.R. Antibacterial activity, optical, mechanical, and barrier properties of corn starch films containing orange essential oil. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 114981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felix de Andrade, M.; Diego de Lima Silva, I.; Alves da Silva, G.; David Cavalcante, P.V.; Thayse da Silva, F.; Bastos de Almeida, Y.M.; Vinhas, G.M.; Hecker de Carvalho, L. A study of poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/orange essential oil films for application in active antimicrobial packaging. LWT 2020, 125, 109148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.-N.; Dorjjugder, N.; Khan, M.Q.; Saito, Y.; Taguchi, G.; Lee, H.; Mukai, Y.; Kim, I.-S. Synthesis and attachment of silver and copper nanoparticles on cellulose nanofibers and comparative antibacterial study. Cellulose 2019, 26, 6629–6640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golmohammadi, M.; Borghei, A.; Zenouzi, A.; Ashrafi, N.; Taherzadeh, M. Optimization of essential oil extraction from orange peels using steam explosion. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Zhong, B.; Luo, X.; Chun, J. Antioxidant and Anticancer Activities of Essential Oil from Gannan Navel Orange Peel. Molecules 2017, 22, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Deng, W.; Hu, W.; Cao, S.; Zhong, B.; Chun, J. Extraction of ‘Gannanzao’ Orange Peel Essential Oil by Response Surface Methodology and its Effect on Cancer Cell Proliferation and Migration. Molecules 2019, 24, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, M.Z.; Roslan, S.A.; Sapuan, S.M.; Rasid, Z.A.; Mohd Nor, A.F.; Md Daud, M.Y.; Dolah, R.; Mohamed Yusoff, M.Z. Mercerization Optimization of Bamboo (Bambusa vulgaris) Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Composite Structures Using a Box–Behnken Design. Polymers 2020, 12, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagaito, A.N.; Yano, H. Toughness enhancement of cellulose nanocomposites by alkali treatment of the reinforcing cellulose nanofibers. Cellulose 2008, 15, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, Y. An architectural exfoliated-graphene carbon aerogel with superhydrophobicity and efficient selectivity. Mater. Des. 2019, 184, 108134. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, F.; Arbab, A.A.; Jatoi, A.W.; Khatri, M.; Memon, N.; Khatri, Z.; Kim, I.S. Ultrasonic-assisted deacetylation of cellulose acetate nanofibers: A rapid method to produce cellulose nanofibers. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 36, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ye, G.; She, X.; Wang, S.; Yang, D.; Yin, Y. Sustainable Route for Molecularly Thin Cellulose Nanoribbons and Derived Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Electrocatalysts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 8729–8737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebi, N.; Taylan, O.; Abusurrah, M.; Sagdic, O. Detection of Orange Essential Oil, Isopropyl Myristate, and Benzyl Alcohol in Lemon Essential Oil by FTIR Spectroscopy Combined with Chemometrics. Foods 2020, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ma, R.; Wu, Z.; He, S.; Chen, Y.; Bai, R.; Wang, J. Visible-Light-Driven Ag-Modified TiO2 Thin Films Anchored on Bamboo Material with Antifungal Memory Activity against Aspergillus niger. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ma, R.; Lu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Su, M.; Jin, K.; Qin, D.; Zhang, R.; Bai, R.; He, S.; et al. A gravity-driven high-flux catalytic filter prepared using a naturally three-dimensional porous rattan biotemplate decorated with Ag nanoparticles. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 6846–6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroufi, L.Y.; Ghorbani, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Pezeshki, A. Improvement of the physico-mechanical properties of antibacterial electrospun poly lactic acid nanofibers by incorporation of guar gum and thyme essential oil. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 622, 126659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh-Sani, M.; Khezerlou, A.; Ehsani, A. Fabrication and characterization of the bionanocomposite film based on whey protein biopolymer loaded with TiO2 nanoparticles, cellulose nanofibers and rosemary essential oil. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 124, 300–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahed, E.; Khaledabad, M.A.; Bari, M.R.; Almasi, H. Effect of cellulose and lignocellulose nanofibers on the properties of Origanum vulgare ssp. gracile essential oil-loaded chitosan films. React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 117, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Saito, Y.; Ullah, S.; Haider, K.; Nawaz, H.; Duy-Nam, P.; Kharaghani, D.; Kim, I.S. Bioactive Sambong oil-loaded electrospun cellulose acetate nanofibers: Preparation, characterization, and in-vitro biocompatibility. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 166, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Mandal, T.; Goswami, S. Fabrication of cellulose acetate nanocomposite films with lignocelluosic nanofiber filler for superior effect on thermal, mechanical and optical properties. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2021, 25, 100642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobias, J.; Bernier-Latmani, R. Silver Release from Silver Nanoparticles in Natural Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4140–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boccalon, E.; Pica, M.; Romani, A.; Casciola, M.; Sterflinger, K.; Pietrella, D.; Nocchetti, M. Facile preparation of organic-inorganic hydrogels containing silver or essential oil with antimicrobial effects. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 190, 105567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhou, W.; Pang, C.; Deng, W.; Xu, C.; Wang, X. Multifunctional chitosan-based coating with liposomes containing laurel essential oils and nanosilver for pork preservation. Food Chem. 2019, 295, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahmandfar, R.; Tirgarian, B.; Dehghan, B.; Nemati, A. Comparison of different drying methods on bitter orange (Citrus aurantium L.) peel waste: Changes in physical (density and color) and essential oil (yield, composition, antioxidant and antibacterial) properties of powders. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2019, 14, 862–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, S.; Almasi, H.; Ghorbani, M.; Ramazani, S. Reinforced ZnONPs/ rosemary essential oil-incorporated zein electrospun nanofibers by κ-carrageenan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 232, 115800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vafania, B.; Fathi, M.; Soleimanian-Zad, S. Nanoencapsulation of thyme essential oil in chitosan-gelatin nanofibers by nozzle-less electrospinning and their application to reduce nitrite in sausages. Food Bioprod. Process. 2019, 116, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| No. | Retention Time (min) | Compounds | Composition (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15.27 | α-Pinene | 5.01 |
| 2 | 16.72 | α-Phellandrene | 2.82 |
| 3 | 17.29 | β-Myrcene | 8.84 |
| 4 | 17.68 | Octanal | 1.28 |
| 5 | 18.83 | D-Limonene | 64.33 |
| 6 | 20.69 | 2-Carene | 0.57 |
| 7 | 20.94 | Linalool | 2.77 |
| 8 | 21.45 | p-Cymene | 0.13 |
| 9 | 21.7 | 2-Caren-4-ol | 0.34 |
| 10 | 22.14 | cis-p-Mentha-2,8-dien-1-ol | 0.93 |
| 11 | 22.27 | (+)-(E)-Limonene oxide | 0.42 |
| 12 | 22.61 | Citronellal | 0.37 |
| 13 | 23.26 | 1-Indanone, 4,5,6,7-tetrahydro | 0.28 |
| 14 | 23.92 | α-Terpineol | 0.71 |
| 15 | 24.2 | Decanal | 1.89 |
| 16 | 24.73 | 2-Cyclohexen-1-ol, 2-methyl-5 | 0.63 |
| 17 | 25.08 | Carveol | 0.32 |
| 18 | 25.32 | Neral | 0.32 |
| 19 | 25.52 | (−)-Carvone | 0.74 |
| 20 | 26.14 | Citral | 0.76 |
| 21 | 26.45 | 2-Caren-10-al | 0.31 |
| 22 | 28.15 | Limonene oxide, trans- | 0.16 |
| 23 | 29.37 | Copaene | 0.41 |
| 24 | 29.71 | γ-Muurolene | 0.46 |
| 25 | 29.88 | Dodecanal | 0.39 |
| 26 | 30.63 | Caryophyllene | 0.31 |
| 27 | 30.83 | Copaene | 0.43 |
| 28 | 32.47 | Caryophyllene | 0.82 |
| 29 | 32.71 | Butylated hydroxytoluene | 0.86 |
| 30 | 33.1 | Cadina-1(10),4-diene | 0.42 |
| 31 | 33.72 | α-Acorenol | 0.18 |
| 32 | 37.04 | α-Longipinene | 0.39 |
| 33 | 38.24 | α-Sinensal | 0.22 |
| 34 | 39.76 | Nootkatone | 0.15 |
| 35 | 42.35 | m-Camphorene | 0.16 |
| 36 | 43.05 | 1-Heptatriacotanol | 0.1 |
| Total | 99.23 |
| Sample | Element (at.%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Nitrogen | Oxygen | Ag | |
| CA | 54.67 | - | 41.90 | - |
| CL | 52.44 | - | 47.56 | - |
| Ag-CL | 44.09 | - | 52.28 | 3.64 |
| Sample | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Young’s Modulus (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CA | 3.32 ± 0.84 | 17.33 ± 5.79 | 144.31 ± 37.74 |
| CL | 8.51 ± 1.93 | 3.85 ± 0.98 | 315.51 ± 45.81 |
| OEO-CL | 7.83 ± 3.08 | 5.23 ± 2.38 | 254.95 ± 50.16 |
| Ag-CL | 6.32 ± 2.81 | 3.63 ± 1.25 | 220.27 ± 66.08 |
| Ag-OEO5%-CL | 5.91 ± 0.93 | 4.5 ± 1.91 | 215.94 ± 30.15 |
| Ag-OEO10%-CL | 5.6 ± 1.03 | 4.96 ± 1.65 | 204.9 ± 40.48 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Phan, D.-N.; Khan, M.Q.; Nguyen, V.-C.; Vu-Manh, H.; Dao, A.-T.; Thanh Thao, P.; Nguyen, N.-M.; Le, V.-T.; Ullah, A.; Khatri, M.; et al. Investigation of Mechanical, Chemical, and Antibacterial Properties of Electrospun Cellulose-Based Scaffolds Containing Orange Essential Oil and Silver Nanoparticles. Polymers 2022, 14, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14010085
Phan D-N, Khan MQ, Nguyen V-C, Vu-Manh H, Dao A-T, Thanh Thao P, Nguyen N-M, Le V-T, Ullah A, Khatri M, et al. Investigation of Mechanical, Chemical, and Antibacterial Properties of Electrospun Cellulose-Based Scaffolds Containing Orange Essential Oil and Silver Nanoparticles. Polymers. 2022; 14(1):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14010085
Chicago/Turabian StylePhan, Duy-Nam, Muhammad Qamar Khan, Van-Chuc Nguyen, Hai Vu-Manh, Anh-Tuan Dao, Phan Thanh Thao, Ngoc-Mai Nguyen, Van-Tuan Le, Azeem Ullah, Muzamil Khatri, and et al. 2022. "Investigation of Mechanical, Chemical, and Antibacterial Properties of Electrospun Cellulose-Based Scaffolds Containing Orange Essential Oil and Silver Nanoparticles" Polymers 14, no. 1: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14010085
APA StylePhan, D. -N., Khan, M. Q., Nguyen, V. -C., Vu-Manh, H., Dao, A. -T., Thanh Thao, P., Nguyen, N. -M., Le, V. -T., Ullah, A., Khatri, M., & Kim, I. -S. (2022). Investigation of Mechanical, Chemical, and Antibacterial Properties of Electrospun Cellulose-Based Scaffolds Containing Orange Essential Oil and Silver Nanoparticles. Polymers, 14(1), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14010085