Gradient Porous Structured MnO2-Nonwoven Composite: A Binder-Free Polymeric Air Filter for Effective Room-Temperature Formaldehyde Removal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of MnO2 Catalysts
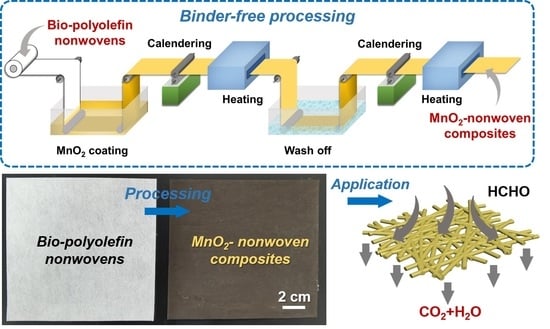
2.3. Preparation of MnO2-Nonwoven Composites
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Production and Characterization of MnO2-Nonwoven Composites
3.2. Evaluation of Pore Size Distribution of Bico-Polyolefin Nonwovens and MnO2-Nonwoven Composites
3.3. HCHO Removal Performance of MnO2-Nonwoven Composites
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kampa, M.; Castanas, E. Human health effects of air pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 151, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, S.P.; Zhang, P.Y.; Yang, Y.J.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.L.; Liu, F. MnO2 Framework for Instantaneous Mineralization of Carcinogenic Airborne Formaldehyde at Room Temperature. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, G.D.; Larsen, S.T.; Wolkoff, P. Re-evaluation of the WHO (2010) formaldehyde indoor air quality guideline for cancer risk assessment. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 35–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salthammer, T. Formaldehyde sources, formaldehyde concentrations and air exchange rates in European housings. Build. Environ. 2019, 150, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salthammer, T.; Mentese, S.; Marutzky, R. Formaldehyde in the Indoor Environment. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2536–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Song, S.; Nielsen, C.P.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, J.; Weschler, L.B.; Xie, S.; Li, J. Residential building materials: An important source of ambient formaldehyde in mainland China. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Lin, C.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, P. Review on noble metal-based catalysts for formaldehyde oxidation at room temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 475, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Yu, Y.; Fan, J.; Cheng, B.; Yu, J.; Ho, W. Room-temperature formaldehyde catalytic decomposition. Environ. Sci. Nano 2020, 7, 3655–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, C.-J.; Yoo, M.-J.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, K.-H. High-performance materials for effective sorptive removal of formaldehyde in air. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Zhou, M.; Le, Y.; Cheng, B.; Yu, J. Three-dimensional carbon foam supported MnO2/Pt for rapid capture and catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde at room temperature. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 267, 118689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, J. Efficient decomposition of formaldehyde at room temperature over Pt/honeycomb ceramics with ultra-low Pt content. Dalton Trans 2014, 43, 12935–12942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.L.; Li, J.E.; Jiang, C.J.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, P.Y.; Yu, J.G. The effect of manganese vacancy in birnessite-type MnO2 on room-temperature oxidation of formaldehyde in air. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2017, 204, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Rong, S.P.; Zhang, P.Y.; Gao, L.L. One-step synthesis of nanocarbon-decorated MnO2 with superior activity for indoor formaldehyde removal at room temperature. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2018, 235, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, W.Z.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, D. Surface oxygen vacancies on Co3O4 mediated catalytic formaldehyde oxidation at room temperature. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 3845–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellat, J.-P.; Bezverkhyy, I.; Weber, G.; Royer, S.; Averlant, R.; Giraudon, J.-M.; Lamonier, J.-F. Capture of formaldehyde by adsorption on nanoporous materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.D.; Huang, Y.; Cao, J.J.; Lee, S.C.; Chen, M.J.; Shen, Z.X. Cobalt nanoparticles encapsulated in porous nitrogen-doped carbon: Oxygen activation and efficient catalytic removal of formaldehyde at room temperature. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2019, 258, 117981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Lee, D.T.; Shi, K.; Wang, S.; Barton, H.F.; Zhu, J.; Yan, J.; Ke, Q.; Parsons, G.N. Fabrication of a freestanding metal organic framework predominant hollow fiber mat and its potential applications in gas separation and catalysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 3803–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Wang, R.T.; Wang, S.J.; Yao, C.Y.; Ren, W.; Chen, C.; Zhang, L. Metal-organic framework-based nanofiber filters for effective indoor air quality control. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 15807–15814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Pradeep, S.; Zhu, J.; Xie, W.; Barton, H.F.; Si, Y.; Ding, B.; Yu, J.; Parsons, G.N. Freestanding Metal Organic Framework-Based Multifunctional Membranes Fabricated via Pseudomorphic Replication toward Liquid- and Gas-Hazards Abatement. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2101178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Cheng, C.; Guo, Y.; Xu, H.; Ke, Q. OMS-2-based catalysts with controllable hierarchical morphologies for highly efficient catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 380, 120890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, S.; Zhang, P.; Liu, F.; Yang, Y. Engineering Crystal Facet of α-MnO2 Nanowire for Highly Efficient Catalytic Oxidation of Carcinogenic Airborne Formaldehyde. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 3435–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Fan, Y.; Ye, R.; Tang, Y.; Cao, X.; Yin, Z.; Zeng, Z. MnO2-Based Materials for Environmental Applications. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2004862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yan, J.; Su, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ke, Q.; Parsons, G.N. An Advanced Dual-Function MnO2-Fabric Air Filter Combining Catalytic Oxidation of Formaldehyde and High-Efficiency Fine Particulate Matter Removal. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2001488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yunus, R.; Li, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, P.; Kim, J. In situ synthesis of manganese oxides on polyester fiber for formaldehyde decomposition at room temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 357, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Yin, L.; Zhou, H.; Wu, L.; Yuan, K.; Pan, B.; Zhong, Z.; Xing, W. Manganese Dioxide-Filled Hierarchical Porous Nanofiber Membrane for Indoor Air Cleaning at Room Temperature. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 605, 118094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Ma, K.; He, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, P. Facile coating of MnO2 nanoparticles onto polymer fibers via friction-heating adhesion for efficient formaldehyde removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, Y.; Nishimura, A. Removal of formaldehyde from indoor air by passive type air-cleaning materials. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 2001–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozicki, M.; Guzik, K. Comparison of VOC Emissions Produced by Different Types of Adhesives Based on Test Chambers. Materials 2021, 14, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.J.; Su, J.F.; Zhu, X.M.; Xu, K.L.; Zhu, J.; Huang, C.; Ke, Q.F. Multifunctional polyethylene (PE)/polypropylene (PP) bicomponent fiber filter with anchored nanocrystalline MnO2 for effective air purification. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 14856–14866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.J.; Yu, X.W.; Huang, C.; Li, M.; Su, J.F.; Guo, Y.P.; Xu, H.; Ke, Q.F. Nanocrystalline MnO2 on an activated carbon fiber for catalytic formaldehyde removal. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 97022–97029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.C. The Infrared Spectra of Polymers II: Polyethylene. Spectroscopy 2021, 36, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Krimm, S.; Liang, C.Y.; Sutherland, G.B.B.M. Infrared Spectra of High Polymers. II. Polyethylene. J. Chem. Phys. 1956, 25, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, R.X.; Yu, J.G.; Xiao, W. Hierarchically porous MnO2 microspheres with enhanced adsorption performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 11682–11690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.F.; Zheng, L.; Huang, C.; Wu, H.B.; Wang, R.W.; Jin, X.Y. Low resistance bicomponent spunbond materials for fresh air filtration with ultra-high dust holding capacity. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 43879–43887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Sample | Concentration of MnO2 in Precursor Solution | MnO2 Content in MnO2-Nonwoven Composite |
|---|---|---|
| 10%MnO2@Polyolefin | 10% | 45% ± 3% |
| 15%MnO2@Polyolefin | 15% | 54% ± 4% |
| 20%MnO2@Polyolefin | 20% | 66% ± 4% |
| MnO2@binder@Polyolefin | 15% | 50% ± 3% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, Z.; Yu, J.; Si, Y. Gradient Porous Structured MnO2-Nonwoven Composite: A Binder-Free Polymeric Air Filter for Effective Room-Temperature Formaldehyde Removal. Polymers 2022, 14, 2504. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14122504
Dai Z, Yu J, Si Y. Gradient Porous Structured MnO2-Nonwoven Composite: A Binder-Free Polymeric Air Filter for Effective Room-Temperature Formaldehyde Removal. Polymers. 2022; 14(12):2504. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14122504
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Zijian, Jianyong Yu, and Yang Si. 2022. "Gradient Porous Structured MnO2-Nonwoven Composite: A Binder-Free Polymeric Air Filter for Effective Room-Temperature Formaldehyde Removal" Polymers 14, no. 12: 2504. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14122504
APA StyleDai, Z., Yu, J., & Si, Y. (2022). Gradient Porous Structured MnO2-Nonwoven Composite: A Binder-Free Polymeric Air Filter for Effective Room-Temperature Formaldehyde Removal. Polymers, 14(12), 2504. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14122504