Layer-By-Layer Self-Assembled Dip Coating for Antifouling Functionalized Finishing of Cotton Textile
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
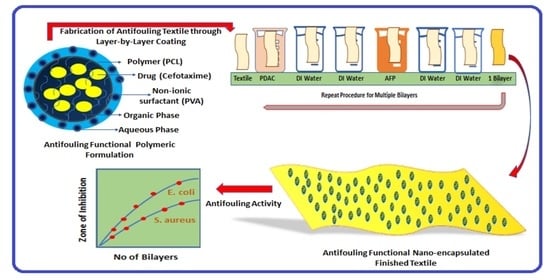
2.1. Synthesis of Antifouling Polymeric Formulation
2.2. Characterization of Antifouling Polymeric Formulation
2.3. Fabrication of Antifouling Polymeric Coating on Textile
2.4. Characterization of Fabricated Cotton Textile Fabric
2.5. In Vitro Antibacterial Bioassay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Antifouling Polymeric Formulation (AFP)
3.2. Characterization of Antifouling Fabricated Cotton Textile
3.2.1. Surface Morphology Studies
3.2.2. Surface Wettability Analyses
3.2.3. Antibacterial Assay of Textile Fabric
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahall, K. Microbiological Damage to Fibers. In Quality Assessment of Textiles; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, D.S.; Guedes, R.M.; Lopes, M.A. Antimicrobial Approaches for Textiles: From Research to Market. Materials 2016, 9, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, H.A.; Ahmad, A.; Mehboob, R. Nosocomial infections and their control strategies. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2015, 5, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abla, H.-H.; Chafia, B.; Abdesselam, L.; Houcine, L.; Kaddour, B.; Farida, S. Multidrug-resistant bacteria isolated from patients hospitalized in Intensive Care Unit in University Hospital of Constantine, Algeria (2011–2015). Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 10, 1328–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paszkiewicz, M.; Gołąbiewska, A.; Rajski, Ł.; Kowal, E.; Sajdak, A.; Zaleska-Medynska, A. The Antibacterial and Antifungal Textile Properties Functionalized by Bimetallic Nanoparticles of Ag/Cu with Different Structures. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 6056980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Windler, L.; Height, M.; Nowack, B. Comparative evaluation of antimicrobials for textile applications. Environ. Int. 2013, 53, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Cranston, R. Recent Advances in Antimicrobial Treatments of Textiles. Text. Res. J. 2008, 78, 60–72. [Google Scholar]
- Höfer, D. Antimicrobial Textiles—Evaluation of Their Effectiveness and Safety. Curr. Probl. Dermatol. 2006, 33, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahltig, B.; Zhang, J.; Wu, L.; Darko, D.; Wendt, M.; Lempa, E.; Rabe, M.; Haase, H. Effect pigments for textile coating: A review of the broad range of advantageous functionalization. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2016, 14, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí, M.; Martínez, V.; Rubio, L.; Coderch, L.; Parra, J.L. Biofunctional textiles prepared with liposomes: In vivo and in vitro assessment. J. Microencapsul. 2011, 28, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, G. Application of microencapsulation in textiles. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 242, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Yuen, M.C.W.; Kan, C.W.; Cheuk, K.K.L.; Chui, C.H.; Lam, K.H. Cosmetic textiles with biological benefits: Gelatin microcapsules containing vitamin C. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2009, 24, 411–419. [Google Scholar]
- Monllor, P.; Bonet-Aracil, M.; Cases, F. Characterization of the behaviour of flavour microcapsules in cotton fabrics. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 2481–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhu, G.; Zhou, R.; Niu, Y. A review of the preparation and application of flavour and essential oils microcapsules based on complex coacervation technology. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 94, 1482–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Yadav, S.C. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles based drug delivery systems. Colloids. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 75, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesca, F.; Limongi, T.; Accardo, A.; Rocchi, A.; Orlando, M.; Shalabaeva, V.; Di Fabrizio, E.; Benfenati, F. Fabrication of biocompatible free-standing nanopatterned films for primary neuronal cultures. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 45696–45702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Limongi, T.; Lizzul, L.; Giugni, A.; Tirinato, L.; Pagliari, F.; Tan, H.; Das, G.; Moretti, M.; Marini, M.; Brusatin, G.; et al. Laboratory injection molder for the fabrication of polymeric porous poly-epsilon-caprolactone scaffolds for preliminary mesenchymal stem cells tissue engineering applications. Microelectron. Eng. 2017, 175, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, V.R.; Bansal, K.; Kaushik, R.; Kumria, R.; Trehan, A. Poly-ϵ-caprolactone microspheres and nanospheres: An overview. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 278, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhaiyan, K.; Sridhar, R.; Sundarrajan, S.; Venugopal, J.R.; Ramakrishna, S. Vitamin B12 loaded polycaprolactone nanofibers: A novel transdermal route for the water soluble energy supplement delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 444, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, C.; Martí, M.; Barba, C.; Lis, M.; Rubio, L.; Coderch, L. Skin penetration and antioxidant effect of cosmeto-textiles with gallic acid. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 156, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, C.; Neufeld, R.J.; Ribeiro, A.; Veiga, F. Nanoencapsulation I. Methods for preparation of drug-loaded polymeric nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2006, 2, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, F.; Cheng, G.; Yi, K.; Ma, L. Nanoencapsulation of capsaicin by complex coacervation of gelatin, acacia, and tannins. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 96, 2225–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moinard-Chécot, D.; Chevalier, Y.; Briancon, S.; Beney, L.; Fessi, H. Mechanism of nanocapsules formation by the emulsion–diffusion process. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 317, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaglia, F.; Ostacolo, L.; Mazzaglia, A.; Villari, V.; Zaccaria, D.; Sciortino, M.T. The intracellular effects of non-ionic amphiphilic cyclodextrin nanoparticles in the delivery of anticancer drugs. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghayempour, S.; Montazer, M. Micro/nanoencapsulation of essential oils and fragrances: Focus on perfumed, antimicrobial, mosquito-repellent and medical textiles. J. Microencapsul. 2016, 33, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartinello, F.; Tallian, C.; Auer, J.; Schön, H.; Vielnascher, R.; Weinberger, S.; Wieland, K.; Weihs, A.M.; Herrero-Rollett, A.; Lendl, B.; et al. Smart textiles in wound care: Functionalization of cotton/PET blends with antimicrobial nanocap-sules. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 6592–6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, K. A Review on Coating & Lamination in Textiles: Processes and Applications. Am. J. Polym. Sci. 2012, 2, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, V.F.; Mogrovejo, V.A.; Tabary, N.; Maton, M.; Chai, F.; Neut, C.; Martel, B.; Blanchemain, N. Evaluation of antibacterial textile covered by layer-by-layer coating and loaded with chlorhexidine for wound dressing application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 100, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirvan, A.R.; Nejad, N.H.; Bashari, A. Antibacterial finishing of cotton fabric via the chitosan/TPP self-assembled nano layers. Fibers Polym. 2014, 15, 1908–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massella, D.; Leone, F.; Peila, R.; Barresi, A.A.; Ferri, A. Functionalization of Cotton Fabrics with Polycaprolactone Nanoparticles for Transdermal Release of Melatonin. J. Funct. Biomater. 2017, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Javaid, S.; Ahmad, N.; Mahmood, A.; Nasir, H.; Iqbal, M.; Ahmad, N.; Irshad, S. Cefotaxime Loaded Polycaprolactone Based Polymeric Nanoparticles with Antifouling Properties for In-Vitro Drug Release Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, E.; Magalhães, L.; Henriques, M.; Oliveira, R. Antimicrobial activity assessment of textiles: Standard methods comparison. Ann. Microbiol. 2010, 61, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrews, J.M. Testing, BSAC standardized disc susceptibility testing method (version 5). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 58, 511–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrander, J.W.; Mamedov, A.A.; Kotov, N.A. Two modes of linear layer-by-layer growth of nanoparticle–polylectrolyte multilayers and different interactions in the layer-by-layer deposition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, P.J.; Urrutia, A.; Goicoechea, J.; Arregui, F.J. Nanomaterials for Functional Textiles and Fibers. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouadil, B.; Amadine, O.; Essamlali, Y.; Cherkaoui, O.; Zahouily, M. A new route for the preparation of hydrophobic and antibacterial textiles fabrics using Ag-loaded graphene nanocomposite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 579, 123713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B. Modern Tribology Handbook, 1st ed.; Two Volume Set; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Glinel, K.; De Smet, D.; Vanneste, M.; Mannu, N.; Kartheuser, B.; Nysten, B.; Jonas, A.M. Environmentally Friendly Super-Water-Repellent Fabrics Prepared from Water-Based Suspensions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 15346–15351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simpson, G.J.; Sedin, D.L.; Rowlen, K.L. Surface Roughness by Contact versus Tapping Mode Atomic Force Microscopy. Langmuir 1999, 15, 1429–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, S.K. Applications of Atomic Force Microscopy in Textiles. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2015, 10, 155892501501000118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, X.; Gao, S.; Huang, J.; Li, S.; Zhu, T.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Lai, Y. A self-roughened and biodegradable superhydrophobic coating with UV shielding, solar-induced self-healing and versatile oil–water separation ability. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 7, 2122–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, A.M.; Cai, R.; Vermeyen, R.; Nysten, B.; Vanneste, M.; De Smet, D.; Glinel, K. How roughness controls the water repellency of woven fabrics. Mater. Des. 2019, 187, 108389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, G.; Lai, Y. A review on special wettability textiles: Theoretical models, fabrication technologies and multifunctional applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 5, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Żenkiewicz, M. Methods for the calculation of surface free energy of solids. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2007, 24, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Ding, B.; Zhang, Q.; Du, Y. Layer-by-layer structured polysaccharides film-coated cellulose nanofibrous mats for cell culture. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 80, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, P.; Ding, B.; Du, Y.; Li, G.; Hu, X.; Yang, J. Enhanced bacterial inhibition activity of layer-by-layer structured polysaccharide film-coated cellulose nanofibrous mats via addition of layered silicate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvimontes, A. The measurement of the surface energy of solids using a laboratory drop tower. NPJ Microgravity 2017, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddig, E.A.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, B.; Wang, T.; Shi, J.; Guo, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J. Plasma-exposed TiO2 nanoparticles on polyethylene terephthalate matrix surface and its effects on the durable hydrophobic coating. Text. Res. J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, H.; Jordan, L.; Keitel, L.; Keil, C.; Mahltig, B. Comparison of methods for determining the effectiveness of antibacterial functionalized textiles. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lalitha, P.; Jayanthi, P.; Sujitha, R. Antimicrobial Activity of Perspiration Pads and Cotton Cloth Fabricated with the Ethyl Acetate Extract of Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms. J. Text. 2014, 2014, 943287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hipler, U.-C.; Elsner, P.; Fluhr, J.W. Antifungal and antibacterial properties of a silver-loaded cellulosic fiber. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2006, 77, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niño-Martínez, N.; Salas Orozco, M.F.; Martínez-Castañón, G.-A.; Torres Méndez, F.; Ruiz, F. Molecular Mechanisms of Bacterial Resistance to Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lefrock, J.L.; Prince, R.A.; Left, R.D. Mechanism of Action, Antimicrobial Activity, Pharmacology, Adverse Effects, and Clinical Efficacy of Cefotaxime. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 1982, 2, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Javaid, S.; Mahmood, A.; Nasir, H.; Iqbal, M.; Ahmed, N.; Ahmad, N.M. Layer-By-Layer Self-Assembled Dip Coating for Antifouling Functionalized Finishing of Cotton Textile. Polymers 2022, 14, 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132540
Javaid S, Mahmood A, Nasir H, Iqbal M, Ahmed N, Ahmad NM. Layer-By-Layer Self-Assembled Dip Coating for Antifouling Functionalized Finishing of Cotton Textile. Polymers. 2022; 14(13):2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132540
Chicago/Turabian StyleJavaid, Sana, Azhar Mahmood, Habib Nasir, Mudassir Iqbal, Naveed Ahmed, and Nasir M. Ahmad. 2022. "Layer-By-Layer Self-Assembled Dip Coating for Antifouling Functionalized Finishing of Cotton Textile" Polymers 14, no. 13: 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132540
APA StyleJavaid, S., Mahmood, A., Nasir, H., Iqbal, M., Ahmed, N., & Ahmad, N. M. (2022). Layer-By-Layer Self-Assembled Dip Coating for Antifouling Functionalized Finishing of Cotton Textile. Polymers, 14(13), 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132540