Conformational Properties of Flaxseed Rhamnogalacturonan-I and Correlation between Primary Structure and Conformation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. High-Performance Size Exclusion Chromatography (HPSEC)
2.3. Conformational Characterization of Flaxseed RG-I
2.3.1. Solution Preparation
2.3.2. Intrinsic Viscosity Measurement
2.3.3. Light Scattering Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Elimination of Flaxseed RG-I Molecular Aggregation in the Solutions
3.2. Static Light Scattering (SLS) Analysis
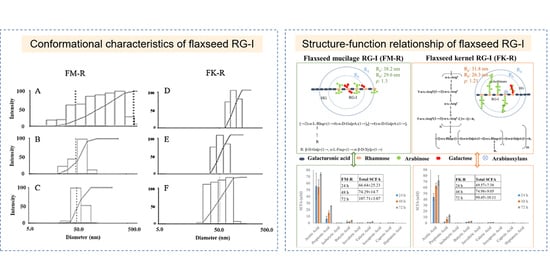
3.3. Conformational Characteristics of Flaxseed RG-I
3.4. Correlation between Primary Structure and Conformation, and Structure–Function Relationship of Flaxseed RG-I
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morris, D.H. Flax—A Health and Nutrition Primer, 4th ed.; Flax Council of Canada: Winnipeg, Canada, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.H.; Cui, S.W.; Goff, H.D.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.; Han, N.F. Soluble polysaccharides from flaxseed kernel as a new source of dietary fibres: Extraction and physicochemical characterization. Food Res. Int. 2014, 56, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.W.; Mazza, G.; Biliaderis, C.G. Chemical Structure, Molecular Size Distributions, and Rheological Properties of Flaxseed Gum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 429, 1891–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.Y.; Cui, S.W.; Nikiforuk, J.; Goff, H.D. Structural elucidation of rhamnogalacturonans from flaxseed hulls. Carbohydr. Res. 2012, 362, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.H.H.; Cui, S.W.; Goff, H.D.; Chen, J.; Wang, Q.; Han, N.F. Arabinan-rich rhamnogalacturonan-I from flaxseed kernel cell wall. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 47, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.H.; Cui, S.W.; Goff, H.D.; Chen, J.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Q. Xyloglucans from flaxseed kernel cell wall: Structural and conformational characterisation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.H.; Qian, K.; Goff, H.D.; Wang, Q.; Cui, S.W. Structural and conformational characterization of arabinoxylans from flaxseed mucilage. Food Chem. 2018, 254, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.Y.; Cui, S.W.; Wu, Y.; Goff, H.D. Flaxseed gum from flaxseed hulls: Extraction, fractionation, and characterization. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 282, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric Method for Determination of Sugars and Related Substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 283, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, M.L. The Viscosity of Dilute Solutions of Long-Chain Molecules. IV. Dependence on Concentration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1943, 6411, 2716–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, E.O. Molecular weights of celluloses and cellulose derivates. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1938, 3010, 1200–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimm, B.H. Apparatus and Methods for Measurement and Interpretation of the Angular Variation of Light Scattering; Preliminary Results on Polystyrene Solutions. J. Chem. Phys. 1948, 1612, 1099–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchard, W. Light Scattering from Polysaccharides. In Polysaccharides: Structural Diversity and Functional Versatility, 2nd ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, S.W.; Wang, Q. Understanding the conformation of polysaccharides. In Food Carbohydrates; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Burchard, W. Light scattering techniques. In Polysaccharides: Physical Techniques for the Study of Food Biopolymers; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 151–213. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, X.; Nakamura, A.; Burchard, W.; Hallett, F.R. Molecular characterisation of soybean polysaccharides: An approach by size exclusion chromatography, dynamic and static light scattering methods. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 34017, 2637–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akihiro, N.; Hitoshi, F.; Hirokazu, M.; Yasunori, N.; Akihiro, Y. Analysis of Structural Components and Molecular Construction of Soybean Soluble Polysaccharides by Stepwise Enzymatic Degradation. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2001, 6510, 2249–2258. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, S.W. Food carbohydrates. Structure analysis of polysaccharides. In Food Carbohydrates; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.H.H.; Cui, S.W.; Goff, H.D.; Gong, J. Short-chain fatty acid profiles from flaxseed dietary fibres after in vitro fermentation of pig colonic digesta: Structure–function relationship. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre. 2015, 62, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.F.; Zhao, C.Y.; Zhao, S.J.; Tian, G.F.; Wang, F.; Li, C.H.; Wang, F.Z.; Zheng, J.K. Alkali + cellulase-extracted citrus pectins exhibit compact conformation and good fermentation properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 106079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.F.; Wang, F.; Zhao, C.Y.; Zhou, S.S.; Zheng, J.K. Orange Pectin with Compact Conformation Effectively Alleviates Acute Colitis in Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 705, 1704–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Ren, W.; Zhao, C.; Gao, W.; Tian, G.; Bao, Y.; Lian, Y.; Zheng, J. The structure-property relationships of acid- and alkali-extracted grapefruit peel pectins. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qiu, W.Y.; Chen, T.T.; Yan, J.K. Effects of structural and conformational characteristics of citrus pectin on its functional properties. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 128064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, A.G.; Nielsen, H.L.; Armagan, I.; Larsen, J.; Sørensen, S.O. The impact of rhamnogalacturonan-I side chain monosaccharides on the rheological properties of citrus pectin. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 47, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.Q.; Chen, J.L.; Zhang, H.L.; Wu, D.M.; Ye, X.Q.; Linardt, R.J.; Chen, S.G. Gelling mechanism of RG-I enriched citrus pectin: Role of arabinose side-chains in cation- and acid-induced gelation. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.X.; Qi, J.R.; Huang, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.Q. Emulsifying properties of high methoxyl pectins in binary systems of water-ethanol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, R.H.; Wang, L.H.; Chen, J.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.M. Alkylated pectin: Synthesis, characterization, viscosity and emulsifying properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 50, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.M.; Guo, X.J.; Liang, R.H.; Liu, W.; Chen, J. Alkylated pectin: Molecular characterization, conformational change and gel property. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 69, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cros, S.; Penhoat, C.H.; Bouchemal, N.; Ohassan, H.; Imberty, A.; Pérez, S. Solution conformation of a pectin fragment disaccharide using molecular modelling and nuclear magnetic resonance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1992, 146, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouwijzer, M.; Schols, H.; Pérez, S. Acetylation of rhamnogalacturonan I and homogalacturonan: Theoretical calculations. Biotechnol. Prog. 1996, 14, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Broadhurst, M.; Cros, S.; Hoffmann, R.; Mackie, W.; Pérez, S. Modelling a pentasaccharide fragment of rhamnogalacturonan I. Biotechnol. Prog. 1996, 14, 517–525. [Google Scholar]
- Boutherin, B.; Mazeau, K.; Tvaroska, I. Conformational statistics of pectin substances in solution by a Metropolis Monte Carlo study. Carbohydr. Polym. 1997, 323, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurjanov, O.P.; Gorshkova, T.A.; Kabel, M.; Schols, H.A.; van Dam, J.E.G. MALDI-TOF MS evidence for the linking of flax bast fibre galactan to rhamnogalacturonan backbone. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 671, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromer, A.; Kirby, A.R.; Gunning, A.P.; Morris, V.J. Interfacial structure of sugar beet pectin studied by atomic force microscopy. Langmuir 2009, 2514, 8012–8018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.A.; Ralet, M.C. The effect of neutral sugar distribution on the dilute solution conformation of sugar beet pectin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 884, 1488–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, G.A.; Ralet, M.C.; Bonnin, E.; Thibault, J.F.; Harding, S.E. Physical characterisation of the rhamnogalacturonan and homogalacturonan fractions of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris) pectin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 824, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bindereif, B.; Karbstein, H.P.; Zahn, K.; Schaaf, U.S. Effect of Conformation of Sugar Beet Pectin on the Interfacial and Emulsifying Properties. Foods 2022, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zareie, M.H.; Gokmen, V.; Javadipour, I. Investigating network, branching, gelation and enzymatic degradation in pectin by atomic force microscopy. J. Food Sci. Technol. Mys. 2003, 402, 169–172. [Google Scholar]
- Makshakova, O.N.; Gorshkova, T.A.; Mikshina, P.V.; Zuev, Y.F.; Perez, S. Metrics of rhamnogalacturonan I with beta-(1→4)-linked galactan side chains and structural basis for its self-aggregation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 158, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikshina, P.V.; Makshakova, O.N.; Petrova, A.A.; Gaifullina, I.Z.; Idiyatullin, B.Z.; Gorshkova, T.A.; Zuev, Y.F. Gelation of rhamnogalacturonan I is based on galactan side chain interaction and does not involve chemical modifications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 171, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikshina, P.V.; Idiyatullin, B.Z.; Petrova, A.A.; Shashkov, A.S.; Zuev, Y.F.; Gorshkova, T.A. Physicochemical properties of complex rhamnogalacturonan I from gelatinous cell walls of flax fibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 117, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makshakova, O.N.; Faizullin, D.A.; Mikshina, P.V.; Gorshkova, T.A.; Zuev, Y.F. Spatial structures of rhamnogalacturonan I in gel and colloidal solution identified by 1D and 2D-FTIR spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 192, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.; Zou, M.Y.; Shao, Y.C.; Yin, J.Y.; Nie, S.P. Structural characteristics of a highly branched and acetylated pectin from Portulaca oleracea L. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 116, 106659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Conformational Characteristic/ Solution System | Mw (kDa) | Rh (nm) | Rg (nm) | A2 (10−4 cm3 mol/g2) | ρ | [η] (mL/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flaxseed Mucilage RG-I (FM-R) | ||||||
| FM-R in 0.1 M NaCl | - | - | - | - | - | 333 ± 0.1 a |
| FM-R in 0.1 M NaNO3 (by HPSEC) | 1510 b and 341 b | - | - | - | - | - |
| FM-R in 0.5 M NaOH | 285 ± 25 | 29.6 ± 2.3 | 38.2 ± 2.7 | 9.3 | 1.30 c | - |
| Flaxseed Kernel RG-I (FK-R) | ||||||
| FK-R in Milli-Q water | 1168 ± 33 | 88.70 ± 0.45 | 88.8 ± 2.4 | 5.00 ± 0.96 | 1.00 c | - |
| FK-R in 0.1 M NaNO3 | 861 ± 7 | 39.10 ± 0.01 | 35.3 ± 1.0 | 0.36 ± 0.20 | 0.90 c | 59 ± 1 a |
| FK-R in 0.1 M NaNO3 (by HPSEC) | 596.1 b | - | 49.6 b | - | - | - |
| FK-R in 6 M NH4OH | 550.4 ± 5 | 26.30 ± 0.06 | 31.8 ± 1.5 | 6.36 ± 0.79 | 1.21 c | 63±1 a |
| FK-R in 0.5 M NaOH | 265.8 ± 3 | 24.90 ± 0.17 | 18.0 ± 0.6 | 2.55 ± 0.6 | 0.72 c | - |
| Sources of the Pectin | Structural Characteristic | Conformation | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Citrus | 61.80% RG-I |
|
| [20,21] |
|
|
| [22] | |
|
|
| [23] | |
| A comparison between untreated and enzymatical debranched pectin. | Longer side chains were associated with increased entanglements between pectin molecules. | Gel strength decreased for pectin gels with lower amount of side chains. | [24] | |
| RG-I enriched pectin contains abundant arabinan side-chains. | In acid-induced gelation, low pH promotes formation of hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions within the HG region and the side-chains create a tighter conformation, eventually allowing for stronger interactions between the pectin chains. |
| [25] | |
| Ethanol could reduce the helix conformation and zeta potential of pectin chain, leading to compact conformation and enhanced interaction among pectin molecules. |
| [26] | |
| Alkylated pectin |
|
| [27] | |
| Alkylated pectin (ALP) |
|
| [28] | |
| Various origins (molecular modeling) | Methylated pectic disaccharide 4-O-α-D-galactopyranurosyl 1-O-Me-α-D-galactopyranuronic 6,6′-dimethyl diester |
| - | [29] |
| Acetylation of RG-I and HG |
| - | [30] | |
| A pentasaccharide fragment of RG-I |
| - | [31] | |
| Various structural models of pectic polysaccharides | The unrefined model of the alternating co-polymer polygalacto-galacturonic acid in vacuum is consistent with the experimentally measured dimension of pectin in salt excess. | - | [32] | |
| Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) stem |
| A complex “secondary” structure of the polymer. | Galactanase did not change the hydrodynamic volume of flax galactan (despite considerable cleavage of Gal moieties). | [33] |
| Sugar beet |
|
| The interfacial pectin film is more resistant to displacement by surfactants than a pure protein film, possibly because of the formation of linkages between the pectin chains. | [34] |
| Acid-extracted pectin is heterogeneous with respect to molar mass, intrinsic viscosity, and composition. |
| These “weight-average” molar mass, intrinsic viscosity or conformation may not necessarily be representative of the distribution of pectin molecules and this has repercussions for their functional properties. | [35] | |
| RG-I and HG fractions from enzymatic hydrolysis of acid extracted sugar beet pectin. |
| The degradation of the HG region has an important impact on intrinsic viscosity, but less on molar mass and the inverse is true for the degradation of RG-I region. | [36] | |
|
|
| [37] | |
| Low-methoxyl pectin |
| Addition of Ca++ ions into the aqueous solution of low-methoxyl pectin caused gelation by means of salt linkages between the carboxyl groups of adjacent pectin molecules. | [38] | |
| Flax fiber cell wall | RG-I containing the galactan side chain |
| Neutral β-galactans lacking charged groups and displaying higher relative stiffness of helices can deeper interpenetrate and maintain the duplex structure throughout van der Waals interactions and hydrogen bonding. | [39] |
| A pure RG-I without consecutive galacturonic residues and modifying groups in the backbone. |
| Removal of half of galactan chains from RG-I leads to loss of a gelling capability pointing out their leading role in this process. | [40] | |
| RG-I and its fragments, obtained after galactanase treatment |
| The formation of RG-I associates with the backbone at the periphery and the interaction between the side chains to form a core zone. | [41] | |
| Flax RG-I |
|
| [42] | |
| Portulaca oleracea L. |
| POWP-H adopted a flexible chain conformation in 0.1 M NaNO3 solution. | - | [43] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Q.; Shan, Z.; Shao, Y.; Wang, N.; Qian, K.; Goff, H.D.; Wang, Q.; Cui, S.W.; Ding, H.H. Conformational Properties of Flaxseed Rhamnogalacturonan-I and Correlation between Primary Structure and Conformation. Polymers 2022, 14, 2667. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132667
Guo Q, Shan Z, Shao Y, Wang N, Qian K, Goff HD, Wang Q, Cui SW, Ding HH. Conformational Properties of Flaxseed Rhamnogalacturonan-I and Correlation between Primary Structure and Conformation. Polymers. 2022; 14(13):2667. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132667
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Qingbin, Zhengxin Shan, Yanhui Shao, Nifei Wang, Keying Qian, H. Douglas Goff, Qi Wang, Steve W. Cui, and Huihuang H. Ding. 2022. "Conformational Properties of Flaxseed Rhamnogalacturonan-I and Correlation between Primary Structure and Conformation" Polymers 14, no. 13: 2667. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132667
APA StyleGuo, Q., Shan, Z., Shao, Y., Wang, N., Qian, K., Goff, H. D., Wang, Q., Cui, S. W., & Ding, H. H. (2022). Conformational Properties of Flaxseed Rhamnogalacturonan-I and Correlation between Primary Structure and Conformation. Polymers, 14(13), 2667. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132667