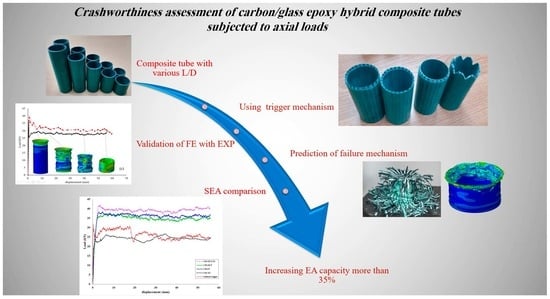
Crashworthiness Assessment of Carbon/Glass Epoxy Hybrid Composite Tubes Subjected to Axial Loads
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Procedure
2.2. Crashworthiness Indicators
2.3. Finite Element Model
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Trigger Mechanism
3.2. Failure Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dionisius, F.; Istiyanto, J.; Sumarsono, D.A.; Prayogo, G.; Baskoro, A.S.; Malawat, M. Modeling of Crashworthiness criteria based on Variation of Hole as Crush Initiator in Thin-Walled Square. Int. J. Automot. Mech. Eng. 2022, 19, 9487–9497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sever, N.K. Hybrid Steel Sheet Trends for Automotive Stampings. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2021, 22, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badgujar, T.Y.; Bobade, S.A. Advances in Sheet Metal Stamping Technology: A Case of Design and Manufacturing of a Car Door Inner Panel Using a Tailor Welded Blank. In Manufacturing and Industrial Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 175–190. [Google Scholar]
- DiGiovanni, C.; Kalashami, A.G.; Goodwin, F.; Biro, E.; Zhou, N. Occurrence of sub-critical heat affected zone liquid metal embrittlement in joining of advanced high strength steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2021, 288, 116917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Peng, T.; Kishita, Y.; Umeda, Y.; Tang, R.; Tang, W.; Hu, L. Critical life cycle inventory for aluminum die casting: A lightweight-vehicle manufacturing enabling technology. Appl. Energy 2021, 304, 117814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhi Nejad, A.; Bin Salim, M.Y.; Rahimian Koloor, S.S.; Petrik, S.; Yahya, M.Y.; Abu Hassan, S.; Mohd Shah, M.K. Hybrid and Synthetic FRP Composites under Different Strain Rates: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zhang, D.; He, Z.; Li, X.; Li, Z. Experimental investigation of the quasi-static and dynamic axial crushing behavior of carbon/glass epoxy hybrid composite tubes. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 26, 101941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, X. Numerical and experimental investigations on the axial crushing response of composite tubes. Compos. Struct. 2009, 91, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. Energy absorption and impact resistance of sandwich composite alloy structures under dynamic impact. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 831, 154771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tan, K. Low-velocity impact response and compression after impact behavior of tubular composite sandwich structures. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 193, 108026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, N.; Sani, M.; Salwani, M.; Husain, N. A review on crashworthiness studies of crash box structure. Thin-Walled Struct. 2020, 153, 106795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Chen, D.; Zhu, G.; Li, Q. Lightweight hybrid materials and structures for energy absorption: A state-of-the-art review and outlook. Thin-Walled Struct. 2022, 172, 108760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lei, H.; Lu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Energy absorption and failure pattern of hybrid composite tubes under quasi-static axial compression. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 198, 108217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, B.; Koloor, S.; Abdullah, M.; Amran, A.; Yahya, M.Y. Effect of strain-rate on flexural behavior of composite sandwich panel. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 229–231, 766–770. [Google Scholar]
- Saba, A.M.; Khan, A.H.; Akhtar, M.N.; Khan, N.A.; Koloor, S.S.R.; Petrů, M.; Radwan, N. Strength and flexural behavior of steel fiber and silica fume incorporated self-compacting concrete. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 12, 1380–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swolfs, Y.; Gorbatikh, L.; Verpoest, I. Fibre hybridisation in polymer composites: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 67, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, D.; Teng, J.; Gattas, J.; Heitzmann, M. Hybrid fibre-reinforced polymer–timber thin-walled structural members. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2018, 21, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, T.; Naveen, J.a.; Satheeshkumar, S. Hybrid fiber reinforced polymer composites–a review. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2014, 33, 454–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wu, X.; Sun, B.; Fan, W.; Han, W.; Yi, H. Investigations of defect effect on dynamic compressive failure of 3D circular braided composite tubes with numerical simulation method. Thin-Walled Struct. 2021, 160, 107381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.H.; Braimah, A. Numerical design optimization of the fiber orientation of glass/phenolic composite tubes based on tensile and radial compression tests. Compos. Struct. 2022, 280, 114898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yin, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xian, G. Mechanical property evolution and service life prediction of pultruded carbon/glass hybrid rod exposed in harsh oil-well condition. Compos. Struct. 2020, 246, 112418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Yan, D. Study on the durability of GFRP bars and carbon/glass hybrid fiber reinforced polymer (HFRP) bars aged in alkaline solution. Compos. Struct. 2021, 261, 113285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claus, J.; Santos, R.A.; Gorbatikh, L.; Swolfs, Y. Effect of matrix and fibre type on the impact resistance of woven composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 183, 107736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, K. Interfacial mechanical properties of carbon/glass hybrid thermoplastic epoxy composite rods. Compos. Struct. 2021, 257, 113129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Ha, N.; Lu, G. Thin-walled corrugated structures: A review of crashworthiness designs and energy absorption characteristics. Thin-Walled Struct. 2020, 157, 106995. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Ran, T.; Nie, L.; Jiang, H. Energy-absorption assessments of perforated CFRP tube induced by inward-splaying trigger with different trigger radius. Thin-Walled Struct. 2021, 167, 108236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supian, A.; Sapuan, S.; Zuhri, M.; Zainudin, E.; Ya, H.H. Hybrid reinforced thermoset polymer composite in energy absorption tube application: A review. Def. Technol. 2018, 14, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazita, M.N.; Khalil, H.A.; Izzati, A.N.A.; Rizal, S. Effects of strain rate on failure mechanisms and energy absorption in polymer composites. In Failure Analysis in Biocomposites, Fibre-Reinforced Composites and Hybrid Composites; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 51–78. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Jiang, H.; Liu, Z. Evaluation of double-and triple-coupled triggering mechanisms to improve crashworthiness of composite tubes. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2019, 157, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivagurunathan, R.; Way, S.L.T.; Sivagurunathan, L.; Yaakob, M.Y. Effects of triggering mechanisms on the crashworthiness characteristics of square woven jute/epoxy composite tubes. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2018, 37, 824–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhi Nejad, A.; Alipour, R.; Shokri Rad, M.; Yazid Yahya, M.; Rahimian Koloor, S.S.; Petrů, M. Using finite element approach for crashworthiness assessment of a polymeric auxetic structure subjected to the axial loading. Polymers 2020, 12, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, D.; Sadeghian, P.; Fam, A. Experimental and analytical investigations of the flexural behavior of hollow ± 55° filament wound GFRP tubes. Thin-Walled Struct. 2021, 159, 107246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalian, H.R.; Alaee, M.H.; Eskandari Jam, J.; Heydari Beni, M.; Eskandari Shahraki, M.; Asiaban, N. Design and Fabrication of a Composite Energy Absorber. ADMT J. 2020, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Y.; Xu, Y. Improvement of crash energy absorption of 2D braided composite tubes through an innovative chamfer external triggers. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2018, 111, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Sun, B.; Gu, B. Damage mechanisms of 3-D rectangular braided composite under multiple impact compressions. Aerospace Science and Technology 2018, 82, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambe, J.-E.; Bouvet, C.; Dorival, O.; Ferrero, J.-F. Energy absorption capacity of composite thin-wall circular tubes under axial crushing with different trigger initiations. J. Compos. Mater. 2020, 54, 1281–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koloor, S.; Abdul-Latif, A.; Tamin, M.N. Mechanics of composite delamination under flexural loading. Key Eng. Mater. 2011, 462–463, 726–731. [Google Scholar]
- Kashyzadeh, K.R.; Rahimian Koloor, S.S.; Omidi Bidgoli, M.; Petrů, M.; Amiri Asfarjani, A. An optimum fatigue design of polymer composite compressed natural gas tank using hybrid finite element-response surface methods. Polymers 2021, 13, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jebellat, E.; Baniassadi, M.; Moshki, A.; Wang, K.; Baghani, M. Numerical investigation of smart auxetic three-dimensional meta-structures based on shape memory polymers via topology optimization. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2020, 31, 1838–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidian, M.; Boddeti, N.; Rosen, D.W.; Weeger, O. Multiscale modelling of soft lattice metamaterials: Micromechanical nonlinear buckling analysis, experimental verification, and macroscale constitutive behaviour. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 188, 105956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhi Nejad, A.; Rahimian Koloor, S.S.; Syed Hamzah, S.M.S.A.; Yahya, M.Y. Mechanical Behaviour of Pin-Reinforced Foam Core Sandwich Panels Subjected to Low Impact Loading. Polymers 2021, 13, 3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nia, A.B.; Nejad, A.F.; Xin, L.; Ayob, A.; Yahya, M.Y. Energy absorption assessment of conical composite structures subjected to quasi-static loading through optimization based method. Mech. Ind. 2020, 21, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, R.; Mohan, N.; Sharma, S.; Pratap, A.; Keni, A.P.; Sodani, D. Mechanical testing and microstructure characterization of glass fiber reinforced isophthalic polyester composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 3653–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, M.S.; Hatami, H.; Alipouri, R.; Nejad, A.F.; Omidinasab, F. Determination of energy absorption in different cellular auxetic structures. Mech. Ind. 2019, 20, 302. [Google Scholar]
- Peirovi, S.; Pourasghar, M.; Nejad, A.F.; Hassan, M. A study on the different finite element approaches for laser cutting of aluminum alloy sheet. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 93, 1399–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejad, A.F.; Chiandussi, G.; Solimine, V.; Serra, A. Estimation of the synchronization time of a transmission system through multi body dynamic analysis. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Robot. Res 2017, 6, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quanjin, M.; Salim, M.; Rejab, M.; Bernhardi, O.-E.; Nasution, A.Y. Quasi-static crushing response of square hybrid carbon/aramid tube for automotive crash box application. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 27, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Composite Tube Elements | Product Name | Manufacturer | Tensile Strength | Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy resin | EPON™ Resin 862 | Westlake | 76 MPa | 1.15 g/cm3 |
| hardener | EPIKURE Curing Agent W | |||
| Carbon fibre | PX35 | ZOLTEK | 4200 MPa | 1.2 g/cm3 |
| Glass fibre | Glass fibre yarn 0.3 mm | Wee Tee Tong Chemicals | 3445 MPa | 2.54 g/cm3 |
| Symbol | Description | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | Kg/m3 | 1520 | |
| Module of elasticity | GPa | 58 | |
| Module of elasticity | GPa | 14.2 | |
| Shear modules | GPa | 11.8 | |
| Shear modules | GPa | 0.85 | |
| Poisson’s ratio | - | 0.29 | |
| Poisson’s ratio | - | 0.14 | |
| Normal tensile strength | MPa | 109 | |
| Normal compressive strength | MPa | 280 | |
| Transverse tensile strength | MPa | 67 | |
| Transverse compressive strength | MPa | 190 | |
| S | Shear strength | MPa | 54 |
| Fracture strain | - | 0.035 | |
| Energy release rate | U/mm2 | 20 |
| Specimen Label | Crush Length (m) | Fmax (Ave) (kN) | EA Avg (kJ) | SEA Avg (kJ/kg) | CFE Avg (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FE | EXP | FE | EXP | FE | EXP | FE | EXP | ||
| L/D-1 | 0.027 | 29.66 | 28.20 | 0.65 | 0.62 | 25.1 | 24.84 | 95.67 | 95.27 |
| L/D-1.5 | 0.04 | 31.9 | 32.45 | 1.21 | 1.19 | 29.92 | 29.78 | 97.85 | 95.74 |
| L/D-2 | 0.056 | 38.75 | 27.13 | 1.1 | 1.008 | 20.24 | 20.16 | 96.63 | 95.20 |
| L/D-2.5 | 0.071 | 31.2 | 29.79 | 1.82 | 1.76 | 25.35 | 25.24 | 96.56 | 98.98 |
| L/D-3 | 0.085 | 41.98 | 33.58 | 2.4 | 2.22 | 22.36 | 22.28 | 98.31 | 96.37 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farokhi Nejad, A.; Koloor, S.S.R.; Arifin, M.L.H.; Shafiei, A.; Hassan, S.A.; Yahya, M.Y. Crashworthiness Assessment of Carbon/Glass Epoxy Hybrid Composite Tubes Subjected to Axial Loads. Polymers 2022, 14, 4083. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194083
Farokhi Nejad A, Koloor SSR, Arifin MLH, Shafiei A, Hassan SA, Yahya MY. Crashworthiness Assessment of Carbon/Glass Epoxy Hybrid Composite Tubes Subjected to Axial Loads. Polymers. 2022; 14(19):4083. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194083
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarokhi Nejad, Ali, Seyed Saeid Rahimian Koloor, Mohd Luqman Hakim Arifin, Ali Shafiei, Shukur Abu Hassan, and Mohd Yazid Yahya. 2022. "Crashworthiness Assessment of Carbon/Glass Epoxy Hybrid Composite Tubes Subjected to Axial Loads" Polymers 14, no. 19: 4083. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194083
APA StyleFarokhi Nejad, A., Koloor, S. S. R., Arifin, M. L. H., Shafiei, A., Hassan, S. A., & Yahya, M. Y. (2022). Crashworthiness Assessment of Carbon/Glass Epoxy Hybrid Composite Tubes Subjected to Axial Loads. Polymers, 14(19), 4083. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194083