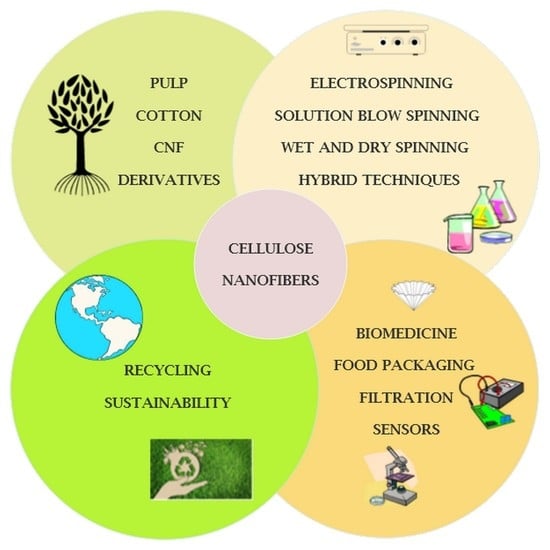
Cellulose-Based Nanofibers Processing Techniques and Methods Based on Bottom-Up Approach—A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cellulose, Structure, Solubility and Cellulose Derivatives
3. Spinning of Cellulose Nanofibers
3.1. Electrospinning
3.2. Dry Spinning
3.3. Solution Blow Spinning
3.4. Wet Spinning
3.5. Hybrid Dry-Jet Wet Spinning
3.6. Interfacial Polyelectrolyte Complex Spinning
4. Spinning of Cellulose Derivatives
4.1. Cellulose Esters
4.2. Cellulose Ethers
Coaxial Electrospinning of Cellulose Ethers
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGU | anhydroglucose unit |
| CA | cellulose (di)acetate |
| CNCs | cellulose nanocrystals |
| CMC | carboxymethyl cellulose |
| CNFs | cellulose nanofibrils |
| CTA | cellulose triacetate |
| DCM | dichloromethane |
| DMAc | N,N-dimethylacetamide |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DMF | N,N-dimethylformamide |
| DS | degree of substitution |
| EC | ethyl cellulose |
| ES | electrospinning |
| HEC | hydroxyethyl cellulose |
| HPC | hydroxypropyl cellulose |
| IL | ionic liquids |
| IMWS | ion mediated wet spinning |
| IPC | Interfacial polyelectrolyte complex spinning |
| KET | ketoprofen |
| MC | methyl cellulose |
| MCC | microcrystalline cellulose |
| Mn | number average molecular weight |
| NMMO | N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide |
| PAN | polyacrylonitrile |
| PVA | poly(vinyl alcohol) |
| PVP | polyvinylpyrrolidone |
| SBS | solution blow spinning |
| SEM | scannning electron microscopy |
| TBFA | tetrabutylammoniumfluoride tryhidrate |
| TEM | transmission electron microscopy |
| TEMPO | (2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidin-1-yl)oxyl |
| TFA | trifluoroacetic acid |
| THF | tetrahydrofuran |
| TOCN | TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibrils |
References
- Klemm, D.; Philipp, B.; Heinze, T.; Heinze, U.; Wagenknecht, W. Comprehensive Cellulose Chemistry Volume l Fundamentals and Analytical Methods; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1998; Volume 1, ISBN 3527294139. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, H.M.; Klingner, A. A review on electrospun polymeric nanofibers: Production parameters and potential applications. Polym. Test. 2020, 90, 106647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenmozhi, S.; Dharmaraj, N.; Kadirvelu, K.; Kim, H.Y. Electrospun nanofibers: New generation materials for advanced applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2017, 217, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhoum, A.; Pal, K.; Rahier, H.; Uludag, H.; Kim, I.S.; Bechelany, M. Nanofibers as new-generation materials: From spinning and nano-spinning fabrication techniques to emerging applications. Appl. Mater. Today 2019, 17, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachs-Herrera, A.; Yousefzade, O.; Del Valle, L.J.; Puiggali, J. Melt electrospinning of polymers: Blends, nanocomposites, additives and applications. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufenus, R.; Yan, Y.; Dauner, M.; Kikutani, T. Melt-spun fibers for textile applications. Materials 2020, 13, 4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, K.; Beukenberg, K.; Langensiepen, F.; Seide, G. A new prototype melt-electrospinning device for the production of biobased thermoplastic sub-microfibers and nanofibers. Biomater. Res. 2019, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aman Mohammadi, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Yousefi, M. Application of electrospinning technique in development of intelligent food packaging: A short review of recent trends. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 4656–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Khalil, H.P.S.; Davoudpour, Y.; Saurabh, C.K.; Hossain, M.S.; Adnan, A.S.; Dungani, R.; Paridah, M.T.; Mohamed, Z.I.S.; Fazita, M.R.N.; Syakir, M.I.; et al. A review on nanocellulosic fibres as new material for sustainable packaging: Process and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 64, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuz, F.; Uyar, T. Antioxidant, antibacterial and antifungal electrospun nanofibers for food packaging applications. Food Res. Int. 2020, 130, 108927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repanas, A.; Andriopoulou, S.; Glasmacher, B. The significance of electrospinning as a method to create fibrous scaffolds for biomedical engineering and drug delivery applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 31, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsara, M.; Agbulut, O.; Kontziampasis, D.; Chen, Y.; Menasché, P. Fibers for hearts: A critical review on electrospinning for cardiac tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2017, 48, 20–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafoor, B.; Aleem, A.; Najabat Ali, M.; Mir, M. Review of the fabrication techniques and applications of polymeric electrospun nanofibers for drug delivery systems. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 48, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Huang, M.; Liu, Y.; Meng, L.; Ma, M. Functionalized electrospun nanofiber membranes for water treatment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadam, V.V.; Wang, L.; Padhye, R. Electrospun nanofibre materials to filter air pollutants—A review. J. Ind. Text. 2018, 47, 2253–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Long, G.; Fan, J.; Chen, H.; Deng, L. A novel fractal solution for permeability and Kozeny-Carman constant of fibrous porous media made up of solid particles and porous fibers. Powder Technol. 2019, 349, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menachem, L. (Ed.) Handbook of Fiber Chemistry; CRC Press Taylor& Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; ISBN 9780824725655. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Clarkson, C.M.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Lamm, M.; Pang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Qian, J.; Tajvidi, M.; Gardner, D.J.; et al. Alignment of Cellulose Nanofibers: Harnessing Nanoscale Properties to Macroscale Benefits. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 3646–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, R.R.; Sahoo, S.K.; Gohil, J.M. Potential of bioinspired cellulose nanomaterials and nanocomposite membranes thereof for water treatment and fuel cell applications. Cellulose 2020, 27, 6719–6746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Luo, W.; Ciesielski, P.N.; Fang, Z.; Zhu, J.Y.; Henriksson, G.; Himmel, M.E.; Hu, L. Wood-Derived Materials for Green Electronics, Biological Devices, and Energy Applications. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 9305–9374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trache, D.; Tarchoun, A.F.; Derradji, M.; Hamidon, T.S.; Masruchin, N.; Brosse, N.; Hussin, M.H. Nanocellulose: From Fundamentals to Advanced Applications. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hsieh, Y. Lo Ultrafine fibrous cellulose membranes from electrospinning of cellulose acetate. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2002, 40, 2119–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulpinski, P. Cellulose nanofibers prepared by the N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide method. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 98, 1855–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khil, M.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Kang, Y.S.; Bang, H.J.; Lee, D.R.; Doo, J.K. Preparation of electrospun oxidized cellulose mats and their in vitro degradation behavior. Macromol. Res. 2005, 13, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sinha-Ray, S. A review on biopolymer-based fibers via electrospinning and solution blowing and their applications. Fibers 2018, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Silva, B.A.; de Sousa Cunha, R.; Valério, A.; De Noni Junior, A.; Hotza, D.; González, S.Y.G. Electrospinning of cellulose using ionic liquids: An overview on processing and applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.N.; Khan, M.Q.; Nguyen, N.T.; Phan, T.T.; Ullah, A.; Khatri, M.; Kien, N.N.; Kim, I.S. A review on the fabrication of several carbohydrate polymers into nanofibrous structures using electrospinning for removal of metal ions and dyes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 252, 117175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, E.J.D.; Kringel, D.H.; Dias, A.R.G.; da Rosa Zavareze, E. Polysaccharides as wall material for the encapsulation of essential oils by electrospun technique. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 265, 118068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, B.; Maleki, H.; Zavagna, L.; de la Ossa, J.G.; Linari, S.; Lazzeri, A.; Danti, S. Bio-based electrospun fibers for wound healing. J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamm, M.E.; Li, K.; Qian, J.; Wang, L.; Lavoine, N.; Newman, R.; Gardner, D.J.; Li, T.; Hu, L.; Ragauskas, A.J.; et al. Recent Advances in Functional Materials through Cellulose Nanofiber Templating. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnick, D.L.; Flores, R.A.; Destefano, M.R.; Scurto, A.M. Cellulose Solubility in Ionic Liquid Mixtures: Temperature, Cosolvent, and Antisolvent Effects. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 7906–7919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zugenmaier, P. Crystalline Cellulose and Derivatives-Characterization and Structures; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; ISBN 9783540739333. [Google Scholar]
- Potthast, A.; Rosenau, T.; Kosma, P.; Saariaho, A.M.; Vuorinen, T. On the nature of carbonyl groups in cellulosic pulps. Cellulose 2005, 12, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinze, T.; Koschella, A. Solvents applied in the field of cellulose chemistry: A mini review. Polímeros 2005, 15, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potthast, A.; Rosenau, T.; Kosma, P. Analysis of Oxidized Functionalities in Cellulose. In Polysaccharides II; Klemm, D., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenau, T.; Potthast, A.; Adorjan, I.; Hofinger, A.; Sixta, H.; Firgo, H.; Kosma, P. Cellulose solutions in N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide (NMMO)-degradation processes and stabilizers. Cellulose 2002, 9, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Yu, Z.; Wang, C.; Jin, S.; Ding, Y.; Wu, G. Dissolution of cellulose with ionic liquids and its application: A mini-review. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, K.; Hayashi, S.; Nishida, A.; Yamamoto, H.; Ducreux, J. Preparation of Pure Cellulose Nanofiber via Electrospinning. Text. Res. J. 2009, 79, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Shu, S.; Chen, R.; Chen, B.; Dong, W. Functionalization of electrospun nanofibers of natural cotton cellulose by cerium dioxide nanoparticles for ultraviolet protection. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 1524–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Xiao, Q.; Lu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Deng, Y. Uniaxially aligned electrospun all-cellulose nanocomposite nanofibers reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals: Scaffold for tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundahl, M.J.; Klar, V.; Wang, L.; Ago, M.; Rojas, O.J. Spinning of cellulose nanofibrils into filaments: A review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, S.; Tajvidi, M.; Gardner, D.J.; Bousfield, D.W.; Shaler, S.M. Effect of wettability and surface free energy of collection substrates on the structure and morphology of dry-spun cellulose nanofibril filaments. Cellulose 2018, 25, 6305–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshmand, S.; Aitomäki, Y.; Norberg, N.; Mathew, A.P.; Oksman, K. Dry-Spun Single-Filament Fibers Comprising Solely Cellulose Nanofibers from Bioresidue. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 13022–13028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshmand, S.; Aitomäki, Y.; Berglund, L.; Mathew, A.P.; Oksman, K. Enhanced alignment and mechanical properties through the use of hydroxyethyl cellulose in solvent-free native cellulose spun filaments. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 150, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Orelma, H.; Sneck, A.; Kataja, K.; Salmela, J.; Qvintus, P.; Suurnäkki, A.; Harlin, A. High velocity dry spinning of nanofibrillated cellulose (CNF) filaments on an adhesion controlled surface with low friction. Cellulose 2016, 23, 3393–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, S.; Tajvidi, M.; Bousfield, D.W.; Gardner, D.J.; Gramlich, W.M. Dry-spun neat cellulose nanofibril filaments: Influence of drying temperature and nanofibril structure on filament properties. Polymers 2017, 9, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Yang, X.; Shi, L.; Cheng, B.; Guan, K.; Kang, W. Solution blowing of submicron-scale cellulose fibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 982–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedvert, K.; Idström, A.; Köhnke, T.; Alkhagen, M. Cellulosic nonwovens produced via efficient solution blowing technique. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Kitayama, H.; Gotoh, Y. High strength ultrafine cellulose fibers generated by solution blow spinning. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 125, 109513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Qiu, C.; Lu, A.; Luo, L.; Guo, J.; Cong, H.; Chen, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Mechanically Strong Multifilament Fibers Spun from Cellulose Solution via Inducing Formation of Nanofibers. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5314–5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Rendon, J.G.; Schacher, F.H.; Ifuku, S.; Walther, A. Mechanical performance of macrofibers of cellulose and chitin nanofibrils aligned by wet-stretching: A critical comparison. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 2709–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, L.; Chen, B.; Peng, X.; Kuang, T. Strength and modulus improvement of wet-spun cellulose I filaments by sequential physical and chemical cross-linking. Mater. Des. 2017, 136, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boy, R.; Narayanan, G.; Chung, C.C.; Kotek, R. Novel cellulose-collagen blend biofibers prepared from an amine/salt solvent system. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, R.; Saito, T.; Isogai, A. TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibril/poly(vinyl alcohol) composite drawn fibers. Polymer (Guildf) 2013, 54, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.Z.; Luo, Z.Q.; Wang, C.Z.; Hao, X.F.; Gao, J.G. Preparation and characterization of bionanocomposite fiber based on cellulose and nano-SiO2 using ionic liquid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafy, A.; Kim, H.C.; Zhai, L.; Kim, J.W.; Van Hai, L.; Kang, T.J.; Kim, J. Cellulose long fibers fabricated from cellulose nanofibers and its strong and tough characteristics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivonen, M.S.; Kurki-Suonio, S.; Wagermaier, W.; Hynninen, V.; Hietala, S.; Ikkala, O. Interfacial Polyelectrolyte Complex Spinning of Cellulose Nanofibrils for Advanced Bicomponent Fibers. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geng, L.; Hu, S.; Cui, M.; Wu, J.; Huang, A.; Shi, S.; Peng, X. Muscle-inspired double-network hydrogels with robust mechanical property, biocompatibility and ionic conductivity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Wen, S.; Peng, X.; Cai, Y.; Geng, L.; Chen, B. Interfacial polyelectrolyte complexation spinning of graphene/cellulose nanofibrils for fiber-shaped electrodes. J. Mater. Res. 2020, 35, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biganska, O.; Navard, P.; Bédué, O. Crystallisation of cellulose/N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide hydrate solutions. Polymer 2002, 43, 6139–6145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.W.; Kim, D.S.; Kang, S.Y.; Marquez, M.; Joo, Y.L. Structural studies of electrospun cellulose nanofibers. Polymer 2006, 47, 5097–5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, W.L.E.; Cao, X.; Ramires, M.A.; Lucia, L.A. Novel all-cellulose composite displaying aligned cellulose nanofibers reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals. Tappi J. 2011, 10, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, R.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, J.; Zheng, Y.; Dong, W. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun nanofibers of high DP natural cotton lines cellulose. Fibers Polym. 2011, 12, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, I.; Njinang, C.N.; Borsali, R. Simple fabrication of cellulose nanofibers via electrospinning of dissolving pulp and tunicate. Cellulose 2017, 24, 3281–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hell, S.; Ohkawa, K.; Amer, H.; Potthast, A.; Rosenau, T. “Dialdehyde Cellulose” Nanofibers by Electrospinning as Polyvinyl Alcohol Blends: Manufacture and Product Characterization. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2018, 38, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacui, I.A.; Nieuwendaal, R.C.; Burnett, D.J.; Stranick, S.J.; Jorfi, M.; Weder, C.; Foster, E.J.; Olsson, R.T.; Gilman, J.W. Comparison of the properties of cellulose nanocrystals and cellulose nanofibrils isolated from bacteria, tunicate, and wood processed using acid, enzymatic, mechanical, and oxidative methods. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 6127–6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashiro, D.; Hamano, R.; Umemura, K. A review of applications using mixed materials of cellulose, nanocellulose and carbon nanotubes. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medeiros, E.S.; Glenn, G.M.; Klamczynski, A.P.; Orts, W.J.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Solution blow spinning: A new method to produce Micro- and Nanofibers from Polymer solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 2322–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, M.; Teno, J.; Nicolás, M.; García-González, R.; Peláez, V.H.; González-Gaitano, G.; González-Benito, J. Conformational changes on PMMA induced by the presence of TiO2 nanoparticles and the processing by Solution Blow Spinning. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2018, 296, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasiri, A.; Domínguez, J.E.; González-Benito, J. Morphology optimization of solution blow spun polystyrene to obtain superhydrophobic materials with high ability of oil absorption. Polym. Test. 2020, 91, 106859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Parize, D.; de Oliveira, J.E.; Williams, T.; Wood, D.; de Jesús Avena-Bustillos, R.; Klamczynski, A.P.; Glenn, G.M.; Marconcini, J.M.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Solution blow spun nanocomposites of poly(lactic acid)/cellulose nanocrystals from Eucalyptus kraft pulp. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- González-Benito, J.; Torres, D.; Ballesteros, C.; Ruiz, V.M.; Teno, J. PVDF based nanocomposites produced by solution blow spinning, structure and morphology induced by the presence of MWCNT and their consequences on some properties. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2019, 297, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Benito, J.; Olmos, D.; Teno, J.; González-Gaitano, G. Nanomorphology and nanomechanical characteristics of solution-blow-spun PVDF-based fibers filled with carbon nanotubes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teno, J.; González-Gaitano, G.; González-Benito, J. Poly (ethylene-co-vinyl acetate) films prepared by solution blow spinning: Surface characterization and its relation with E. coli adhesion. Polym. Test. 2017, 60, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, D.; Philipp, B.; Heinze, T.; Heinze, U.; Wagenknecht, W. Comprehensive Cellulose Chemistry Volume 2 Functionalization of Cellulose; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1998; Volume 2, ISBN 3527294899. [Google Scholar]
- Hardick, O.; Stevens, B.; Bracewell, D.G. Nanofibre fabrication in a temperature and humidity controlled environment for improved fibre consistency. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 3890–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Nishino, M.; Sohn, D.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, I.S. Control of the morphology of cellulose acetate nanofibers via electrospinning. Cellulose 2018, 25, 2829–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadol, G.C.; Lim, K.J.A.; Cabatingan, L.K.; Tan, N.P.B. Solution blow spinning-polyacrylonitrile-assisted cellulose acetate nanofiber membrane. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 345602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.; Chantre, C.O.; Gannon, A.R.; Lind, J.U.; Campbell, P.H.; Grevesse, T.; O’Connor, B.B.; Parker, K.K. Soy Protein/Cellulose Nanofiber Scaffolds Mimicking Skin Extracellular Matrix for Enhanced Wound Healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, R.; Tang, C.; Wang, H.; Zhuang, X.; Liu, Y.; Kang, W.; Shi, L. Cellulose nanofiber-embedded sulfonated poly (ether sulfone) membranes for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 184, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swapnil, S.I.; Datta, N.; Mahmud, M.M.; Jahan, R.A.; Arafat, M.T. Morphology, mechanical, and physical properties of wet-spun cellulose acetate fiber in different solvent-coagulant systems and in-situ crosslinked environment. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundahl, M.J.; Klar, V.; Ajdary, R.; Norberg, N.; Ago, M.; Cunha, A.G.; Rojas, O.J. Absorbent Filaments from Cellulose Nanofibril Hydrogels through Continuous Coaxial Wet Spinning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 27287–27296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, G.; Lundahl, M.J.; Alejandro-Martín, S.; Arteaga-Pérez, L.E.; Oviedo, C.; King, A.W.T.; Rojas, O.J. Coaxial Spinning of All-Cellulose Systems for Enhanced Toughness: Filaments of Oxidized Nanofibrils Sheathed in Cellulose II Regenerated from a Protic Ionic Liquid. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Sauceda, I.; Castillo-Ortega, M.M.; del Castillo-Castro, T.; Armenta-Villegas, L.; Ramírez-Bon, R. Electrospun cellulose acetate fibers for the photodecolorization of methylene blue solutions under natural sunlight. Polym. Bull. 2021, 78, 4419–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Fujimoto, K.; Shiratori, S. Preparation and characterization of self-assembled polyelectrolyte multilayered films on electrospun nanofibers. Thin Solid Film. 2005, 491, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Wu, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhan, X.; Liu, H. Aligned electrospun cellulose fibers reinforced epoxy resin composite films with high visible light transmittance. Cellulose 2012, 19, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.H.; Ki, S.J.; Jeon, J.H.; Che, H.L.; Park, I.K.; Kee, C.D.; Oh, I.K. Electroactive bio-composite actuators based on cellulose acetate nanofibers with specially chopped polyaniline nanoparticles through electrospinning. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 87, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Li, Y.; Deng, H.; Hu, Y.; Li, B. Antibacterial multilayer films fabricated by layer-by-layer immobilizing lysozyme and gold nanoparticles on nanofibers. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 116, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakunuri, M.; Wanasekara, N.D.; Sharma, C.S.; Khandelwal, M.; Eichhorn, S.J. Three-dimensional electrospun micropatterned cellulose acetate nanofiber surfaces with tunable wettability. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitpong, N.; Husson, S.M. Polyacid functionalized cellulose nanofiber membranes for removal of heavy metals from impaired waters. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 523, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Ayoub Arbab, A.; Jatoi, A.W.; Khatri, M.; Memon, N.; Khatri, Z.; Kim, I.S. Ultrasonic-assisted deacetylation of cellulose acetate nanofibers: A rapid method to produce cellulose nanofibers. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 36, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryoo, D.; Oh, Y.; Rojanarata, T.; Sriphong, L.; Chung, H. Fast and non-destructive determination of active pharmaceutical ingredient concentration in an electrospun nanofiber patch using infrared spectroscopy. Microchem. J. 2018, 140, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhela, A.; Kasinathan, G.N.; Rath, S.N.; Sasikala, M.; Sharma, C.S. Electrospun freestanding hydrophobic fabric as a potential polymer semi-permeable membrane for islet encapsulation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 118, 111409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, B.; Gong, J.; Kim, J.; Shiratori, S. Polyoxometalate nanotubes from layer-by-layer coating and thermal removal of electrospun nanofibres. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Ding, B.; Sone, Y.; Shiratori, S. Super-hydrophobic surfaces of layer-by-layer structured film-coated electrospun nanofibrous membranes. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 165607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tang, C. Electrospinning of cellulose acetate in solvent mixture N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMAc)/acetone. Polym. J. 2007, 39, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vrieze, S.; Van Camp, T.; Nelvig, A.; Hagström, B.; Westbroek, P.; De Clerck, K. The effect of temperature and humidity on electrospinning. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsioptsias, C.; Sakellariou, K.G.; Tsivintzelis, I.; Papadopoulou, L.; Panayiotou, C. Preparation and characterization of cellulose acetate-Fe2O3 composite nanofibrous materials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Wu, M.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H. Effects of fiber surface chemistry and size on the structure and properties of poly(vinyl alcohol) composite films reinforced with electrospun fibers. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yu, D.G. Smoothening electrospinning and obtaining high-quality cellulose acetate nanofibers using a modified coaxial process. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 7138–7147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejos, M.E.; Peresin, M.S.; Rojas, O.J. All-Cellulose Composite Fibers Obtained by Electrospinning Dispersions of Cellulose Acetate and Cellulose Nanocrystals. J. Polym. Environ. 2012, 20, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun cellulose nanofiber as affinity membrane. J. Memb. Sci. 2005, 265, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.O.; Youk, J.H.; Min, K.D.; Kang, Y.O.; Park, W.H. Electrospinning of cellulose acetate nanofibers using a mixed solvent of acetic acid/water: Effects of solvent composition on the fiber diameter. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 759–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.H.; Kang, Y.O.; Lee, T.S.; Park, W.H. Photocatalytic activities of cellulose-based nanofibers with different silver phases: Silver ions and nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 102, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Han, S.O.; Sim, I.N.; Cheon, J.Y.; Park, W.H. Fabrication and characterization of cellulose acetate/montmorillonite composite nanofibers by electrospinning. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 27523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, L.; Cao, Z.; Deng, Y.; Liu, L.; Fong, H.; Sun, Y. Electrospun composite nanofiber fabrics containing uniformly dispersed antimicrobial agents as an innovative type of polymeric materials with superior antimicrobial efficacy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 952–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Hou, D.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, T.; Menkhaus, T.J.; Fong, H. Electrospun regenerated cellulose nanofibrous membranes surface-grafted with polymer chains/brushes via the atom transfer radical polymerization method for catalase immobilization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 20958–20967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsasulak, S.; Patapeejumruswong, M.; Weiss, J.; Supaphol, P.; Yoovidhya, T. Electrospinning of food-grade nanofibers from cellulose acetate and egg albumen blends. J. Food Eng. 2010, 98, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.W.; Niamnont, N.; Hare, C.D.; Sukwattanasinitt, M.; Cheng, Q. Nanofibers doped with dendritic fluorophores for protein detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 1798–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, D.; Heinrich, S.; Greil, P. Solvent control of cellulose acetate nanofibre felt structure produced by electrospinning. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athauda, T.J.; Butt, U.; Ozer, R.R. One-dimensional hierarchical composite materials based on ZnO nanowires and electrospun blend nanofibers. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 21431–21438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, E.; Bayer, I.S.; Nanni, G.; Heredia-Guerrero, J.A.; Ruffilli, R.; Ayadi, F.; Marini, L.; Cingolani, R.; Athanassiou, A. Biomimetic approach for liquid encapsulation with nanofibrillar cloaks. Langmuir 2014, 30, 2896–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Sun, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Qu, J.; Li, J. Ionic liquid assisted electrospun cellulose acetate fibers for aqueous removal of triclosan. Langmuir 2015, 31, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matulevicius, J.; Kliucininkas, L.; Prasauskas, T.; Buivydiene, D.; Martuzevicius, D. The comparative study of aerosol filtration by electrospun polyamide, polyvinyl acetate, polyacrylonitrile and cellulose acetate nanofiber media. J. Aerosol Sci. 2016, 92, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, N.; Zainal, A. Cellulose acetate electrospun nanofibrous membrane fabrication, characterization, drug loading and antibacterial properties. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2016, 39, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ertas, Y.; Uyar, T. Fabrication of cellulose acetate/polybenzoxazine cross-linked electrospun nanofibrous membrane for water treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 177, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, T.I.; El-Kady, M.F.; Zaki, A.E.H.M.; El-Kholy, S.M. Preparation and application of magnetite nanoparticles immobilized on cellulose acetate nanofibers for lead removal from polluted water. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2017, 17, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.S.; Elkady, M.F.; Farghali, A.A.; Salem, A.M.; AbdEl-Hamid, A.I. Fabrication of novel magnetic zinc oxide cellulose acetate hybrid nano-fiber to be utilized for phenol decontamination. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 78, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorani, B.; Goswami, P.; Blackburn, R.S.; Russell, S.J. Enrichment of cellulose acetate nanofibre assemblies for therapeutic delivery of L-tryptophan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, N.; Kimura, S.; Hotta, A. Mechanical properties of poly(butylene succinate) composites with aligned cellulose-acetate nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Quan, Z.; Zhang, H.; Qin, X.; Wang, R.; Yu, J. Electrospun cellulose acetate nanofiber upscaling with a metal plate needleless spinneret. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 1250e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chang, S.; Bai, Y.; Du, Y.; Yu, D.G. Electrospun triaxial nanofibers with middle blank cellulose acetate layers for accurate dual-stage drug release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 243, 116477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Teng, D.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, Y. Design of helical groove/hollow nanofibers via tri-fluid electrospinning. Mater. Des. 2021, 205, 109705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, O.; Aytac, Z.; Uyar, T. Superhydrophobic, Hybrid, Electrospun Cellulose Acetate Nanofibrous Mats for Oil/Water Separation by Tailored Surface Modification. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 19747–19754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi, H.S.; Akram, T.; Shabir, N.; Vasita, R.; Jadhav, A.H.; Sheikh, F.A. Regenerated cellulose nanofibers from cellulose acetate: Incorporating hydroxyapatite (HAp) and silver (Ag) nanoparticles (NPs), as a scaffold for tissue engineering applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 118, 111547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Shi, X.; Du, Y.; Luo, Y.; Deng, H. TiO2/rectorite-trapped cellulose composite nanofibrous mats for multiple heavy metal adsorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, H.M.; Hussein, K.H.; Sayed, M.M.; Abd El-Rahman, M.K.; Woo, H.M. Development and characterization of cellulose/iron acetate nanofibers for bone tissue engineering applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, A.G.B.; Fajardo, A.R.; Gerola, A.P.; Rodrigues, J.H.S.; Nakamura, C.V.; Muniz, E.C.; Hsieh, Y. Lo First report of electrospun cellulose acetate nanofibers mats with chitin and chitosan nanowhiskers: Fabrication, characterization, and antibacterial activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 250, 116954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian-Fard-Fini, S.; Ghanbari, D.; Amiri, O.; Salavati-Niasari, M. Electro-spinning of cellulose acetate nanofibers/Fe/carbon dot as photoluminescence sensor for mercury (II) and lead (II) ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojstršek, A.; Fakin, D.; Hribernik, S.; Fakin, T.; Bračič, M.; Kurečič, M. Electrospun nanofibrous composites from cellulose acetate/ultra-high silica zeolites and their potential for VOC adsorption from air. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 116071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, D.S.; Duarte, E.H.; Hashimoto, E.M.; Turbiani, F.R.; Muniz, E.C.; de Souza, P.R.; Gimenes, M.L.; Martins, L.D. Development and characterization of electrospun cellulose acetate nanofibers modified by cationic surfactant. Polym. Test. 2020, 81, 106206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizge, N.; Shaulsky, E.; Karanikola, V. Electrospun cellulose nanofibers for superhydrophobic and oleophobic membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 590, 117271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Huang, X.; Liang, H.; Tao, Q. Enhanced hydrophilic and antibacterial efficiencies by the synergetic effect TiO2 nanofiber and graphene oxide in cellulose acetate nanofibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 132, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazbouz, M.B.; Russell, S.J. Cellulose acetate/sodium-activated natural bentonite clay nanofibres produced by free surface electrospinning. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 10891–10909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vatankhah, E. Rosmarinic acid-loaded electrospun nanofibers: In vitro release kinetic study and bioactivity assessment. Eng. Life Sci. 2018, 18, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thakur, N.; Baji, A.; Ranganath, A.S. Thermoresponsive electrospun fibers for water harvesting applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 433, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, T.; Li, G.; An, L.; Li, F.; Zhang, Z. Electrospun H4SiW12O40/cellulose acetate composite nanofibrous membrane for photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline and methyl orange with different mechanism. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 168, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuancharoensri, N.; Ross, G.M.; Mahasaranon, S.; Topham, P.D.; Ross, S. Ternary blend nanofibres of poly(lactic acid), polycaprolactone and cellulose acetate butyrate for skin tissue scaffolds: Influence of blend ratio and polycaprolactone molecular mass on miscibility, morphology, crystallinity and thermal properties. Polym. Int. 2017, 66, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, F.; Li, Z. Cellulose acetate nanofibers coated layer-by-layer with polyethylenimine and graphene oxide on a quartz crystal microbalance for use as a highly sensitive ammonia sensor. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 148, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Ma, Q.; Wang, S.D.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.Z.; Bao, W.; Zhang, K.Q.; Ling, L.Z. Electrospinning of silver nanoparticles loaded highly porous cellulose acetate nanofibrous membrane for treatment of dye wastewater. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2016, 122, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulos, N.; Harbottle, D.; Hebden, A.; Goswami, P.; Blackburn, R.S. Kinetic Analysis of Cellulose Acetate/Cellulose II Hybrid Fiber Formation by Alkaline Hydrolysis. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 4936–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, J.; Hsieh, Y. Lo Cellulose/chitosan hybrid nanofibers from electrospinning of their ester derivatives. Cellulose 2009, 16, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, J.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Ding, B. Equipment-free chromatic determination of formaldehyde by utilizing pararosaniline-functionalized cellulose nanofibrous membranes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 203, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Fu, Q.; Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Highly Carbonylated Cellulose Nanofibrous Membranes Utilizing Maleic Anhydride Grafting for Efficient Lysozyme Adsorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 15658–15666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Sun, R.; Liu, C.; Xiong, J.; Qin, X. Mass production of nanofibers from needleless electrospinning by a novel annular spinneret. Mater. Des. 2019, 179, 107885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Xu, Y.; Peng, B.; Su, Y.; Jiang, F.; Hsieh, Y.L.; Wei, Q. Coaxial electrospun cellulose-core fluoropolymer-shell fibrous membrane from recycled cigarette filter as separator for high performance lithium-ion battery. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Vincent Edwards, J.; Prevost, N.; Huang, Y.; Chen, J.Y. Physico- and bio-activities of nanoscale regenerated cellulose nonwoven immobilized with lysozyme. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 91, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundahl, M.J.; Berta, M.; Ago, M.; Stading, M.; Rojas, O.J. Shear and extensional rheology of aqueous suspensions of cellulose nanofibrils for biopolymer-assisted filament spinning. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 109, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, S.; Liu, Q.; Kong, B.; Wang, H. Fabrication and characterization of cinnamaldehyde loaded polysaccharide composite nanofiber film as potential antimicrobial packaging material. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 26, 100600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, B.; Liu, Q.; Kong, B.; Wang, H. Fabrication and characterization of a novel polysaccharide based composite nanofiber films with tunable physical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 116054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, L.; Zhang, C.; Feng, F.; Zhang, H. Tunable Physical Properties of Ethylcellulose/Gelatin Composite Nanofibers by Electrospinning. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1907–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.G.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.H.; Bligh, S.W.A.; Williams, G.R. Nanofibers Fabricated Using Triaxial Electrospinning as Zero Order Drug Delivery Systems. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 18891–18897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.Y.; Kim, J.I.; Lee, I.H. Fabrication and characterization of antimicrobial ethyl cellulose nanofibers using electrospinning techniques. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 5672–5675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.G.; Li, X.Y.; Chian, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Influence of sheath solvents on the quality of ethyl cellulose nanofibers in a coaxial electrospinning process. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2014, 24, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewster, M.E.; Verreck, G.; Chun, I.; Rosenblatt, J.; Mensch, J.; Van Dijck, A.; Noppe, M.; Ariën, A.; Bruining, M.; Peeters, J. The use of polymer-based electrospun nanofibers containing amorphous drug dispersions for the delivery of poorly water-soluble pharmaceuticals. Pharmazie 2004, 59, 387–391. [Google Scholar]
- Kazsoki, A.; Szabó, P.; Zelkó, R. Prediction of the hydroxypropyl cellulose—Poly(vinyl alcohol) ratio in aqueous solution containing papaverine hydrochloride in terms of drug loaded electrospun fiber formation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 138, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Newehy, M.H.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Alotaiby, S.; El-Hamshary, H.; Moydeen, M.; Al-Deyab, S. Green electrospining of hydroxypropyl cellulose nanofibres for drug delivery applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazsoki, A.; Domján, A.; Süvegh, K.; Zelkó, R. Microstructural characterization of papaverine-loaded HPC/PVA gels, films and nanofibers. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 122, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorshidi, S.; Solouk, A.; Karkhaneh, A.; Mirzadeh, H.; Sharifi, S.; Mazinani, S. Effect of crosslinking procedure on structural, thermal, and functional performances of cellulosic nanofibers: A comparison between chemical and photochemical crosslinking. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, S.; Hussain, F.S.J.; Kumar, A.; Rasad, M.S.B.A.; Yusoff, M.M. Fabrication, characterization and in vitro biocompatibility of electrospun hydroxyethyl cellulose/poly (vinyl) alcohol nanofibrous composite biomaterial for bone tissue engineering. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 144, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zulkifli, F.H.; Jahir Hussain, F.S.; Abdull Rasad, M.S.B.; Mohd Yusoff, M. Improved cellular response of chemically crosslinked collagen incorporated hydroxyethyl cellulose/poly(vinyl) alcohol nanofibers scaffold. J. Biomater. Appl. 2015, 29, 1014–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rošic, R.; Kocbek, P.; Baumgartner, S.; Kristl, J. Electro-spun hydroxyethyl cellulose nanofibers: The relationship between structure and process. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2011, 21, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Nie, H.; Li, S.; White, C.J.B.; Zhu, L. Crosslinking of electrospun polyacrylonitrile/hydroxyethyl cellulose composite nanofibers. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 1199–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kwak, H.W.; Yun, H.; Kim, Y.W.; Lee, K.H. Methyl cellulose nanofibrous mat for lipase immobilization via cross-linked enzyme aggregates. Macromol. Res. 2016, 24, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gašparič, P.; Kurečič, M.; Kargl, R.; Maver, U.; Gradišnik, L.; Hribernik, S.; Kleinschek, K.S.; Smole, M.S. Nanofibrous polysaccharide hydroxyapatite composites with biocompatibility against human osteoblasts. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 177, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigger, I.; Dubernet, C.; Couvreur, P. Nanoparticles in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 631–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Yu, D.G.; Li, Y.; Liao, Y.Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, L. Dual drug release electrospun core-shell nanofibers with tunable dose in the second phase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.G.; Yu, J.H.; Chen, L.; Williams, G.R.; Wang, X. Modified coaxial electrospinning for the preparation of high-quality ketoprofen-loaded cellulose acetate nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouda, M.; Aljaafari, A.; Al-Omair, M.A. Functional electrospun cellulosic nanofiber mats for antibacterial bandages. Fibers Polym. 2017, 18, 2379–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Steckl, A.J. Coaxial Electrospinning Formation of Complex Polymer Fibers and their Applications. Chempluschem 2019, 84, 1453–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.-G.; Li, X.-X.; Ge, J.-W.; Ye, P.-P.; Wang, X. The Influence of Sheath Solvent’s Flow Rate on the Quality of Electrospun Ethyl Cellulose Nanofibers. Model. Numer. Simul. Mater. Sci. 2013, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.G.; Wang, X.; Li, X.Y.; Chian, W.; Li, Y.; Liao, Y.Z. Electrospun biphasic drug release polyvinylpyrrolidone/ethyl cellulose core/sheath nanofibers. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 5665–5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, Z.H.; Yu, D.G.; Williams, G.R. Tunable biphasic drug release from ethyl cellulose nanofibers fabricated using a modified coaxial electrospinning process. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, D.G.; Yang, C.; Jin, M.; Williams, G.R.; Zou, H.; Wang, X.; Annie Bligh, S.W. Medicated Janus fibers fabricated using a Teflon-coated side-by-side spinneret. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 138, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esmaeili, A.; Haseli, M. Electrospinning of thermoplastic carboxymethyl cellulose/poly(ethylene oxide) nanofibers for use in drug-release systems. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 77, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





















| Source of Cellulose | Content of Cellulose, % | Degree of Polymerization | Crystallinity, % | Degradation Temperature, °C | Water Vapor sorption, % | Water Retention, % | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| native cotton | 88–96 | 10,000–12,000 | 60–90 | 225–300 | 6–7 | 50 | [1,17,32] |
| various pulps | 40–50 | 500–2000 | 50–56 | 220–330 | ~8 | 60–135 | |
| regenerated cellulose (viscose rayon) fibers | 100 | 250–500 | 25–40 | ~240 | ~12 | 85–95 |
| Spinning Technique | Spinning Precursor | Solvents | Application | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| electrospinning | softwood and hardwood pulp, cotton, CNCs | NMMO, LiCl/DMAc, TFA, DMF, dichloroethane | biomedical application, wound dressing, drug delivery, UV protection, scaffolds | [24,38,39,40] |
| dry spinning | water suspension of CNFs isolated from various sources | water | high mechanical strength filaments for reinforcements in various composite materials | [41,42,43,44,45,46] |
| solution blow spinning | pulp | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate, 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium diethyl phosphate, LiCl/DMAc | high-strength nonwovens | [47,48,49] |
| wet spinning | cotton pulp, CNFs | NaOH/LiOH/Urea/H2O, aqueous dispersions | high-strength cellulose filaments for textile materials production | [50,51,52] |
| dry-jet wet spinning | pulp, CNFs | 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride | high-strength and thermally stable fibers | [53,54,55,56] |
| IPC | CNFs and TOCN | / | biological application, supercapacitors | [57,58,59] |
| Spinning Technique | Nanofibers Diameter | Advantage | Disadvantage | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| electrospinning | 60–5000 nm | established protocols and stable reproducible production of membranes | use of high-voltage electrical field; low production rate | [76,77] |
| solution blow spinning | 140–1000 nm | high production rate; | obtaining of smooth fibers only with assisted spinning with other polymers | [78] |
| rotary jet spinning | ~300 nm | / | / | [79] |
| electrostatic induction assisted solution blow spinning | 150–1000 nm | stable preparation of nanofibers | low production rate | [80] |
| wet spinning | 20 μm | possibility to spin cellulose acetate with CNFs or CNCs; obtaining of mechanically strong filaments | use of coagulation bath; increased use of chemicals | [81,82] |
| Concentration of CA in Solution | Solvent System | Avg. Diameters of Nanofibers, nm | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10–20% | Acetone/DMAc | 100–1000 | [22,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101] |
| 16% | Acetone/DMF/Trifluoroethylene | 200–1000 | [102] |
| 16–17% | Acetic acid/H2O (75/25) | 180 | [103,104,105] |
| 20% | THF/DMSO | ~1000 nm | [106,107] |
| 20% | Acetic acid (85/15) | ~265 | [108] |
| 17% | Acetone/H2O (8:1) | 400–2000 | [109] |
| 8–24% | Acetone, benzyl alcohol, methyl ethyl ketone, 1,2 Propanediol, Ethyl alcohol, DMSO | 90–5000 | [110] |
| 20% | Acetone/DMF/Ethanol | 150–1000 | [76] |
| 20% | DMF | ~470 | [111] |
| 15% | Acetone | 550 | [112] |
| 9% | Chloroform/methanol + 1% of IL 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazo-liumhexaflfluorophosphate (BMIPF6) | 100–400 | [113] |
| 11% | Acetone/Dichlormethan/DMF | ~350 | [114] |
| 10–14% | Acetic acid/acetone, Acetone/Dichlormethane, Acetic acid/H2O | 200–1056 | [115] |
| 12% | DCM/Methanol (4:1) | 720 | [116] |
| 15% | Acetone/DMF (2:1) | ~150 | [117] |
| 10% | Acetic acid/H2O, Acetone/DMF, Acetone/DMAc | 67–1500 | [118] |
| 13% | Acetone/DMAc/Methanol (2:1:2) | 520–1010 | [119] |
| 20% | Acetone/DMF (6:4) | ~400 | [120] |
| 16% | Acetone/DMSO | 273–760 | [121] |
| 4–11% | Acetone/H2O (8:2) | ~1100 | [84] |
| 11% | Ethanol/Acetone/DMAc (1:4:1) | / | [122] |
| 15% | Acetone/DMAc + LiCl | / | [123] |
| Substance | Loading | Application Proposed by Authors | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroxyapatite | Pre spinning | tissue engineering/scaffolds | [125] |
| AgNP | post spinning | ||
| TiO2 or silicate rectorite | pre spinning | heavy metal ions removal (Pb2+, Cu2+ Cd2+) | [126] |
| Fe(CO2CH3)2 | pre spinning | bone tissue engineering | [127] |
| Chitin nanowiskers | pre spinning | wound dressing, hygienic products, tissue engineering | [128] |
| Chitosan nanowiskers | post spinning | ||
| FeNP | pre spinning | sensor for detection of Hg2+ and Pb2+ | [129] |
| Carbon dots (CDs) | post spinning | ||
| Ultrahigh silica zeolites | pre spinning | adsorption of volatile organic compounds | [130] |
| cationic cetylpiridinium bromide | pre spinning | air filter | [131] |
| SiNP and fluoroalkylsilane | post spinning | omniphobic membrane | [132] |
| TiO2 nanofibers and graphene oxide | pre spinning | antibacterial (biomedical application) | [133] |
| Bentonite clay | pre spinning | increased absorptive properties and cation exchange capacity | [134] |
| Rosmarinic acid | pre spinning | transdermal drug delivery system | [135] |
| poly N isopropylacrylamide | pre spinning and core shell | moisture harvesting | [136] |
| H4SiW12O40 | pre spinning | photocatalytic degradation of organic compounds and dyes | [137] |
| Poly(glycidyl metacrilate) and Poly(acrylic acid) | post spinning | removal of heavy metal ions (Cd2+) | [90] |
| Fe3O4NP | pre spinning | removal of heavy metal ions (Pb2+) | [117] |
| Magnetite ZnO | post spinning | phenol removal | [118] |
| Poly(lactic acid) and polycaprolactone | pre spinning (ternary blend) | skin tissue scaffold | [138] |
| polyethylenimine and graphene oxide | post spinning | sensor for ammonia | [139] |
| perfluoro alkoxysilanes | pre spinning | oil/water separation | [124] |
| AgNP | pre spinning | dyes absorption from H2O | [140] |
| Cellulose Ether | Degree of Substitution | Solvent Used for Electrospinning | Resulting Diameter of Nanofibers, nm | Application | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ethylcellulose/pullulan | 2.4–2.5 | formic acid | 167–300 | active food packaging or encapsulation material | [150] |
| ethylcellulose/pullulan/cinammaldehyde | 2.4–2.5 | formic acid | 200–230 | antimicrobial film | [149] |
| elhylcellulose/gelatin | not reported | wather/ethanol/acetic acid | 400–650 | bioactive encapsulation, food packaging films | [151] |
| ethylcellulose/streptomycin | not reported | THF/DMAc | / | drug release fibers | [153] |
| methylcellulose | 1.9 | water/ethanol | 50–80 | enzyme immobilization | [164] |
| carboxymethyl cellulose/CuNP or ZnNP | not reported | LiCl/DMAc | 150–200 | antibacterial bandages | [169] |
| carboxymethylcellulose/PEO/hydroxyapatite | 0.7 | water | 200–800 | tissue scaffold | [165] |
| hydroxyethylcellulose | not reported | water, water with salts, surfactants or organic solvents | 30–100 | wound dressing, tissue scaffold | [162] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kramar, A.; González-Benito, F.J. Cellulose-Based Nanofibers Processing Techniques and Methods Based on Bottom-Up Approach—A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14020286
Kramar A, González-Benito FJ. Cellulose-Based Nanofibers Processing Techniques and Methods Based on Bottom-Up Approach—A Review. Polymers. 2022; 14(2):286. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14020286
Chicago/Turabian StyleKramar, Ana, and Francisco Javier González-Benito. 2022. "Cellulose-Based Nanofibers Processing Techniques and Methods Based on Bottom-Up Approach—A Review" Polymers 14, no. 2: 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14020286
APA StyleKramar, A., & González-Benito, F. J. (2022). Cellulose-Based Nanofibers Processing Techniques and Methods Based on Bottom-Up Approach—A Review. Polymers, 14(2), 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14020286