Kinetic and Isothermal Investigations on the Use of Low Cost Coconut Fiber-Polyaniline Composites for the Removal of Chromium from Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Pre-Treatment of Coconut Fibers
2.1.2. Synthesis of Polyaniline (PANI) and Polyaniline-Coconut Fiber (PANI-CF) Composites
3. Characterization
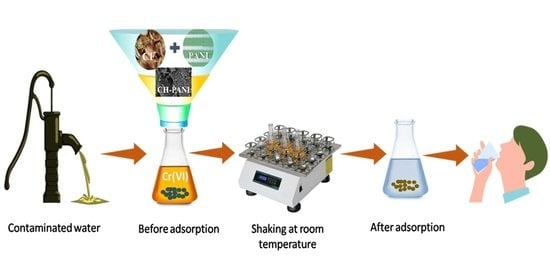
4. Adsorption Studies
5. Results and Discussions
5.1. Characterization of the Samples
5.1.1. Thermal Stability Analysis
5.1.2. Functional Group Analysis
5.1.3. Morphological Analysis
5.2. Adsorption Study
5.3. Kinetic Studies
5.4. Isotherm Study
5.5. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage on Chromium Adsorption
5.6. Effect of pH
5.7. Adsorption Mechanism
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology of Hazardous Heavy Metals: Environmental Persistence, Toxicity, and Bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy Metal Pollution in the Environment and their Toxicological Effects on Humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. Mol. Clin. Environ. Toxicol. 2012, 101, 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobs, J.A.; Avakian, C.P. Chromium (VI) Handbook; Taylor & Francis: Oxfordshire, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur, S.B. Toxicological profile for chromium: US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service. Agency Toxic Subst. Dis. Regist. 2000, 67, 1054S–1060S. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, N.K.; Basu, S. Potentiality of Waste Human Hair Towards Removal of Chromium (VI) from Solution: Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palaniappan, P.; Karthikeyan, S. Bioaccumulation and Depuration of Chromium in the Selected Organs and Whole Body Tissues of Freshwater fish Cirrhinusmrigala Individually and in Binary Solutions with Nickel. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norseth, T. The Carcinogenicity of Chromium and its Salts. Occup. Environ. Med. 1986, 43, 649–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ambaye, T.G.; Vaccari, M.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Amrane, A.; Rtimi, S. Mechanisms and Adsorption Capacities of Biochar for the Removal of Organic and Inorganic Pollutants from Industrial Wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 18, 3273–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möbius, C.H. Adsorption and Ion Exchange Processes for Treatment of White Water and Waste Water of Paper Mills. Water Pollut. Res. Dev. 1981, 13, 681–695. [Google Scholar]
- Trishitman, D.; Cassano, A.; Basile, A.; Rastogi, N.K. Reverse osmosis for industrial wastewater treatment. In Current Trends and Future Developments on (Bio-) Membranes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 207–228. [Google Scholar]
- Fontanier, V.; Farines, V.; Albet, J.; Baig, S.; Molinier, J. Study of Catalyzed Ozonation for Advanced Treatment of Pulp and Paper Mill Effluents. Water Res. 2006, 40, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Choppala, G.K.; Bolan, N.S.; Chung, J.W.; Chuasavathi, T. Biochar Reduces the Bioavailability and Phytotoxicity of Heavy Metals. Plant Soil 2011, 348, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, F.; Bertrand, N.; Lima, E.; Langer, R. Nanoparticles with Photoinduced Precipitation for the Extraction of Pollutants from Water and Soil. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rashed, M.N. Adsorption technique for the removal of organic pollutants from water and wastewater. Org. Pollut. Monit. Risk Treat. 2013, 7, 167–194. [Google Scholar]
- Sadegh, H.; Ali, G.A. Potential applications of nanomaterials in wastewater treatment: Nanoadsorbents performance. In Research Anthology on Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications of Nanomaterials; IGI Global: Hershay, PA, USA, 2021; pp. 1230–1240. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.; Saeed, K.; Mabood, F. Removal of Chromium (VI) from Aqueous Medium Using Chemically Modified Banana Peels as Efficient Low-Cost Adsorbent. Alex. Eng. J. 2016, 55, 2933–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mondal, N.K.; Basu, S.; Sen, K.; Debnath, P. Potentiality of Mosambi (Citrus limetta) Peel Dust toward Removal of Cr (VI) from Aqueous Solution: An Optimization Study. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, W.; Ooi, S.; Lee, C. Removal of Chromium (VI) from Solution by Coconut Husk and Palm Pressed Fibres. Environ. Technol. 1993, 14, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, H.; Mathur, R.; Mehrotra, I. Removal of Chromium from Industrial Effluents by Adsorption on Sawdust. Environ. Technol. Lett. 1986, 7, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutongo, F.; Kuipa, O.; Kuipa, P.K. Removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solutions using powder of potato peelings as a low cost sorbent. BioinorgChem Appl. 2014, 2014, 973153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maponya, T.C.; Hato, M.J.; Somo, T.R.; Ramohlola, K.E.; Makhafola, M.D.; Monama, G.R.; Maity, A.; Modibane, K.D.; Matata-Seru, L.M. Polyaniline-based nanocomposites for environmental remediation. In Trace Metals in the Environment-New Approaches and Recent Advances; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Samadi, A.; Xie, M.; Li, J.; Shon, H.; Zheng, C.; Zhao, S. Polyaniline-Based Adsorbents for Aqueous Pollutants Removal: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 418, 129425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, G.; Zeng, H.C. Integrated Nanocatalysts with Mesoporous Silica/Silicate and Microporous MOF Materials. Co-ord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 320-321, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, E.; Kosari, M.; Farahani, M.H.D.A.; Khiavi, N.D.; Saeedikhani, M.; Katal, R.; Zarinejad, M. A Review on Polyaniline-Based Materials Applications in Heavy Metals Removal and Catalytic Processes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 231, 115901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Srivastava, S.K.; Gupta, A.K. Polypyrrole–Polyaniline Copolymer Coated Green Rice Husk Ash as an Effective Adsorbent for the Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Contaminated Water. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 2431–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.A.; Chakraborty, S.; Ray, M. Removal and Recovery of Chromium from Wastewater Using Short Chain Polyaniline Synthesized on Jute Fiber. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 141, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Fang, Y.; Pang, Y.; Zeng, G.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, Y.; Yang, G.; Cai, Y.; Chen, J. Synergistic Adsorption and Reduction of Hexavalent Chromium Using Highly Uniform Polyaniline–Magnetic Mesoporous Silica Composite. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Lashkenari, M.S.; Eisazadeh, H. Application of Polyaniline Nanocomposite Coated on Rice Husk Ash for Removal of Hg (II) from Aqueous Media. Synth. Met. 2011, 161, 1430–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Wang, C.; Chen, W.; He, M.; Huang, B. Polyaniline Magnetic Chitosan Nanomaterials for Highly Efficient Simultaneous Adsorption and In-Situ Chemical Reduction of Hexavalent Chromium: Removal Efficacy and Mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmi; Julinawati; Nina, M.; Fathana, H.; Iqhrammullah, M. Preparation and Characterization of New Magnetic Chitosan-Glycine-PEGDE (Fe3O4/Ch-G-P) Beads for Aqueous Cd (II) Removal. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 45, 102493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmi, R.; Lelifajri, L.; Iqbal, M.; Fathurrahmi, F.; Jalaluddin, J.; Sembiring, R.; Farida, M.; Iqhrammullah, M. Preparation, Characterization and Adsorption Study of PEDGE-Cross-linked Magnetic Chitosan (PEDGE-MCh) Microspheres for Cd2+ Removal. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciano, J.S.; Ferreira, R.R.; de Souza, A.G.; Barbosa, R.F.S.; de Moura Junior, A.J.; Rosa, D.S. Biodegradable Gelatin Composite Hydrogels Filled with Cellulose for Chromium (VI) Adsorption from Contaminated Water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 181, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, R.T.; da Silva, R.C.S.; Pereira, A.C.; Borges, K.B. Self-Assembly Pipette Tip-Based Cigarette Filters for Micro-Solid Phase Extraction of Ketoconazole Cis-Enantiomers in Urine Samples Followed by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Diode Array Detection. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 7270–7279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Huang, A.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q. Effect of Different Heat Treatment Temperatures on the Chemical Composition and Structure of Chinese Fir Wood. BioResources 2016, 11, 4006–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dutra, F.V.A.; Pires, B.C.; Nascimento, T.A.; Mano, V.; Borges, K.B. Polyaniline-Deposited Cellulose Fiber Composite Prepared Via in Situ Polymerization: Enhancing Adsorption Properties for Removal of Meloxicam from Aqueous Media. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 12639–12649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhadra, S.; Singha, N.K.; Khastgir, D. Polyaniline by New Miniemulsion Polymerization and the Effect of Reducing Agent on Conductivity. Synth. Met. 2006, 156, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniappan, S. Chemical and Electrochemical Polymerization of Aniline Using Tartaric Acid. Eur. Polym. J. 2001, 37, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Hsueh, K.F.; Jang, G.W. A Study of Leucoemeraldine and Effect of Redox Reactions on Molecular Weight of Chemically Prepared Polyaniline. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Jamal, R.; Xu, F.; Ubul, A.; Abdiryim, T. The Effect of a Small Amount of Water on the Structure and Electrochemical Properties of Solid-State Synthesized Polyaniline. Materials 2012, 5, 1811–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, R.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, W. Walnut Shell-Based Activated Carbon with Excellent Copper (II) Adsorption and Lower Chromium (VI) Removal Prepared by Acid-Base Modification. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2012, 32, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqhrammullah, M.; Suyanto, H.; Rahmi; Pardede, M.; Karnadi, I.; Kurniawan, K.H.; Chiari, W.; Abdulmadjid, S.N. Cellulose Acetate-Polyurethane Film Adsorbent with Analyte Enrichment for in-Situ Detection and Analysis of Aqueous Pb Using Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS). Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 16, 100516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dula, T.; Siraj, K.; Kitte, S.A. Adsorption of Hexavalent Chromium from Aqueous Solution Using Chemically Activated Carbon Prepared from Locally Available Waste of Bamboo (Oxytenantheraabyssinica). ISRN Environ. Chem. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solgi, M.; Najib, T.; Ahmadnejad, S.; Nasernejad, B. Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Activated Carbon from Medlar Seed for Chromium Removal: Experimental Analysis and Modeling with Artificial Neural Network and Support Vector Regression. Resour. Technol. 2017, 3, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooto, N.D. Removal of Toxic Hexavalent Chromium (Cr (VI)) and Divalent Lead (Pb (II)) Ions from Aqueous Solution by Modified Rhizomes of Acorus calamus. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 20, 100624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, V.; De Riccardis, M.F.; Carbone, D.; Rotolo, P.; Bozzini, B.; Mele, C. Electrodeposition of Polyaniline–Carbon Nanotubes Composite Films and Investigation on Their Role in Corrosion Protection of Austenitic Stainless Steel by SNIFTIR Analysis. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 6035–6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheha, R.R.; El-Zahhar, A.A. Synthesis of Some Ferromagnetic Composite Resins and Their Metal Removal Characteristics in Aqueous Solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pholosi, A.; Naidoo, E.B.; Ofomaja, A.E. Intraparticle Diffusion of Cr (VI) Through Biomass and Magnetite Coated Biomass: A Comparative Kinetic and Diffusion Study. South Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 32, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.-C.; Tseng, R.-L.; Juang, R.-S. Characteristics of Elovich Equation Used for the Analysis of Adsorption Kinetics In Dye-Chitosan Systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Luna, J.; Ramírez-Montes, L.E.; Martinez-Vargas, S.; Martínez, A.I.; Mijangos-Ricardez, O.F.; González-Chávez, M.D.C.A.; Carrillo-González, R.; Solís-Domínguez, F.A.; Cuevas-Díaz, M.D.C.; Vázquez-Hipólito, V. Linear and Nonlinear Kinetic and Isotherm Adsorption Models for Arsenic Removal by Manganese Ferrite Nanoparticles. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aworanti, O.; Agarry, S.E. Kinetics, Isothermal and Thermodynamic Modelling Studies of Hexavalent Chromium Ions Adsorption from Simulated Wastewater onto ParkiaBiglobosa-Sawdust Derived Acid-Steam Activated Carbon. Methods 2017, 10, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.; Deng, H.; Jiang, Y.; Ye, C. High-Efficiency Removal of Cr (VI) from Wastewater by Mg-Loaded Biochars: Adsorption Process and Removal Mechanism. Materials 2020, 13, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piccin, J.S.; Dotto, G.L.; Pinto, L.A.A. Adsorption Isotherms and Thermochemical Data of FD&C Red n 40 binding by Chitosan. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 28, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dada, A.; Olalekan, A.; Olatunya, A.; Dada, O. Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin-RadushkevichIsotherms Studies of Equilibrium Sorption of Zn2+ Unto Phosphoric Acid Modified Rice Husk. J. Appl. Chem. 2012, 3, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra, M.; Suresh, S.; Garg, A. Tea Waste Derived Activated Carbon for the Adsorption of Sodium Diclofenac from Wastewater: Adsorbent Characteristics, Adsorption Isotherms, Kinetics, and Thermodynamics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 32210–32220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulimenko, T.; Stejskal, J.; Prokeš, J. Poly (Phenylenediamine) Dispersions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 236, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stejskal, J.; Hlavatá, D.; Holler, P.; Trchová, M.; Prokeš, J.; Sapurina, I. Polyaniline Prepared in the Presence of Various Acids: A Conductivity Study. Polym. Int. 2004, 53, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, R.; Yu, P.; Guo, S.; Wang, X. Adsorption and Reduction of Chromium (VI) from Aqueous Solution Using Polypyrrole/Calcium Rectorite Composite Adsorbent. Water Res. 2019, 160, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daradmare, S.; Xia, M.; Le, V.N.; Kim, J.; Park, B.J. Metal–Organic Frameworks/Alginate Composite Beads as Effective Adsorbents for the Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Aqueous Solution. Chemosphere 2020, 270, 129487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, F.; Nagai, N.; Itami, R.; Nakamura, T.; Kawasaki, N. Potential of Virgin and Calcined Wheat Bran Biomass for the Removal of Chromium (VI) Ion from a Synthetic Aqueous Solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.H.; Saha, J.; Saha, A.; Rao, A.K.; Chakraborty, B.; Dey, S. Adsorption Study of Chromium (VI) by Dried Biomass of Tea Leaves. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2019, 96, 447–454. [Google Scholar]
- Hanafiah, M.M.; Hashim, N.A.; Ahmed, S.; Ashraf, M.A. Removal of Chromium from Aqueous Solutions Using a Palm Kernel Shell Adsorbent. Desalination Water Treat. 2018, 118, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatan, O.G.; Alaba, P.A.; Oni, B.A.; Akpojevwe, K.; Efeovbokhan, V.; Abnisa, F. Performance of Eggshells Powder as an Adsorbent for Adsorption of Hexavalent Chromium and Cadmium from Wastewater. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, B.; Tiwary, R.K.; Yadav, M.; Singh, K.M.P. Nonlinear Regression Analysis and Response Surface Modeling of Cr (VI) Removal from Synthetic Wastewater by an Agro-Waste Cocos Nucifera: Box-Behnken Design (BBD). Int. J. Phytoremediation 2020, 23, 791–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, H.; Ghaedi, M.; Fazeli, M.; Sabzehmeidani, M.M. Removal of Hexavalent Chromium Ions and Acid Red 18 By Superparamagnetic Cofe2o4/Polyaniline Nanocomposites under External Ultrasonic Fields. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 324, 111275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsini, A.; Naciri, Y.; Laabd, M.; El Ouardi, M.; Ajmal, Z.; Lakhmiri, R.; Boukherroub, R.; Albourine, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Arginine-Doped Polyaniline/Walnut Shell Hybrid Composite with Superior Clean-Up Ability for Chromium (VI) from Aqueous Media: Equilibrium, Reusability and Process Optimization. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 316, 113832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiaee, S.; Samani, M.R.; Toghraie, D. Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Aqueous Media Using Pomegranate Peels Modified by Polymeric Coatings: Effects of Various Composite Synthesis Parameters. Synth. Met. 2020, 265, 116416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, U.K.; Kaur, M.; Garg, V.; Sud, D. Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Aqueous Solution by Agricultural Waste Biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 140, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, A.; Lu, J.; Niu, X.; Jiang, M.; Ma, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, M. Adsorption Mechanism of Hexavalent Chromium on Biochar: Kinetic, Thermodynamic, and Characterization Studies. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 27323–27331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Ting, Y.P. Polyethylenimine-Modified Fungal Biomass as a High-Capacity Biosorbent for Cr (VI) Anions: Sorption Capacity and Uptake Mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 8490–8496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chigondo, M.; Paumo, H.K.; Bhaumik, M.; Pillay, K.; Maity, A. Magnetic arginine-functionalized polypyrrole with improved and selective chromium (VI) ions removal from water. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 275, 778–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample Code | CF (gm) | Weight of PANI (gm) | Weight of APS (gm) | Weight of Product (gm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CFC15 | 0.5 | 0.075 | 0.231 | 0.34 |
| CFC25 | 0.5 | 0.15 | 1.54 | 0.36 |
| CFC50 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.54 | 0.81 |
| CFC75 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 4.63 | 1.25 |
| Sample Code | % Weight Loading of PANI (Theoretical) | Decomposition Temperature (Td) | % Weight Loss from TGA |
|---|---|---|---|
| CF | 0 | 343 | 79.5 |
| CFC15 | 15 | 396 | 79.9 |
| CFC25 | 25 | 424 | 77.6 |
| CFC50 | 50 | 440 | 78 |
| CFC75 | 75 | 455 | 77 |
| PANI | 100 | 485 | 84.8 |
| Sample Code | Qe(mg/gm) | First Order | Second Order | Pseudo First Order | Pseudo Second Order | Elovich | Intra-Particle Diffusion | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | R2 | K | R2 | K | R2 | K | R2 | R2 | Kd | R2 | ||
| PANI | 35.36 | 0.06592 | 0.8460 | 0.0242 | 0.9547 | 0.1172 | 0.8846 | 0.012 | 0.9836 | 0.8390 | 4.254 | 0.7478 |
| CFC15 | 7.15 | 0.00419 | 0.473 | 0.00043 | 0.4727 | 0.0175 | 0.3347 | 0.134 | 0.9362 | 0.0549 | 0.198 | 0.1022 |
| CFC25 | 29.52 | 0.03436 | 0.7558 | 0.007 | 0.8755 | 0.0503 | 0.9768 | 0.023 | 0.9884 | 0.9182 | 2.143 | 0.9427 |
| CFC50 | 37.24 | 0.0733 | 0.8733 | 0.0383 | 0.8765 | 0.0981 | 0.9100 | 0.020 | 0.9937 | 0.9625 | 2.725 | 0.9630 |
| CFC75 | 33.04 | 0.04476 | 0.5923 | 0.0134 | 0.7085 | 0.0718 | 0.7314 | 0.065 | 0.9984 | 0.7985 | 1.253 | 0.7239 |
| Freundlich | Langmuir | Temkin | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | Kf | n | R2 | B | qmax | R2 | KT |
| 0.9730 | 2.534 | 5.420 | 0.9888 | 36.630 | 2.4024 | 0.9867 | 1.586 |
| Adsorbent | Dosage of Adsorbent (g/L) | Time | Removal (%) | Qe(mg/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice husk ash—Ppy—PANI | 0.8 | 300 min | 98% | [26] | |
| Polypyrole-calcium rectorite composite | 1 | - | 714.29 | [58] | |
| Metal-organic framework-alginate beads | 50 | - | 98% | [59] | |
| PANI—jute | 2 | 180 min | 62.9 | [27] | |
| PANI—silica | 0.8 | 430 min | 193.85% | [28] | |
| Calcinated wheat bran | 1 | 24 h | 29.3 | [60] | |
| Tea leaves | - | 24 h | 84.5% | [61] | |
| Palm kernel | 0.5 | 45 min | 19 | [62] | |
| Eggshell powder | 125 | 120 min | 60.96% | [63] | |
| PANI—sugarcane bagasse | 1 | 100 min | 35.2 | [64] | |
| CoFe(2)O4—PANI | 0.5 | 14 min | 103.11 | [65] | |
| Arginine doped PANI—walnut shell | 0.3 | 3 h | 99% | [66] | |
| Pomegranate peels—Ppy—PANI | 10 | 90 min | 95.35% | [67] | |
| Sugarcane bagasse Oil cake Maize corn | 20 | 60 min | 92% 97% 62% | [68] | |
| Coconut fiber-polyaniline composite | 0.25 | 30 min | 93.11% | 37.24 | Present study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jha, S.; Gaur, R.; Shahabuddin, S.; Ahmad, I.; Sridewi, N. Kinetic and Isothermal Investigations on the Use of Low Cost Coconut Fiber-Polyaniline Composites for the Removal of Chromium from Wastewater. Polymers 2022, 14, 4264. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204264
Jha S, Gaur R, Shahabuddin S, Ahmad I, Sridewi N. Kinetic and Isothermal Investigations on the Use of Low Cost Coconut Fiber-Polyaniline Composites for the Removal of Chromium from Wastewater. Polymers. 2022; 14(20):4264. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204264
Chicago/Turabian StyleJha, Stuti, Rama Gaur, Syed Shahabuddin, Irfan Ahmad, and Nanthini Sridewi. 2022. "Kinetic and Isothermal Investigations on the Use of Low Cost Coconut Fiber-Polyaniline Composites for the Removal of Chromium from Wastewater" Polymers 14, no. 20: 4264. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204264
APA StyleJha, S., Gaur, R., Shahabuddin, S., Ahmad, I., & Sridewi, N. (2022). Kinetic and Isothermal Investigations on the Use of Low Cost Coconut Fiber-Polyaniline Composites for the Removal of Chromium from Wastewater. Polymers, 14(20), 4264. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204264