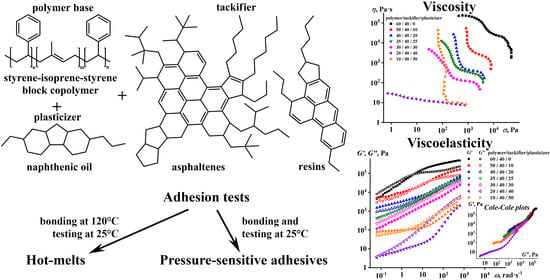
Hot-Melt and Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives Based on Styrene-Isoprene-Styrene Triblock Copolymer, Asphaltene/Resin Blend and Naphthenic Oil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Blend Preparation
2.3. Methods
3. Results
3.1. The Effect of Naphthenic Oil and ARB on SIS Properties
3.2. The Effect of the ARB Concentration on the Adhesive Properties
3.3. The Effect of the Block Copolymer and Naphthenic Oil Ratio on the Properties of Adhesives
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- −
- Both ARB and the oil do not disturb the microphase separation of the block copolymer and dissolve predominantly in the microphase of the polyisoprene blocks.
- −
- The oil seems to be unlimitedly soluble in the block copolymer, whereas ARB dissolves up to a concentration of about 20% and then forms a separate phase. In addition, ARB and the oil are not fully miscible, which becomes apparent when the SIS content in the mixture is less than 20%.
- −
- Dissolution of ARB and the oil increases the volume fraction of the polyisoprene microphase, which leads to a decrease in the viscosity of SIS and gives it the ability of irreversible deformation at very low frequencies (long observation times), thus causing stickiness. At the same time, the preservation of microphase separation ensures the dominance of elasticity at normal observation times, thus providing the strength of the formed adhesive joints.
- −
- An increase in ARB concentration improves the cohesive and adhesive characteristics of the mixture, while an increase in the oil content gradually shifts the mixture from being a hot melt to being a pressure-sensitive adhesive with a simultaneous decline in the cohesive and adhesive performance. In this respect, the role of ARB is as both a tackifier and a filler, while the role of the oil is to be a plasticizer.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manso, A.P.; Marquezini, L., Jr.; Silva, S.M.; Pashley, D.H.; Tay, F.R.; Carvalho, R.M. Stability of wet versus dry bonding with different solvent-based adhesives. Dent. Mater. 2008, 24, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.M.; Alrahlah, A.; Matinlinna, J.P.; Hamama, H.H. Effect of adhesive air-drying time on bond strength to dentin: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2019, 90, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodiuk, H.; Kenig, S. Low temperature curing epoxies for structural repair. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1994, 19, 439–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, Z. Nanostructured epoxy adhesives: A review. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 135, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkesson, D.; Skrifvars, M.; Lv, S.; Shi, W.; Adekunle, K.; Seppälä, J.; Turunen, M. Preparation of nanocomposites from biobased thermoset resins by UV-curing. Prog. Org. Coat. 2010, 67, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, A.; Trusiano, G.; Bongiovanni, R. UV-Curing of Adhesives: A Critical Review. In Progress in Adhesion and Adhesives; Mittal, K.L., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA; Scrivener: Beverly, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 3, pp. 101–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St John, N.A.; George, G.A. Diglycidyl amine-epoxy resin networks: Kinetics and mechanisms of cure. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1994, 19, 755–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatenko, V.Y.; Ilyin, S.O.; Kostyuk, A.V.; Bondarenko, G.N.; Antonov, S.V. Acceleration of epoxy resin curing by using a combination of aliphatic and aromatic amines. Polym. Bull. 2019, 77, 1519–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapari, S.; Mestry, S.; Mhaske, S.T. Developments in pressure-sensitive adhesives: A review. Polym. Bull. 2021, 78, 4075–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X. Progress on rubber-based pressure-sensitive adhesives. J. Adhes. 2018, 94, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedek, I.; Feldstein, M.M. Application of pressure-sensitive products. In Handbook of Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives and Products, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinnaratip, R.; Bhuiyan, M.S.A.; Meyers, K.; Rajachar, R.M.; Lee, B.P. Multifunctional Biomedical Adhesives. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1801568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, A.F.M. Handbook of Solubility Parameters and Other Cohesion Parameters, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.P. Viscoelastic properties of pressure-sensitive adhesives. J. Adhes. 1997, 60, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibert, F.X.; Allal, A.; Marin, G.; Derail, C. Effect of the rheological properties of industrial hot-melt and pressure-sensitive adhesives on the peel behavior. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 1999, 13, 1029–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Creton, C.; Doi, M. Simple Model on Debonding of Soft Adhesives. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 6206–6213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharde, S.; Sharma, G.; Kandasubramanian, B. Hot-Melt Adhesives: Fundamentals, Formulations, and Applications: A Critical Review. In Progress in Adhesion and Adhesives; Mittal, K.L., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, M.F. Hot melt adhesive model: Interfacial adhesion and polymer/tackifier/wax interactions. J. Adhes. 1998, 66, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Bouzidi, L.; Narine, S.S. Current research and development status and prospect of hot-melt adhesives: A review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 7524–7532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tout, R. A review of adhesives for furniture. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2000, 20, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristri, M.A.; Lubis, M.A.R.; Yadav, S.M.; Antov, P.; Papadopoulos, A.N.; Pizzi, A.; Fatriasari, W.; Ismayati, M.; Iswanto, A.H. Recent Developments in Lignin- and Tannin-Based Non-Isocyanate Polyurethane Resins for Wood Adhesives—A Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orgilés-Calpena, E.; Arán-Aís, F.; Torró-Palau, A.M.; Sánchez, M.A.M. Adhesives in the Footwear Industry: A Critical Review. Rev. Adhes. Adhes. 2019, 7, 69–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, M.P.C.; Limiñana, M.Á.P.; Silvestre, C.R.; Calpena, E.O.; Aís, F.A. Sustainable Reactive Polyurethane Hot Melt Adhesives Based on Vegetable Polyols for Footwear Industry. Polymers 2022, 14, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedek, I. Pressure-Sensitive Design, Theoretical Aspects, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalish, J.P.; Ramalingam, S.; Wamuo, O.; Vyavahare, O.; Wu, Y.; Hsu, S.L.; Paul, C.W.; Eodice, A. Role of n-alkane-based additives in hot melt adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2014, 55, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, C.W. Hot-melt adhesives. MRS Bull. 2003, 28, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einsla, M.; Griffith, W.; Himmelberger, D.; Zolynski, S.; Zhang, S.; Powell, T.; Malotky, D. Heat-Activated Pressure Sensitive Adhesives for Linerless Labels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, E.P.; Germinario, L.T.; Robe, G.R.; Williams, T.; Atkins, D.G.; Moroney, D.A.; Peters, M.A. Fundamentals of hot-melt pressure-sensitive adhesive tapes: The effect of tackifier aromaticity. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2007, 21, 637–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibert, F.X.; Marin, G.; Derail, C.; Allal, A.; Lechat, J. Rheological properties of hot melt pressure-sensitive adhesives based on styrene--isoprene copolymers. Part 1: A rheological model for [SIS-SI] formulations. J. Adhes. 2003, 79, 825–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, S.A.; Marques, C.L.; Cardozo, N.S.M. Composition and performance of styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) and styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS) hot melt pressure sensitive adhesives. J. Adhes. 2012, 88, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, P.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, X.; Liu, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, F. Hot-Melt Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives Based on SIS-g-PB Copolymer for Transdermal Delivery of Hydrophilic Drugs. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2019, 91, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L. Feasibility of Processing Hot-Melt Pressure-Sensitive Adhesive (HMPSA) with Solvent in the Lab. Processes 2021, 9, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velloso, I.; Bastos, J.B.V.; Luz, R.; Candido, L.F.; Mello, B.; Cazumbá, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Polyester Derived from Renewable Source and Its Application as Tackifiers Resins in Hot Melt Pressure Sensitive Adhesives (HMPSA). Macromol. Symp. 2020, 394, 2000114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemoto, M.; Kajiyama, M.; Mizumachi, H.; Takemura, A.; Ono, H. Miscibility and adhesive properties of ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA)-based hot-melt adhesives. I. Adhesive tensile strength. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 83, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shcherbina, A.A.; Gladkikh, Y.Y.; Chalykh, A.E. Kinetics and mechanism of formation of adhesive joints based on ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers. Polym. Sci. Ser. A. 2012, 54, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyano, M.A.; París, R.; Martín-Martínez, J.M. Viscoelastic and adhesion properties of hot-melts made with blends of ethylene-co-n-butyl acrylate (EBA) and ethylene-co-vinyl acetate (EVA) copolymers. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2019, 88, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.H.; Huang, W.H.; Chuang, K.S.; Shen, B.H. Adhesion and viscoelastic property of poly (ethylene-co-vinyl acetate) based hot melt adhesives-effects of tackifier and wax. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2020, 99, 102586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Zhu, K.; Zhu, X.; Lin, Z. Preparation and characterization of self-crosslinking fluorinated polyacrylate latexes and their pressure sensitive adhesive applications. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2019, 95, 102417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Zhou, F.; Zhu, X. The application research of benzyl methacrylate (BzMA) in acrylate latex pressure sensitive adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2021, 107, 102861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febrianto, F.; Karliati, T.; Sahri, M.H.; Syafii, W. Trans-1,4-isoprene rubber as hot melt adhesive. J. Biol. Sci. 2006, 6, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostyuk, A.; Ignatenko, V.; Smirnova, N.; Brantseva, T.; Ilyin, S.; Antonov, S. Rheology and adhesive properties of filled PIB-based pressure-sensitive adhesives. I. Rheology and shear resistance. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 1831–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, A.S.; Cordeiro, J.B.; Simões, P.A.; Gameiro, D.; Rocha, F.A.; Serra, A.C.; Coelho, J.F.J.; Fonseca, A.C. Poly(β-Pinene) as an Efficient Biobased Tackifier for Metallocene Poly(Ethylene) Based Hotmelt Adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2022, 114, 103111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Joo, H.S.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, Y.K. Adhesion and rheological properties of EVA-based hot-melt adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2006, 26, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolt, M.; Viljanmaa, M.; Södergård, A.; Törmälä, P. Blends of poly (ε-caprolactone-b-lactic acid) and poly (lactic acid) for hot-melt applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 91, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhong, H.; Jia, L.; Ling, J.; Tang, R.; Qiao, J.; Zhang, Z. Polyesteramides used for hot melt adhesives: Synthesis and effect of inherent viscosity on properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 81, 2696–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Hong, L.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Evaluation of the cure kinetics of isocyanate reactive hot-melt adhesives with differential scanning calorimetry. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 89, 2708–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsamut, C.; Suwanpreedee, R.; Manuspiya, H. Thermoplastic polyurethane-based polycarbonate diol hot melt adhesives: The effect of hard-soft segment ratio on adhesion properties. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2020, 102, 102677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuensanta, M.; Martín-Martínez, J.M. Thermoplastic polyurethane pressure sensitive adhesives made with mixtures of polypropylene glycols of different molecular weights. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2019, 88, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Dong, C.; Zhuang, W.; Shi, D.; Dong, W.; Chen, M.; Kaneko, D. Bio-Based Hotmelt Adhesives with Well-Adhesion in Water. Polymers 2021, 13, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendra, V. Rosin product review. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2019, 890, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destephen, A.; González de San Román, E.; Martínez-Tong, D.E.; Ballard, N. Cationic Polymerization of β-Pinene Using B(C6F5)3 as a Lewis Acid for the Synthesis of Tackifiers in Pressure Sensitive Adhesives. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2021, 306, 2100194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, E.G.; Lombardi, A.; Solaro, R.; Chiellini, E. Thermal characterization of three-component blends for hot-melt adhesives. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 80, 2889–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocius, A.V.; Dillard, D.A. Adhesion Science and Engineering: Surfaces, Chemistry and Applications, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Creton, C.; Papon, E. Materials science of adhesives: How to bond things together. MRS Bull. 2003, 28, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ilyin, S.O.; Petrukhina, N.N.; Kostyuk, A.V.; Dzhabarov, E.G.; Filatova, M.P.; Antonov, S.V.; Maksimov, A.L. Hydrogenation of indene–coumarone resin on palladium catalysts for use in polymer adhesives. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2019, 92, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, H.; Nomura, Y.; Hamano, R.; Yamada, R.; Matsuda, S.; Kakibe, T.; Oka, Y.; Urahama, Y. Impact Energy Absorption of Block Copolymer/Tackifier Blends: Effect of Compatibility, Viscoelasticity, and Laminate Structures. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e52654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalish, J.P.; Ramalingam, S.; Bao, H.; Hall, D.; Wamuo, O.; Hsu, S.L.; Paul, C.W.; Eodice, A.; Low, Y.G. An analysis of the role of wax in hot melt adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2015, 60, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostyuk, A.V.; Ignatenko, V.Y.; Makarova, V.V.; Antonov, S.V.; Ilyin, S.O. Polyethylene wax as an alternative to mineral fillers for preparation of reinforced pressure-sensitive adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2020, 102, 102689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.; van Reenen, A.; Duveskog, H. A comprehensive investigation into the structure-property relationship of wax and how it influences the properties of hot melt adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2020, 99, 102559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.; van Reenen, A.; Duveskog, H.; Brady, F. A comparative study of the application-based properties of hot melt adhesives (HMAs) formulated with different waxes. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2021, 111, 102974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, S.F.; Nguyen, D.V.; Kochhar, J.S.; Liu, X.Y.; Kang, L. UV-curable pressure sensitive adhesive films: Effects of biocompatible plasticizers on mechanical and adhesion properties. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 6270–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantseva, T.; Antonov, S.; Kostyuk, A.; Ignatenko, V.; Smirnova, N.; Korolev, Y.; Tereshin, A.; Ilyin, S. Rheological and adhesive properties of PIB-based pressure-sensitive adhesives with montmorillonite-type nanofillers. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 76, 228–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomina, E.V. Hot-melt adhesives based on polyamides of dimerized fatty acids and adhesive compositions from oligoamidoamines and epoxy resins. Polym. Sci. Ser. D 2012, 5, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunanopparat, T.; Menut, P.; Morel, M.H.; Guilbert, S. Plasticized wheat gluten reinforcement with natural fibers: Effect of thermal treatment on the fiber/matrix adhesion. Compos. Part A 2008, 39, 1787–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semsarzadeh, M.A.; Mehrabzadeh, M.; Arabshahi, S.S. Dynamic mechanical behavior of the dioctyl phthalate plasticized polyvinyl chloride–epoxidized soya bean oil. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadogan, D.F.; Howick, C.J. Plasticizers. In Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, 5th ed.; Othmer, K., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Gao, L.; Zheng, M.; Qiao, L.; Cui, L.; Wang, K.; Huang, D. Short-and medium-chain chlorinated paraffins in commercial rubber track products and raw materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 380, 120854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostyuk, A.V.; Ignatenko, V.Y.; Antonov, S.V.; Ilyin, S.O. Effect of surface contamination on the durability and strength of stainless steel–polyisobutylene pressure-sensitive adhesive bonds. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2019, 95, 102434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.F.; Wang, X.L.; Liu, B.W.; Ding, X.M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.Z. Fully bio-based pressure-sensitive adhesives with high adhesivity derived from epoxidized soybean oil and rosin acid. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 13261–13270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Sethi, S.K.; Manik, G. Pressure-sensitive adhesives based on acrylated epoxidized linseed oil: A computational approach. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2022, 112, 103031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodulina, T.; Bermesheva, E.; Smirnova, N.; Ilyin, S.; Brantseva, T.; Antonov, S. Adhesive properties of liquid crystalline hydroxypropyl cellulose–propylene glycol blends. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2014, 28, 1629–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocqué, M.; Voirin, C.; Lapinte, V.; Caillol, S.; Robin, J.J. Petro-based and bio-based plasticizers: Chemical structures to plasticizing properties. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2016, 54, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelletto, V.; Hamley, I.W. Morphologies of block copolymer melts. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2004, 8, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakula, T.; Koynov, K.; Boerner, H.; Huang, J.; Lee, H.I.; Pietrasik, J.; Sumerlin, B.; Matyjaszewski, K. Effect of chain topology on the self-organization and the mechanical properties of poly (n-butyl acrylate)-b-polystyrene block copolymers. Polymer 2011, 52, 2576–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, M.F.; Jacob, L. Pressure sensitive adhesives based on vectorR SIS polymers I. Rheological model and adhesive design pathways. J. Adhes. 1996, 56, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostyuk, A.V.; Smirnova, N.M.; Antonov, S.V.; Ilyin, S.O. Rheological and adhesion properties of hot-melt adhesives based on hydrocarbon resins and poly (ethylene-vinyl acetate). Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2021, 63, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, S.O.; Kostyuk, A.V.; Ignatenko, V.Y.; Smirnova, N.M.; Alekseeva, O.A.; Petrukhina, N.N.; Antonov, S.V. The effect of tackifier on the properties of pressure-sensitive adhesives based on styrene-butadiene-styrene rubber. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2018, 91, 1945–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohuriaan-Mehr, M.J.; Omidian, H. Petroleum resins: An overview. J. Macromol. Sci., Polym. Rev. 2000, 40, 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mildenberg, R.; Zander, M.; Collin, G. Hydrocarbon Resins, 1st ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mullins, O.C. The asphaltenes. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2011, 4, 393–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignatenko, V.Y.; Kostyuk, A.V.; Smirnova, N.M.; Antonov, S.V.; Ilyin, S.O. Asphaltenes as a tackifier for hot-melt adhesives based on the styrene-isoprene-styrene block copolymer. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2020, 60, 2224–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatenko, V.Y.; Kostyuk, A.V.; Kostina, J.V.; Bakhtin, D.S.; Makarova, V.V.; Antonov, S.V.; Ilyin, S.O. Heavy crude oil asphaltenes as a nanofiller for epoxy resin. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2020, 60, 1530–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, S.; Arinina, M.; Polyakova, M.; Bondarenko, G.; Konstantinov, I.; Kulichikhin, V.; Malkin, A. Asphaltenes in heavy crude oil: Designation, precipitation, solutions, and effects on viscosity. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 147, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, S.O.; Pakhmanova, O.A.; Kostyuk, A.V.; Antonov, S.V. Effect of the asphaltene, resin, and wax contents on the physicochemical properties and quality parameters of crude oils. Pet. Chem. 2017, 57, 1141–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.N. Studies of different properties of polystyrene-asphaltene composites. Macromol. Symp. 2015, 354, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.N. Preparation and properties of polypropylene-asphaltene composites. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 1957–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Thakur, V.K.; Kessler, M.R. Novel low-cost hybrid composites from asphaltene/SBS tri-block copolymer with improved thermal and mechanical properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 2394–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Kessler, M.R. Asphaltene: Structural characterization, molecular functionalization, and application as a low-cost filler in epoxy composites. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 24264–24273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ignatenko, V.Y.; Antonov, S.V.; Kostyuk, A.V.; Smirnova, N.M.; Makarova, V.V.; Ilyin, S.O. Composites based on polystyrene and asphaltenes. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2019, 92, 1712–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamkar, M.; Natale, G. A review on novel applications of asphaltenes: A valuable waste. Fuel 2021, 285, 119272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshraghian, A.; Kamkar, M.; Sundararaj, U. Asphaltene/Polymer Composites: Morphology, Compatibility, and Rheological Properties. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2022; early view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speight, J.G. The Chemistry and Technology of Petroleum, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini, Y.; Becerra, M.; Shaw, J.M. Phase behavior and thermophysical properties of Peace River bitumen+propane mixtures from 303 K to 393 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2016, 61, 2659–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez Claro, Y.A.; Schoeggl, F.F.; Taylor, S.D.; Yarranton, H.W. Phase behavior of mixtures of bitumen and n-butane. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 8530–8543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, S.O.; Ignatenko, V.Y.; Kostyuk, A.V.; Levin, I.S.; Bondarenko, G.N. Deasphalting of heavy crude oil by hexamethyldisiloxane: The effect of a solvent/oil ratio on the structure, composition, and properties of precipitated asphaltenes. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 208, 109329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, S.; Borges, B.; Quintero, F.; Piscitelly, V.; Gutierrez, L.B. Asphaltenes and other natural surfactants from Cerro Negro crude oil. Stepwise adsorption at the water/toluene interface: Film formation and hydrophobic effects. Energy Fuels 2005, 19, 1948–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Simon, S.; Sjoblom, J. Interfacial shear rheology of asphaltenes at oil–water interface and its relation to emulsion stability: Influence of concentration, solvent aromaticity and nonionic surfactant. Colloids Surf. A 2010, 366, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, P.; Harbottle, D.; Tchoukov, P.; Masliyah, J.; Sjoblom, J.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Z. Fractionation of asphaltenes in understanding their role in petroleum emulsion stability and fouling. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 3330–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbacheva, S.N.; Ilyin, S.O. Structure, rheology and possible application of water-in-oil emulsions stabilized by asphaltenes. Colloids Surf. A 2021, 618, 126442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, S.I.; Speight, J.G. Petroleum resins: Separation, character, and role in petroleum. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2001, 19, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiehe, I.A.; Yarranton, H.W.; Akbarzadeh, K.; Rahimi, P.M.; Teclemariam, A. The paradox of asphaltene precipitation with normal paraffins. Energy Fuels 2005, 19, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Shim, G.-S.; Park, J.-W.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, Y. Adhesion Performance and Recovery of Acrylic Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives Thermally Crosslinked with Styrene–Isoprene–Styrene Elastomer Blends for Flexible Display Applications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 78, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, V.; Fleury, A.; Villey, R.; Creton, C.; Ciccotti, M. Linking Peel and Tack Performances of Pressure Sensitive Adhesives. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 3267–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherbina, A.A.; Chalykh, A.E. Adhesive Compositions Based on Styrene–Isoprene–Styrene Three-Block Copolymer with Different Modifiers. Polym. Sci. Ser. D 2018, 11, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, S.O.; Strelets, L.A. Basic fundamentals of petroleum rheology and their application for the investigation of crude oils of different natures. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, S.O.; Arinina, M.P.; Polyakova, M.Y.; Kulichikhin, V.G.; Malkin, A.Y. Rheological comparison of light and heavy crude oils. Fuel 2016, 186, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatenko, V.Y.; Kostina, Y.V.; Antonov, S.V.; Ilyin, S.O. Oxidative functionalization of asphaltenes from heavy crude oil. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2018, 91, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostyuk, A.V.; Smirnova, N.M.; Ilyin, S.O. Two-Functional Phase-Change Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives Based on Polyisobutylene Matrix Filled with Paraffin Wax. J. Energy Storage 2022, 52, 104797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, G. A Practical Approach to Rheology and Rheometry, 2nd ed.; Gebrueder HAAKE: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yadykova, A.Y.; Ilyin, S.O. Rheological and adhesive properties of nanocomposite bitumen binders based on hydrophilic or hydrophobic silica and modified with bio-oil. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 342, 127946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utracki, L.A. On the viscosity-concentration dependence of immiscible polymer blends. J. Rheol. 1991, 35, 1615–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, S.O.; Makarova, V.V.; Polyakova, M.Y.; Kulichikhin, V.G. Phase state and rheology of polyisobutylene blends with silicone resin. Rheol. Acta 2020, 59, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acierno, D.; Collyer, A.A. Rheology and Processing of Liquid Crystal Polymers, 1st ed.; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 2013; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ilyin, S.O.; Makarova, V.V.; Polyakova, M.Y.; Kulichikhin, V.G. Phase behavior and rheology of miscible and immiscible blends of linear and hyperbranched siloxane macromolecules. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 22, 100833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velankar, S.; Cooper, S.L. Microphase separation and rheological properties of polyurethane melts. 3. Effect of block incompatibility on the viscoelastic properties. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Li, M.; Liu, A. A review on mechanical properties of pressure sensitive adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2013, 41, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, S.O.; Kulichikhin, V.G.; Malkin, A.Y. Unusual rheological effects observed in polyacrylonitrile solutions. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2013, 55, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkin, A.Y.; Ilyin, S.O.; Arinina, M.P.; Kulichikhin, V.G. The rheological state of suspensions in varying the surface area of nano-silica particles and molecular weight of the poly (ethylene oxide) matrix. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 2017, 295, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, S.O.; Malkin, A.Y.; Kulichikhin, V.G.; Shaulov, A.Y.; Stegno, E.V.; Berlin, A.A.; Patlazhan, S.A. Rheological properties of polyethylene/metaboric acid thermoplastic blends. Rheol. Acta 2014, 53, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, S.O.; Arinina, M.P.; Mamulat, Y.S.; Malkin, A.Y.; Kulichikhin, V.G. Rheological properties of road bitumens modified with polymer and solid nanosized additives. Colloid J. 2014, 76, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadykova, A.Y.; Ilyin, S.O. Compatibility and rheology of bio-oil blends with light and heavy crude oils. Fuel 2022, 314, 122761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkwood, B.R.; Sterne, J.A.C. Essential Medical Statistics, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Malkin, A.; Kulichikhin, V.; Ilyin, S. A modern look on yield stress fluids. Rheol. Acta 2017, 56, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, H.K.; Han, C.D. Rheological behavior of polymer blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1984, 29, 2205–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.D.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.K. Determination of the order-disorder transition temperature of block copolymers. Macromolecules 1989, 22, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhaure, J.; Kim, S. A Review of the State of Dry Adhesives: Biomimetic Structures and the Alternative Designs They Inspire. Micromachines 2017, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feldstein, M.M.; Dormidontova, E.E.; Khokhlov, A.R. Pressure Sensitive Adhesives Based on Interpolymer Complexes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 42, 79–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikov, M.B.; Borodulina, T.A.; Kotomin, S.V.; Kulichikhin, V.G.; Feldstein, M.M. Relaxation Properties of Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives upon Withdrawal of Bonding Pressure. J. Adhes. 2005, 81, 77–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gdalin, B.E.; Bermesheva, E.V.; Shandryuk, G.A.; Feldstein, M.M. Effect of Temperature on Probe Tack Adhesion: Extension of the Dahlquist Criterion of Tack. J. Adhes. 2011, 87, 111–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Modifier | τc, MPa | τs,HMA, kPa | τt,HMA, kPa | τp,PSA, N m−1 | τt,PSA, kPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | 4.2 ± 0.8 | 1300 ± 80 | 890 ± 350 | 0 | 0 |
| ARB | 6.5 ± 1.4 1,b | 1350 ± 230 d | 720 ± 340 d | 52 ± 11 b | 8 ± 13 d |
| Oil | 1.4 ± 0.1 a | 490 ± 55 a | 1100 ± 120 d | 3.5 ± 3.0 d | 35 ± 10 b |
| SIS/ARB/Oil | τc, MPa | τs,HMA, kPa | τt,HMA, kPa | τp,PSA, N m−1 | τt,PSA, kPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50/0/50 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 2 ± 5 | 260 ± 30 | 0.1 ± 0.2 | 42 ± 5 |
| 45/10/45 | 1.0 ± 0.1 1,d | 9 ± 4 a | 700 ± 660 d | 240 ± 10 a | 50 ± 30 d |
| 40/20/40 | 0.6 ± 0.1 b | 420 ± 180 b | 700 ± 400 d | 490 ± 40 a | 60 ± 20 d |
| 35/30/35 | 0.7 ± 0.1 b | 590 ± 150 b | 600 ± 100 b | 710 ± 20 a | 52 ± 6 a |
| 30/40/30 | 1.0 ± 0.1 d | 750 ± 200 b | 1200 ± 300 b | 660 ± 150 a | 24 ± 11 b |
| SIS/ARB/Oil | τc, MPa | τs,HMA, kPa | τt,HMA, kPa | τp,PSA, N m−1 | τt,PSA, kPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60/40/0 | 4.2 ± 0.4 1,a | 1350 ± 230 a | 720 ± 340 a | 52 ± 11 b | 8 ± 13 a |
| 50/40/10 | 2.0 ± 0.3 b | 980 ± 140 a | 1990 ± 270 a | 12 ± 1 b | 11 ± 4 c |
| 40/40/20 | 1.70 ± 0.02 a | 780 ± 210 b | 2220 ± 280 a | 53 ± 3 b | 20 ± 11 d |
| 35/40/25 | 1.1 ± 0.4 d | 820 ± 90 d | 1710 ± 260 a | 160 ± 20 b | 22 ± 2 d |
| 30/40/30 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 750 ± 200 | 1200 ± 300 | 660 ± 150 | 24 ± 11 |
| 20/40/40 | 0.40 ± 0.05 a | 250 ± 50 b | 960 ± 170 c | 600 ± 60 d | 103 ± 12 a |
| 10/40/50 | 0.20 ± 0.03 a | 110 ± 40 b | 900 ± 240 b | 440 ± 100 b | 94 ± 22 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ilyin, S.O.; Melekhina, V.Y.; Kostyuk, A.V.; Smirnova, N.M. Hot-Melt and Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives Based on Styrene-Isoprene-Styrene Triblock Copolymer, Asphaltene/Resin Blend and Naphthenic Oil. Polymers 2022, 14, 4296. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204296
Ilyin SO, Melekhina VY, Kostyuk AV, Smirnova NM. Hot-Melt and Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives Based on Styrene-Isoprene-Styrene Triblock Copolymer, Asphaltene/Resin Blend and Naphthenic Oil. Polymers. 2022; 14(20):4296. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204296
Chicago/Turabian StyleIlyin, Sergey O., Viktoria Y. Melekhina, Anna V. Kostyuk, and Nina M. Smirnova. 2022. "Hot-Melt and Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives Based on Styrene-Isoprene-Styrene Triblock Copolymer, Asphaltene/Resin Blend and Naphthenic Oil" Polymers 14, no. 20: 4296. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204296
APA StyleIlyin, S. O., Melekhina, V. Y., Kostyuk, A. V., & Smirnova, N. M. (2022). Hot-Melt and Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives Based on Styrene-Isoprene-Styrene Triblock Copolymer, Asphaltene/Resin Blend and Naphthenic Oil. Polymers, 14(20), 4296. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204296





.png)