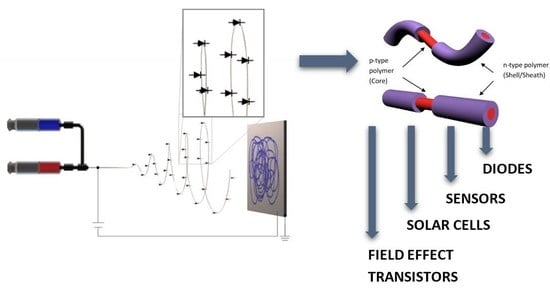
Electrospinning Technique for Fabrication of Coaxial Nanofibers of Semiconductive Polymers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, S.; Si, Y.; Han, Y.; Wu, T.; Iqbal, M.I.; Fei, B.; Li, R.K.Y.; Hu, J.; Qu, J. Recent Progress in Protective Membranes Fabricated via Electrospinning: Advanced Materials, Biomimetic Structures, and Functional Applications. Adv. Mater. 2021, 34, 2107938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Kang, S.; Park, J.; Hwang, J.J. Fabrication of silver nanowire coated fibrous air filter medium via a two-step process of electrospinning and electrospray for anti-bioaerosol treatment. Haz. Mat. 2021, 411, 125043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, D.; Liu, Y.; Zou, Q.; Xu, S.; Luo, S.; Ye, C. Coaxial bioelectrospinning of P34HB/PVA microfibers biomimetic scaffolds with simultaneity cell-laden for improving bone regeneration. Mat. Des. 2022, 213, 110349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Steckl, A.J. Coaxial electrospinning formation of complex polymer fibers and their applications. Chem. Plus Chem. 2019, 84, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Abdelhakim, H.E. Drug Delivery Applications of Coaxial Electrospun Nanofibres in Cancer Therapy. Molecules 2022, 27, 1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Garcia, W.; Jayathilaka, W.A.D.M.; Chinnappan, A.; Tran, T.Q.; Baskar, C.; Thomas, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Nanocomposites for electronic applications that can be embedded for textiles and wearables. Sci. China. Tech. Sci. 2019, 62, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayathilaka, W.A.D.M.; Qi, K.; Qin, Y.; Chinnappan, A.; Serrano-Garcia, W.; Chinnappan, B.; Wang, H.; He, J.; Cui, S.; Thomas, S.; et al. Significance of nanomaterials in wearables: A review on wearable actuators and sensors. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1805921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayan, M.A.H.; Taromi, F.A.; Lanzi, M.; Pierini, F. Enhanced efficiency in hollow core electrospun nanofiber-based organic solar cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Yang, C.; Gong, X.; Lee, K.; Heeger, A.J. Thermally stable, efficient polymer solar cells with nanoscale control of the interpenetrating network morphology. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Takeda, Y.; Mizukami, M.; Kumaki, D.; Tokito, S. Fully solution-processed flexible organic thin film transistor arrays with high mobility and exceptional uniformity. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luzio, A.; Canesi, E.V.; Bertarelli, C.; Caironi, M. Electrospun polymer fibers for electronic applications. Materials 2014, 7, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinschmidt, A.T.; Root, S.E.; Lipomi, D.J. Poly(3-hexylthiophene) (P3HT): Fruit fly or outlier in organic solar cell research? Mater. Chem. 2017, 5, 11396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.C.; Liu, C.L.; Chen, W.C. Flexible nonvolatile transistor memory devices based on One-Dimensional electrospun P3HT: Au hybrid nanofibers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimia-Vladu, M. “Green” electronics: Biodegradable and biocompatible materials and devices for sustainable future. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, G.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Kai, D.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun photosensitive nanofibers: Potential for photocurrent therapy in skin regeneration. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2012, 12, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, V.; Altobelli, R.; Cirillo, V.; Cummaro, A.; Ambrosio, L. Additive electrospraying: A route to process electrospun scaffolds for controlled molecular release. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2015, 26, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moge, A.K.; Gupta, B.S. Co-axial electrospinning for nanofiber structures: Preparation and applications. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ding, S.; Zhu, W.; Feng, L.; Dong, H.; Hu, W.J. Recent advances in one-dimensional organic p-n heterojunctions for optoelectronic device applications. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 9388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleshin, A.N. Polymer Nanofibers and Nanotubes: Charge Transport and Device Applications. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzales, R.; Pinto, N.J. Electrospun poly (3-hexylthiophene-2, 5-diyl) fiber field effect transistor. Synth. Met. 2005, 151, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.F.; Sun, B.; Breiby, D.W.; Nielsen, M.M.; Sölling, T.I.; Giles, M.; McCulloch, I.; Sirringhaus, H. Enhanced mobility of poly (3-hexylthiophene) transistors by spin-coating from high-boiling-point solvents. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlo, J.A.; Frisbie, C.D.J. Field effect transport and trapping in regioregular polythiophene nanofibers. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 19169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, A.; Jenekhe, S.A. High electron mobility in ladder polymer field-effect transistors. JACS 2003, 125, 13656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briseno, A.L.; Mansfeld, S.C.B.; Shamberger, P.J.; Ohuchi, F.S.; Bao, Z.; Jenekhe, S.A.; Xia, Y. Self-assembly, molecular packing, and electron transport in n-type polymer semiconductor nanobelts. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, W.; Pinto, N.J. Electrospun fibers of poly (vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene)/poly (3-hexylthiophene) blends from tetrahydrofuran. Ferroelectrics 2012, 432, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serrano, W.; Meléndez, A.; Ramos, I.; Pinto, N.J. Poly (lactic acid)/poly (3-hexylthiophene) composite nanofiber fabrication for electronic applications. Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.S.; Kim, T.G.; Park, T.G. Surface-functionalized electrospun nanofibers for tissue engineering and drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, M.O.; Morfa, A.J.; White, M.S.; Kopidakis, N.; Shaheen, S.E.; Rumbles, G.; Ginley, D.S. Pathways for the degradation of organic photovoltaic P3HT:PCBM based devices. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 2008, 92, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briseno, A.L.; Kim, F.S.; Babel, A.; Xia, Y.; Jenekhe, S.A. n-Channel polymer thin film transistors with long-term air-stability and durability and their use in complementary inverters. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 16461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, J.E. Addressing challenges. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Garcia, W. Advanced Organic Polymers for the Nanoscale Fabrication of Fiber-Based Electronics Using the Electrospinning Technique. USF Tampa Graduate Theses and Dissertations. 2021. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usf.edu/etd/9228 (accessed on 24 October 2022).
- Sundarrajan, S.; Murugan, R.; Nair, A.S.; Ramakrishna, S. Fabrication of P3HT/PCBM solar cloth by electrospinning technique. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, P.; Schiffman, J.D. Beyond the single-nozzle: Coaxial electrospinning enables innovative nanofiber chemistries, geometries, and applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, N.J.; Carrasquillo, K.V.; Rodd, C.M.; Agarwal, R. Rectifying junctions of tin oxide and poly (3-hexylthiophene) nanofibers fabricated via electrospinning. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 083504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Q.; Meguro, H.; Okamoto, S.; Kimura, M. Flexible tactile sensor using the reversible deformation of poly (3-hexylthiophene) nanofiber assemblies. Langmuir 2012, 28, 17593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Moon, G.D.; Jeong, U.J. Continuous production of uniform poly (3-hexylthiophene)(P3HT) nanofibers by electrospinning and their electrical properties. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, J.H.; Koh, W.G.; Myoung, J.M.; Hur, J.H.; Park, J.J.; Cho, J.H.; Jeong, U. Periodic array of polyelectrolyte-gated organic transistors from electrospun poly (3-hexylthiophene) nanofibers. Nano. Lett. 2010, 10, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, A.; Wind, J.D.; Jenekhe, S.A. Ambipolar charge transport in air-stable polymer blend thin-film transistors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2004, 14, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenekhe, S.A.; Yi, S. Efficient photovoltaic cells from semiconducting polymer heterojunctions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 77, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.M.; Jenekhe, S.A. Efficient solar cells from layered nanostructures of donor and acceptor conjugated polymers. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Wang, X.; Lee, W.H.; Lim, J.A.; Kim, J.S.; Kwak, D.; Cho, K. Organic thin-film transistors based on blends of poly (3-hexylthiophene) and polystyrene with a solubility-induced low percolation threshold. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Lim, J.A.; Wang, X.; Lee, W.H.; Hwang, M.; Cho, K. Versatile use of vertical-phase-separation-induced bilayer structures in organic thin-film transistors. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 1141–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, J.; Cha, S.N.; Im, K.; Lee, S.W.; Jeong, U.; Kim, J.; Park, J.J. P3HT-PS blend nanofiber FET based on electrospinning. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Nanotechnology: Joint Symposium with NANO Korea 2010, Ilsan, Republic of Korea, 17–20 August 2010; pp. 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, W.; Meléndez, A.; Ramos, I.; Pinto, N.J. Electrospun composite poly (lactic acid)/polyaniline nanofibers from low concentrations in CHCl3: Making a biocompatible polyester electro-active. Polymer 2014, 55, 5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenekhe, S.A.; de Paor, L.R.; Chen, X.L.; Tarkka, R.M. Photoinduced electron transfer in binary blends of conjugated polymers. Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Park, K.; Dai, L.J. Liquid crystalline polymers for efficient bilayer-bulk-heterojunction solar cells. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 7892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, K.S.; Taylor-Hamilton, B.E.; Spry, R.J.; Ferguson, J.B. Photoconducting properties of a ladder polymer. J. Appl. Phys. 1995, 77, 3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serrano-Garcia, W.; Ramakrishna, S.; Thomas, S.W. Electrospinning Technique for Fabrication of Coaxial Nanofibers of Semiconductive Polymers. Polymers 2022, 14, 5073. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235073
Serrano-Garcia W, Ramakrishna S, Thomas SW. Electrospinning Technique for Fabrication of Coaxial Nanofibers of Semiconductive Polymers. Polymers. 2022; 14(23):5073. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235073
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerrano-Garcia, William, Seeram Ramakrishna, and Sylvia W. Thomas. 2022. "Electrospinning Technique for Fabrication of Coaxial Nanofibers of Semiconductive Polymers" Polymers 14, no. 23: 5073. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235073
APA StyleSerrano-Garcia, W., Ramakrishna, S., & Thomas, S. W. (2022). Electrospinning Technique for Fabrication of Coaxial Nanofibers of Semiconductive Polymers. Polymers, 14(23), 5073. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235073