Development of High Temperature Resistant Stereocomplex PLA for Injection Moulding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
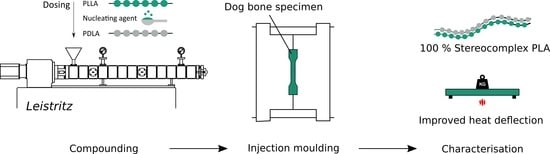
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Measurements
2.3.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.3.2. Wide-Angle X-ray Diffraction (WAXD)
2.3.3. (Thermo-)Mechanical Test
3. Results
3.1. Screening Nucleating Agents
3.2. Influence of the Cooling Rate on the Crystallisation Behaviour
3.3. Injection Moulding
3.4. (Thermo-) Mechanical Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Name | Mould Temp. (°C) | Injection Pressure (bar) | Injection Time (s) | Holding Pressure (bar) | Holding Time (s) | Cycle Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Finn | 33 | 200 | 2.51 | 30 | 10 | 46 |
| 106 | 200 | 2.05 | 35 | 50 | 126 | |
| 121 | 200 | 2.05 | 35 | 50 | 126 | |
| NA-21 | 33 | 200 | 2.51 | 40 | 10 | 50 |
| 106 | 200 | 2.09 | 50 | 10 | 47 | |
| 121 | 200 | 2.29 | 10 | 10 | 47 | |
| 142 | 200 | 2.05 | 10 | 10 | 47 | |
| NA/Finn | 33 | 200 | 0.5 | 45 | 3 | 19 |
| 106 | 200 | 2.05 | 10 | 10 | 47 | |
| 121 | 200 | 2.05 | 10 | 10 | 47 | |
| 142 | 200 | 2.05 | 35 | 15 | 53 | |
| 158 | 200 | 2.05 | 35 | 15 | 53 |
References
- The Commission Calls for a Climate Neutral Europe by 2050*. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/en/IP_18_6543 (accessed on 27 October 2020).
- Yates, M.R.; Barlow, C.Y. Life cycle assessments of biodegradable, commercial biopolymers—A critical review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2013, 78, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auras, R.A.; Lim, L.-T. Poly(Lactic Acid): Synthesis, Structures, Properties, Processing, and Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; ISBN 9780470293669. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, L.; Lei, J.; Yan, Z.; Zhong, G.; Li, Z. Simultaneously improving stiffness, toughness, and heat deflection resistance of polylactide using the strategy of orientation crystallization amplified by interfacial interactions. Polym. Cryst. 2018, 1, e10004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urayama, H.; Kanamori, T.; Kimura, Y. Microstructure and thermomechanical properties of glassy polylactides with different optical purity of the lactate units. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2001, 286, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Dever, M.; Fair, N.; Benson, R.S. Thermal and mechanical properties of poly(lactic Acid) and poly(ethylene/butylene Succinate) blends. J. Environ. Polym. Degrad. 1997, 5, 225–235. [Google Scholar]
- Lostocco, M.R.; Borzacchiello, A.; Huang, S.J. Binary and ternary poly(lactic acid)/poly(ϵ-caprolactone) blends: The effects of oligo-ϵ-caprolactones upon mechanical properties. Macromol. Symp. 1998, 130, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, O.; Avérous, L. Poly(lactic acid): Plasticization and properties of biodegradable multiphase systems. Polymer 2001, 42, 6209–6219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofar, M.; Salehiyan, R.; Ciftci, U.; Jalali, A.; Durmuş, A. Ductility improvements of PLA-based binary and ternary blends with controlled morphology using PBAT, PBSA, and nanoclay. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 182, 107661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huneault, M.A. Effect of nucleation and plasticization on the crystallization of poly(lactic acid). Polymer 2007, 48, 6855–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Focarete, M.L.; Scandola, M.; Dobrzynski, P.; Marek, K. Miscibility and Mechanical Properties of Blends of (l)-Lactide Copolymers with Atactic Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate). Macromolecules 2002, 35, 8472–8477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiki, S.; Miyamoto, M.; Kimura, Y. Synthesis and characterization of hydroxy-terminated [RS]-poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and its utilization to block copolymerization with l-lactide to obtain a biodegradable thermoplastic elastomer. Polymer 2000, 41, 7369–7379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi-Rovshandeh, J.; Farnia, S.M.F.; Sarbolouki, M.N. Synthesis and characterization of novel ABA triblock copolymers fromL-lactide, glycolide, and PEG. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 2004–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinga-Carrasco, G.; Zarna, C.; Rodríguez-Fabià, S.; Leirset, I.; Tanase-Opedal, M.; Molteberg, D.; Echtermeyer, A.; Hindersland, L.K. Side streams from flooring laminate production—Characterisation and recycling in biocomposite formulations for injection moulding. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 153, 106723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Wang, G.; Zhao, H.; Lin, J.; Zhao, G.; Park, C.B. Strong and super thermally insulating in-situ nanofibrillar PLA/PET composite foam fabricated by high-pressure microcellular injection molding. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 390, 124520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barczewski, M.; Hejna, A.; Aniśko, J.; Andrzejewski, J.; Piasecki, A.; Mysiukiewicz, O.; Bąk, M.; Gapiński, B.; Ortega, Z. Rotational molding of polylactide (PLA) composites filled with copper slag as a waste filler from metallurgical industry. Polym. Test. 2022, 106, 107449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, V.; Zhang, K.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Overcoming the fundamental challenges in improving the impact strength and crystallinity of PLA biocomposites: Influence of nucleating agent and mold temperature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 11203–11214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielen, M. Biokunststoffe Grundlagen, Anwendungen, Markte; Polymedia Publisher GmbH: Mönchengladbach, Germany, 2014; ISBN 3981498100. [Google Scholar]
- Soroudi, A.; Jakubowicz, I. Recycling of bioplastics, their blends and biocomposites: A review. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 2839–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sato, H.; Tsuji, H.; Noda, I.; Ozaki, Y. Infrared Spectroscopic Study of CH3···OC Interaction during Poly(l-lactide)/Poly(d-lactide) Stereocomplex Formation. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 1822–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasua, J.-R.; López Rodríguez, N.; López Arraiza, A.; Meaurio, E. Stereoselective Crystallization and Specific Interactions in Polylactides. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 8362–8371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Yang, J.; Shan, G.; Bao, Y.; Weng, Z.; Cao, A.; Yazawa, K.; Inoue, Y. Temperature-Variable FTIR and Solid-State 13C NMR Investigations on Crystalline Structure and Molecular Dynamics of Polymorphic Poly(l-lactide) and Poly(l-lactide)/Poly(d-lactide) Stereocomplex. Macromolecules 2011, 45, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Hyu Hyon, S.; Ikada, Y. Stereocomplex formation between enantiomeric poly(lactic acid)s. 3. Calorimetric studies on blend films cast from dilute solution. Macromolecules 1991, 24, 5651–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Ikada, Y. Stereocomplex formation between enantiomeric poly(lactic acids). 9. Stereocomplexation from the melt. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 6918–6926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Ikada, Y. Stereocomplex formation between enantiomeric poly(lactic acid)s. XI. Mechanical properties and morphology of solution-cast films. Polymer 1999, 40, 6699–6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Rodríguez, N.; Martínez de Arenaza, I.; Meaurio, E.; Sarasua, J.R. Improvement of toughness by stereocomplex crystal formation in optically pure polylactides of high molecular weight. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 37, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, M.; Kimura, Y. Thermomechanical properties of stereoblock poly(lactic acid)s with different PLLA/PDLA block compositions. Polymer 2008, 49, 2656–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, S.R.; Hakkarainen, M.; Inkinen, S.; Södergård, A.; Albertsson, A.C. Customizing the hydrolytic degradation rate of stereocomplex PLA through different PDLA architectures. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 1212–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Fukui, I. Enhanced thermal stability of poly(lactide)s in the melt by enantiomeric polymer blending. Polymer 2003, 44, 2891–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Yamashita, Y. Highly accelerated stereocomplex crystallization by blending star-shaped 4-armed stereo diblock poly(lactide)s with poly(d-lactide) and poly(l-lactide) cores. Polymer 2014, 55, 6444–6450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakuta, M.; Hirata, M.; Kimura, Y. Stereoblock polylactides as high-performance bio-based polymers. Polym. Rev. 2009, 49, 107–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnama, P.; Kim, S.H. Stereocomplex formation of high-molecular-weight polylactide using Supercritical fluid. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnama, P.; Jung, Y.; Kim, S.H. Stereocomplexation of poly (l-lactide) and random copolymer poly (d-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone) to enhance melt stability. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 4012–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biela, T.; Duda, A.; Penczek, S. Enhanced melt stability of star-shaped stereocomplexes as compared with linear stereocomplexes. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 3710–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, R.Y.; Yang, W.; Jiang, W.R.; Liu, Z.Y.; Xie, B.H.; Yang, M.B.; Fu, Q. Stereocomplex formation of high-molecular-weight polylactide: A low temperature approach. Polymer 2012, 53, 5449–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhang, X.; Wen, T.; De Vos, S.; Joziasse, C.; Wang, D. Temperature dependence of crystalline transition of highly-oriented poly(l-lactide)/poly(d-lactide) blend: In-situ synchrotron X-ray scattering study. Polymer 2013, 54, 964–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tashiro, K.; Tsuji, H.; Domb, A.J. Investigation of phase transitional behavior of poly(L-lactide)/ poly(D-lactide) blend used to prepare the highly-oriented stereocomplex. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urayama, H.; Kanamori, T.; Fukushima, K.; Kimura, Y. Controlled crystal nucleation in the melt-crystallization of poly(L-lactide) and poly(L-lactide)/poly(D-lactide) stereocomplex. Polymer 2003, 44, 5635–5641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Pan, P.; Shan, G.; Bao, Y. Stereocomplex crystallization of high-molecular-weight poly(l-lactic acid)/poly(d-lactic acid) racemic blends promoted by a selective nucleator. Polymer 2015, 63, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, R.; De Vos, S.; Wang, R.; Joziasse, C.A.P.; Wang, D. Favorable formation of stereocomplex crystals in poly(l-lactide)/poly(d-lactide) blends by selective nucleation. Polymer 2015, 76, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, R.Y.; Yang, W.; Wei, X.F.; Xie, B.H.; Yang, M.B. Enhanced formation of stereocomplex crystallites of high molecular weight poly(l -lactide)/poly(d -lactide) blends from melt by using poly(ethylene glycol). ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2301–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzeziński, M.; Bogusławska, M.; Ilčíková, M.; Mosnáček, J.; Biela, T. Unusual thermal properties of polylactides and polylactide stereocomplexes containing polylactide-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 8714–8721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Liang, Z.; Cao, A.; Inoue, Y. Layered metal phosphonate reinforced poly(L-lactide) composites with a highly enhanced crystallization rate. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbion Total PLA Documentation, Certificates & Statements. Available online: https://www.total-corbion.com/downloads/ (accessed on 19 October 2014).
- Nakazawa, K.; Tobita, E.; Yukino, T.; Urayama, H.; Kanamori, T.; Okuyama, H. Polylactic Acid-Based Resin Compositions, Molded Arcticles and Process for Producing the Same. 2002. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/EP1460107A1/en (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Tsuji, H.; Horii, F.; Nakagawa, M.; Ikada, Y.; Odani, H.; Kitamaru, R. Stereocomplex formation between enantiomeric poly(lactic acid)s. 7. Phase structure of the stereocomplex crystallized from a dilute acetonitrile solution as studied by high-resolution solid-state carbon-13 NMR spectroscopy. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 4114–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolstad, J.J. Crystallization kinetics of poly(L-lactide-co-meso-lactide). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 62, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Tezuka, Y. Stereocomplex formation between enantiometric poly(lactic acid)s. 12. Spherulite growth of low-molecular-weight poly(lactic acid)s from the melt. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, K.; Kimura, Y. Stereocomplexed polylactides (Neo-PLA) as high-performance bio-based polymers: Their formation, properties, and application. Polym. Int. 2006, 55, 626–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, H.; Sasai, K. Effect of the addition of poly(d-lactic acid) on the thermal property of poly(l-lactic acid). Polymer 2003, 44, 2569–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Takai, H.; Saha, S.K. Isothermal and non-isothermal crystallization behavior of poly(l-lactic acid): Effects of stereocomplex as nucleating agent. Polymer 2006, 47, 3826–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.C.; Hillmyer, M.A. Polylactide stereocomplex crystallites as nucleating agents for isotactic polylactide. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2001, 39, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tashiro, K.; Tsuji, H.; Domb, A.J. Disorder-to-Order Phase Transition and Multiple Melting Behavior of Poly(l-lactide) Investigated by Simultaneous Measurements of WAXD and DSC. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 1352–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohmeyer, N.; Müller, B.; Behrendt, N.; Hillenbrand, J.; Klaiber, M.; Zhang, X.; Smith, P.; Altstädt, V.; Sessler, G.M.; Schmidt, H.-W. Nucleation of isotactic polypropylene by triphenylamine-based trisamide derivatives and their influence on charge-storage properties. Polymer 2004, 45, 6655–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Yu, Z.; Cai, Y.; Hu, D.; Yan, S.; Chen, X.; Yin, J. Crystallization behavior and crystallite morphology control of poly(L-lactic acid) through N, N′-bis(benzoyl)sebacic acid dihydrazide. Polym. Int. 2013, 62, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulinski, Z.; Piorkowska, E. Crystallization, structure and properties of plasticized poly(l-lactide). Polymer 2005, 46, 10290–10300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Shanks, R.A.; Stachurski, Z.H. Kinetics of polymer crystallisation. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1995, 20, 651–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocic, N. Bestimmung des Keimbildungsexponenten für die Kristallisation von Polymeren Durch Nicht-Isotherme DSC-Analyse, Phd, Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg, Würzbug 18-11-2014. Available online: https://opus.bibliothek.uni-wuerzburg.de/frontdoor/index/index/year/2015/docId/11395 (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Saeidlou, S.; Huneault, M.A.; Li, H.; Park, C.B. Poly(lactic acid) crystallization. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1657–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogsteen, W.; Postema, A.R.; Pennings, A.J.; Ten Brinke, G.; Zugenmaier, P. Crystal structure, conformation and morphology of solution-spun poly(L-lactide) fibers. Macromolecules 2002, 23, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizzolara, D.; Cantow, H.J.; Diederichs, K.; Keller, E.; Domb, A.J. Mechanism of the Stereocomplex Formation between Enantiomeric Poly(lactide)s. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikada, Y.; Jamshidi, K.; Tsuji, H.; Hyu Hyon, S. Stereocomplex formation between enantiomeric poly(lactides). Macromolecules 1987, 20, 904–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talc R050087—RRUFF Database: Raman, X-ray, Infrared, and Chemistry. Available online: http://rruff.info/talc/R050087 (accessed on 8 October 2019).
- Tarkhanov, E.; Lehmann, A.; Menrath, A. Halfway to Technical Stereocomplex PLA Products—An Arduous Path to a Breakthrough. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 2000417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rösler, J.; Harders, H.; Bäker, M. Mechanisches Verhalten der Polymere; Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cocca, M.; Lorenzo, M.L.D.; Malinconico, M.; Frezza, V. Influence of crystal polymorphism on mechanical and barrier properties of poly(l-lactic acid). Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menges, G.; Haberstroh, E.; Michaeli, W.; Schmachtenberg, E. Menges Werkstoffkunde Kunststoffe; Carl Hanser Verlag GmbH & Co. KG: München, Germany, 2011; ISBN 978-3-446-42762-4. [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa, Y.; Abe, H.; Fujita, M.; Iwata, T.; Inoue, Y.; Doi, Y. Crystal Growth in Poly(L-lactide) Thin Film Revealed by in situ Atomic Force Microscopy. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2003, 204, 1822–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, A.; Huneault, M.A.; Saı¨d Elkoun, S. Effect of thermal history on nucleation and crystallization of poly(lactic acid). J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 7768–7779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Name | Matrix | Additive | Publication | Processing Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L130 | L130 | - | [44] | - |
| L130/D070 | L130 + D070 | - | - | - |
| Finn | L130 + D070 | 1% Finntalc-M03 | - | - |
| NA-21 | L130 + D070 | 1% NA-21 | [38,45] | Solvent casting, chloroform |
| NA-21/Finn | L130 + D070 | 1% NA-21 + 1% Finntalc-M03 | [38,45] | Solvent casting, chloroform |
| TMB-5 | L130 + D070 | 0.5% TMB-5 | [40] | Solvent casting, chloroform |
| PPZn | L130 + D070 | 1% PPZn | [39] | Solvent casting, chloroform |
| PEG 400 | L130 + D070 | 10% PEG 400 | [41] | Solvent casting, dichloromethane |
| PEG 1500 | L130 + D070 | 10% PEG 1500 | [41] | Solvent casting, dichloromethane |
| Name | Tc (C) | Δhc (J/g) | Tc, sc (°C) | Δhc, sc (J/g) | Tcc (°C) | Δhcc (J/g) | Tm, hm (°C) | Δhm, hm (J/g) | Tm, sc (°C) | Δhm, sc (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L130 | - | - | - | - | 136.2 | 12.2 | 172.6 | 12.8 | ||
| L130/D070 | 104.1 | 14.1 | - | - | 101.1 | 17.5 | 174.2 | 40.5 | 220.8 | 13.8 |
| 1% PPZn | 134.2 | 35.8 | 168.9 | 15.7 | - | - | 173.9 | 39.8 | 220.8 | 15.3 |
| 1% Finntalc-M03 | 135.3 | 38.2 | 165.8 | 15.4 | - | - | 173.9 | 40.7 | 220.6 | 14.2 |
| 0.5% TMB-5 | 128.1 | 47.1 | - | - | - | - | 174.0 | 41.3 | 221.1 | 15.6 |
| 10% PEG 400 | 128.3 | 24.2 | 146.1 | 25.1 | - | - | 166.4 | 24.1 | 219.0 | 37.5 |
| 10% PEG 1500 | 110.6 | 24.9 | 126.3 | 13.7 | - | - | 172.9 | 35.0 | 219.6 | 23.7 |
| 1% NA-21 | - | - | 149.0 | 54.3 | - | - | - | - | 217.5 | 52.2 |
| 1% NA-21 + 1% Finn | - | - | 168.4 | 59.3 | - | - | - | - | 216.7 | 57.2 |
| Rate (K/min) | Tc (°C) | Δhc (J/g) | Δhcc (J/g) | Tm, hm (°C) | Δhm, hm (J/g) | Tm, sc (°C) | Δhm, sc (J/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1% NA-21 | 20 | 142.1 | 40.9 | - | - | - | 219.7 | 45.5 |
| 30 | 135.9 | 35.3 | 3.1 | 165.4 | 3.7 | 221.1 | 46.1 | |
| 40 | 131.5 | 31.7 | 4.6 | 165.8 | 5.7 | 220.7 | 47.3 | |
| 50 | 127.6 | 27.9 | 6.0 | 166.1 | 6.1 | 220.4 | 47.8 | |
| 60 | 123.0 | 28.9 | 6.7 | 166.2 | 7.1 | 220.7 | 50.8 | |
| 70 | 121.4 | 27.2 | 6.0 | 165.5 | 5.6 | 220.8 | 51.8 | |
| 1% NA-21 + 1% Finn | 20 | 162.6 | 56.0 | - | - | - | 219.0 | 54.6 |
| 30 | 157.2 | 51.5 | - | - | - | 220.6 | 55.5 | |
| 40 | 151.4 | 47.8 | - | - | - | 221.9 | 51.4 | |
| 50 | 147.5 | 44.4 | - | - | - | 221.4 | 48.4 | |
| 60 | 142.5 | 41.1 | - | - | - | 221.6 | 48.5 | |
| 70 | 137.6 | 37.6 | - | - | - | 222.0 | 45.7 |
| Name | Mould Temp. (°C) | Xc,sc (%) | Xc,hm (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1% Finn | 33 °C | 3.44 | 1.23 |
| 107 °C | 23.68 | 7.08 | |
| 123 °C | 25.90 | 7.63 | |
| 1% NA-21 | 33 °C | 19.17 | - |
| 106 °C | 39.47 | - | |
| 121 °C | 46.10 | - | |
| 142 °C | 48.05 | - | |
| 1% NA-21 + 1% Finn | 33 °C | 30.62 | - |
| 108 °C | 39.45 | - | |
| 123 °C | 37.59 | - | |
| 143 °C | 41.36 | - | |
| 158 °C | 43.41 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Körber, S.; Moser, K.; Diemert, J. Development of High Temperature Resistant Stereocomplex PLA for Injection Moulding. Polymers 2022, 14, 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030384
Körber S, Moser K, Diemert J. Development of High Temperature Resistant Stereocomplex PLA for Injection Moulding. Polymers. 2022; 14(3):384. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030384
Chicago/Turabian StyleKörber, Sebastian, Kevin Moser, and Jan Diemert. 2022. "Development of High Temperature Resistant Stereocomplex PLA for Injection Moulding" Polymers 14, no. 3: 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030384
APA StyleKörber, S., Moser, K., & Diemert, J. (2022). Development of High Temperature Resistant Stereocomplex PLA for Injection Moulding. Polymers, 14(3), 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030384