Fabrication of Paper-Based Microfluidics by Spray on Printed Paper
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication and Characterization of Paper-Based Microfluidic Chips
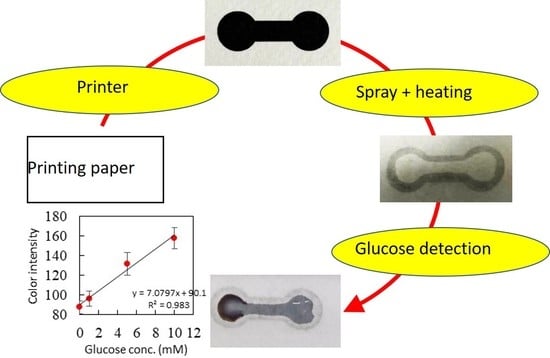
2.2. Glucose Detection
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fabrication of the Paper-Based Microfluidic Chips by Spray on the Printed Paper
3.1.1. Water Repellent and Water Wax as the Spraying Agent
3.1.2. PDMS Mixture as the Spraying Agent
3.2. Flow Characterization of Paper-Based Microfluidic Chips
3.3. Glucose Detection
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Convery, N.; Gadegaard, N. 30 years of microfluidics. Micro Nano Eng. 2019, 2, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Wen, D.; Wu, J.; Liu, L.; Wu, W.; Fang, X.; Kong, J. Microfluidic immunoassays for sensitive and simultaneous detection of IgG/IgM/Antigen of SARS-CoV-2 within 15 min. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 9454–9458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cromartie, R.L.; Wardlow, A.; Duncanb, G.; McCord, B.R. Development of a microfluidic device (mPADs) for forensic serological analysis. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, A.-G.; Chircov, C.; Bîrcă, A.C.; Grumezescu, A.M. Fabrication and Applications of Microfluidic Devices: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yew, M.; Ren, Y.; Koh, K.S.; Sun, C.; Snape, C. A Review of State-of-the-Art Microfluidic Technologies for Environmental Applications: Detection and Remediation. Glob. Chall. 2019, 3, 1800060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, P.; Wang, S. Application of microfluidic chip technology in pharmaceutical analysis: A review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2019, 9, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Austin, R.H. Applications of microfluidics in stem cell biology. BioNanoScience 2012, 2, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, Y.-J.; Chang, J.S. Applications of microfluidics in microalgae biotechnology: A review. Biotechnol. J. 2016, 11, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, Y.S.; Trujillo-de Santiago, G.; Moisés Alvarez, M.; Ribas, J.; Jonas, S.J.; Weiss, P.S.; Andrews, A.M.; Aizenberg, J.; Khademhosseini, A. Interplay between materials and microfluidics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Zhou, J.; Wu, H. Materials for microfluidic chip fabrication. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2396–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Noviana, E.; Nguyen, M.P.; Geiss, B.J.; Dandy, D.S.; Henry, C.S. Paper-based microfluidic devices: Emerging themes and applications. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cate, D.M.; Adkins, J.A.; Mettakoonpitak, J.; Henry, C.S. Recent developments in paper-based microfluidic devices. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Whitesides, G.M.; Carrilho, E. Diagnostics for the developing world: Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noviana, E.; Ozer, T.; Carrell, C.S.; Link, J.S.; McMahon, C.; Jang, I.; Henry, C.S. Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices: From design to applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 11835–11885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Ga, L.; Zhao, R.; Ai, J. Research progress on the applications of paper chips. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 8793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.T.; Lantigua, D.; Meka, A.; Taing, S.; Pandher, M.; Camci-Unal, G. Paper-based sensors: Emerging themes and applications. Sensors 2018, 18, 2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cinti, S.; Mazzaracchio, V.; Cacciotti, I.; Moscone, D.; Arduini, F. Carbon black-modified electrodes screen-printed onto paper towel, waxed paper, and ParafilmM®. Sensors 2017, 17, 2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrov, N.; Jimenez, M.; Billerbeck, S.; Brisbois, J.; Matragrano, J.; Ager, A.; Cornish, V.W. A modular yeast biosensor for low-cost point-of-care pathogen detection. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1603221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.W.; Lee, D.; Kim, Y.T.; Lee, E.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Seo, T.S. Low-cost and facile fabrication of a paper-based capillary electrophoresis microdevice for pathogen detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Weib, S.; Kong, J. Paper-based microfluidics with high resolution, cut on a glass fiber membrane for bioassays. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, N.; Breedveld, V.; Hess, D.W. Semi-enclosed microfluidic device on glass-fiber membrane with enhanced signal quality for colorimetric analyte detection in whole blood. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2021, 25, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soum, V.; Kim, Y.; Park, S.; Chuong, M.; Ryu, S.R.; Lee, S.H.; Tanev, G.; Madsen, J.; Kwon, O.-S.; Shin, K. Affordable fabrication of conductive electrodes and dielectric films for a paperbased digital microfuidic chip. Micromachines 2019, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghaderinezhad, F.; Amin, R.; Temirel, M.; Yenilmez, B.; Wentworth, A.; Tasoglu, S. High-throughput rapid-prototyping of low-cost paper-based microfluidics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishat, S.; Jafry, A.T.; Martinez, A.W.; Awan, F.R. Paper-based microfluidics: Simplified fabrication and assay methods. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 2021, 336, 129681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Zhou, J.; Kanungo, M.; Jia, N.; Dinsmore, A.D. Wax spreading in paper under controlled pressure and temperature. Langmuir 2018, 34, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Tarso Garcia, P.; Garcia Cardoso, T.M.; Garcia, C.D.; Carrilho, E.; Tomazelli Coltro, W.K. A handheld stamping process to fabricate microfluidic paper-based analytical devices with chemically modified surface for clinical assays. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 37637–37644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curto, V.F.; Lopez-Ruiz, N.; Capitan-Vallvey, L.F.; Palma, A.J.; Benito-Lopez, F.; Diamond, D. Fast prototyping of paper-based microfluidic devices by contact stamping using indelible ink. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 18811–18816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornelas, K.L.; Dossi, N.; Piccin, E. A simple method for patterning poly (dimethylsiloxane) barriers in paper using contactprinting with low-cost rubber stamps. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 858, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, T.M.; de Souza, F.R.; Garcia, P.T.; Rabelo, D.; Henry, C.S.; Coltro, W.K. Versatile fabrication of paper-based microfluidic devices with high chemical resistance using scholar glue and magnetic masks. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 974, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurak, T.; Praphairaksit, N.; Chailapakul, O. Fabrication of paper-based devices by lacquer spraying method for the determination of nickel (II) ion in waste water. Talanta 2013, 114, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuo, M.M.; Martinez, R.V.; Lan, W.-J.; Liu, X.; Barber, J.; Atkinson, M.B.J.; Bandarage, D.; Bloch, J.-F.; Whitesides, G.M. Fabrication of low-cost paper-based microfluidic devices by embossing or cut-and-stack methods. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 4230–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, J.H.; Park, J.; Park, J.-K. Organic solvent and surfactant resistant paper-fluidic devices fabricated by one-step embossing of nonwoven polypropylene sheet. Micromachines 2017, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oyola-Reynoso, S.; Frankiewicz, C.; Chang, B.; Chen, J.; Bloch, J.-F.; Thuo, M.M. Paper-based microfluidic devices by asymmetric calendaring. Biomicrofluidics 2017, 11, 014104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juang, Y.J.; Chen, P.S.; Wang, Y. Rapid fabrication of microfluidic paper-based analytical devices by microembossing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 283, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, Y.J.; Wang, Y.; Hsu, S.K. One-step hot microembossing for fabrication of paper-based microfluidic chips in 10 seconds. Polymers 2020, 12, 2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruzewicz, D.A.; Reches, M.; Whitesides, G.M. Low-cost printing of poly(dimethylsiloxane) barriers to define microchannels in paper. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 3387–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruen, D.; Delaney, C.; Florea, L.; Diamond, D. Glucose sensing for diabetes monitoring: Recent developments. Sensors 2017, 17, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oyola-Reynoso, S.; Heim, A.P.; Halbertsma-Black, J.; Zhao, C.; Tevis, I.D.; Çınar, S.; Cademartiri, R.; Liu, X.; Bloch, J.-F.; Thuo, M.M. Draw your assay: Fabrication of low-cost paper-based diagnostic and multi-well test zones by drawing on a paper. Talanta 2015, 144, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Maeki, M.; Mohamadi, R.M.; Ishida, A.; Tani, H.; Tokeshi, M. An instrument-free, screen-printed paper microfluidic device that enables bio and chemical sensing. Analyst 2015, 140, 6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhong, M.; Lai, H.; Huang, J. Fabrication of a microfluidic paper-based analytical device by silanization of filter cellulose using a paper mask for glucose assay. Analyst 2014, 139, 4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Fu, L.; Zhang, W.; Feng, W.; Chen, L. Portable paper-based device forquantitative colorimetric assays relyingon light reflectance principle. Electrophoresis 2014, 35, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, M.P.; Meredith, N.A.; Kelly, S.P.; Henry, C.S. Design considerations for reducing sample loss in microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1017, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Processing Time (s) | Heating Time (s) | Heating Temp. (°C) | Equipment Cost (USD) | Substrate | Potential for Scalability | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solid wax printing | Depends on μPAD design | 30–600 | 100–175 | ~500 | Filter paper (~100 USD/m2) | Medium |
| Craft cutting | Depends on μPAD design | No | No | ~250 | Filter paper (100 USD/m2) | Medium |
| Spray on printed paper | ~20 * | ~300 | 120 | ~300 | Printing paper (0.1 USD/m2) | High |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Juang, Y.-J.; Hsu, S.-K. Fabrication of Paper-Based Microfluidics by Spray on Printed Paper. Polymers 2022, 14, 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030639
Juang Y-J, Hsu S-K. Fabrication of Paper-Based Microfluidics by Spray on Printed Paper. Polymers. 2022; 14(3):639. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030639
Chicago/Turabian StyleJuang, Yi-Je, and Shu-Kai Hsu. 2022. "Fabrication of Paper-Based Microfluidics by Spray on Printed Paper" Polymers 14, no. 3: 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030639
APA StyleJuang, Y. -J., & Hsu, S. -K. (2022). Fabrication of Paper-Based Microfluidics by Spray on Printed Paper. Polymers, 14(3), 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030639