Polymeric Hydrogels as Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome Delivery System in Biomedical Applications
Abstract
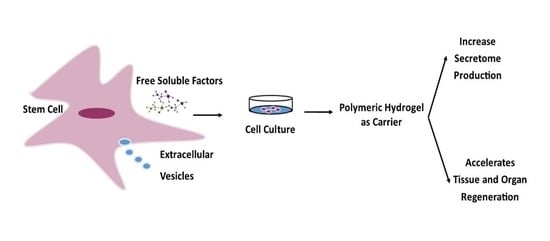
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)
2.1. MSCs as a Secretome Source
2.2. Secretome
2.3. Secretome Composition
3. Biomedical Applications of Secretome
4. Secretome Delivery Systems in Biomedical Applications
4.1. Hydrogels as Secretome Delivery Systems
4.2. Hydrogel-Based Polymerics as Secretome Carriers
4.2.1. Hyaluronic Acid (HA)
4.2.2. Alginate
4.2.3. Carrageenan (CG)
4.2.4. Gellan Gum (GG)
4.2.5. Collagen
4.2.6. Gelatin
4.2.7. Polyethylene Glycol (PEG)
4.2.8. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (pNIPAm)
4.2.9. Poly(lactic acid-co-glycolic) (PLGA)
4.2.10. Others
5. Author’s Perspective
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| MSCs | Mesenchymal stem cells |
| hMSCs | Human mesenchymal stem cells |
| hASCs | Human adipose stem cells |
| BMMSCs | Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells |
| hUCMSCs | Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells |
| ADMSCs | Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells |
| SDMSCs | Skin-derived mesenchymal stem cells |
| pADSC | SMC-like adipose-derived stem cells |
| WJMSCs | Wharton’s Jelly mesenchymal stem cells |
| hUCESCs | Human uterine cervical stem cells |
| UCPVCs | Umbilical cord perivascular cells |
| PDLSCs | Periodontal ligament stem cells |
| EPCs | Endothelial progenitor cells |
| SMC | Smooth muscle cells |
| RAA-MSCs | Rat Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells |
| rACs | Rabbit articular chondrocytes |
| HA | Hyaluronic Acid |
| CG | Carrageenan |
| RGD | Arginyl glycyl aspartic acid peptide |
| NIPAAm | N-Isopropylacrylamide |
| SHIELD | Shearthinning hidrogels for injectable encapsulation and long-term delivery |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| FN | Fibronectin |
| DCN | Decorin |
| PDGFR β | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor β |
| Ang-1 | Angiotensin-1 |
| GDNF | Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor |
| FGF | Fibroblast growth factor |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| IGFBP | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein |
| SGF | Secrete growth factors |
| SCF | Stem cell factor |
| LIF | Leukemia inhibitory factor |
| SDF | Stromal cell-derived factor |
| PlGF-1 | Placenta growth factor-1 |
| ICAM3 | Intercellular adhesion molecule 3 |
| MCP3, also called CCL7 | Monocyte-specific chemokine 3 |
| MIF | Migration inhibitory factor |
| sgp130 | Soluble glycoprotein 130 |
| KC | Keratinocyte-derivedchemokine |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor and |
| (PG)E2 | Prostaglandin |
| PEDF | Pigment epithelium-derived factor |
References
- Bari, E.; Ferrarotti, I.; Torre, M.L.; Corsico, A.G.; Perteghella, S. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell secretome for lung regeneration: The long way through “pharmaceuticalization” for the best formulation. J. Control. Release 2019, 309, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conese, M.; Cassano, R.; Gavini, E.; Trapani, G.; Rassu, G.; Sanna, E.; Di Gioia, S.; Trapani, A. Harnessing Stem Cells and Neurotrophic Factors with Novel Technologies in the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 14, 549–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavala, G.; Ramos, M.P.; Figueroa-Valdés, A.I.; Cisternas, P.; Wyneken, U.; Hernández, M.; Toa, P.; Salmons, B.; Dangerfield, J.; Gunzburg, W.H.; et al. Semipermeable Cellulose Beads Allow Selective and Continuous Release of Small Extracellular Vesicles (SEV) From Encapsulated Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaubey, S.; Thueson, S.; Ponnalagu, D.; Alam, M.A.; Gheorghe, C.P.; Aghai, Z.; Singh, H.; Bhandari, V. Early Gestational Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome Attenuates Experimental Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Part via Exosome-Associated Factor TSG-6. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizoso, F.J.; Eiro, N.; Cid, S.; Schneider, J.; Perez-Fernandez, R. Mesenchymal stem cell secretome: Toward cell-free therapeutic strategies in regenerative medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrzejewska, A.; Lukomska, B.; Janowski, M. Concise Review: Mesenchymal Stem Cells: From Roots to Boost. Stem Cells 2019, 37, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robert, A.W.; Azevedo Gomes, F.; Rode, M.P.; Marques da Silva, M.; da Rocha Veleirinho, M.B.; Maraschin, M.; Hayashi, L.; Wosgrau Calloni, G.; Stimamiglio, M.A. The Skin Regeneration Potential of a Pro-Angiogenic Secretome from Human Skin-Derived Multipotent Stromal Cells. J. Tissue Eng. 2019, 10, 3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tögel, F.; Hu, Z.; Weiss, K.; Isaac, J.; Lange, C.; Westenfelder, C. Administered mesenchymal stem cells protect against ischemic acute renal failure through differentiation-independent mechanisms. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2005, 289, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vizoso, F.J.; Eiro, N.; Costa, L.; Esparza, P.; Landin, M.; Diaz-Rodriguez, P.; Schneider, J.; Perez-Fernandez, R. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Homeostasis and Systemic Diseases: Hypothesis, Evidences, and Therapeutic Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caplan, A.; Dennis, J.E. Mesenchymal stem cells as trophic mediators. J. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 98, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugerell, A.; Gouya-Lechner, G.; Hofbauer, H.; Laggner, M.; Trautinger, F.; Almer, G.; Peterbauer-Scherb, A.; Seibold, M.; Hoetzenecker, W.; Dreschl, C.; et al. Safety and Clinical Efficacy of the Secretome of Stressed Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcer—Study Protocol of the Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Multicenter, International Phase II Clinical Trial MARSYA. Trials 2021, 22, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakota, E.L.; Wang, Y.; Danesh, F.R.; Hartgerink, J.D. Injectable multidomain peptide nanofiber hydrogel as a delivery agent for stem cell secretome. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 1651–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crivelli, B.; Chlapanidas, T.; Perteghella, S.; Lucarelli, E.; Pascucci, L.; Brini, A.T.; Ferrero, I.; Marazzi, M.; Pessina, A.; Torre, M.L. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell Extracellular Vesicles: From Active Principle to next Generation Drug Delivery System. J. Control. Release 2017, 262, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, S.K.; De Kleijn, D.P.V.; Chai, R.; Khia, E.; Tan, W.; Zhao, H.; Yeo, K.S.; Low, T.Y.; Lian, Q.; Lee, C.N.; et al. Elucidating the Secretion Proteome of Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2007, 6, 1680–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waters, R.; Alam, P.; Pacelli, S.; Chakravarti, A.R.; Ahmed, R.P.H.; Paul, A. Stem cell-inspired secretome-rich injectable hydrogel to repair injured cardiac tissue. Acta Biomater. 2018, 69, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Nguyen, K.T.; Leong, D.T.; Tan, N.S.; Tay, C.Y. Soft Material Approach to Induce Oxidative Stress in Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Functional Tissue Repair. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 26591–26599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez, M.A.; Sendon-lago, J.; Eiro, N.; Trevi, M.; Gonzalez, F.; Yebra-pimentel, E.; Giraldez, M.J.; Macia, M.; Lamelas, M.L.; Saa, J.; et al. Corneal Epithelial Wound Healing and Bactericidal Effect of Conditioned Medium From Human Uterine Cervical Stem Cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Hosseini-beheshti, E.; Grau, G.E.; Zreiqat, H. Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Treating Joint Injury and Osteoarthritis. Nanomaterials 2006, 9, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chierchia, A.; Chirico, N.; Boeri, L.; Raimondi, I.; Riva, G.A.; Raimondi, M.T.; Tunesi, M.; Giordano, C.; Forloni, G.; Albani, D. Secretome Released from Hydrogel-Embedded Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protects against the Parkinson’s Disease Related Toxin 6-Hydroxydopamine. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 121, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porzionato, A.; Zaramella, P.; Dedja, A.; Guidolin, D.; Van Wemmel, K.; Macchi, V.; Jurga, M.; Perilongo, G.; De Caro, R.; Baraldi, E.; et al. Intratracheal administration of clinical-grade mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles reduces lung injury in a rat model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2018, 316, L6–L19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.Y.; Jang, Y.J.; Lim, H.J.; Han, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, G.; Park, J.Y.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Do, B.R.; et al. Milk Fat Globule-EGF Factor 8, Secreted by Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Protects Against Liver Fibrosis in Mice. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1174–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Decker, J.T.; Lemke, M.M.; Tomaszweski, C.E.; Shea, L.D.; Arnold, K.B.; Shikanov, A. Synergy of Paracrine Signaling During Early-Stage Mouse Ovarian Follicle Development In Vitro. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2018, 11, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakirova, E.Y.; Valeeva, A.N.; Aimaletdinov, A.M.; Nefedovskaya, L.V.; Akhmetshin, R.F.; Rutland, C.S.; Rizvanov, A.A. Potential Therapeutic Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Ophthalmology. Exp. Eye Res. 2019, 189, 107863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Hu, S.; Yang, H.; Li, Z.; Huang, K.; Su, T.; Wang, S.; Cheng, K. Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Integrated with Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Secretome to Treat Endometrial Injury in a Rat Model of Asherman’s Syndrome. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1900411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roşca, A.M.; Ţuţuianu, R.; Titorencu, I.D. Mesenchymal stromal cells derived exosomes as tools for chronic wound healing therapy. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2018, 59, 655–662. [Google Scholar]
- Sart, S.; Agathos, S.N.; Li, Y.; Ma, T. Regulation of Mesenchymal Stem Cell 3D Microenvironment: From Macro to Microfluidic Bioreactors. Biotechnol. J. 2016, 11, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, N.A.; Moreira, J.; Ribeiro-Samy, S.; Gomes, E.D.; Tam, R.Y.; Shoichet, M.S.; Reis, R.L.; Sousa, N.; Salgado, A.J. Modulation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome by ECM-like Hydrogels. Biochimie 2013, 95, 2314–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rostami, Z.; Khorashadizadeh, M.; Naseri, M. Immunoregulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells: Micro-RNAs. Immunol. Lett. 2020, 219, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinney, D.G.; Prockop, D.J. Concise Review: Mesenchymal Stem/Multipotent Stromal Cells: The State of Transdifferentiation and Modes of Tissue Repair-Current Views. Stem Cells 2007, 25, 2896–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisan, M.; Yap, S.; Casteilla, L.; Chen, C.W.; Corselli, M.; Park, T.S.; Andriolo, G.; Sun, B.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, L.; et al. A Perivascular Origin for Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Multiple Human Organs. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 3, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barberi, T.; Willis, L.M.; Socci, N.D.; Studer, L. Derivation of multipotent mesenchymal precursors from human embryonic stem cells. PLoS Med. 2005, 2, e161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabapathy, V.; Kumar, S. hiPSC-derived iMSCs: NextGen MSCs as an advanced therapeutically active cell resource for regenerative medicine. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 1571–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biancone, L.; Bruno, S.; Deregibus, M.C.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Microvesicles. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 3037–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Liu, G.; Zhang, J. Secretome from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: A promising, cell-free therapy for allergic rhinitis. Med. Hypotheses 2018, 121, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xie, N.; Li, W.; Yuan, B.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y. Immunobiology of mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnecchi, M.; He, H.; Noiseux, N.; Liang, O.D.; Zhang, L.; Morello, F.; Mu, H.; Melo, L.G.; Pratt, R.E.; Ingwall, J.S.; et al. Evidence Supporting Paracrine Hypothesis for Akt-modified Mesenchymal Stem Cell-mediated Cardiac Protection and Functional Improvement. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, G. Stem cell therapy without the cells. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2013, 6, e26631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, N.; Subramanyam, D.; Lee, M.Y. Molecular signatures of secretomes from mesenchymal stem cells: Therapeutic benefits. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2017, 13, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawitan, J.A. Prospect of Stem Cell Conditioned Medium in. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhang, S.H.; Lee, S.; Shin, J.Y.; Lee, T.J.; Jang, H.K.; Kim, B.S. Efficacious and clinically relevant conditioned medium of human adipose-derived stem cells for therapeutic angiogenesis. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beer, L.; Mildner, M.; Ankersmit, H.J. Cell secretome based drug substances in regenerative medicine: When regulatory affairs meet basic science. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muhammad, S.A.; Abbas, A.Y.; Saidu, Y.; Fakurazi, S.; Bilbis, L.S. Therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stromal cells and secretome in pulmonary arterial hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biochimie 2019, 168, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalnikova, H.; Motlik, J.; Gadher, S.J.; Kovarova, H. Mapping of the secretome of primary isolates of mammalian cells, stem cells and derived cell lines. Proteomics 2011, 11, 691–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.R.; Kim, J.W.; Jun, H.S.; Roh, J.Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Hong, I.S. Stem Cell Secretome and Its Effect on Cellular Mechanisms Relevant to Wound Healing. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kusuma, G.D.; Carthew, J.; Lim, R.; Frith, J.E. Effect of the Microenvironment on Mesenchymal Stem Cell Paracrine Signaling: Opportunities to Engineer the Therapeutic Effect. Stem Cells Dev. 2017, 26, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronckaers, A.; Hilkens, P.; Martens, W.; Gervois, P.; Ratajczak, J.; Struys, T.; Lambrichts, I. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells as a Pharmacological and Therapeutic Approach to Accelerate Angiogenesis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 143, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, C.; Damaser, M.S. Stem Cells as Drug Delivery Methods: Application of Stem Cell Secretome for Regeneration. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 82, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benias, P.C.; Wells, R.G.; Sackey-Aboagye, B.; Klavan, H.; Reidy, J.; Buonocore, D.; Miranda, M.; Kornacki, S.; Wayne, M.; Carr-Locke, D.L.; et al. Structure and Distribution of an Unrecognized Interstitium in Human Tissues. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiró, N.; Sendon-lago, J.; Seoane, S.; Bermúdez, M.A.; Vizoso, F.J. Potential Therapeutic Effect of the Secretome from Human Uterine Cervical Stem Cells against Both Cancer and Stromal Cells Compared with Adipose Tissue Stem Cells. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 10692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bermudez, M.A.; Sendon-lago, J.; Seoane, S.; Eiro, N.; Saa, J.; Vizoso, F.; Perez-fernandez, R. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Conditioned Medium from Human Uterine Cervical Stem Cells in Uveitis. Exp. Eye Res. 2016, 149, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osugi, M.; Katagiri, W.; Yoshimi, R.; Inukai, T.; Hibi, H.; Ueda, M. Conditioned media from mesenchymal stem cells enhanced bone regeneration in rat calvarial bone defects. Tissue Eng. Part A 2012, 18, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haque, N.; Abdullah, B.J.J.; Kasim, N.H.A. Secretome: Pharmaceuticals for Cell-Free Regenerative Therapy. In Stem Cell Drugs—A New Generation of Biopharmaceuticals; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrigal, M.; Rao, K.S.; Riordan, N.H. A Review of Therapeutic Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretions and Induction of Secretory Modification by Different Culture Methods. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Timmers, L.; Lim, S.K.; Arslan, F.; Armstrong, J.S.; Hoefer, I.E.; Doevendans, P.A.; Piek, J.J.; El Oakley, R.M.; Choo, A.; Lee, C.N.; et al. Reduction of Myocardial Infarct Size by Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Conditioned Medium. Stem Cell Res. 2008, 1, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baberg, F.; Geyh, S.; Waldera-Lupa, D.; Stefanski, A.; Zilkens, C.; Haas, R.; Schroeder, T.; Stühler, K. Secretome Analysis of Human Bone Marrow Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2019, 1867, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaggiari, G.M.; Capobianco, A.; Abdelrazik, H.; Becchetti, F.; Mingari, M.C.; Moretta, L. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit natural killer-cell proliferation, cytotoxicity, and cytokine production: Role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and prostaglandin E2. Blood 2008, 111, 1327–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, V.; Konala, R.; Mamidi, M.K.; Bhonde, R.; Das, A.K.; Pochampally, R.; Pal, R. The Current Landscape of Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Secretome: A New Paradigm for Cell-Free Regeneration. Cytotherapy 2015, 18, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rong, X.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Shi, L.; Jiang, T. Human Fetal Skin-Derived Stem Cell Secretome Enhances Radiation-Induced Skin Injury Therapeutic Effects by Promoting Angiogenesis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, F.G.; Carvalho, M.M.; Panchalingam, K.M.; Rodrigues, A.; Mendes-Pinheiro, B.; Anjo, S.; Manadas, B.; Behie, L.A.; Sousa, N.; Salgado, A.J. Impact of the secretome of human mesenchymal stem cells on brain structure and animal behavior in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandalam, S.; Sindji, L.; Delcroix, G.J.R.; Violet, F.; Garric, X.; André, E.M.; Schiller, P.C.; Venier-Julienne, M.C.; des Rieux, A.; Guicheux, J.; et al. Pharmacologically Active Microcarriers Delivering BDNF within a Hydrogel: Novel Strategy for Human Bone Marrow-Derived Stem Cells Neural/Neuronal Differentiation Guidance and Therapeutic Secretome Enhancement. Acta Biomater. 2017, 49, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onzi, G.R.; Ledur, P.F.; Hainzenreder, L.D.; Bertoni, A.P.S.; Silva, A.O.; Lenz, G.; Wink, M.R. Analysis of the Safety of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Secretome for Glioblastoma Treatment. Cytotherapy 2016, 18, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes-Cunha, G.M.; Na, K.S.; Putra, I.; Lee, H.J.; Hull, S.; Cheng, Y.C.; Blanco, I.J.; Eslani, M.; Djalilian, A.R.; Myung, D. Corneal Wound Healing Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome Delivered Within a Viscoelastic Gel Carrier. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2019, 8, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Surgery, M.; Hospital, S.; Surgery, M.; Key, S.; Processing, F.; Park, G.-Y.; Kwon, D.R.; Lee, S.C.; Surgery, M.; Hospital, S.; et al. Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine Concise Review: Cell-Based Strategies in Bone Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2014, 4, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, L.P.; Santos, T.C.; Rodrigues, D.B.; Pirraco, R.P.; Cerqueira, M.T.; Reis, R.L.; Correlo, V.M.; Marques, A.P. Stem Cell-Containing Hyaluronic Acid-Based Spongy Hydrogels for Integrated Diabetic Wound Healing. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1541–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deshpande, R.; Kanitkar, M.; Kadam, S.; Dixit, K.; Chhabra, H.; Bellare, J.; Datar, S.; Kale, V.P. Matrix-Entrapped Cellular Secretome Rescues Diabetes-Induced EPC Dysfunction and Accelerates Wound Healing in Diabetic Mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, M.; Liu, W.; Peng, Z.; Lv, S.; Guan, Y.; An, G.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, T.; Wang, Y. The Therapeutic Effect of Secretome from Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Age-Related Osteoporosis. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waters, R.; Pacelli, S.; Maloney, R.; Medhi, I.; Ahmed, R.P.H.; Paul, A. Stem cell secretome-rich nanoclay hydrogel: A dual action therapy for cardiovascular regeneration. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 7371–7376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Cheam, N.M.J.; Cao, H.; Lee, M.K.H.; Sze, S.K.; Tan, N.S.; Tay, C.Y. Materials Stiffness-Dependent Redox Metabolic Reprogramming of Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Secretome-Based Therapeutic Angiogenesis. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1900929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Dewi, R.E.; Goldstone, A.B.; Cohen, J.E.; Steele, A.N.; Woo, Y.J.; Heilshorn, S.C. Regulating Stem Cell Secretome Using Injectable Hydrogels with In Situ Network Formation. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 2758–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estrada, R.; Li, N.; Sarojini, H.; An, J.; Lee, M.J.; Wang, E. Secretome from mesenchymal stem cells induces angiogenesis via Cyr61. J. Cell. Physiol. 2009, 219, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mo, X.; Guo, S.; Xie, H.; Deng, L.; Zhi, W.; Xiang, Z. Variations in the ratios of co-cultured mesenchymal stem cells and chondrocytes regulate the expression of cartilaginous and osseous phenotype in alginate constructs. Bone 2009, 45, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famian, M.H.; Saheb, S.M.; Montaseri, A. Conditioned Medium of Wharton’s jelly derived stem cells can enhance the cartilage specific genes expression by chondrocytes in monolayer and mass culture systems. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 7, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, A.B.; Zimmermann, J.A.; Burnsed, O.A.; Yakubovich, D.C.; Stevens, H.Y.; Gazit, Z.; McDevitt, T.C.; Guldberg, R.E. Environmental Manipulation to Promote Stem Cell Survival: In Vivo: Use of Aggregation, Oxygen Carrier, and BMP-2 Co-Delivery Strategies. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 3594–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.C.; Barnes, C.A.; Bryant, S.J. Characterization of the chondrocyte secretome in photoclickable poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogels. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 114, 2096–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côrtes, I.; Matsui, R.A.M.; Azevedo, M.S.; Beatrici, A.; Souza, K.L.A.; Launay, G.; Delolme, F.; Granjeiro, J.M.; Moali, C.; Baptista, L.S. A Scaffold- and Serum-Free Method to Mimic Human Stable Cartilage Validated by Secretome. Tissue Eng. Part A 2021, 27, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolar, J.; De Nardo, D.; Reichmann, E.; Gobet, R.; Eberli, D.; Horst, M. Detrusor bioengineering using a cell-enriched compressed collagen hydrogel. J. Biomed. Mater Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2020, 108, 3045–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingato, D.; Lee, J.U.; Sim, S.J.; Kwon, Y.J. Good things come in small packages: Overcoming challenges to harness extracellular vesicles for therapeutic delivery. J. Control. Release 2016, 241, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daneshmandi, L.; Shah, S.; Jafari, T.; Bhattacharjee, M.; Momah, D.; Saveh-shemshaki, N.; Lo, K.W. Emergence of the Stem Cell Secretome in Regenerative Engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slaughter, B.V.; Khurshid, S.S.; Fisher, O.Z.; Khademhosseini, A.; Peppas, N.A. Hydrogels in regenerative medicine. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 3307–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barajaa, M.A.; Nair, L.S.; Laurencin, C.T. Bioinspired Scaffold Designs for Regenerating Musculoskeletal Tissue Interfaces. Regen. Eng. Transl. Med. 2020, 6, 451–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, B.; Venuti, V.; D’Amico, F.; Gessini, A.; Mele, A.; Punta, C.; Melone, L.; Crupi, V.; Majolino, D.; Masciovecchio, C. Guest-Matrix Interactions Affect the Solvation of Cyclodextrin-Based Polymeric Hydrogels: A UV Raman Scattering Study. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 8861–8868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.H.; Kim, A.; Shin, W.; Heo, M.B.; Noh, H.J.; Hong, K.S.; Cho, J.H.; Lim, Y.T. Photothermal-Modulated Drug Delivery and Magnetic Relaxation Based on Collagen/Poly(γ-Glutamic Acid) Hydrogel. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 2607–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chassenieux, C.; Tsitsilianis, C. Recent trends in pH/thermo-responsive self-assembling hydrogels: From polyions to peptide-based polymeric gelators. Soft Matter. 2016, 12, 1344–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.; Oner, E.T.; Eroglu, M.S. Novel levan and pNIPA temperature sensitive hydrogels for 5-ASA controlled release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 165, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoma Suresh, K.; Bhat, S.; Guru, B.R.; Muttigi, M.S.; Seetharam, R.N. A Nanocomposite Hydrogel Delivery System for Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Secretome. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yang, L.; Yang, P.; Jiang, S.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. Polydopamine Free Radical Scavengers. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 4940–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Yang, P.; Duan, G.; Liu, X.; Gu, Z.; Li, Y. Polyphenol Scaffolds in Tissue Engineering. Mater. Horizons 2021, 8, 145–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Lin, S.; Sun, Y.; Feng, Q.; Li, G.; Bian, L. Hydrogels functionalized with N-cadherin mimetic peptide enhance osteogenesis of hMSCs by emulating the osteogenic niche. Biomaterials 2016, 77, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdick, J.A.; Prestwich, G.D. Hyaluronic acid hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, D.D.; Grande-Allen, K.J. Review. Hyaluronan: A powerful tissue engineering tool. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 2131–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Rodrigues, J.; Tomás, H. Injectable and biodegradable hydrogels: Gelation, biodegradation and biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2193–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshaverinia, A.; Chen, C.; Xu, X.; Ansari, S.; Zadeh, H.H.; Schricker, S.R.; Paine, M.L.; Moradian-Oldak, J.; Khademhosseini, A.; Snead, M.L.; et al. Regulation of the Stem Cell-Host Immune System Interplay Using Hydrogel Coencapsulation System with an Anti-Inflammatory Drug. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2296–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Choi, J.K.; Rao, W.; Zhao, S.; Agarwal, P.; Zhao, G.; He, X. Alginate Hydrogel Microencapsulation Inhibits Devitrification and Enables Large-Volume Low-CPA Cell Vitrification. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 6839–6850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chevallay, B.; Herbage, D. Collagen-based biomaterials as 3D scaffold for cell cultures: Applications for tissue engineering and gene therapy. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2000, 38, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helminger, M.; Wu, B.; Kollmann, T.; Benke, D.; Schwahn, D.; Pipich, V.; Faivre, D.; Zahn, D.; Cölfen, H. Synthesis and Characterization of Gelatin-Based Magnetic Hydrogels. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3187–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, P.Y.; Ding, Q.X.; Fan, M.; Liao, J.F.; Qian, Z.Y.; Luo, J.C.; Li, X.Q.; Luo, F.; Yang, Z.M.; Wei, Y.Q. Injectable Thermosensitive PEG-PCL-PEG Hydrogel/Acellular Bone Matrix Composite for Bone Regeneration in Cranial Defects. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Serpe, M.J. Understanding and controlling the self-folding behavior of poly (N-Isopropylacrylamide) microgel-based devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4119–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandow, C.E.; Georges, P.C.; Janmey, P.A.; Beningo, K.A. Polyacrylamide Hydrogels for Cell Mechanics: Steps Toward Optimization and Alternative Uses. Methods Cell Biol. 2007, 83, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morille, M.; Van-Thanh, T.; Garric, X.; Cayon, J.; Coudane, J.; Noël, D.; Venier-Julienne, M.C.; Montero-Menei, C.N. New PLGA-P188-PLGA Matrix Enhances TGF-Β3 Release from Pharmacologically Active Microcarriers and Promotes Chondrogenesis of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J. Control. Release 2013, 170, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, D.; Griffith, M.; Venkatraman, S.S. Polycaprolactone-based biomaterials for tissue engineering and drug delivery: Current scenario and challenges. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2016, 65, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melke, J.; Midha, S.; Ghosh, S.; Ito, K.; Hofmann, S. Silk fibroin as biomaterial for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2016, 31, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teixeira, F.G.; Carvalho, M.M.; Sousa, N.; Salgado, A.J. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Secretome: A New Paradigm for Central Nervous System Regeneration? Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 3871–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, A.O.; Mendes-Pinheiro, B.; Teixeira, F.G.; Anjo, S.I.; Ribeiro-Samy, S.; Gomes, E.D.; Serra, S.C.; Silva, N.A.; Manadas, B.; Sousa, N. Unveiling the differences of secretome of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, adipose tissue-derived stem cells, and human umbilical cord perivascular cells: A proteomic analysis. Stem Cells Dev. 2016, 25, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsou, Y.H.; Khoneisser, J.; Huang, P.C.; Xu, X. Hydrogel as a bioactive material to regulate stem cell fate. Bioact. Mater. 2016, 1, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Source Secretome | Bioactive Molecules | Biomedical Apps | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| SD-MSCs | VEGF, MMP2, PDGFR-β, FN1, DCN, Collagen 1, Collagen 3, TGF-β1, and Ang-1 | Skin regeneration after injury | [7,58] |
| hASCs | collagen XVIII and HGF | Treating myocardial infarction | [15] |
| RAA-MSCs, WJMSCs | BDNF, NGF, VEGF, GDNF, FGF-2, IGF-1, HGF | Parkinson’s disease | [19,59] |
| ECM | VEGF-A and angiopoietin- 2 | Growing ovarian follicles | [22] |
| BMMSCs | EGF, IGF, FGF, IGFBP | Asherman’s Syndrome (USA) | [24] |
| BMMSCs | BDNF, b-NGF, SCF, HGF, LIF, PlGF-1, SDF-1α, VEGF-A& D | Treatment of neurological disorders | [27,60] |
| hUCESCs, hASCs | EGFR, FGF 4 and 9, IL–6, VEGFD, ICAM3, MCP3, MIF, sgp130 | Cancer | [49,61] |
| BMMSCs, hUCESCs | MMP 1 and 2, FGF 6 and 7, urokinase receptor, and HGF | Corneal epithelial wound healing | [17,62] |
| EPCs & renal-MSCs | IL-10, IL-4, IL-6, and KC | Acute kidney injury | [63] |
| ADSCs, EPCs | IL-6, Ang-1, GM-CSF and (PG)E2 | Diabetic wound repair | [64,65] |
| hUCMSCs | TGF-β, EGF, FGF, IGF-1, VEGF | Osteoporosis therapy | [66] |
| MSCs | VEGF and FGF | Heart tissue repair | [67] |
| ADMSCs | VEGF, PEDF and PDGF | Angiogenesis therapy | [68,69,70] |
| hMSCs & rACs | TGF-β, BMPs and IGF-1 | Osteoarthritis clinical therapy | [71,72] |
| hMSCs, ASCs | TGF-β3, TGF-β1, IL-6, and IL-8 | Cartilage repair | [73,74,75] |
| ADMSCs | VEGF-A and -D | Bladder regeneration | [76] |
| UCMSCs | Milk fat globule-EGF factor 8 (MFGE8) | Liver fibrosis | [21] |
| Polymer | MSC Secretome Source | Type of Hydrogel | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carrageenan or PVA | SDMSCs | Hydrogel | [7] |
| Bovine collagen (COLL 1) with HA or PEG | RAA-MSCs | [19] | |
| Alginate | Extracellular matrix | [22] | |
| Hyaluronic acid | hBMSCs | [24] | |
| Gellan gum and glucuronic acid | BMMSCs | [27] | |
| Hyaluronic acid | EPCs, renal MSCs | [63] | |
| Si-HPMC and PLGA | MIAMI | [60] | |
| Silk fibroin | hUCMSCs | [66] | |
| FN-PAAm | ADMSCs | [68] | |
| Alginate | hMSC, rMSCs | [73] | |
| HA and Chondroitin sulfate | BMMSCs | Viscoelastic gel | [62] |
| Gelatin and phyllosilicate (LAPONITE)® | hASCs | Nanocomposite injectable hydrogel | [15] |
| Phyllosilicate (LAPONITE)® nanosilicates and collagen | MSCs | Nanocomposite hydrogels | [67] |
| Gelatin and HA | BM-MSCs | [85] | |
| PEG and pNIPAm | ASCs | Encapsulation in hydrogels | [69] |
| Alginate | hMSCs, rACs | [71] | |
| PEG | Chondrocyte secretome | [74] | |
| HA and gellan gum | hASCs | Spongy-like hydrogels | [64] |
| Polycaprolactone (PC) and gelatin | EPCs | 3D electrospun nanofiber | [65] |
| Hyaluronic acid | ASCs | Micro-molded non-adhesive hydrogel | [75] |
| Collagen | pADSC and SMC | Compressed hydrogel | [76] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arifka, M.; Wilar, G.; Elamin, K.M.; Wathoni, N. Polymeric Hydrogels as Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome Delivery System in Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14061218
Arifka M, Wilar G, Elamin KM, Wathoni N. Polymeric Hydrogels as Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome Delivery System in Biomedical Applications. Polymers. 2022; 14(6):1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14061218
Chicago/Turabian StyleArifka, Mia, Gofarana Wilar, Khaled M. Elamin, and Nasrul Wathoni. 2022. "Polymeric Hydrogels as Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome Delivery System in Biomedical Applications" Polymers 14, no. 6: 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14061218
APA StyleArifka, M., Wilar, G., Elamin, K. M., & Wathoni, N. (2022). Polymeric Hydrogels as Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome Delivery System in Biomedical Applications. Polymers, 14(6), 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14061218