Investigation on Centrifugally Spun Fibrous PCL/3-Methyl Mannoside Mats for Wound Healing Application
Abstract
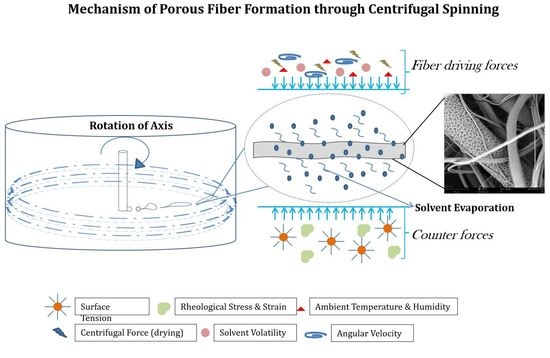
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of CA Extract
2.3. Preparation of Solution for Centrifugal Spinning
2.4. Centrifugal Spinning Process
2.5. Instrumental Characterization
2.6. Protein Denaturation Assay
2.7. Cell Viability Using MTT Assay
2.8. Cell Morphology and Adhesion Evaluation
2.9. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Identification of CA Extract Compounds
3.2. Optimization of PCL Concentration in Fibrous Mats
3.3. Surface Morphology of Fibrous Mats
3.4. Functional Groups and Crystallinity of PCL-CA Fibrous Mats
3.5. Thermal Stability, Wettability and Mechanical Properties of Fibrous Mats
3.6. Effect of Protein Denaturation
3.7. Cell Proliferation and Adhesion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vig, K.; Chaudhari, A.; Tripathi, S.; Dixit, S.; Sahu, R.; Pillai, S.; Dennis, V.A.; Singh, S.R. Advances in skin regeneration using tissue engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Negut, I.; Grumezescu, V.; Grumezescu, A.M. Treatment strategies for infected wounds. Molecules 2018, 23, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, S.A.; DiPietro, L.A. Factors affecting wound healing. J. Dental Res. 2010, 89, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RezvaniGhomi, E.; Khalili, S.; Nouri Khorasani, S.; EsmaeelyNeisiany, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Wound dressings: Current advances and future directions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamoun, E.A.; Kenawy, E.R.S.; Chen, X. A review on polymeric hydrogel membranes for wound dressing applications: PVA-based hydrogel dressings. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 8, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, B.; Carlson, M.A.; Gombart, A.F.; Reilly, D.A.; Xie, J. Recent advances in electrospun nanofibers for wound healing. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 1335–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almetwally, A.A.; El-Sakhawy, M.; Elshakankery, M.H.; Kasem, M.H. Technology of nano-fibers: Production techniques and properties-Critical review. J. Text. Assoc. 2017, 78, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Textile Blog. 2021. Available online: https://www.textileblog.com/properties-manufacturing-and-application-of-ultrafine-fiber/ (accessed on 13 December 2022).
- Zander, N.E. Formation of melt and solution spun polycaprolactone fibers by centrifugal spinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golecki, H.M.; Yuan, H.; Glavin, C.; Potter, B.; Badrossamay, M.R.; Goss, J.A.; Phillips, M.D.; Parker, K.K. Effect of solvent evaporation on fiber morphology in rotary jet spinning. Langmuir 2014, 30, 13369–13374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xu, G.; Fu, K.; Lee, H.; Zhang, X. Parameter study and characterization for polyacrylonitrile nanofibers fabricated via centrifugal spinning process. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 3834–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrossamay, M.R.; Balachandran, K.; Capulli, A.K.; Golecki, H.M.; Agarwal, A.; Goss, J.A.; Kim, H.; Shin, K.; Parker, K.K. Engineering hybrid polymer-protein super-aligned nanofibers via rotary jet spinning. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 3188–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thinakaran, S.; Loordhuswamy, A.; Rengaswami, G.V. Electrophoretic deposition of chitosan/nano silver embedded micro sphere on centrifugal spun fibrous matrices–A facile biofilm resistant biocompatible material. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammami, M.A.; Krifa, M.; Harzallah, O. Centrifugal force spinning of PA6 nanofibers–processability and morphology of solution-spun fibers. J. Text. Inst. 2014, 105, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mary, L.A.; Senthilram, T.; Suganya, S.; Nagarajan, L.; Venugopal, J.; Ramakrishna, S.; Giri Dev, V.R. Centrifugal spun ultrafine fibrous web as a potential drug delivery vehicle. Express Polym. Lett. 2013, 7, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Dang, G.; Guo, J.; Liu, Y.; Gong, Y. Sodium alginate/feather keratin-g-allyloxy polyethylene glycol composite phase change fiber. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravishankar, P.; Khang, A.; Laredo, M.; Balachandran, K. Using dimensionless numbers to predict centrifugal jet-spun nanofiber morphology. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 4639658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, Y. Centrifugal spinning: An alternative approach to fabricate nanofibers at high speed and low cost. Polym. Rev. 2014, 54, 677–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, L.; Matej, B.; Karolina, V.; Tereza, K.; Zbynek, T.; Miroslav, D.; Veronika, B.; Andrej, L.; Vera, S.; Barbora, V.; et al. Osteoinductive 3D scaffolds prepared by blend centrifugal spinning for long-term delivery of osteogenic supplements. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 21889–21904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agnes Mary, S.; Giri Dev, V.R. Electrospun herbal nanofibrous wound dressings for skin tissue engineering. J. Text. Inst. 2015, 106, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nille, G.C.; Mishra, S.K.; Chaudhary, A.K.; Reddy, K.R.C. Ethnopharmacological, phytochemical, pharmacological, and toxicological review on senna auriculata (L.) Roxb.: A special insight to antidiabetic property. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 647887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundharajan, S.R.; Ponnusamy, R.D. Chemical composition and characterization studies of Cassia auriculata flower extract. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 327–330. [Google Scholar]
- Vaidyanathan, L.; Thanikachalam, D.; Sivaswamy, L.T. Evaluation of wound healing potency of Cassia auriculata flower extracts using chick embryo wound model. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2014, 27, 222–227. [Google Scholar]
- Sundaramoorthy, S.; Gunasekaran, S.; Arunachalam, S.; Sathiavelu, M. A phytopharmacological review on Cassia species. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2016, 8, 260. [Google Scholar]
- Salma, B.; Muthukumar, S.P.; Avinasha, S.; Manjula, S.N. Review on ethnobotany, phytochemistry, and pharmacological properties of Cassia auriculata. Pharm. Pharmacol. Int. 2020, 8, 106–111. [Google Scholar]
- Mwangi, R.W.; Macharia, J.M.; Wagara, I.N.; Bence, R.L. The medicinal properties of Cassia fistula L: A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 144, 112240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hromadko, L.; Koudelkova, E.; Bulanek, R.; Macak, J.M. SiO2 Fibers by centrifugal spinning with excellent textural properties and water adsorption performance. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 5052–5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buzgo, M.; Rampichova, M.; Vocetkova, K.; Sovkova, V.; Lukasova, V.; Doupnik, M.; Mickova, A.; Rustichelli, F.; Amler, E. Emulsion centrifugal spinning for production of 3D drug releasing nanofibers with core/shell structure. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cipitria, A.; Skelton, A.; Dargaville, T.R.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W. Design, fabrication and characterization of PCL electrospun scaffolds—A review. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 9419–9453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gambhire, M.; Juvekar, A.; Wankhede, S. Evaluation of the anti-inflammatory activity of methanol extract of Barleria leaves by in vivo and in vitro methods. Int. J. Pharmacol 2009, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pavunraj, M.; Rajeshkumar, S.; Bhuvana, L.; Babujanarthanam, R. Preparation of Cassia auriculata plant extracts using different solvents and its antibacterial and antifungal activity against clinical pathogens. Drug Invent. Today 2019, 11, 142–146. [Google Scholar]
- Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Greener synthesis of lignin nanoparticles and their applications. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 612–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, V.; Krishnegowda, A.; Nachiappan, V. Antihyperlipidemic activity of Cassia auriculata flower extract in oleic acid induced hyperlipidemia in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 2965–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Liu, Y.; Ramakrishna, S. Recent development of centrifugal electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socrates, S.H.; Mohan, S.C. Phytochemical analysis of flower extracts of different Cassia species by using gas chromatography mass spectrometry. Int. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhadran, S.; George, S.A.; Sudhakar Malla, H.B. Screening of bioprotective properties of various plant extracts and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry profiling of adenanthera pavonina stem extract. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2017, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kytidou, K.; Artola, M.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Aerts, J.M. Plant glycosides and glycosidases: A treasure-trove for therapeutics. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Mei, S.; Dong, Y.; She, F.; Kong, L. High efficiency fabrication of chitosan composite nanofibers with uniform morphology via centrifugal spinning. Polymers 2019, 11, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muller, F.; Jokisch, S.; Bargel, H.; Scheibel, T. Centrifugal electrospinning enables the production of meshes of ultrathin polymer fibers. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 4360–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitz, R.T.; Harnau, L.; Rauschenbach, S.; Burghard, M.; Kern, K. Polymer nanofibers via nozzle-free centrifugal spinning. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1187–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stojanovska, E.; Kurtulus, M.; Abdelgawad, A.; Candan, Z.; Kilic, A. Developing lignin-based bio-nanofibers by centrifugal spinning technique. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Ozisik, R.; Kotha, S.P.; Underhill, P.T. Highly efficient fabrication of polymer nanofiber assembly by centrifugal jet spinning: Process and characterization. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 2593–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, I.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kang, M.S.; Hyon, S.H.; Selvaraj, A.R.; Prabakar, K.; Han, D.W. The predominant factor influencing cellular behavior on electrospun nanoibrous scaffolds: Wettability or surface morphology? Mater. Des. 2022, 216, 110580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchiers, J.; Meurs, W.; Deferme, W.; Peeters, R.; Buntinx, M.; Reddy, N.K. Influence of polymer concentration and nozzle material on centrifugal fiber spinning. Polymers 2020, 12, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chakrapani, V.Y.; Gnanamani, A.; Giridev, V.R.; Madhusoothanan, M.; Sekaran, G. Electrospinning of type I collagen and PCL nanofibers using acetic acid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 3221–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Chen, W.; Zhao, P.; Yang, Y.; Yu, D.G. Electrospun porous nanofibers: Pore− forming mechanisms and applications for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in wastewater. Polymers 2022, 14, 3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoidy, W.H.; Ahmad, M.B.; Al-Mulla, E.A.J.; Ibrahim, N.A.B. Preparation and characterization of polylactic acid/polycaprolactone clay nanocomposites. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 10, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciardelli, G.; Chiono, V.; Vozzi, G.; Pracella, M.; Ahluwalia, A.; Barbani, N.; Cristallini, C. Giusti, Blends of poly-(ε-caprolactone) and polysaccharides in tissue engineering applications. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1961–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, K.L.; Jones, L. The impact of contact angle on the biocompatibility of biomaterials. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2010, 87, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Chen, R.Y.; Zhang, G.Z.; Zhang, H.C.; Qu, J. Recent advances in centrifugal spinning preparation of nanofibers. In Advanced Materials Research; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Bäch, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 1015, pp. 170–176. [Google Scholar]
- Morales-González, M.; Díaz, L.E.; Dominguez-Paz, C.; Valero, M.F. Insights into the design of polyurethane dressings suitable for the stages of skin wound-healing: A systematic review. Polymers 2022, 14, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilková, A.; Paulovičová, E.; Paulovičová, L.; Poláková, M. Antimicrobial activity of mannose-derived glycosides. Monatsh. Chem. 2015, 146, 1707–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, Y.K.; Panda, S.K.; Biswas, K.; Tamang, A.; Bandyopadhyay, J.; De, D.; Mohanta, D.; Bastia, A.K. Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Cassia fistula (Linn.): In vitro assessment of their antioxidant, antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 10, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajialyani, M.; Tewari, D.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E.; Nabavi, S.M.; Farzaei, M.H.; Abdollahi, M. Natural product-based nanomedicines for wound healing purposes: Therapeutic targets and drug delivery systems. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]









| Peak No. | Retention Time (min) | Compound Name | Peak Area (%) | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.702 | L- Alanyl-L- Methionine | 16.64 | C8H16N2O3S | 291.37 |
| 2 | 16.641 | n-Hexylmethylamine | 8.56 | C7H17N | 115.22 |
| 3 | 23.755 | 3-methyl mannoside | 58.97 | C7H14O6 | 194.18 |
| 4 | 28.881 | Di-sec-butyl-phthalate | 5.03 | C₁₆H₁₈O₄ | 278.34 |
| 5 | 37.086 | N-Methyl-N-octadecylamine | 4.67 | C19H41N | 283.53 |
| Sample No | Blend Combination | Thickness | Apparent Density of the Fiber (g/cc3) | Porosity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PCL (100%) | 0.425 ± 0.002 | 0.030 ± 0.03 | 97% |
| 2 | PCL + 0.5% CA | 0.525 ± 0.003 | 0.038 ± 0.04 | 97% |
| 3 | PCL + 1% CA | 0.425 ± 0.002 | 0.015 ± 0.03 | 98.7% |
| 4 | PCL + 1.5% CA | 0.380 ± 0.004 | 0.040 ± 0.03 | 96.5% |
| Sample No | Sample | Load (N) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (MPa) | Maximum Extension (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PCL | 2.22 | 1.85 | 63 ± 2.5 | 12.72 |
| 2 | PCL + 0.5% CA | 2.16 | 1.80 | 64 ± 2 | 12.87 |
| 3 | PCL + 1% CA | 1.43 | 0.96 | 94 ± 2.3 | 18.83 |
| 4 | PCL + 1.5% CA | 2.36 | 0.94 | 102 ± 2.3 | 20.40 |
| Antibacterial Activity of CA Extract on Selected Bacterial Pathogens | Effect of CA Extract on Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) Denaturation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample No | Test Organisms | CA Extract (1.5%) Zone of Inhibition (mm) | Concentration of Sample (µg/mL) | % of Inhibition |
| 1. | Escherichia coli | 13 mm | 10 | 40 |
| 2. | Bacillus cereus | 15 mm | 20 | 64 |
| 3. | Staphylococcus aureus | 12 mm | 40 | 70 |
| 4. | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 10 mm | 60 | 76 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mary, S.A.; Ariram, N.; Gopinath, A.; Chinnaiyan, S.K.; Raja, I.S.; Sahu, B.; Giri Dev, V.R.; Han, D.-W.; Madhan, B. Investigation on Centrifugally Spun Fibrous PCL/3-Methyl Mannoside Mats for Wound Healing Application. Polymers 2023, 15, 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15051293
Mary SA, Ariram N, Gopinath A, Chinnaiyan SK, Raja IS, Sahu B, Giri Dev VR, Han D-W, Madhan B. Investigation on Centrifugally Spun Fibrous PCL/3-Methyl Mannoside Mats for Wound Healing Application. Polymers. 2023; 15(5):1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15051293
Chicago/Turabian StyleMary, Soloman Agnes, Naisini Ariram, Arun Gopinath, Senthil Kumar Chinnaiyan, Iruthayapandi Selestin Raja, Bindia Sahu, Venkateshwarapuram Rengaswami Giri Dev, Dong-Wook Han, and Balaraman Madhan. 2023. "Investigation on Centrifugally Spun Fibrous PCL/3-Methyl Mannoside Mats for Wound Healing Application" Polymers 15, no. 5: 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15051293
APA StyleMary, S. A., Ariram, N., Gopinath, A., Chinnaiyan, S. K., Raja, I. S., Sahu, B., Giri Dev, V. R., Han, D. -W., & Madhan, B. (2023). Investigation on Centrifugally Spun Fibrous PCL/3-Methyl Mannoside Mats for Wound Healing Application. Polymers, 15(5), 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15051293