Review of the Application of Microwave Heating Technology in Asphalt Pavement Self-Healing and De-icing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Microwave Heating Properties of the Asphalt Mixtures
2.1. Microwave Sensitivity
2.2. Heating Uniformity
3. Self-Healing Properties of Asphalt Concrete under Microwave Heating
3.1. Self-Healing Mechanism
3.2. Evaluation Indicators of Self-Healing Properties
3.3. Factors Influencing Self-Healing Properties
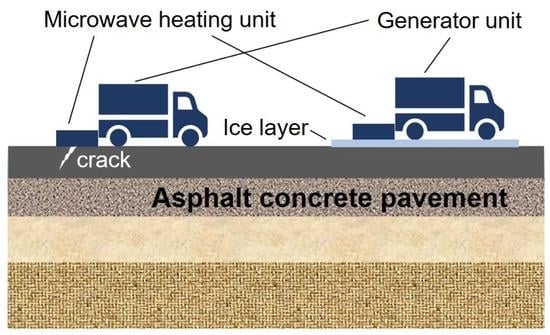
4. Asphalt Pavement De-icing Using Microwave Heating
4.1. Microwave De-icing Mechanism and Efficiency Evaluation
4.2. Microwave De-icing Characteristics
5. Asphalt Aging in Microwave Heating Process
6. Summary
7. Outlooks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Metaxas, A.A.; Meredith, R.J. Industrial Microwave Heating; IET: Stevenage, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Belanger, J.M.R.; Pare, J.R.J.; Poon, O.; Fairbridge, C.; Ng, S.; Mutyala, S.; Hawkins, R. Remarks on various applications of microwave energy. J. Microw. Power Electromagn. Energy 2008, 42, 24–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosisio, R.; Spooner, J.; Grαnger, J. Asphalt road maintenance with a mobile microwave power unit. J. Microw. Power 1974, 9, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, T.L.; Hutcheson, W.R. Asphalt Compounds and Method for Asphalt Reconditioning Using Microwave Radiation. US4849020A, 18 July 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Yalcin, E. Effects of microwave and induction heating on the mechanical and self-healing characteristics of the asphalt mixtures containing waste metal. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 286, 122965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q.; Zeng, W.; Chen, Z.; Ye, Q.; Pan, P. Self-healing performance of asphalt mixtures through heating fibers or aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 150, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Garcia, A. Self-healing of asphalt mixture by microwave and induction heating. Mater. Des. 2016, 106, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W. Study on Enhancement Mechanisim and Healing Evaluation of Microwave Absorption of Asphalt Mixture; Southeast University: Nanjing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, T.; Chen, H.; Chen, X. Synthesis, characterization and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of asphalt carbon coated graphene/magnetic NiFe2O4 modified multi-wall carbon nanotube composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 721, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, T.; Chen, H.; Chen, X. Preparation and microwave absorption properties of asphalt carbon coated reduced graphene oxide/magnetic CoFe2O4 hollow particles modified multi-wall carbon nanotube composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 723, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, S.; Chen, Z.; Shu, B.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, Q. Synthesis of Fe3O4-decorated Mg-Al layered double hydroxides magnetic nanosheets to improve anti-ultraviolet aging and microwave absorption properties used in asphalt materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 220, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, D. Improving the Electromagnetic Properties of Bitumen Using SiC—Fe3O4 Composites. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2021, 33, 04021326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, S.; Shu, B.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z. Microwave absorption and anti-aging properties of modified bitumen contained SiC attached layered double hydroxides. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 227, 116714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, D. Microwave absorption enhancement of asphalt concrete with SiC-Fe3O4 mixtures modifier. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 254, 119209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Ma, J.; Lu, T.; Sun, D. Enhanced heating-healing performance of asphalt concrete modified with heterogenous microwave sensitive admixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 299, 123949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, B.; Sha, A.; Barbieri, D.M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, W. Improved microwave heating uniformity and self-healing properties of steel slag asphalt containing ferrite filler. Mater. Struct./Mater. Et Constr. 2021, 54, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yan, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Z. Research on SiC sand as fine aggregate to reinforce thermal performance of asphalt concrete. SiC. Zhongnan Daxue Xuebao (Ziran Kexue Ban)/J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2021, 52, 2459–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Yang, T.; Xiong, R.; Wang, Y. Electromagnetic wave absorbing properties of asphalt mixture with natural magnetite powder. Jianzhu Cailiao Xuebao/J. Build. Mater. 2016, 19, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Luo, S. Engineering properties and microwave heating induced ice-melting performance of asphalt mixture with activated carbon powder filler. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 197, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ye, F.; Cai, Y.; Birgisson, B.; Lee, K. Self-healing properties of ferrite-filled open-graded friction course (OGFC) asphalt mixture after moisture damage. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; An, D.; Ai, T.; Zhao, P. Laboratory investigation on deicing characteristics of asphalt mixtures using magnetite aggregate as microwave-absorbing materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 124, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, Y.; Hu, Z.; Fan, X.; Zheng, Y. Utilization of low-grade pyrite cinder for synthesis of microwave heating ceramics and their microwave deicing performance in dense-graded asphalt mixtures. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigos, L.; Gallego, J.; Escavy, J.I. Heating potential of aggregates in asphalt mixtures exposed to microwaves radiation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 230, 117035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J. Study on Self Healing Performance of Basalt Fiber Asphalt Mixture Based on Microwave Heating; Yangzhou University: Yangzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wu, S.; Chen, Z.; Tao, G.; Xiao, Y. Enhanced heat release and self-healing properties of steel slag filler based asphalt materials under microwave irradiation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 193, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zeng, G.; Zhou, M.; Fang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, Y.; Ding, S.; Yuan, M.; Li, H.; Wu, S. Controllable synthesis of SiC wrapped LDHs to reinforce microwave absorption and exothermic properties of styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS) polymer modified asphalt. Mater. Res. Express 2021, 8, 035501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, S.; Lu, G.; Cao, L. Laboratory and Numerical Investigation of Microwave Heating Properties of Asphalt Mixture. Materials 2019, 12, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Lu, G.; Liu, X. Accelerated healing in asphalt concrete via laboratory microwave heating. J. Test. Eval. 2020, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yang, J.; Yang, R.; Zhu, J.; Liu, S. Preparation and properties of microwave-absorbing asphalt mixtures containing graphite and magnetite powder. J. Test. Eval. 2021, 49, 573–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, S.; Gu, X. Improving microwave heating efficiency of asphalt concrete by increasing surface magnetic loss of aggregates. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2020, 21, 950–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khavandi Khiavi, A.; Asadi, M. Effect of specific heat capacity of aggregates and nano-graphite on self-healing of hot mix asphalt under microwave radiation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 328, 127091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Investigation on Properties of Steel Wool Fiber Reinforced Asphalt Mixture Based on Induction Heating; Chang’an University: Xi’an, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L. The Study of Asphalt’s Electric and Thermal Field Based on Microwave Heating and Its Control; Anhui Polytechnic University: Wuhu, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.-Q.; Shi, J.-F.; Sun, T.-S.; McGean, T.J. Heat transfer model and numerical simulation for microwave hot in-place recycling of asphalt pavements. In Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Transportation and Development Innovative Best Practices 2008, TDIBP 2008, Beijing, China, 24–26 April 2008; pp. 462–467. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, J. Temperature control strategies for microwave hot inplace recycling of asphalt pavements. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Workshop on Intelligent Systems and Applications, ISA 2009, Wuhan, China, 23–24 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, L. Research on electromagnetic field optimization for microwave hot recycling of asphalt mixtures. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Material Science and Engineering Technology, ICMSET 2011, Zhengzhou, China, 11–13 November 2011; pp. 575–579. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T. Optimized antenna for asphalt mixture recycling based on microwave heating. J. Microw. Power Electromagn. Energy 2015, 49, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, M.; Bahmai, B.B.; Javadi, S.; Sharafi, M. An evaluation of the mechanical and self-healing properties of warm mix asphalt containing scrap metal additives. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 253, 119963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J. Important topics in development of asphalt concrete technology in China. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2008, 39, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar]
- Bazin, P.; Saunier, J. Deformability, fatigue and healing properties of asphalt mixes. In Proceedings of the International Conference on the Structural Design of Asphalt Pavements, Ann Arbor, MI, USA; 1967; pp. 553–569. Available online: https://trid.trb.org/view/100855 (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Al-Ohaly, A.A.; Terrel, R.L. Effect of Microwave Heating on Adhesion and Moisture Damage of Asphalt Mixtures; National Research Council, Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 1988; Available online: https://trid.trb.org/view/295675 (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Gallego, J.; del Val, M.A.; Contreras, V.; Páez, A. Heating asphalt mixtures with microwaves to promote self-healing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 42, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hao, P.; Zhang, M. Fabrication, characterization and assessment of the capsules containing rejuvenator for improving the self-healing performance of asphalt materials: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 287, 125079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anupam, B.R.; Sahoo, U.C.; Chandrappa, A.K. A methodological review on self-healing asphalt pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 321, 126395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapery, R.A. On the mechanics of crack closing and bonding in linear viscoelastic media. Int. J. Fract. 1989, 39, 163–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytton, R.L.; Uzan, J.; Fernando, E.G.; Roque, R.; Hiltunen, D.; Stoffels, S.M. Development and Validation of Performance Prediction Models and Specifications for Asphalt Binders and Paving Mixes; Strategic Highway Research Program: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; Volume 357. [Google Scholar]
- De Gennes, P.-G. Reptation of a polymer chain in the presence of fixed obstacles. J. Chem. Phys. 1971, 55, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wool, R.P.; O’Connor, K.M. A theory crack healing in polymers. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 5953–5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, D.N.; Bhasin, A. Exploring Mechanism of healing in asphalt mixtures and quantifying its impact. Self-Heal. Mater. 2008, 100, 205–218. [Google Scholar]
- Loeber, L.; Sutton, O.; Morel, J.; Valleton, J.M.; Muller, G. New direct observations of asphalts and asphalt binders by scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy. J. Microsc. 1996, 182, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kringos, N.; Scarpas, A.; Pauli, T.; Robertson, R. A thermodynamic approach to healing in bitumen. In Advanced Testing and Characterization of Bituminous Materials, Two Volume Set; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- García, Á. Self-healing of open cracks in asphalt mastic. Fuel 2012, 93, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.; Bueno, M.; Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Partl, M.N. Induction healing of dense asphalt concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargari, A.; Arabani, M.; Mirabdolazimi, S.M. Effect of palm oil capsules on the self-healing properties of aged and unaged asphalt mixtures gained by resting period and microwave heating. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 316, 125901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xiong, Y.; Ma, X.; Guo, Y.; Yue, M.; Yue, J. Investigating the differences between steel slag and natural limestone in asphalt mixes in terms of microscopic mechanism, fatigue behavior and microwave-induced healing performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 328, 127107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franesqui, M.A.; Yepes, J.; Gallego, J. Ultrasound Monitoring and Microwave Self-healing of Top-Down Cracks in Asphalt Pavements. In Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 76, pp. 263–273. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, B.; Sha, A.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, W.; Cui, X. Effect of metallic-waste aggregates on microwave self-healing performances of asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 246, 118510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Schlangen, E.; Van De Ven, M.; Van Bochove, G.; Van Montfort, J. Evaluation of the induction healing effect of porous asphalt concrete through four point bending fatigue test. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 29, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Tan, Y.; Richard Kim, Y. Establishment of a universal healing evaluation index for asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 48, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, J.S.; Kim, Y.R. Laboratory Evaluation of Fatigue Damage and Healing of Asphalt Mixtures. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2001, 13, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-R.; Little, D.N.; Lytton, R.L. Fatigue and Healing Characterization of Asphalt Mixtures. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2003, 15, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Gonzalez, A.; Concha, J.L.; Gonzalez-Torre, I.; Schlangen, E. Effect of metallic waste addition on the electrical, thermophysical and microwave crack-healing properties of asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 187, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Gonzalez-Torre, I. Influence of the Microwave Heating Time on the Self-Healing Properties of Asphalt Mixtures. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, A.; Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Storey, L.; Schlangen, E. Effect of RAP and fibers addition on asphalt mixtures with self-healing properties gained by microwave radiation heating. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 159, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Yuan, H.; Liu, Y.; Fan, S.; Ding, Y. Evaluation of Self-Healing Performance of Asphalt Concrete for Macrocracks via Microwave Heating. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 04020248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dai, Q.; Porter, D.; You, Z. Investigation of microwave healing performance of electrically conductive carbon fiber modified asphalt mixture beams. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 126, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.M.; Park, D.-W.; Le, T.H.M. Crack healing performance of hot mix asphalt containing steel slag by microwaves heating. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 180, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Valderrama, J.; Norambuena-Contreras, J. Microwave crack healing on conventional and modified asphalt mixtures with different additives: An experimental approach. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2019, 20, S149–S162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Liu, Q.; Wu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, S.; Zou, Y.; Rao, W.; Yu, X. A novel microwave induced oil release pattern of calcium alginate/ nano-Fe3O4 composite capsules for asphalt self-healing. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuemmel, D.; Hanbali, R. Accident Analysis of Ice Control Operations. 1992. Available online: https://epublications.marquette.edu/transportation_trc-ice/2/ (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Liu, J.-B.; Du, C.-G. Study on prediction model of friction coefficient of ICY road surface. In Proceedings of the 19th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals: Transportation in China—Connecting the World, CICTP 2019, Nanjing, China, 6–8 July 2019; pp. 3389–3396. [Google Scholar]
- Öberg, G. Friction and Journey Speed on Roads with Various Winter Road Maintenance. 1981. Available online: https://trid.trb.org/view/187066 (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Malin, F.; Norros, I.; Innamaa, S. Accident risk of road and weather conditions on different road types. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2019, 122, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.; Xing, C.; Tan, Y.; Gong, X. Safety aspects on icy asphalt pavement in cold region through field investigations. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2019, 161, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelisejevs, B. Alternative methods of de-icing on highways. Mot. Riga 2001, 3, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.D.; Du, S.R.; Shen, B.C.; Wang, L.H. Mechanical Property Analysis on Cutting Tool of the Ice and Snow Removing Machine Based on ANSYS. Appl. Mech. Mater 2015, 779, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Jungwirth, S.; Akin, M.; Wright, R.; Fay, L.; Veneziano, D.A.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, J.; Ye, Z. Evaluating snow and ice control chemicals for environmentally sustainable highway maintenance operations. J. Transp. Eng. 2014, 140, 05014005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, W.A. Improved Cutting Edges for Ice Removal; Strategic Highway Research Program: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Liu, H. Research progress and prospect of testing and application technology of highway snow-melting agent at home and abroad. In Proceedings of the 2011 2nd International Conference on Mechanic Automation and Control Engineering, MACE 2011, Inner Mongolia, China, 15–17 July 2011; pp. 6807–6811. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Luo, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y. Evaluation of Performance Deterioration Characteristics of Asphalt Mixture in Corrosion Environment Formed by Snow-Melting Agents. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2022, 34, 04021481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xu, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, H. Surface during microwave deicing of airport pavement. Materials 2020, 13, 3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Xu, P.; Wang, F.; Jin, C.; Huang, M.; Dai, D.; Fu, C. Deicing efficiency analysis and economic-environment assessment of a novel induction heating asphalt pavement. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 123123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Wu, S.; Xiao, F.; Pang, L.; Xiao, Y. Conductive asphalt concrete: A review on structure design, performance, and practical applications. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 26, 755–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Geng, H.; Tan, S.; Lv, J.; Wang, H.; He, Z.; Wang, J. Highly efficient solar anti-icing/deicing: Via a hierarchical structured surface. Mater. Horiz. 2020, 7, 2097–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, G.; Wu, Z. Deicing and corrosive performances of calcium acetate deicer made from bamboo-Vinegar. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2010, 41, 506–511. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Sha, A.; Wang, Z.; Tong, Z.; Liu, Z. Utilization of steel slag as aggregate in asphalt mixtures for microwave deicing. Journal of Cleaner Production 2017, 152, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Xia, H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, H.; Yan, M. Pavement anti-icing coating based on a functional composite of NaCl microcapsules. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 307, 125010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterji, S. Aspects of the freezing process in a porous material–water system: Part 1. Freezing and the properties of water and ice. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, R.J. Engineers’ Handbook of Industrial Microwave Heating; IET: Stevenage, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Xu, Y.G.; Liu, F.L. Application of microwave heating for ice removal on streets. Harbin Gongye Daxue Xuebao/J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2003, 35, 1342–1343. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Han, Z.; Sha, A.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, W. A review of electromagnetic wave absorbing materials used in microwave deicing pavement. Mater. Rep. 2016, 30, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.W.; Jiao, S.J.; Gao, Z.Y.; Xu, X.L. Study of 5.8 GHz magnetron in microwave deicing. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2008, 22, 1351–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.-J.; Tang, X.-W.; Gao, Z.-Y.; Wang, Q. Study of key technology on microwave deicing efficiency. Zhongguo Gonglu Xuebao/China J. Highw. Transp. 2008, 21, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Q.; Fang, H.; Wu, S.; Tang, J.; Ye, Q. Ice melting properties of steel slag asphalt concrete with microwave heating. In Proceedings of the 17th IUMRS International Conference in Asia, IUMRS-ICA 2016, Qingdao, China, 20–24 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yang, B. Microwave deicing for asphalt mixture containing steel wool fibers. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 206, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.-J.; Tang, X.-W.; Gao, Z.-Y.; Wang, Q. Influence of environmental temperature on road de-icing efficiency using microwave. Chang. Daxue Xuebao (Ziran Kexue Ban)/J. Chang. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2008, 28, 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Kulash, D. Strategic Highway Research Program; American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Long, W.H. Asphaltic Compositions and Uses Therefor. US6193793B1, 27 February 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hopstock, D. Microwave-Absorbing Road Construction and Repair Material. Final Report to NRRI on Idea Evaluation Subcontract. 2003.
- Hopstock, D.M.; Zanko, L.M. Minnesota Taconite as a Microwave-Absorbing Road Aggregate Material for Deicing and Pothole Patching Applications. 2005. Available online: https://www.cts.umn.edu/publications/report/minnesota-taconite-as-a-microwave-absorbing-road-aggregate-material-for-deicing-and-pothole-patching-applications (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Zhao, P.; Ai, T.; Wang, Z. A Composition of Slag Asphalt Concrete Pavement Material for Microwave Heating. CN101774786B, 16 January 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Wang, Z.; Ai, T. A Microwave Absorbing Asphalt Concrete Pavement Material Composition. CN101736671B, 29 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wei, Q.; Zhou, P.; Cai, L.; Yuan, C.; Feng, G.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Tang, Y.; Li, L.; et al. A Microwave Absorbing Asphalt Pavement Mixture and Its Preparation Method. CN104310860A, 28 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Ding, L.; Fu, L. Microwave sensitive coating materials and equipment for snow removal. J. Chang. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2018, 38, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, M.-H.; Xu, Y.-G.; Lu, T.-J.; Xu, C.-H. Application of microwave heating on removing ice on streets. Beifang Jiaotong Daxue Xuebao/J. North. Jiaotong Univ. 2003, 27, 79. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.-H.; Zhao, Q.; Li, H.-F.; Sun, X.; Ju, H.-J. Design of sloped horn antenna for microwave deicing of asphalt pavements. Qiangjiguang Yu Lizishu/High Power Laser Part. Beams 2007, 19, 1883–1886. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, L.T.; Wang, X.C.; Zhang, W.G.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.Q. Microwave Deicing Efficiency: Study on the Difference between Microwave Frequencies and Road Structure Materials. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, J.; Ai, T.; Zhao, P. Laboratory investigation on microwave deicing function of micro surfacing asphalt mixtures reinforced by carbon fiber. J. Test. Eval. 2014, 42, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, G.; Gallego, J.; Giuliani, F.; Autelitano, F. Aging of asphalt binder in hot pavement rehabilitation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 187, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yang, J.; Yang, R.; Zhu, J.; Liu, S. Investigation on Microwave Heating Technology for Rutting Maintenance in Asphalt Pavement. J. Test. Eval. 2018, 48, 2998–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.; Canon, G.; Leischner, S.; Rochlani, M.; Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Gonzalez, A. Effects of microwave heating and long-term aging on the rheological and chemical properties of recovered bitumen. Materials 2021, 14, 7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, B.; Sha, A.; Barbieri, D.M.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Hoff, I. Evaluation of microwave aging impact on asphalt mixtures. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2022, 24, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, A.; Lou, B.; Barbieri, D.M.; Hoff, I. Microwave Heating as an Innovative Road Maintenance Technology: Aging Effect on Binder and Feasibility Evaluation. Materials 2022, 15, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Materials | Electromagnetic Frequency (GHz) | Thickness (mm) | RL (db) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asphalt carbon-coated graphene/magnetic NiFe2O4-modified multi-wall carbon nanotube composites [9] | 4.6 | 3.2 | −45.9 |
| Asphalt carbon-coated reduced graphene oxide/magnetic CoFe2O4 hollow-particle-modified multi-wall carbon nanotube composites [10] | 11.6 | 1.6 | −46.8 |
| Mg-Al layered double hydroxides (LDHs) [11] | 15.71 | 8 | −4.79 |
| LDHs:Fe3O4 = 1:1 | 11.71 | 10 | −6.88 |
| LDHs:Fe3O4 = 2:1 | 11.88 | 10 | −5.25 |
| LDHs:Fe3O4 = 1:2 | 11.28 | 8 | −10.73 |
| SiC [12] | 16.12 | 28 | −12.53 |
| SiC:Fe3O4 = 1:1 | 11.21 | 30 | −18.93 |
| SiC:Fe3O4 = 2:1 | 11.26 | 29.5 | −15.82 |
| SiC:Fe3O4 = 1:2 | 17.92 | 26 | −22.18 |
| LDHs [13] | 15.49 | 8 | −5.21 |
| SiC attached LDHs | 17.5 | 10 | −13.65 |
| SiC:Fe3O4 is 3:1 [14] | 2.45 | 25 | −28 |
| Limestone filler [15] | 16.1 | - | −6.8 |
| Manganese dioxide powder | 11.6 | - | −18.83 |
| Carbon powder | 2.36 | - | −33.53 |
| Ferrite powder | 12.3 | - | −41.68 |
| Limestone [16] | 15.88 | - | −2.67 |
| Ferrite | 3.89 | - | −10.62 |
| Ferrite | 13.67 | - | −30.28 |
| Fine SiC [17] | 13.68 | 2 | −22.34 |
| Fine SiC | 2.45 | 10 | −13.55 |
| Coarse SiC | 8.08 | 10 | −15.27 |
| Coarse SiC | 2.45 | 10 | −10.51 |
| Asphalt mixture added with natural magnetite power in grade of 80 [18] | 2.9 | 30 | −38 |
| Asphalt mixture added with natural magnetite power in grade of 70 | 3 | 30 | −27 |
| Asphalt mixture added with natural magnetite power in grade of 60 | 3.15 | 30 | −25 |
| Asphalt Mixtures | Aggregates | Heating Rate (°C/s) |
|---|---|---|
| Normal asphalt mixture [27,28,29,30] | Basalt | 0.252–0.76 |
| Normal asphalt mixture [14,17,31] | Limestone | 0.2–0.548 |
| Normal asphalt mixture [31] | Dolomite limestone | 0.618 |
| Normal asphalt mixture [31] | Granite | 0.757 |
| Normal asphalt mixture [6] | Andesite | 0.355 |
| Asphalt mixture with steel slag aggregates [27] | Basalt | 0.623 |
| Asphalt mixture with SiC and Fe3O4 powder [14] | Limestone | 0.244–0.367 |
| Asphalt mixture with SiC aggregates [17] | Limestone | 0.458–0.476 |
| Asphalt mixture with steel fiber and graphite [28] | Basalt | 0.9–1.02 |
| Asphalt mixture with graphite powder and magnetite powder [29] | Basalt | 0.372 |
| Asphalt mixture with aggregates coated by magnetic Fe3O4 films [30] | Basalt | 0.888–0.9 |
| Asphalt mixture with nano-graphite [31] | Limestone | 0.579–0.815 |
| Asphalt mixture with nano-graphite [31] | Dolomite limestone | 0.658–0.92 |
| Asphalt mixture with nano-graphite [31] | Granite | 0.831–1.184 |
| Asphalt mixture with steel fiber [6] | Andesite | 0.804 |
| Asphalt mixture with steel slag aggregate [6] | Andesite | 0.696 |
| MSAs | Volume/Mass Fraction of MSAs | IT (mm) | ET (°C) | Efficiency Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferrite [93] | 10% | 10 | −10 | 3.1 times |
| 10 | −15 | 2.8 times | ||
| 10 | −19 | 2.9 times | ||
| Magnetite [21] | 80% | 10 | −5 | 8.6 times |
| 10 | −10 | 8.1 times | ||
| 10 | −15 | 6.3 times | ||
| Steel slag [86] | 80% | - | −5 | 3.1 times |
| - | −20 | 2.6 times | ||
| MHCs [22] | 100% | 30 | −10 | 5.8 times |
| 20 | −10 | 6.1 times | ||
| 15 | −10 | 6.6 times | ||
| 10 | −10 | 8.9 times | ||
| 5 | −10 | 9.2 times | ||
| 10 | −20 | 7.8 times | ||
| 2# steel wool fibers [95] | 1% | - | −5 | 7 times |
| - | −10 | 5.5 times | ||
| 0# steel wool fibers | 0.7% | - | −5 | 4.6 times |
| - | −10 | 4.4 times | ||
| 000# steel wool fibers | 0.3% | - | −5 | 3.9 times |
| - | −10 | 3.1 times | ||
| ACP [19] | 100% | 50 | −15 | 2.5 times |
| Carbon fiber [108] | 0.45% | - | −10 | 2.7 times |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, W.; Miao, Y. Review of the Application of Microwave Heating Technology in Asphalt Pavement Self-Healing and De-icing. Polymers 2023, 15, 1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071696
Zhang L, Zhang Z, Yu W, Miao Y. Review of the Application of Microwave Heating Technology in Asphalt Pavement Self-Healing and De-icing. Polymers. 2023; 15(7):1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071696
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Letao, Zihan Zhang, Weixiao Yu, and Yinghao Miao. 2023. "Review of the Application of Microwave Heating Technology in Asphalt Pavement Self-Healing and De-icing" Polymers 15, no. 7: 1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071696
APA StyleZhang, L., Zhang, Z., Yu, W., & Miao, Y. (2023). Review of the Application of Microwave Heating Technology in Asphalt Pavement Self-Healing and De-icing. Polymers, 15(7), 1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071696