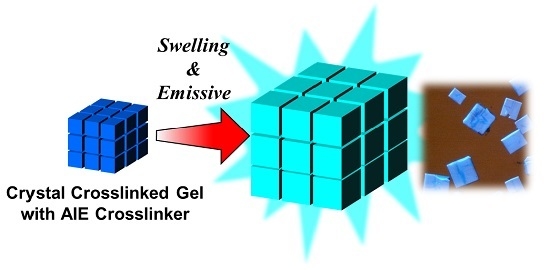
Crystal Crosslinked Gels with Aggregation-Induced Emissive Crosslinker Exhibiting Swelling Degree-Dependent Photoluminescence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of AzKU (Azide-Functionalized KUMOF)
2.2. Preparation of CLKU(TPE) (Crosslinked KUMOF with TPE-CL4)
2.3. Preparation of KUCCG(TPE) (Crystal Crosslinked Gel from KUMOF)
2.4. Preparation of AzIR15 (Azide-Functionalized IRMOF-15)
2.5. Preparation of CLIR15(TPE) (Crosslinked IRMOF15 with TPE-CL4)
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mei, J.; Leung, N.L.C.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Jacky, W.Y.L.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-Induced Emission: Together We Shine, United We Soar! Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, J.; Hong, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Qin, A.; Tang, Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission: The whole is more brilliant than the parts. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5429–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Tao, L.; Chi, Z.; Xu, J.; Wei, Y. Aggregation induced emission-based fluorescent nanoparticles: Fabrication methodologies and biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4398–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, A.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Luminogenic polymers with aggregation-induced emissioncharacteristics. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 182–209. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5361–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission: Phenomenon, mechanism and applications. Chem. Commun. 2009, 29, 4332–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Barashkov, N.N.; Irgibaeva, I.S.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Hu, R.; Birimzhanova, D.; Yu, Y.; Tang, B.Z. Fluorescent Chemosensor for Detection and Quantitation of Carbon Dioxide Gas. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 13951–13953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shustova, N.B.; McCarthy, B.D.; Dincă, M. Turn-On fluorescence in tetraphenylethylene-based metal–organic frameworks: An alternative to aggregation-induced emission. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 20126–20129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.; Feng, X.; Tong, B.; Shi, J.; Chen, L.; Zhi, J.; Dong, Y. A novel “turn-on” fluorescent chemosensor for the selective detection of Al3+ based on aggregation-induced emission. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 416–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Xu, B.; Dong, Y.; Chen, F.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; He, J.; Li, H.; Tian, W. Novel Fluorescent pH Sensors and a Biological Probe Based on Anthracene Derivatives with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics. Langmuir 2010, 26, 6838–6844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Bian, N.; Cao, C.; Qiu, X.-L.; Qi, A.-D.; Han, B.-H. Glucosamine hydrochloride functionalized tetraphenylethylene: A novel fluorescent probe for alkaline phosphatase based on the aggregation-induced emission. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 4067–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Gao, M.; Feng, G.; Liu, B. Mitochondria-targeted cancer therapy using a light-up probe with aggregation-induced-emission characteristics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 14225–14229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Chan, C.Y.K.; Chen, S.; Deng, C.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Jim, C.K.W.; Hong, Y.; Lu, P.; Chang, Z.; Chen, X. Using tetraphenylethene and carbazole to create efficient luminophores with aggregation-induced emission, high thermal stability, and good hole-transporting property. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 4527–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, S.; Liang, G.; Zhao, W.; Kwok, H.S.; Tang, B.Z. Red emissive AIE luminogens with high hole-transporting properties for efficient non-doped OLEDs. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 7321–7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, Y.; Qian, S.; Cao, Y.; Tian, H. Aggregation-induced emission (AIE)—Active starburst triarylamine fluorophores as potential non-doped red emitters for organic light-emitting diodes and Cl2 gas chemodosimeter. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 3799–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Roy, B.; Yoshihara, D.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Shinkai, S. Cyclization-induced turn-on fluorescence system applicable to dicarboxylate sensing. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Zheng, H.-F.; Li, D.-M.; Wang, J.-H.; Feng, H.-T.; Zhu, Z.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Zheng, Y.-S. Monomer emission and aggregate emission of TPE derivatives in the presence of γ-cyclodextrin. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 2170–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.-J.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Wu, B. Anion-coordination-induced turn-on fluorescence of an oligourea-functionalized tetraphenylethene in a wide concentration range. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 6632–6636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokado, K.; Chujo, Y. Emission via Aggregation of Alternating Polymers with o-Carborane and p-Phenylene–Ethynylene Sequences. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 1418–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokado, K.; Nagai, A.; Chujo, Y. Poly(γ-glutamic acid) hydrogels with water-sensitive luminescence derived from aggregation-induced emission of o-carborane. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 6463–6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, R.; Yamada, T.; Sada, K.; Kokado, K. Stimuli-responsive fluorescence of AIE elastomer based on PDMS and tetraphenylethene. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 6382–6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokado, K.; Taniguchi, R.; Sada, K. Rigidity-induced emission enhancement of network polymers crosslinked by tetraphenylethene derivatives. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 8504–8509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, Y.; Ishiwata, T.; Sugikawa, K.; Kokado, K.; Sada, K. Nano- and microsized cubic gel particles from cyclodextrin metal–organic frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10566–10569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiwata, T.; Furukawa, Y.; Sugikawa, K.; Kokado, K.; Sada, K. Transformation of metal-organic framework to polymer gel by cross-linking the organic ligands preorganized in metal–organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 5427–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, Y.; Sato, H.; Shinkai, S.; Sada, K. “Clickable” metal-organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14354–14355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, K.K.; Cohen, S.M. Postsynthetic modification of metal–organic frameworks—A progress report. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 498–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Cao, X.; Chen, X.; Ayres, N.; Zhang, P. Triplet–triplet annihilation upconversion from rationally designed polymeric emitters with tunable inter-chromophore distances. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, S.; Sato, H.; Sugikawa, K.; Kokado, K.; Sada, K. Conversion of azide to primary amine via Staudinger reaction in metal—Organic frameworks. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 4137–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.-H.; Chen, C.; Hu, P.; Wang, B.-Q.; Redshaw, C.; Zhao, K.-Q. Tetraphenylethene–triphenylene oligomers with an aggregation-induced emission effect and discotic columnar mesophase. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 14099–14105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, K.S.; Go, Y.B.; Shin, S.M.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.; Yaghi, O.M.; Jeong, N. Asymmetric catalytic reactions by NbO-type chiral metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddaoudi, M.; Kim, J.; Rosi, N.; Vodak, D.; Wachter, J.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Systematic design of pore size and functionality in isoreticular MOFs and their application in methane storage. Science 2002, 295, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Sample | Solvent | ΦF (%) | Q |
|---|---|---|---|
| KUCCG(TPE) | water | 0.7 | 0.86 |
| DMF | 3.0 | 1.84 | |
| KUCCG(TPE)-Na | water | 8.4 | 3.17 |
| DMF | 14.8 | 3.64 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oura, T.; Taniguchi, R.; Kokado, K.; Sada, K. Crystal Crosslinked Gels with Aggregation-Induced Emissive Crosslinker Exhibiting Swelling Degree-Dependent Photoluminescence. Polymers 2017, 9, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9010019
Oura T, Taniguchi R, Kokado K, Sada K. Crystal Crosslinked Gels with Aggregation-Induced Emissive Crosslinker Exhibiting Swelling Degree-Dependent Photoluminescence. Polymers. 2017; 9(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleOura, Tsuyoshi, Ryosuke Taniguchi, Kenta Kokado, and Kazuki Sada. 2017. "Crystal Crosslinked Gels with Aggregation-Induced Emissive Crosslinker Exhibiting Swelling Degree-Dependent Photoluminescence" Polymers 9, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9010019
APA StyleOura, T., Taniguchi, R., Kokado, K., & Sada, K. (2017). Crystal Crosslinked Gels with Aggregation-Induced Emissive Crosslinker Exhibiting Swelling Degree-Dependent Photoluminescence. Polymers, 9(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9010019