Chitosan Combined with ZnO, TiO2 and Ag Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Wound Healing Applications: A Mini Review of the Research Trends
Abstract
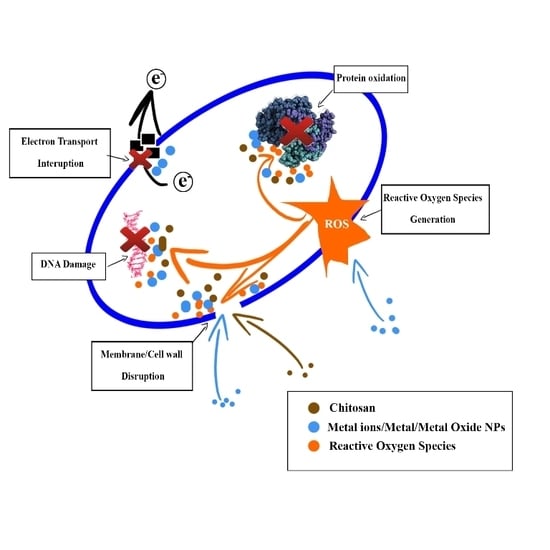
:1. Introduction
2. Antimicrobial Properties of Chitosan
3. Nanotechnology in Antimicrobial Wound-Dressing Applications
3.1. Nanocomposite Materials Based on Chitosan and ZnO NPs
3.1.1. Antimicrobial Properties of ZnO NPs
3.1.2. Applications of Chitosan/ZnO Nanocomposites in Wound Healing
3.2. Nanocomposites Based on Chitosan and TiO2 NPs
3.2.1. Antimicrobial Properties of TiO2 NPs
3.2.2. Applications of Chitosan/TiO2 Nanocomposites in Wound Healing
3.3. Nanocomposites Based on Chitosan and Ag NPs
3.3.1. Antimicrobial Properties of Ag NPs
3.3.2. Applications of Chitosan/Ag Nanocomposites in Wound Healing
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boucher, H.W. Challenges in anti-infective development in the era of bad bugs, no drugs: A regulatory perspective using the example of bloodstream infection as an indication. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50 (Suppl. 1), S4–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, H.W.; Talbot, G.H.; Bradley, J.S.; Edward, J.E., Jr.; Gilbert, D.; Rice, L.B.; Scheld, M.; Spellberg, B.; Barlett, J. Bad bugs, no drugs: No ESKAPE! An update from the infectious disease society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannousi, K.; Menelaou, M.; Arvanitidis, J.; Angelakeris, M.; Pantazaki, A.; Dendrinou-Samara, C. Hetero-nanocomposites of magnetic and antifungal nanoparticle as a platform for magnetomechanical stress in induction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 5341–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Sun, W.; Qian, W.; Ye, Y.; Ma, X. The synthesis of chitosan-based silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial activity. Carbohydr. Res. 2009, 344, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hang, A.T.; Tae, B.; Park, J.S. Non-woven mats of poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan blends containing silver nanopartiocles: Fabrication and characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, S.; Seino, H.; Akiyama, Y.; Nonaka, I. Chitosan: A biocompatible material for oral and intravenous administrations. In Progress in Biomedical Polymers; Gebelein, C.G., Dunn, R.L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Kurita, K. Chemistry and application of chitin and chitosan. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1998, 59, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.-S.; Choi, Y.-R.; Shon, Y.-H. Evaluation of the antimutagenic potential of chitosan oligosaccharide: Rec, Ames and Umu tests. Biotechnol. Lett. 2001, 23, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Chen, X.G.; Xing, K.; Park, H.J. Antimicrobial properties of chitosan and mode of action: A state of the art review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 144, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vold, I.M.N.; Varum, K.M.; Guibal, E.; Smidsrod, O. Binding of ions to chitosan-selectively studies. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003, 54, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschel, D.; Zhang, K.; Fischer, S.; Groth, T. Modulation of osteogenic acivity of BMP-2 by cellulose and chitosan derivatives. Acta Biomater. 2011, 8, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petkova, P.; Francesko, A.; Fernandes, M.M.; Mendoza, E.; Perels, I.; Gedanken, A.; Tzanov, T. Sonochemical coating of texiles with hybrids ZnO/chitosan antimicrobial nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 1164–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Du, Y.; Fan, L.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y. Chitosan-metal complexes as antimicrobial agent: Synthesis, characterization and structure-activity study. Polym. Bull. 2005, 55, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.N.V.R. A review of chitin and chitosan applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 46, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.-K.F.; Matthew, H.W.T. Application of chitin-based polysaccharide biomaterials in cartilage tissue engineering: A review. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2589–2598. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, T.; Tazuke, S.; Suzuki, Y. Biologically active polycations, 4. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of poly(trialkylvinylbenzylammonium chloride)s. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1984, 185, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.-C.; Su, Y.-P.; Chen, C.-C.; Jia, G.; Wang, H.-L.; Wu, J.C.G.; Lin, J.-G. Relationship between antibacterial activity of chitosan and surface characteristics of cell wall. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2004, 25, 932–936. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- No, H.K.; Park, N.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Meyers, S.P. Antibacterial activity of chitosans and chitosan oligomers with different molecular weights. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 74, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Cai, S.; Li, P. Synthesis of acyl thiourea derivatives of chitosan and their antimicrobial activities in vitro. Carbohydr. Res. 2008, 343, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Du, Y.; Liu, H. Preparation, characterization and antimicrobial acticity of chitosan-Zn complex. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 56, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roller, S.; Covill, N. The antifungal properties of chitosan in laboratory media and apple juice. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1999, 47, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, S. Cell Surface Analysis; Mozes, N., Handley, P.S., Busscher, H.J., Rouxhet, P.G., Eds.; VCH Publishers: Weinheim, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Jucker, B.A.; Harms, H.; Hug, S.J.; Zehnder, A.J.B. Adsorption of bacterial surface polysaccharides on mineral oxides is mediated by hydrogen bonds. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 1997, 9, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jucker, B.A.; Zehnder, A.J.B.; Harms, H. Quantification of polymer interactions in bacterial adhesion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2909–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Chen, X.G.; Liu, C.S.; Liu, C.G.; Meng, X.H.; Yu, L.J. Antibacterial mechanism of chitosan microspheres in a solid dispersing system against E. coli. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 65, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Z.; Cooper, S.L. Interactions between dendrimer biocides and bacterial membranes. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 3359–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archana, D.; Dutta, J.; Dutta, P.K. Evaluation of chitosan nano dressing for wound healing: Characterization, in vitro and in vivo study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 57, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.K.; Ray, A.R. Biomedical applications of chitin, chitosan, and their derivaties. J. Macromol. Sci. C Polym. Rev. 2000, 40, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, B.A.; Aebischer, P. Chitosan as a matrix for mammalian cell encapsulation. Biomaterials 1994, 15, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiji, M. Permeability and blood compatibility properties of chitosan-poly(ethylene oxide) blend membranes for haemodialysis. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.-H.; Hudson, S.M. Review of chitosan and its derivatives as antimicrobial agents and their uses as textile chemicals. J. Macromol. Sci. C Polym. Rev. 2013, 43, 223–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Choi, J.W.; Chun, H.J.; Choi, K.S. Synthesis of chitosan derivaties with quaternary ammonium salt and their antibacterial activity. Polym. Bull. 1997, 38, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Guan, Y.L.; Yang, D.Z.; Li, Z.; Yao, K.D. Antibacterial action of chitosan and carboxymethlyated chitosan. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 79, 1324–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.S.; Su, J.C.; Tsai, G.J. Antimicrobial effect and physical properties of sulfonbenzoyl chitosan. In Advances in Chitin Science; Chen, R.H., Chen, H.C., Eds.; Rita Advertising Co., Ltd.: Taipei, Taiwan, 1998; Volume 3, pp. 278–282. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.S.; Su, J.C.; Tsai, G.J. Antimicrobial effect and physical properties of sulfonated chitosan. In Advances in Chitin Science; Chen, R.H., Chen, H.C., Eds.; Rita Advertising Co., Ltd.: Taipei, Taiwan, 1998; Volume 3, pp. 273–277. [Google Scholar]
- Kurita, K.; Kojima, T.; Nishiyama, Y.; Shimojoh, M. Synthesis and some properties of nonnatural amino polysaccharides: Branched chitin and chitosan. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 4711–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.-J.; Kim, S.-K. Effect of antimicrobial activity by chitosan oligosaccharide n-conjugated with asparagine. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 11, 281–286. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.T.S.; Laskmanan, V.-K.; Anilkumar, T.V.; Ramya, C.; Reshmi, P.; Unnikrishnan, A.G.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. Flexible and microporous chitosan hydrogel/nano ZnO composite bandages for wound dressing: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2618–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.A.; Daya, M.R.; Worley, J.A. Experience with chitosan dressing in a civilian EMS system. J. Emerg. Med. 2007, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Lu, J.G. Zinc oxide nanostructure: Synthesis and properties. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2005, 5, 1561–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirelkhatim, A.; Mahmud, S.; Seeni, A.; Kaus, N.H.M.; Ann, L.C.; Bakhori, S.K.M.; Hasan, H.; Mohamad, D. Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: Antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano Micro Lett. 2015, 7, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawai, J. Quantitative evaluation of antibacterial activities of metallic oxide powders (ZnO, MgO and CaO) by conductimetric assay. J. Microbiol. Methods 2003, 54, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brayner, R.; Ferrari-Iliou, R.; Brivois, N.; Djediat, S.; Benedetti, M.F.; Fievet, F. Toxicological impact studied based on Escherichia coli bacteria in ultrafine ZnO nanoparticles colloidal medium. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Yan, D.; Yin, G.; Liao, X.; Kang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Huang, D.; Hao, B. Toxicological effect of ZnO nanoparticles based on bacteria. Langmuir 2008, 24, 4140–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, N.; Ray, B.; Ranjit, K.T.; Manna, A.C. Antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles suspension on a broad spectrum of microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 279, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, N.M.; Rogers, N.J.; Apte, S.C.; Batley, G.E.; Gadd, G.E.; Casey, P.S. Comparative toxicity of nanoparticulate ZnO, bulk ZnO, and ZnCl2 to a freshwater microaga (Pseudokirchneriella subcapotata): The importance of particle solubility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8484–8490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Kelf, T.A.; Sanchez, W.H.; Roberts, M.S.; Ricka, J.; Frenz, M.; Zvyagin, A.V. Characterization of optical properties of ZnO nanoparticle for quantitative imaging of transdermal transport. Biomed. Opt. Express 2011, 2, 3321–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stankovic, A.; Dimetrijevic, S.; Uskokovic, D. Influence of size scale and morphology on antibacterial properties of ZnO powders hydrothermally synthesized using different surface stabilizing agents. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmavathy, N.; Vijayaraghavan, R. Enhanced bioactivity of ZnO nanoparticles—An antimicrobial study. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2008, 9, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emami-Karvani, Z.; Chehrazi, P. Antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticle on gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2011, 5, 1368–1373. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, K.M.; Ferris, K.; Bell, J.; Wingett, D.G.; Hanley, C.; Punnoose, A. Selective toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles to procaryotic and eukaryotic systems. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 213902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atmaca, S.; Gul, K.; Cicek, R. The effect of zinc on microbial growth. J. Med. Sci. 1998, 28, 595–597. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Zhang, W.; Qiao, Y.; Jiang, X.; Liu, X.; Ding, C. Antibacterial activity and increased bone marrow stem cell functions of Zn-incorporated TiO2 coatings on titanium. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 904–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; He, Y.; Irwin, P.L.; Jin, T.; Shi, X. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Campylobacter jejuni. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2325–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, W.; Leitner, D.R.; Zingl, F.G.; Schratter, G.; Prassl, R.; Goessler, W.; Reidl, J.; Schild, S. Antibacterial activity of silver and zinc nanoparticles against Vibrio cholerae and enterotoxic Escherichia coli. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 305, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalal, R.; Goharshadi, E.K.; Abareshi, M.; Moosavi, M. Zno nanofluids: Green synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 121, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, O. Influence of particle size on the antibacterial activity of zinc oxide. Int. J. Inorg. Mater. 2001, 3, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawai, J.; Shoji, S.; Igarashi, H.; Hashimoto, A.; Kokugan, T.; Shimizu, M.; Kojima, H. Hydrogen peroxide as an antibacterial factor in zinc oxide powder slurry. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1998, 86, 521–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ding, Y.; Povey, M.; York, D. ZnO nanofluids—A potential antibacterial agent. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2008, 18, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghupathi, K.R.; Koodali, R.T.; Manna, A.C. Size-dependent bacterial growth inhibition and mechanism of antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Langmuir 2011, 27, 4020–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Povey, M.; York, D. Investigation into the antibacterial behaviour of suspensions of ZnO nanoparticles (ZnO nanofluids). J. Nanopart. Res. 2007, 9, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawai, J.; Kawada, E.; Kanou, F.; Igarashi, H.; Hashimoto, A.; Kokugan, T.; Shimizu, M. Detection of active oxygen generated from ceramic powders having antibacterial activity. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 1996, 29, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premanathan, M.; Karthikeyan, K.; Jeyasubramanian, K.; Manivannan, G. Selective toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles toward gram-positive bacteria and cancer cells by apoptosis through lipid peroxidation. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2011, 7, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhu, L.; Lin, D. Toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles to Escherichia coli: Mechanism and the influence of medium component. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1977–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Zhang, J.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Ding, F.; Li, L.; Sun, Z. Role of the dissolved zinc ion and reactive oxygen species in cytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 199, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hainlaan, M.; Ivask, A.; Blinova, I.; Dubourguier, H.-C.; Kahru, A. Toxicity of nanosized and bulk ZnO, CuO and TiO2 to bacteria Vibrio fischeri and crustaceans Daphnia magna and Thamnocephalus platyurus. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevinc, B.A.; Hanley, L. Antibacterial activity of dental composites containing zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 94, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Pasquet, J.; Chevalier, Y.; Pelletier, J.; Couval, E.; Bouvier, D.; Bolzinger, M.-A. The contribution of zinc ions to the antimicrobial activity of zinc oxide. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 457, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasemets, K.; Ivask, A.; Dubourguier, H.-C.; Kahru, A. Toxicity of nanoparticles of ZnO, CuO and TiO2 to yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Toxicol. In Vitro 2009, 23, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Mashayekhi, H.; Xing, B. Bacterial toxicity comparison between nano- and micro-scaled oxide particles. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoimenov, P.K.; Klinger, R.L.; Marchinm, G.L.; Klabunde, K.J. Metal oxide nanoparticles as bactericidal agents. Langmuir 2002, 18, 6679–6686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Visurraga, J.; Gutierrez, C.; von Plessing, C.; Garcia, A. Metal nanostructures as antibacterial agents. In Science against Microbial Pathogens: Communicating Current Research and Technology Advances; Mendez-Vilas, A., Ed.; Formatex: Badajoz, Spain, 2011; pp. 210–218. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, V.; Shukla, R.K.; Saxena, N.; Parmar, D.; Das, M.; Dhawan, A. DNA damaging potential of zinc oxide nanoparticles in human epidermal cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 185, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, C.; Layne, J.; Punnoose, A.; Reddy, K.M.; Coombs, I.; Coombs, A.; Feris, K.; Wingett, D. Preferential killing of cancer cells and activated human T cells using ZnO nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 295103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicentini, D.S.; Smania, A., Jr.; Laranjeira, M.C.M. Chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) films containing ZnO nanoparticles and plasticizers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2010, 30, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samzadeh-Kermani, A.; Miri, S. Synthesis, characterization and bacrerial property of chitosan-graft-polyaniline/montmorillonite/ZnO nanocomposite. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 32, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karahaliloglu, Z.; Kilicay, E.; Denkbas, E.B. Antibacterial chitosan/silk sericin 3D porous scaffolds as a wound dressing material. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Mao, S.S. Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: Synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2891–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagi, T.; Kamei, M.; Mitsuhashi, T.; Ishigaki, T.; Yamazaki, A. Charge separation at the rutile/anatase interface: A dominant factor of photocatalytic activity. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 390, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Taya, M. Enhancement of phage inactivation using photocatalytic titanium dioxide particles with different crystalline structures. Biochem. Eng. J. 2006, 28, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.R.; Kaewgun, S.; Lee, B.I.; Tzeng, T.-R.J. The antibacterial effects of biphasic brookite-anatase titanium dioxide nanoparticles on multiple-drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2008, 4, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, H.A.; Ditta, I.B.; Varghese, S.; Steele, A. Photocatalytic disinfection using titanium dioxide: Spectrum and mechanism of antimicrobial activity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 90, 1847–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujishima, A.; Zhang, X. Titanium dioxide photocatalysis: Present situation and future approaches. C. R. Chim. 2006, 9, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Iwase, T.; Horie, J.; Morioka, T. Mode of photocatalytic bactericidal action of powdered semiconductor TiO2 on mutans streptococci. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 1992, 14, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Guo, J.; Qu, J.; Hu, X. Photocatalytic degradation of pathogenic bacteria with AgI/TiO2 under visible light irradiation. Langmuir 2007, 23, 4982–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambala, V.S.; Naidu, R. Disinfection studies on TiO2 thin films prepared by a sol-gel method. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2009, 5, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Maness, P.-C.; Blake, D.M.; Wolfrum, E.J.; Smolinski, S.L.; Jacoby, W.A. Bactericidal mode of titanium dioxide photocatalysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2000, 130, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amezaga-Madrid, P.; Nevarez-Moorillon, G.V.; Orrantia-Borunda, E.; Miki-Yoshida, M. Photoinduced bactericidal activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa by TiO2 based thin films. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2002, 211, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amezaga-Madrid, P.; Silveyra-Morales, R.; Cordoba-Fierro, L.; Nevarez-Moorillon, G.V.; Miki-Yoshida, M.; Orrantia-Borunda, E.; Solis, F.J. TEM evidence of ultrastructural alteration on Pseudomonas aeruginosa by photocatalytic TiO2 thin films. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2003, 70, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maness, P.-C.; Smolinski, S.L.; Blake, D.M.; Huang, Z.; Wolfrum, E.J.; Jacoby, W.A. Bactericidal activity of photocatalytic TiO2 reaction: Toward an understanding of its killing mechanism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 4094–4098. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salih, F.M. Enhancement of solar inactivation of Escherichia coli by titanium dioxide photocatalytic oxidation. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 92, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, Y.; Sunada, K.; Iyoda, T.; Hashimoto, K.; Fujishima, A. Photocatalytic bactericidal effect of TiO2 thin films: Dynamic view of the active oxygen species responsible for the effect. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 1997, 106, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillard, C.; Bui, T.-H.; Felix, C.; Moules, V.; Lina, B.; Lejeune, P. Microbiological disinfection of water and air by photocatalysis. C. R. Chim. 2008, 11, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Chakraborty, A.; Mukherjee, A. Cytotoxic, genotoxic and the hemolytic effect of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles on human erythrocyte and lymphocyte cells in vitro. J. Appl.Toxicol. 2013, 33, 1097–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saquib, Q.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Abou-Tarboush, F.M.; Azam, A.; Musarrat, J. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induced cytotoxicity, oxidative stress and DNA damage in human amnion epithelial (wish) cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2012, 26, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kongseng, S.; Yoovathaworn, K.; Wongprasert, K.; Chunhabundit, R.; Sukwong, P.; Pissuwan, D. Cytotoxic and inflammatory response of tio2 nanoparticles on human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2016, 36, 1364–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Eltgroth, M.L.; LaTempa, T.J.; Grimes, C.A.; Desai, T.A. The effect of TiO2 nanotubes on endothelial function and smooth muscle proliferation. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 1268–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brammer, K.S.; Oh, S.; Gallager, J.O.; Jin, S. Enhanced cellular mobility guided by TiO2 nanotube surfaces. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakumar, R.; Ramachandran, R.; Divyarani, V.V.; Chennazhi, K.P.; Tamura, H.; Nair, S.V. Fabrication of chitin/chitosan/nano TiO2-composite scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 48, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, C.H.; Choi, Y.C.; Choi, J.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Cho, Y.W. A bilayer composite composed of TiO2-incorporated electrospun chitosan membrane and human extracellular matrix sheet as a wound dressing. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2015, 26, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, J.A.; Maddux, B.L.S.; Hutchison, J.E. Toward greener nanosynthesis. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2228–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzello, L.; Pompa, P.P. Nanosilver-based antibacterial drugs and devices: Mechanisms, methodological: Drawbacks and guidelines. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 1501–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.H.; Oh, H.C.; Noh, H.S.; Ji, J.H.; Kim, S.S. Metal nanoparticle generation using a small ceramic heater with a local heating area. J. Aerosol Sci. 2006, 37, 1662–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, T.; Iryo, K.; Watanabe, N.; Tsuji, M. Preparation of silver nanoparticles by laser ablation in solution: Influence of laser wavelength on particle size. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 202, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, M.; Ouyang, J.; Li, X.; Xing, M.M.Q. Nanosilver particles in medical applications: Synthesis, performance, and toxicity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 2399–2407. [Google Scholar]
- Evanoff, D.D., Jr.; Chumanov, G. Synthesis and optical properties of silver nanoparticles and arrays. ChemPhysChem 2005, 6, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyatenko, A.; Yamaguchi, M.; Suzuki, M. Synthesis of spherical silver nanoparticles with controllable sizes in aqueous solutions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 7910–7917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Andujar, C.; Tung, L.D.; Thanh, N.T.K. Synthetic of nanoparticles for biomedical applications. R. Soc. Chem. Annu. Rep. A 2010, 106, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K. A new silver dressing for wound with delayed healing. Wound UK 2006, 2, 70–78. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, R.R.; Stringer, S.J.; Argawal, G.; Johnes, S.E.; Stone, M.O. Biomimetic synthesis and patterning of silver nanoparticles. Nat. Mater. 2002, 1, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anisha, B.S.; Biswas, R.; Chennazhi, K.P.; Jayakumar, R. Chitosan-hyaluronic acid/nano silver composite sponges for drugs resistant bacteria infected diabetic wounds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sintubin, L.; de Windt, W.; Dick, J.; Mast, J.; van der Ha, D.; Verstraete, W.; Boon, N. Lactic acid bacteria as reducing and capping agent for the fast and efficient production of silver nanoparticles. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Situbin, L.; Verstraete, W.; Boon, N. Biologically produced nanosilver: Current state and future perspectives. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 2422–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, S.S.; Ahmad, A.; Sastry, M. Gerenium leaf assisted biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles. Biotechnol. Prog. 2003, 19, 1627–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.A.; Abyanch, M.K.; Gosavi, S.W.; Kulkarni, S.K.; Pasricha, R.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, M.I. Nitrate reductase-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles from AgNO3. Biotechonol. Lett. 2006, 29, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, B.; Garmaroudi, F.S.; Hashemi, M.; Nezhad, H.R.; Nasrollahi, A.; Ardalan, S.; Ardalan, S. Comparison of the anti-bacterial activity on the nanosilver shapes: Nanoparticles, nanorods and nanoplates. Adv. Powder Technol. 2012, 23, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Tak, Y.K.; Song, J.M. Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotiriou, G.A.; Pratsinis, S.E. Antibacterial activity of nanosilver ions and particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morones, J.R.; Elechiguerra, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, J.B.; Ramirez, J.T.; Yacaman, M.J. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, O.; Hu, Z. Size dependent and reactive oxygen species related nanosilver toxicity to nitrifying bacteria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4583–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sondi, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: A case study on E. coli as a model for gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Kuk, E.; Yu, K.N.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.K.; Park, Y.H.; Hwang, C.-Y.; et al. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2007, 3, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, Y.; Yoshikara, K.; Kunisaki, S.-I.; Tsuchido, T. Mode of bactericidal action of silver zeolite and its comparison with that of silver nitrate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4278–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, S.; Bera, T.; Roy, A.; Singh, G.; Ramachanrarao, P.; Dash, D. Characterization of enhanced antibacterial effects of novel silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 225103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kone, B.C.; Kaleta, M.; Gullans, S.R. Silver ion (Ag+)-induced increases in cell membrane K+ and Na+ permeability in the renal proximal tubule: Reversal by thiol reagents. J. Membr. Biol. 1988, 102, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, C.; Hussain, S.M.; Shrand, A.M.; Braydich-Stolle, L.K.; Hess, K.L.; Jones, R.L.; Schlager, J.J. Unique cellular interaction of silver nanobarticles: Size-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 13608–13619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsin, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-F.; Huang, S.; Shih, T.-S.; Lai, P.-S.; Chueh, P.J. The apoptotic effect of nanosilver is mediated by a ROS- and JNK-dependent mechanism involving the mitochondrial pathway in NIH3T3 cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 179, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, J.S.; Cho, H.S.; Rha, D.S.; Kim, J.M.; Park, J.D.; Choi, B.S.; Lim, R.; Chang, H.K.; Chung, Y.H.; et al. Twenty-eight-day oral toxicity, genotoxicity, and gender-related tissue distribution of silver nanoparticles in sprague-dawley rats. Inhal. Toxicol. 2008, 20, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.J.; Nallathamby, P.D.; Browning, L.M.; Osgood, C.J.; Xu, X.-H.N. In vivo imaging of transport and biocompatibility of single silver nanoparticles in early development of zebrafish embryos. ACS Nano 2007, 1, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.H.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, S.S.; Yoon, J.-U.; Park, J.D.; Choi, B.S.; Chung, Y.H.; Kwon, I.H.; Jeong, J.; Han, B.S.; et al. Twenty-eight-day inhalation toxicity study of silver nanoparticles in Sprague-Dawley rats. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19, 857–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiVicenzo, G.D.; Giordano, C.J.; Schriever, L.S. Biologic monitoring of workers exposed to silver. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 1985, 56, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.B.; Lim, J.J.; Shameli, K.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Tay, M.Y. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles in chitosan, gelatin and chitosan/gelatin bionanocomposites by a chemical reducing agent and their characterization. Molecules 2011, 16, 7237–7248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, W.-E.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun nanofibers as a platform for multifunctional, hierarchically organized nanocomposite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1804–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelgawad, A.M.; Hudson, S.M.; Rojas, O.J. Antimicrobial wound dressing nanofiber mats from multicomponent (chitosan/siver-NPs/polyvinyl alcohol) systems. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 100, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, S.-Y.; Wu, J.; Moochhala, S.M.; Tan, M.-H.; Lu, J. Development of a chitosan-based wound dressing with improved hemostatic and antimicrobial properties. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4323–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Gao, W.; Gu, H.Y. Construction, application and biosafety of silver nanocrystalline chitosan wound dressing. Burns 2007, 34, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celebi, H.; Gurbuz, M.; Koparal, S.; Dogan, A. Development of antibacterial electrospun chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers containing silver ion-incorporated hap nanoparticles. Compos. Interfaces 2013, 20, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebeish, A.A.; Ramadan, M.A.; Montaser, A.S.; Farag, A.M. Preparation, characterization and antibacterial activity of chitosan-g-poly acrylonitrile/silver nanocomposite. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 68, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, V.; Yallapu, M.M.; Sreedhar, B.; Bajpai, S.K. Fabrication, characterizatrion of chitosan/nanosilver film and its potential antibacterial application. J. Biomater. Sci. 2009, 20, 2129–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.-H.; Deng, J.-C.; Deng, H.-R.; Liu, Z.-L.; Li, X.-L. Preparation, characterization and antimicrobial activities of chitosan/Ag/ZnO blend films. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 160, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zahry, M.R.; Mahmoud, A.; Refaar, I.H.; Mohamed, H.A.; Bohlmann, H.; Lendl, B. Antibacterial effect of various shapes of silver nanoparticles monitored by sers. Talanta 2015, 138, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi-Polyachenko, N.; Jacob, R.; Day, C.; Kuthirummal, N. Chitosan wound dressing with hexagonal silver nanoparticles for hyperthermia and enhanced delivery of small molecules. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 142, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Gutierrez, F.; Olive, P.L.; Banuelos, A.; Orrantia, E.; Nino, N.; Sanchez, E.M.; Ruiz, F.; Bach, H.; Av-Gay, Y. Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of antimicrobial and cytotoxic effect of silver and titanium nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Sierra, J.F.; Ruiz, F.; Pena, D.C.C.; Martinez-Gutierrez, F.; Martinez, A.E.; de Jesús Pozos Guillén, A.; Tapia-Perez, H.; Castanon, G.M. The antimicrobial sensitivity of Streptococcus mutans to nanoparticles of silver, zinc oxide, and gold. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2008, 4, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besinis, A.; Peralta, T.D.; Handy, R.D. The antibacterial effects of silver, titanium dioxide and silica dioxide nanoparticles compared to the dental disinfectant chlorhexidine on Streptococcus mutans using a suite of bioassays. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.-C.; Lien, C.-C.; Yeh, H.-J.; Yu, C.-M.; Hsu, S.-H. Bacterial cellulose and bacterial cellulose-chitosan membranes for wound dressing applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caetano, G.F.; Frade, M.A.C.; Andrade, T.A.M.; Leite, M.N.; Bueno, C.Z.; Moraes, A.M.; Ribeiro-Paes, J.T. Chitosan-alginate membranes accelerate wound healing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2015, 103, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Li, T.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Gao, C.; Zhang, S.; Xie, E. Graphene-based composite materials beneficial to wound healing. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 2978–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekaran, G.; Han, H.-K.; Kim, G.-J.; Shin, H.-J. Antimicrobial activity of delaminated aminopropyl functionalized magnesium phyllosilicates. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 53, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Authors | Materials | Products | Remarkable Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kumar et al. (2012) [38] | Chitosan + ZnO NPs | Bandages |
|
| Vicentini et al. (2009) [75] | Chitosan + ZnO NPs + poly(vinyl alcohol) + Tween 80 | Films |
|
| Samzadeh-Kermani and Miri (2014) [76] | Chitosan + polyaniline + montmorillonite + ZnO NPs | Films |
|
| Petkova et al. (2014) [12] | Chitosan + ZnO NPs | Textiles |
|
| Karahaliloglu et al. (2016) [77] | Chitosan + ZnO NPs + silk sericin | Scaffolds |
|
| Jayakumar et al. (2011) [99] | Chitin/chitosan + TiO2 NPs | Scaffolds |
|
| Archana et al. (2013) [27] | Chitosan + pectin + TiO2 NPs | Films |
|
| Woo et al. (2015) [100] | Chitosan + TiO2 NPs | Bilayer composite |
|
| Hang et al. (2010) [5] | Chitosan + poly(vinyl alcohol) + Ag NPs | Fiber mats |
|
| Abdelgawad et al. (2012) [134] | Chitosan + poly(vinyl alcohol) + Ag NPs | Fiber mats |
|
| Ong et al. (2008) [135] | Chitosan + polyphosphate + Ag NPs | Films |
|
| Lu et al. (2008) [136] | Chitosan + Ag NPs | Films |
|
| Anisha et al. (2013) [111] | Chitosan + poly(vinyl alcohol) + Ag NPs | Sponges |
|
| Celebi et al. (2013) [137] | Chitosan + poly(vinyl alcohol) + hydroxyapatite | Fiber mats |
|
| Hebeish et al. (2014) [138] | Chitosan + poly acrylonitrile + Ag NPs | Graft nanocomposite |
|
| Thomas et al. (2012) [139] | Chitosan + Ag NPs | Films |
|
| Li et al. (2010) [140] | Chitosan + Ag NPs + ZnO NPs | Films |
|
| Levi-Polyachenko et al. (2016) [142] | Chitosan + Ag NPs | Films |
|
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bui, V.K.H.; Park, D.; Lee, Y.-C. Chitosan Combined with ZnO, TiO2 and Ag Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Wound Healing Applications: A Mini Review of the Research Trends. Polymers 2017, 9, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9010021
Bui VKH, Park D, Lee Y-C. Chitosan Combined with ZnO, TiO2 and Ag Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Wound Healing Applications: A Mini Review of the Research Trends. Polymers. 2017; 9(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleBui, Vu Khac Hoang, Duckshin Park, and Young-Chul Lee. 2017. "Chitosan Combined with ZnO, TiO2 and Ag Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Wound Healing Applications: A Mini Review of the Research Trends" Polymers 9, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9010021
APA StyleBui, V. K. H., Park, D., & Lee, Y. -C. (2017). Chitosan Combined with ZnO, TiO2 and Ag Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Wound Healing Applications: A Mini Review of the Research Trends. Polymers, 9(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9010021