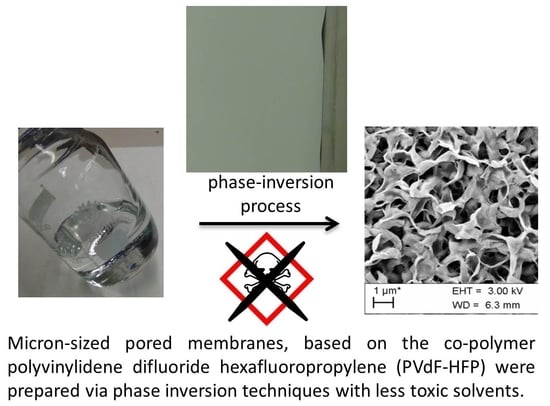
Micron-Sized Pored Membranes Based on Polyvinylidene Difluoride Hexafluoropropylene Prepared by Phase Inversion Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hansen Solubility
3.2. Preparation via Phase Inversion Techniques
3.3. SEM Analysis
3.4. Membrane Characteristics: Membrane Characteristics and Mechanical Strength
3.5. Membrane Characteristics: Membrane–Solvent Interactions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Xie, J. Template-Assisted Fabrication of Thin-Film Composite Forward-Osmosis Membrane with Controllable Internal Concentration Polarization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 5327–5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xie, J. Development of electro-active forward osmosis membranes to remove phenolic compounds and reject salts. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2017, 3, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Du, B.; Nasaruddin, R.R.; Chen, T.; Xie, J. Golden Carbon Nanotube Membrane for Continuous Flow Catalysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 2999–3007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Fu, L.; Wu, Y. A porous gel-type composite membrane reinforced by nonwoven: Promising polymer electrolyte with high performance for sodium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 224, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, N.; Mishra, K.; Hashmi, S.A. Optimization of porous polymer electrolyte for quasi-solid-state electrical double layer supercapacitor. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 235, 570–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, W.; He, X.; Wang, L.; Jiang, C.; Wan, C. Preparation of PVDF–HFP microporous membrane for Li-ion batteries by phase inversion. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 272, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Osinska, M.; Walkowiak, M.; Zalewska, A.; Jesionowski, T. Study of the role of ceramic filler in composite gel electrolytes based on microporous polymer membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 326, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.; Zhang, Z. Battery Separators. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4419–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarascon, J.M.; Gozdz, A.S.; Schmutz, C.; Shokoohi, F.; Warren, P.C. Performance of Bellcore’s plastic rechargeable Li-ion batteries. Solid State Ion. 1996, 86, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, A.; Schulz, M.; Hanemann, T. Gel Electrolytes based on Ionic Liquids for Advanced Lithium Polymer Batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 89, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozdz, A.S.; Schmutz, C.N.; Tarascon, J.-M. Rechargeable Lithium Intercalation Battery with Hybrid Polymeric Electrolyte. U.S. Patent 5296318 A, 22 March 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, H.; Huang, J.; Xu, J.J.; Khalfan, A.; Greenbaum, S.G. Li ion conducting polymer gel electrolytes based on ionic liquid/PVDF-HFP blends. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, A1048–A1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, T.-H.; Chen, L.-W. Pore formation mechanism of membranes from phase inversion process. Desalination 1995, 103, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, A.M.; Renganathan, N.G.; Gopukumar, S.; Teeters, D. Cycling behavior of poly(vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoro propylene) (PVdF-HFP) membranes prepared by phase inversion method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2004, 85, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Jeong, S.K.; Nahm, K.S.; Stephan, A.M. Electrochemical studies on poly(vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoropropylene) membranes prepared by phase inversion method. Eur.Polym. J. 2007, 43, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravindan, V.; Vickraman, P.; Madhavi, S.; Sivashanmugam, A.; Thirunakaran, R.; Gopukumar, S. Improved performance of polyvinylidenefluoride-hexafluoropropylene based nanocomposite polymer membranes containing lithium bis(oxalato)borate by phase inversion for lithium batteries. Solid State Sci. 2011, 13, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Yang, S.; Fan, L. Preparation of thermal stable porous polyimide membranes by phase inversion process for lithium-ion battery. Polymer 2013, 54, 6339–6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravindan, V.; Vickraman, P.; Sivashanmugam, A.; Thirunakaran, R.; Gopukumar, S. Comparison among the performance of LiBOB, LiDFOB and LiFAP impregnated polyvinylidenefluoride-hexafluoropropylene nanocomposite membranes by phase inversion for lithium batteries. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2013, 13, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.; Choi, Y.; Chung, K.Y.; Park, J.H. Controlled pore evolution during phase inversion from the combinatorial non-solvent approach: Application to battery separators. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 9496–9501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.S.; Noh, J.H.; Hwang, C.G.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.Y. Effect of Solvent-Nonsolvent Miscibility on Morphology and Electrochemical Performance of SiO2/PVdF-HFP-Based Composite Separator Membranes for Safer Lithium-Ion Batteries. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2010, 211, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Zhu, H.-J.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.-M.; Yang, H. Study of PVDF-HFP/PMMA blended micro-porous gel polymer electrolyte incorporating ionic liquid [BMIM]BF4 for Lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 133, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Guo, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, B. Performance of PVDF-HFP-based gel polymer electrolytes with different pore forming agents. Iran. Polym. J. 2012, 21, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jang, K.-S.; Choi, H.-D.; Choi, S.-H.; Kwon, S.-J.; Kim, I.-D.; Lim, J.A.; Hong, J.-M. Porous Polyimide Membranes Prepared by Wet Phase Inversion for Use in Low Dielectric Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 8698–8707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, C.M. Hansen Solubility Parameters, a User’s Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Stephan, A.M. Review on gel polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Eur. Polym. J. 2006, 42, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Yanilmaz, M.; Toprakci, O.; Fu, K.; Zhang, X. A review of recent developments in membrane separators for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 3857–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X. Separator technologies for lithium-ion batteries. J. Sol. State Electrochem. 2010, 15, 649–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djian, D.; Alloin, F.; Martinet, S.; Lignier, H.; Sanchez, J.Y. Lithium-ion batteries with high charge rate capacity: Influence of the porous separator. J. Power Sources 2007, 172, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, S.; Yamamoto, H. HSPiP Software, 5th ed. Steven Abbott TCNF Ltd.: UK, 2015. Available online: https://www.hansen-solubility.com/downloads.php(accessed on 22 February 2013).
- Hofmann, A.; Kaufmann, C.; Müller, M.; Hanemann, T. Interaction of High Flash Point Electrolytes and PE-Based Separators for Li-Ion Batteries. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 20258–20276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Fitting Procedure 1 | Fit Accuracy | Wrong Correlated Solvents (s) and Non-Solvents (ns) 2 | Sphere 1 | Sphere 2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δD | δP | δH | R0 | δD | δP | δH | R0 | |||
| A-1 | 0.972 | 1 s out, 1 ns in | 15.7 | 8.8 | 7.1 | 5.6 | 17.9 | 15.8 | 8.3 | 6.5 |
| A-2 | 0.972 | 1 s out, 1 ns in | 18.1 | 16.1 | 9.2 | 6.9 | 14.9 | 9.1 | 7.1 | 6.2 |
| A-3 | 0.972 | 1 s out, 1 ns in | 15.4 | 0.6 | 8.2 | 4.5 | 15.4 | 13.2 | 8.4 | 8.5 |
| B | --- | 4 s out | 15.9 | 7.7 | 7.3 | 4.8 | 17.2 | 14.6 | 7.1 | 4.4 |
| Parameter | M-1 | M-2 |
|---|---|---|
| Gurley related to a membrane thickness of 25 µm (/100 cm3) (n = 5) according to (permeability∙25)/(membrane thickness [in µm]) | 114 ± 7 | 131 ± 26 |
| typical membrane thickness (µm) | 80–110 | 80–120 |
| typical membrane weight (mg/cm2) (n = 6) | 95 ± 2 | 93 ± 2 |
| solvent uptake (n-decane) related to membrane thickness of 25 µm (µL/cm2) (n = 3) | 1.74 ± 0.09 | 1.51 ± 0.03 |
| solvent uptake (n-decane) (% related to membrane weight) (n = 3) | 88 ± 6 | 69 ± 2 |
| porosity (P) (n = 6) based on solvent uptake | 70 ± 2 | 56 ± 2 |
| pore size distribution (SEM) | inhomogeneous | inhomogeneous |
| pore size (maximum length; SEM) | <18 µm | <1.4 µm |
| Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) surface area (m2/g) | 5.73 | 15.80 |
| Emod/GPa (n = 3) | 0.16 ± 0.06 | 0.25 ± 0.08 |
| σy/MPa (n = 3) | 3.5 ± 0.1 | 5.1 ± 0.3 |
| σmax/MPa (n = 3) | 4.35 ± 0.09 | 5.90 ± 0.02 |
| εmax | 1.7 ± 0.2 | 1.0 ± 0.2 |
| Parameter | M-1 | M-2 |
|---|---|---|
| McMullin number; electrolyte: EC/DMC(a) 1:1 wt % + 1 M LiPF6 | 3.7 | 1.9 |
| ionic conductivity (mS·cm−1) (n = 5)(b) | 3.2 ± 0.2 | 6.0 ± 0.2 |
| tortuosity | 1.6 | 1.0 |
| contact angle immediately after take drop (°) (top) | 27 ± 2 (n = 9) | 48 ± 1 (n = 37) |
| contact angle immediately after take drop (°) (bottom) | 41 ± 1 (n = 9) | 49 ± 2 (n = 30) |
| time up to contact angle of 20° (s) (top) | <2 (n = 17) | 104 ± 6 (n = 37) |
| time up to contact angle of 20° (s) (bottom) | 18 ± 2 (n = 17) | 106 ± 7 (n = 30) |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hofmann, A.; Thißen, E.; Migeot, M.; Bohn, N.; Dietrich, S.; Hanemann, T. Micron-Sized Pored Membranes Based on Polyvinylidene Difluoride Hexafluoropropylene Prepared by Phase Inversion Techniques. Polymers 2017, 9, 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9100489
Hofmann A, Thißen E, Migeot M, Bohn N, Dietrich S, Hanemann T. Micron-Sized Pored Membranes Based on Polyvinylidene Difluoride Hexafluoropropylene Prepared by Phase Inversion Techniques. Polymers. 2017; 9(10):489. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9100489
Chicago/Turabian StyleHofmann, Andreas, Eva Thißen, Matthias Migeot, Nicole Bohn, Stefan Dietrich, and Thomas Hanemann. 2017. "Micron-Sized Pored Membranes Based on Polyvinylidene Difluoride Hexafluoropropylene Prepared by Phase Inversion Techniques" Polymers 9, no. 10: 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9100489
APA StyleHofmann, A., Thißen, E., Migeot, M., Bohn, N., Dietrich, S., & Hanemann, T. (2017). Micron-Sized Pored Membranes Based on Polyvinylidene Difluoride Hexafluoropropylene Prepared by Phase Inversion Techniques. Polymers, 9(10), 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9100489