Matrix Topographical Cue-Mediated Myogenic Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cell Derivatives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Maintenance of Human Embryonic Stem Cells (hESCs)
2.2. Derivation of PDGFRA+ Mesodermal Progenitors from hESCs
2.3. Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) Analysis
2.4. Fabrication of Micropatterned PDMS Substrates
2.5. Surface Characterization by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.6. Preparation of PDMS Substrates for Cell Culture
2.7. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.8. Image Analysis
2.9. RNA Isolation and Quantitative PCR
2.10. Cell Transplantation in NOD/SCID Cardiotoxin Injury Model
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
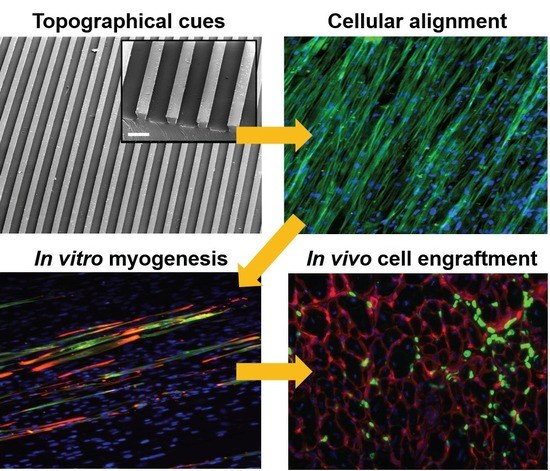
3.1. Substrate Topographical Cue-Mediated Actin Cytoskeletal Organization and Cellular Alignment
3.2. Effect of Matrix Topographical Cue-Mediated Cellular Alignment on In Vitro Myogenesis of hESC-Derived PDGFRA+ Cells
3.3. In Vivo Engraftment of hESC-Derived Myogenic Progenitors
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goudenege, S.; Lebel, C.; Huot, N.B.; Dufour, C.; Fujii, I.; Gekas, J.; Rousseau, J.; Tremblay, J.P. Myoblasts derived from normal hescs and dystrophic hipscs efficiently fuse with existing muscle fibers following transplantation. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 2153–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberi, T.; Bradbury, M.; Dincer, Z.; Panagiotakos, G.; Socci, N.D.; Studer, L. Derivation of engraftable skeletal myoblasts from human embryonic stem cells. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darabi, R.; Arpke, R.W.; Irion, S.; Dimos, J.T.; Grskovic, M.; Kyba, M.; Perlingeiro, R.C. Human ES- and iPS-derived myogenic progenitors restore dystrophin and improve contractility upon transplantation in dystrophic mice. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 10, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darabi, R.; Gehlbach, K.; Bachoo, R.M.; Kamath, S.; Osawa, M.; Kamm, K.E.; Kyba, M.; Perlingeiro, R.C. Functional skeletal muscle regeneration from differentiating embryonic stem cells. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brack, A.S.; Conboy, I.M.; Conboy, M.J.; Shen, J.; Rando, T.A. A temporal switch from notch to wnt signaling in muscle stem cells is necessary for normal adult myogenesis. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 2, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchin, B.; Chen, J.; Barberi, T. Derivation and facs-mediated purification of pax3+/pax7+ skeletal muscle precursors from human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2013, 1, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wigmore, P.M.; Dunglison, G.F. The generation of fiber diversity during myogenesis. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 1998, 42, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wakelam, M.J. The fusion of myoblasts. Biochem. J. 1985, 228, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala, R.; Zhang, C.; Yang, D.; Hwang, Y.; Aung, A.; Shroff, S.S.; Arce, F.T.; Lal, R.; Arya, G.; Varghese, S. Engineering the cell-material interface for controlling stem cell adhesion, migration, and differentiation. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3700–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, N.F.; Li, S. Regulation of the matrix microenvironment for stem cell engineering and regenerative medicine. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 39, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdick, J.A.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G. Engineered microenvironments for controlled stem cell differentiation. Tissue Eng. A 2009, 15, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engler, A.J.; Sen, S.; Sweeney, H.L.; Discher, D.E. Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell 2006, 126, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabra, H.; Hwang, Y.; Lim, H.L.; Kar, M.; Arya, G.; Varghese, S. Biomimetic material-assisted delivery of human embryonic stem cell derivatives for enhanced in vivo survival and engraftment. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 1, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quarta, M.; Brett, J.O.; DiMarco, R.; De Morree, A.; Boutet, S.C.; Chacon, R.; Gibbons, M.C.; Garcia, V.A.; Su, J.; Shrager, J.B.; et al. An artificial niche preserves the quiescence of muscle stem cells and enhances their therapeutic efficacy. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, M.; Vernon Shih, Y.R.; Velez, D.O.; Cabrales, P.; Varghese, S. Poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogels with cell cleavable groups for autonomous cell delivery. Biomaterials 2016, 77, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altomare, L.; Gadegaard, N.; Visai, L.; Tanzi, M.C.; Fare, S. Biodegradable microgrooved polymeric surfaces obtained by photolithography for skeletal muscle cell orientation and myotube development. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1948–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palama, I.E.; D’Amone, S.; Coluccia, A.M.; Gigli, G. Micropatterned polyelectrolyte nanofilms promote alignment and myogenic differentiation of c2c12 cells in standard growth media. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2013, 110, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, K.; Fujita, H.; Nagamori, E. Alignment of skeletal muscle myoblasts and myotubes using linear micropatterned surfaces ground with abrasives. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 103, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, M.T.; Sim, S.; Zhu, X.; Takayama, S. The effect of continuous wavy micropatterns on silicone substrates on the alignment of skeletal muscle myoblasts and myotubes. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 4340–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, A.; Pickett, A.; Shakesheff, K.M. Reconstruction of spatially orientated myotubes in vitro using electrospun, parallel microfibre arrays. Eur. Cell Mater. 2007, 14, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Park, C.B. Synergic effects of nanofiber alignment and electroactivity on myoblast differentiation. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6098–6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, T.; Hauschka, S.D.; Sanders, J.E. Tissue engineering of skeletal muscle using polymer fiber arrays. Tissue Eng. 2003, 9, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, N.F.; Lee, R.J.; Li, S. Engineering of aligned skeletal muscle by micropatterning. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2010, 2, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, P.; Reddy, B., Jr.; Millet, L.; Wei, C.; Zorlutuna, P.; Bao, G.; Bashir, R. Patterning the differentiation of c2c12 skeletal myoblasts. Integr. Biol. (Camb.) 2011, 3, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.S.; Vincent, L.G.; Lee, A.R.; Kretchmer, K.C.; Chirasatitsin, S.; Dobke, M.K.; Engler, A.J. The alignment and fusion assembly of adipose-derived stem cells on mechanically patterned matrices. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6943–6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.; Suk, S.; Shih, Y.R.; Seo, T.; Du, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Varghese, S. Wnt3a promotes myogenesis of human embryonic stem cells and enhances in vivo engraftment. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.; Suk, S.; Lin, S.; Tierney, M.; Du, B.; Seo, T.; Mitchell, A.; Sacco, A.; Varghese, S. Directed in vitro myogenesis of human embryonic stem cells and their in vivo engraftment. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.W.; Hwang, Y.; Brafman, D.; Hagan, T.; Phung, C.; Varghese, S. Engineering cell-material interfaces for long-term expansion of human pluripotent stem cells. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, N.F.; Patel, S.; Thakar, R.G.; Wu, J.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B.; Lee, R.J.; Li, S. Myotube assembly on nanofibrous and micropatterned polymers. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaw, K.C.; Manimaran, M.; Tay, F.E.; Swaminathan, S. Matrigel coated polydimethylsiloxane based microfluidic devices for studying metastatic and non-metastatic cancer cell invasion and migration. Biomed. Microdevices 2007, 9, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubin, H.; Nichol, J.W.; Hutson, C.B.; Bae, H.; Sieminski, A.L.; Cropek, D.M.; Akhyari, P.; Khademhosseini, A. Directed 3d cell alignment and elongation in microengineered hydrogels. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 6941–6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangaj, N.; Kyriakakis, P.; Yang, D.; Chang, C.W.; Arya, G.; Varghese, S. Heparin mimicking polymer promotes myogenic differentiation of muscle progenitor cells. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 3294–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghese, S.; Hwang, N.S.; Ferran, A.; Hillel, A.; Theprungsirikul, P.; Canver, A.C.; Zhang, Z.; Gearhart, J.; Elisseeff, J. Engineering musculoskeletal tissues with human embryonic germ cell derivatives. Stem Cells 2010, 28, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, S.J.; Nahirney, P.C.; Hadjantonakis, A.K.; Baylies, M.K. Nap1-mediated actin remodeling is essential for mammalian myoblast fusion. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 3282–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, W.W.; Wolfram, T.; Goldyn, A.M.; Bruellhoff, K.; Rioja, B.A.; Moller, M.; Spatz, J.P.; Saif, T.A.; Groll, J.; Kemkemer, R. Myoblast morphology and organization on biochemically micro-patterned hydrogel coatings under cyclic mechanical strain. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, N.S.; Varghese, S.; Lee, H.J.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, Z.; Bae, J.; Cheng, L.; Elisseeff, J. In vivo commitment and functional tissue regeneration using human embryonic stem cell-derived mesenchymal cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20641–20646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, Y.; Seo, T.; Hariri, S.; Choi, C.; Varghese, S. Matrix Topographical Cue-Mediated Myogenic Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cell Derivatives. Polymers 2017, 9, 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9110580
Hwang Y, Seo T, Hariri S, Choi C, Varghese S. Matrix Topographical Cue-Mediated Myogenic Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cell Derivatives. Polymers. 2017; 9(11):580. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9110580
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Yongsung, Timothy Seo, Sara Hariri, Chulmin Choi, and Shyni Varghese. 2017. "Matrix Topographical Cue-Mediated Myogenic Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cell Derivatives" Polymers 9, no. 11: 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9110580
APA StyleHwang, Y., Seo, T., Hariri, S., Choi, C., & Varghese, S. (2017). Matrix Topographical Cue-Mediated Myogenic Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cell Derivatives. Polymers, 9(11), 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9110580