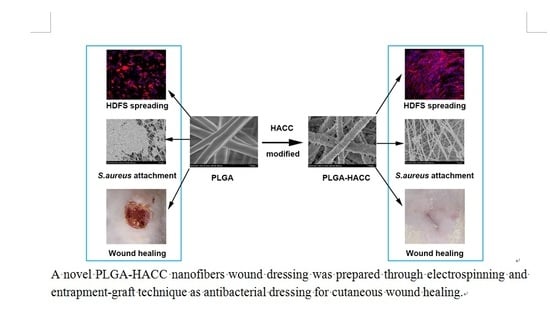
Hydroxypropyltrimethyl Ammonium Chloride Chitosan Functionalized-PLGA Electrospun Fibrous Membranes as Antibacterial Wound Dressing: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PLGA Nanofibrous Membranes
2.3. Preparation of HACC, CS-Conjugated PLGA Nanofibrous Membranes
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Antibacterial Assays
2.6. Cell Attachment and Proliferation
2.7. HDFs Migration Assay
2.8. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.9. Western Blot Analysis
2.10. In Vivo Studies Using a Full-Thickness Excision Wound Healing Mice Model
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physical Characteristics
3.2. Attachment, Spreading and Proliferation of HDFs and HaCaTs
3.3. Cellular Morphology
3.4. Enhanced Regenerative Activities of Skin Cells Cultured on PLGA-HACC In Vitro
3.5. Antibacterial Efficacy of Different Membranes
3.6. In Vivo Wound Healing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boateng, J.S.; Matthews, K.H.; Stevens, H.N.; Eccleston, G.M. Wound healing dressings and drug delivery systems: A review. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boateng, J.; Catanzano, O. Advanced Therapeutic Dressings for Effective Wound Healing—A Review. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 3653–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, L.I.; Dias, A.M.; Carvalho, E.; de Sousa, H.C. Recent advances on the development of wound dressings for diabetic foot ulcer treatment—A review. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 7093–7114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrigo, M.; McArthur, S.L.; Kingshott, P. Electrospun nanofibers as dressings for chronic wound care: Advances, challenges, and future prospects. Macromol. Biosci. 2014, 14, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.; Low, W.L.; Amin, M.C.; Radecka, I.; Raj, P.; Kenward, K. Current trends in the development of wound dressings, biomaterials and devices. Pharm. Pat. Anal. 2013, 2, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Lu, F.; Li, Q.; Zou, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, B.; Liu, J.; Dai, F.; Wu, D.; Lan, G. Accelerated wound-healing capabilities of a dressing fabricated from silkworm cocoon. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 901–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muwaffak, Z.; Goyanes, A.; Clark, V.; Basit, A.W.; Hilton, S.T.; Gaisford, S. Patient-specific 3D scanned and 3D printed antimicrobial polycaprolactone wound dressings. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 527, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninan, N.; Forget, A.; Shastri, V.P.; Voelcker, N.H.; Blencowe, A. Anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory pH-responsive tannic acid-carboxylated agarose composite hydrogels for wound healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 28511–28521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forget, A.; Arya, N.; Randriantsilefisoa, R.; Miessmer, F.; Buck, M.; Ahmadi, V.; Jonas, D.; Blencowe, A.; Shastri, V.P. Nonwoven Carboxylated Agarose-Based Fiber Meshes with Antimicrobial Properties. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 4021–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, S.J.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.M.; Pantarat, N.; Sulistio, A.; Wong, E.H.H.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Lenzo, J.C.; Holden, J.A.; Blencowe, A.; Reynolds, E.C.; et al. Combating multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria with structurally nanoengineered antimicrobial peptide polymers. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miguel, S.P.; Ribeiro, M.P.; Coutinho, P.; Correia, I.J. Electrospun Polycaprolactone/Aloe Vera_Chitosan Nanofibrous Asymmetric Membranes Aimed for Wound Healing Applications. Polymers 2017, 9, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabionet, M.; Yeste, M.; Puig, T.; Ciurana, J. Electrospinning PCL Scaffolds Manufacture for Three-Dimensional Breast Cancer Cell Culture. Polymers 2017, 9, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.H.; Lee, C.Y.; Huang, C.H.; Chen, Y.S.; Chen, K.Y. Novel bilayer wound dressing based on electrospun gelatin/keratin nanofibrous mats for skin wound repair. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 79, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.; Geng, H.; Gong, M.; Ye, J.; Wu, C.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L. Long-acting and broad-spectrum antimicrobial electrospun poly (ε-caprolactone)/gelatin micro/nanofibers for wound dressing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 509, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foraida, Z.I.; Kamaldinov, T.; Nelson, D.A.; Larsen, M.; Castracane, J. Elastin-PLGA hybrid electrospun nanofiber scaffolds for salivary epithelial cell self-organization and polarization. Acta Biomater. 2017, 62, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Jun, Y.; Qin, J.; Lee, S.H. Electrospinning versus microfluidic spinning of functional fibers for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2017, 114, 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhang, R.; Lan, W.; Qin, W. Fabrication of Electrospun Polylactic Acid/Cinnamaldehyde/β-Cyclodextrin Fibers as an Antimicrobial Wound Dressing. Polymers 2017, 9, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutting, K.F.; White, R.J.; Mahoney, P. Wound infection, dressings and pain, is there a relationship in the chronic wound? Int. Wound J. 2013, 10, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, A.; Kumar, N. A new, bioactive, antibacterial-eluting, composite graft for infection-free wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2014, 22, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mockford, K.; O’Grady, H. Prevention of surgical site infections. Surgery (Oxf.) 2017, 35, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buja, A.; Zampieron, A.; Cavalet, S.; Chiffi, D.; Sandonà, P.; Vinelli, A.; Baldovin, T.; Baldo, V. An update review on risk factors and scales for prediction of deep sternal wound infections. Int. Wound J. 2012, 9, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdali, H.; Ajji, A. Preparation of Electrospun Nanocomposite Nanofibers of Polyaniline/Poly(methyl methacrylate) with Amino-Functionalized Graphene. Polymers 2017, 9, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasithevar, M.; Periakaruppan, P.; Muthupandian, S.; Mohan, M. Antibacterial efficacy of silver nanoparticles against multi-drug resistant clinical isolates from post-surgical wound infections. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 107, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, A.; Hang, R.; Chu, P.K. Recent advances in anti-infection surfaces fabricated on biomedical implants by plasma-based technology. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 312, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.J.; Lee, Y.; Phuong, L.T.; Seon, G.M.; Kim, E.; Park, J.C.; Yoon, H.; Park, K.D. Zwitterionic sulfobetaine polymer-immobilized surface by simple tyrosinase-mediated grafting for enhanced antifouling property. Acta Biomater. 2017, 61, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backlund, C.J.; Worley, B.V.; Schoenfisch, M.H. Anti-Biofilm Action of Nitric Oxide-Releasing Alkyl-Modified Poly(amidoamine) Dendrimers against Streptococcus mutans. Acta Biomater. 2015, 29, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Tian, T.; Niu, T.; Wang, P. Molecular characterization of antibiotic resistance in cultivable multidrug-resistant bacteria from livestock manure. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varaprasad, K.; Mohan, Y.M.; Vimala, K.; Mohana Raju, K. Synthesis and characterization of hydrogel-silver nanoparticle-curcumin composites for wound dressing and antibacterial application. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 121, 784–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Lu, F.; Zou, Y.; Liu, J.; Rong, B.; Li, Z.; Dai, F.; Wu, D.; Lan, G. In situ reduction of silver nanoparticles by chitosan-l-glutamic acid/hyaluronic acid: Enhancing antimicrobial and wound-healing activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 173, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velázquez-Velázquez, J.L.; Santos-Flores, A.; Araujo-Meléndez, J.; Sánchez-Sánchez, R.; Velasquillo, C.; González, C.; Martínez-Castañon, G.; Martinez-Gutierrez, F. Anti-biofilm and cytotoxicity activity of impregnated dressings with silver nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 49, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Du, C.; Wang, Z.; Han, X.; Zhang, K.; Liu, L. Reduced cytotoxicity of silver ions to mammalian cells at high concentration due to the formation of silver chloride. Toxicol. In Vitro 2013, 27, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiravova, J.; Tomankova, K.B.; Harvanova, M.; Malina, L.; Malohlava, J.; Luhova, L.; Panacek, A.; Manisova, B.; Kolarova, H. The effect of silver nanoparticles and silver ions on mammalian and plant cells in vitro. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 96, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.X.; Wang, L.; Du, L.; Guo, S.R.; Wang, X.Q.; Tang, T.T. Adjustment of the antibacterial activity and biocompatibility of hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan by varying the degree of substitution of quaternary ammonium. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Ao, H.; Zhang, H.; Qin, L.; Guillaume, O.; Eglin, D.; Richards, R.G.; et al. Anti-infective efficacy, cytocompatibility and biocompatibility of a 3D-printed osteoconductive composite scaffold functionalized with quaternized chitosan. Acta Biomater. 2016, 46, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Peng, Z.; Li, Q.; Xu, X.; Guo, S.; Tang, T. The use of quaternised chitosan-loaded PMMA to inhibit biofilm formation and downregulate the virulence-associated gene expression of antibiotic-resistant staphylococcus. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Ao, H.; Wang, L.; Guo, S.; Tang, T. Quaternised chitosan coating on titanium provides a self-protective surface that prevents bacterial colonisation and implant-associated infections. Rsc Adv. 2015, 5, 54304–54311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ao, H.; Wang, Y.; Lin, W.; Yang, S.; Zhang, S.; Yu, Z.; Tang, T. Cytocompatibility with osteogenic cells and enhanced in vivo anti-infection potential of quaternized chitosan-loaded titania nanotubes. Bone Res. 2016, 4, 16027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, S.B.; Wang, Y.G.; Zhang, S.H.; Yu, Z.F.; Tang, T.T. Bacterial inhibition potential of quaternised chitosan-coated VICRYL absorbable suture: An invitro and invivo study. J. Orthop. Transl. 2017, 8, 49–61. [Google Scholar]
- Mir, M.; Ahmed, N.; Rehman, A.U. Recent applications of PLGA based nanostructures in drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 159, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Z.X.; Zeng, Q.T.; Sun, Z.Z.; Xu, X.X.; Wang, Y.S.; Zheng, W.; Zheng, Y.F. Immobilizing natural macromolecule on PLGA electrospun nanofiber with surface entrapment and entrapment-graft techniques. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 94, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.D.; Sun, Z.Z.; Zhou, M.; Xu, X.X.; Ma, J.Y.; Zheng, W.; Zhou, H.M.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y.F. Electrospun Chitosan-graft-PLGA nanofibres with significantly enhanced hydrophilicity and improved mechanical property. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catanzano, O.; D’Esposito, V.; Formisano, P.; Boateng, J.S.; Quaglia, F. Composite Alginate-Hyaluronan Sponges for the Delivery of Tranexamic Acid in Post-Extractive Alveolar Wounds. J Pharm. Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galzie, Z.; Kinsella, A.R.; Smith, J.A. Fibroblast growth factors and their receptors. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997, 75, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Williams, G.R.; Wu, J.; Lv, Y.; Sun, X.; Wu, H.; Zhu, L.-M. Thermosensitive nanofibers loaded with ciprofloxacin as antibacterial wound dressing materials. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 517, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.Y.; Chang, H.Y.; Lu, J.K.; Huang, Y.C.; Harroun, S.G.; Tseng, Y.T.; Li, Y.J.; Huang, C.C.; Chang, H.T. Self-Assembly of Antimicrobial Peptides on Gold Nanodots: Against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria and Wound-Healing Application. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 25, 7189–7199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Luo, G.; Xia, H.; He, W.; Zhao, J.; Liu, B.; Tan, J.; Zhou, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y. Novel bilayer wound dressing composed of silicone rubber with particular micropores enhanced wound re-epithelialization and contraction. Biomaterials 2015, 40, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Hu, J.; Huang, H.; Han, J.; Hu, H. Study of multi-functional electrospun composite nanofibrous mats for smart wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridley, A.J.; Schwartz, M.A.; Burridge, K.; Burridge, K.; Firtel, R.A.; Ginsberg, M.H.; Borisy, G.; Parsons, J.T.; Horwitz, A.R. Cell migration: Integrating signals from front to back. Science 2003, 302, 1704–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peplow, P.V.; Baxter, G.D. Gene expression and release of growth factors during delayed wound healing: A review of studies in diabetic animals and possible combined laser phototherapy and growth factor treatment to enhance healing. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2012, 30, 617–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, W. Fabrication of PLGA/MWNTs composite electrospun fibrous scaffolds for improved myogenic differentiation of C2C12 cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 123, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babitha, S.; Rachita, L.; Karthikeyan, K.; Shoba, E.; Janani, I.; Poornima, B.; Sai, K.P. Electrospun Protein Nanofibers in Healthcare: A Review. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 523, 52–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Omair, A.M. Synthesis of Antibacterial Silver–Poly(caprolactone)-Methacrylic Acid Graft Copolymer Nanofibers and Their Evaluation as Potential Wound Dressing. Polymers 2015, 7, 1464–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Gao, J.; He, Q.; Wu, J.; Liang, D.; Yang, H.; Chen, R. Enhanced antibacterial and wound healing activities of microporous chitosan-Ag/ZnO composite dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 156 (Suppl. C), 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marambiojones, C.; Hoek, E.M.V. A review of the antibacterial effects of silver nanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environment. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 1531–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inthanon, K.; Saranwong, N.; Wongkham, W.; Wanichapichart, P.; Prakrajang, K.; Suwannakachorn, D.; Yu, L.D. PIII-induced enhancement and inhibition of human cell attachment on chitosan membranes. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 229 (Suppl. C), 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Machado, G.; García-Tuñón, E.; Bell, R.V.; Alini, M.; Saiz, E.; Peroglio, M. Calcium phosphate substrates with emulsion-derived roughness: Processing, characterisation and interaction with human mesenchymal stem cells. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, N.J.; Brown, T.S.; Evans, K.N.; Hawksworth, J.S.; Sean Hussey, M.D.; Tadaki, D.K.; Elster, E.A. Monitoring the healing of combat wounds using Raman spectroscopic mapping. Wound Repair Regen. 2010, 18, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Sample | Fiber Diameter (nm) | Pore Size (um) | Porosity (%) | Average Roughness (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLGA | 325.9 ± 32.5 | 3.3 ± 0.5 | 71.5 ± 5.6 | 0.12 ± 0.09 |
| PLGA-CS | 421.3 ± 38.5 | 2.8 ± 0.7 | 66.8 ± 8.5 | 1.35 ± 0.18 |
| PLGA-HACC | 480.1 ± 41.5 | 2.6 ± 0.6 | 62.9 ± 5.9 | 1.76 ± 0.28 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Han, X.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tang, T. Hydroxypropyltrimethyl Ammonium Chloride Chitosan Functionalized-PLGA Electrospun Fibrous Membranes as Antibacterial Wound Dressing: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. Polymers 2017, 9, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120697
Yang S, Han X, Jia Y, Zhang H, Tang T. Hydroxypropyltrimethyl Ammonium Chloride Chitosan Functionalized-PLGA Electrospun Fibrous Membranes as Antibacterial Wound Dressing: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. Polymers. 2017; 9(12):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120697
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Shengbing, Xiuguo Han, Yuhang Jia, Hongbo Zhang, and Tingting Tang. 2017. "Hydroxypropyltrimethyl Ammonium Chloride Chitosan Functionalized-PLGA Electrospun Fibrous Membranes as Antibacterial Wound Dressing: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation" Polymers 9, no. 12: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120697
APA StyleYang, S., Han, X., Jia, Y., Zhang, H., & Tang, T. (2017). Hydroxypropyltrimethyl Ammonium Chloride Chitosan Functionalized-PLGA Electrospun Fibrous Membranes as Antibacterial Wound Dressing: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. Polymers, 9(12), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120697