Glucose Oxidase-Based Glucose-Sensitive Drug Delivery for Diabetes Treatment
Abstract
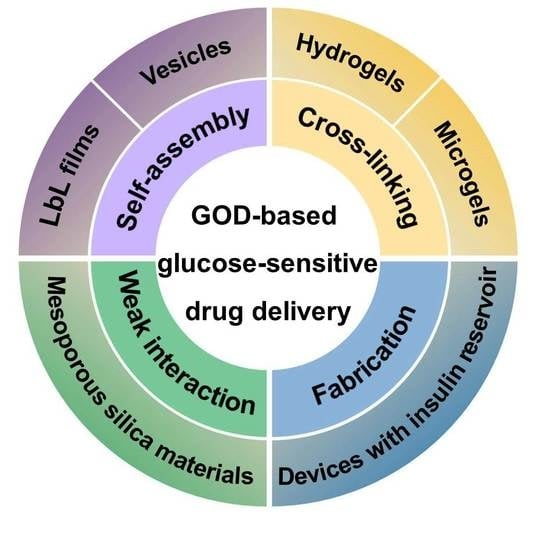
:1. Introduction
2. GOD-Mediated Films and Vesicles
2.1. GOD-Mediated Films
2.2. GOD-Incorporated Vesicles
3. GOD-Mediated Hydrogels and Microgels
3.1. GOD-Incorporated Hydrogels
3.2. GOD-Incorporated Microgels
4. GOD-Mediated Hybrid Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
5. GOD-Mediated Microdevices
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wild, S.; Roglic, G.; Green, A.; Sicree, R.; King, H. Global prevalence of diabetes—Estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Xiao, C.; Wang, L.; Gai, G.; Ding, J. Glucose-sensitive polymer nanoparticles for self-regulated drug delivery. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 7633–7652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Yoshida, K.; Takahashi, S.; Anzai, J. pH- and sugar-sensitive layer-by-layer films and microcapsules for drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Xiao, C.; Ding, J.; Zhuang, X.; Gai, G.; Wang, L.; Chen, X. Competitive binding-accelerated insulin release from a polypeptide nanogel for potential therapy of diabetes. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 3807–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xiao, C.; Ding, J.; He, P.; Tang, Z.; Pang, X.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X. Facile one-pot synthesis of glucose-sensitive nanogel via thiol-ene click chemistry for self-regulated drug delivery. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6535–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Xiao, S.; Bi, F.; Ding, J. Boronic acid as glucose-sensitive agent regulates drug delivery for diabetes treatment. Materials 2017, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.H.; Wang, H.D.; Liang, Y.J. Control of pore size and permeability of a glucose-responsive gating membrane for insulin delivery. J. Control. Release 2004, 97, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Shi, L. Phenylboronic acid-based glucose-responsive polymeric nanoparticles: Synthesis and applications in drug delivery. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 1503–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Ding, J.; Xiao, C.; He, P.; Tang, Z.; Pang, X.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X. Glucose-sensitive polypeptide micelles for self-regulated insulin release at physiological pH. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 12319–12328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Hasebe, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Sato, K.; Anzai, J.I. Layer-by-layer deposited nano- and micro-assemblies for insulin delivery: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 34, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, R.; Della Ventura, B.; De Nicola, S.; Altucci, C.; Velotta, R.; Mita, D.G.; Lepore, M. Glucose sensing by time-resolved fluorescence of sol-gel immobilized glucose oxidase. Sensors 2011, 11, 3483–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Cao, S.; Chen, X.; Liu, S.; Tan, H.; Wu, W.; Li, J. Super long-term glycemic control in diabetic rats by glucose-sensitive lbl films constructed of supramolecular insulin assembly. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 8733–8742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díez, P.; Sánchez, A.; Gamella, M.; Martínez-Ruíz, P.; Aznar, E.; de la Torre, C.; Murguía, J.R.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Villalonga, R.; Pingarrón, J.M. Toward the design of smart delivery systems controlled by integrated enzyme-based biocomputing ensembles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 9116–9123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, H.; He, Q.; Li, Y.; Gu, J.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Shi, J. A glucose-responsive controlled release of insulin system based on enzyme multilayers-coated mesoporous silica particles. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 9459–9461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, L.; Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z. Organization of glucose-responsive systems and their properties. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 7855–7875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traitel, T.; Cohen, Y.; Kost, J. Characterization of glucose-sensitive insulin release systems in simulated in vivo conditions. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Yan, X.; Fei, J.; Wang, A.; Cui, Y.; Li, J. Triggered release of insulin from glucose-sensitive enzyme multilayer shells. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2799–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordijo, C.R.; Shuhendler, A.J.; Wu, X.Y. Glucose-responsive bioinorganic nanohybrid membrane for self-regulated insulin release. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Yan, X.; Duan, L.; Cui, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, J. Glucose-sensitive microcapsules from glutaraldehyde cross-linked hemoglobin and glucose oxidase. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1212–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.; Duan, L.; Li, J. Fabrication of glucose-sensitive protein microcapsules and their applications. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.M.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, J.C. Glucose-sensitivity of liposomes incorporating conjugates of glucose oxidase and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-methacrylic acid-co-octadecylacrylate). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2009, 45, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.J.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, J.C. Alginate beads containing pH-sensitive liposomes and glucose oxidase: Glucose-sensitive release. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2009, 287, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.M.; Kim, J.C. Glucose-triggered release from liposomes incorporating poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-methacrylic acid-co-octadecylacrylate) and glucose oxidase. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2008, 287, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.K.; Amit, K.C.; Chalasani, K.B.; Jain, A.K.; Chourasia, M.K.; Jain, A.; Jain, N.K. Enzyme triggered pH sensitive liposomes for insulin delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2007, 17, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdekhodaie, M.J.; Wu, X.Y. Modeling of a cationic glucose-sensitive membrane with consideration of oxygen limitation. Membr. Sci. 2005, 254, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wu, X.Y. Modulated insulin permeation across a glucose-sensitive polymeric composite membrane. J. Control. Release 2002, 80, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.Y.; Liang, Y.J.; Chen, W.M.; Ju, X.J.; Wang, H.D. Preparation of glucose-sensitive microcapsules with a porous membrane and functional gates. Colloids Surf. B 2004, 37, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.; Li, H.; Lam, K.Y. Modeling the effect of environmental solution pH on the mechanical characteristics of glucose-sensitive hydrogels. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Luo, R.; Birgersson, E.; Lam, K.Y. A chemo-electro-mechanical model for simulation of responsive deformation of glucose-sensitive hydrogels with the effect of enzyme catalysis. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2009, 57, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Luo, R. Modeling and characterization of glucose-sensitive hydrogel: Effect of young’s modulus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3630–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzelczak, M.; Vermant, J.; Furst, E.M.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Directed self-assembly of nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3591–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P. Directed self-assembly: Expectations and achievements. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, A.S.; Paul, K. Self-assembly: A review of scope and applications. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 9, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, W.; Song, X.; Gao, C. Layer-by-layer assembly of microcapsules and their biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 6103–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohl, B.M.; Engbersen, J.F.J. Responsive layer-by-layer materials for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2012, 158, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Takahashi, S.; Anzai, J.I. Layer-by-layer thin films and microcapsules for biosensors and controlled release. Anal. Sci. 2012, 28, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, K.X.; Zhou, H.M. Immobilization of glucose oxidase in alginate-chitosan microcapsules. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 3042–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishigawa, T.; Tagami, Y.; Narita, T.; Oishi, Y. Volume change behavior of poly(l-lysine-alt-terephthalic acid) microcapsules encapsulating glucose oxidase. Chem. Lett. 2012, 41, 1148–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kashiwada, A.; Yamada, K.; Hirata, M. Preparation of grafted ePTFE film targeting application for drug-release device in the body. J. Photopolym. Sci. Technol. 2012, 25, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwa, K.; Sato, K.; Anzai, J. Preparation of multilayer films consisting of glucose oxidase and poly(amidoamine) dendrimer and their stability. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2015, 293, 2713–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, W.; Guo, Z.; Xin, J.; Li, J. Controlled insulin release from glucose-sensitive self-assembled multilayer films based on 21-arm star polymer. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 1759–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchegbu, I.F. Pharmaceutical nanotechnology: Polymeric vesicles for drug and gene delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2006, 3, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Shang, H.; Wu, W.; Li, S.; Lin, Z.; Duan, J.; Xu, L.; Li, J. Glucose-responsive micelles for controlled insulin release based on transformation from amphiphilic to double hydrophilic. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 5457–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, W.; Mo, R.; Di, J.; Subramanian, V.; Gu, X.; Buse, J.B.; Gu, Z. Bio-inspired synthetic nanovesicles for glucose-responsive release of insulin. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 3495–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Y.; DiSanto, R.; Sun, W.; Ranson, D.; Ligler, F.S.; Buse, J.B.; Gu, Z. Microneedle-array patches loaded with hypoxia-sensitive vesicles provide fast glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8260–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napoli, A.; Boerakker, M.J.; Tirelli, N.; Nolte, R.J.M.; Sommerdijk, N.A.J.M.; Hubbell, J.A. Glucose-oxidase based self-destructing polymeric vesicles. Langmuir 2004, 20, 3487–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Yu, J.; Qian, C.; Lu, Y.; Kahkoska, A.R.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X.; Buse, J.B.; Gu, Z. H2O2-responsive vesicles integrated with transcutaneous patches for glucose-mediated insulin delivery. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Qian, C.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Ligler, F.S.; Buse, J.B.; Gu, Z. Hypoxia and H2O2 dual-sensitive vesicles for enhanced glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.; Li, H. Parameter study of glucose-sensitive hydrogel: Effect of immobilized glucose oxidase on diffusion and deformation. Soft Mater 2013, 11, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Luo, R. Modeling the influence of initial geometry on the equilibrium responses of glucose-sensitive hydrogel. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2011, 22, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.R.; Ritter, D.W.; McShane, M.J. A design full of holes: Functional nanofilm-coated microdomains in alginate hydrogels. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 3195–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Fu, M.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C.; Deng, X.; Dhinakar, A.; Huang, W.; Qian, H.; Ge, L. pH-sensitive peptide hydrogel for glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Acta Biomater. 2017, 51, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahani, B.V.; Ghasemzaheh, H.; Afraz, S. Intelligent semi-IPN chitosan-PEG-PAAm hydrogel for closed-loop insulin delivery and kinetic modeling. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 26590–26598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Rubin, J.P.; Marra, K.G. Injectable in situ forming biodegradable chitosan-hyaluronic acid based hydrogels for adipose tissue regeneration. Organogenesis 2010, 6, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Kim, J.C. Β-cyclodextrin grafted polyethyleneimine hydrogel immobilizing hydrophobically modified glucose oxidase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 48, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marek, S.R.; Peppas, N.A. Insulin release dynamics from poly(diethylaminoethyl methacrylate) hydrogel systems. AIChE J. 2013, 59, 3578–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Dang, T.T.; Ma, M.; Tang, B.C.; Cheng, H.; Jiang, S.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Anderson, D.G. Glucose-responsive microgels integrated with enzyme nanocapsules for closed-loop insulin delivery. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6758–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Nair, A.S.; Nair, S.S. Enzyme coated beta-cyclodextrin for effective adsorption and glucose-responsive closed-loop insulin delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, J.; Yu, J.; Ye, Y.; Ranson, D.; Jindal, A.; Gu, Z. Engineering synthetic insulin-secreting cells using hyaluronic acid microgels integrated with glucose-responsive nanoparticles. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2015, 8, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Bai, X.; Jiang, X.; Wu, Q.; Chen, S.; Qu, A.; Huang, J.; Shen, J.; Wu, W. Glucose-responsive microgels based on apo-enzyme recognition. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 2847–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, E.; Scheja, S.; Domanskyi, S.; Gamella, M.; Wormwood, K.L.; Darie, C.C.; Poghossian, A.; Schöning, M.J.; Melman, A.; Privman, V. Glucose-triggered insulin release from Fe3+-cross-linked alginate hydrogel: Experimental study and theoretical modeling. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2017, 1439–7641. [Google Scholar]
- Jivan, F.; Yegappan, R.; Pearce, H.; Carrow, J.K.; McShane, M.; Gaharwar, A.K.; Alge, D.L. Sequential thiol–ene and tetrazine click reactions for the polymerization and functionalization of hydrogel microparticles. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 3516–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douroumis, D.; Onyesom, I.; Maniruzzaman, M.; Mitchell, J. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in nanotechnology. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2013, 33, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nafisi, S.; Schäfer-Korting, M.; Maibach, H.I. Perspectives on percutaneous penetration: Silica nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology 2015, 9, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, S.J.P.; Voelcker, N.H. Silicon–polymer hybrid materials for drug delivery. Future Med. Chem. 2009, 1, 1051–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Qin, X.; Yang, Z.; Qi, H.; Xu, Q.; Diao, G. A novel mesoporous silica nanosphere matrix for the immobilization of proteins and their applications as electrochemical biosensor. Talanta 2013, 104, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roggers, R.; Kanvinde, S.; Boonsith, S.; Oupický, D. The practicality of mesoporous silica nanoparticles as drug delivery devices and progress toward this goal. AAPS PharmSciTech 2014, 15, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Li, L.; Chen, D. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Synthesis, biocompatibility and drug delivery. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1504–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trewyn, B.G.; Giri, S.; Slowing, I.I.; Lin, V.S.Y. Mesoporous silica nanoparticle based controlled release, drug delivery, and biosensor systems. Chem. Commun. 2007, 3236–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Gao, L.; Fei, J.; Dai, L.; Zhao, J.; Li, J. Fabrication of autofluorescent protein coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for biological application. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 12167–12169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhou, L.; Ma, L.; He, Y.; Jia, F. Biomimetic preparation of organic-inorganic composite microcapsules for glucose oxidase immobilization. Chin. J. Catal. 2013, 34, 1627–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Huang, C.; He, C.; Zhu, W.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Y. A glucose-responsive controlled release system using glucose oxidase-gated mesoporous silica nanocontainers. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 9522–9524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aznar, E.; Villalonga, R.; Gimenez, C.; Sancenon, F.; Marcos, M.D.; Martinez-Manez, R.; Diez, P.; Pingarron, J.M.; Amoros, P. Glucose-triggered release using enzyme-gated mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 6391–6393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oroval, M.; Díez, P.; Aznar, E.; Coll, C.; Marcos, M.D.; Sancenón, F.; Villalonga, R.; Martínez-Máñez, R. Self-regulated glucose-sensitive neoglycoenzyme-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for insulin delivery. Chem. A Eur. J. 2017, 23, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordijo, C.R.; Koulajian, K.; Shuhendler, A.J.; Bonifacio, L.D.; Huang, H.Y.; Chiang, S.; Ozin, G.A.; Giacca, A.; Wu, X.Y. Nanotechnology-enabled closed loop insulin delivery device: In vitro and in vivo evaluation of glucose-regulated insulin release for diabetes control. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.K.L.; Chen, J.; Gordijo, C.R.; Chiang, S.; Ivovic, A.; Koulajian, K.; Giacca, A.; Wu, X.Y.; Sun, Y. In vitro and in vivo testing of glucose-responsive insulin-delivery microdevices in diabetic rats. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2533–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
















| Method | Platform | Drug Delivery Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Self-assembly | LbL films | Glucose-induced decomposition of films with insulin permeation |
| Vesicles | Dissociation or destruction of vesicles induced by gluconic acid, H2O2, and hypoxia | |
| Cross-linking | Hydrogels | Structural changes in response to pH changes of microenvironments, or acidic biodegradation of pH-sensitive materials |
| Microgels | ||
| Weak physical interaction | Mesoporous silica materials | Permeation changes of multilayers coated on mesoporous silica materials, or open of pores on mesoporous silica materials due to the glucose-induced uncapping of gated materials |
| Fabrication | Devices with an insulin reservoir | Permeation changes of membrane used for sealing of insulin reservoir |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Bi, F.; Zhao, J.; Gai, G.; Ding, J. Glucose Oxidase-Based Glucose-Sensitive Drug Delivery for Diabetes Treatment. Polymers 2017, 9, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9070255
Zhao L, Wang L, Zhang Y, Xiao S, Bi F, Zhao J, Gai G, Ding J. Glucose Oxidase-Based Glucose-Sensitive Drug Delivery for Diabetes Treatment. Polymers. 2017; 9(7):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9070255
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Li, Liyan Wang, Yuhan Zhang, Shanshan Xiao, Fei Bi, Jianyu Zhao, Guangqing Gai, and Jianxun Ding. 2017. "Glucose Oxidase-Based Glucose-Sensitive Drug Delivery for Diabetes Treatment" Polymers 9, no. 7: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9070255
APA StyleZhao, L., Wang, L., Zhang, Y., Xiao, S., Bi, F., Zhao, J., Gai, G., & Ding, J. (2017). Glucose Oxidase-Based Glucose-Sensitive Drug Delivery for Diabetes Treatment. Polymers, 9(7), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9070255