Theoretical Analysis of Critical Flowable Physical Gel Cross-Linked by Metal Ions and Polyacrylamide-Derivative Associating Polymers Containing Imidazole Groups
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theory of Critical Physical Gelation
2.1. Size of Clusters
2.2. Relaxation Time of Clusters
2.3. Dynamic Mechanical Properties of Solution (Pregel)
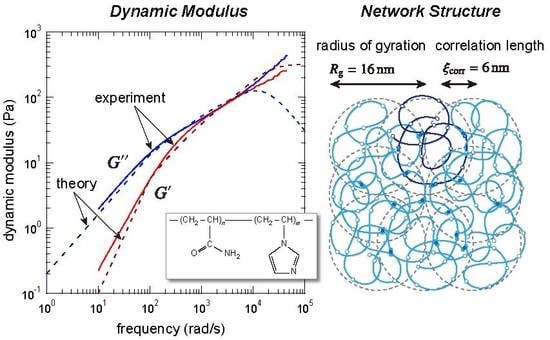
2.4. Dynamic Mechanical Properties at Physical Gel Point
2.5. Fractal Dimension
3. Results
3.1. Viscoelastic Exponent n for the Dynamic Modulus
3.2. Rouse Relaxation Time of a Precursor Chain
3.3. Determination of the Other Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of the Experimental Conditions
4.2. Comparison of the Parameters
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DLS | Dynamic Light Scattering |
| DWS | Diffusing-Wave Spectroscopy |
| PAAmVIm | Poly(AcrylAmide-co-1-VinylImidazole) |
| [Polyacrylamide-derivative associating polymers containing imidazole groups] | |
| PVA | Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) |
| SLS | Static Light Scattering |
| WC | Winter–Chambon |
References
- Flory, P.J. Principles of Polymer Chemistry; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- De Gennes, P.G. Scaling Concepts in Polymer Physics; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein, M.; Colby, R.H. Polym. Phys.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer, D.; Coniglio, A.; Adam, M. Gelation and critical phenomena. Adv. Polym. Sci. 1982, 44, 103–158. [Google Scholar]
- Almdal, K.; Dyre, J.; Hvidt, S.; Kramer, O. Towards a phenomenological definition of the term ‘gel’. Polym. Gels Netw. 1993, 1, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, M.; Semenov, A.N. Thermoreversible gelation in solutions of associating polymers. 2. Linear dynamics. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 1386–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, H.; Indei, T.; Koga, T.; Narita, T. Physical gelation of supramolecular hydrogels cross-linked by metal-ligand interactions: Dynamic light scattering and microrheological studies. Polymer 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holten-Andersen, N.; Harrington, M.J.; Birkedal, H.; Lee, B.P.; Messersmith, P.B.; Lee, K.Y.C.; Waite, J.H. pH-induced metal-ligand cross-links inspired by mussel yield self-healing polymer networks with near-covalent elastic moduli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2651–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fullenkamp, D.E.; He, L.; Barrett, D.G.; Burghardt, W.R.; Messersmith, P.B. Mussel-inspired histidine-based transient network metal coordination hydrogels. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yount, W.C.; Loveless, D.M.; Craig, S.L. Small-molecule dynamics and mechanisms underlying the macroscopic mechanical properties of coordinatively cross-linked polymer networks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 14488–14496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grindy, S.C.; Lenz, M.; Holten-Andersen, N. Engineering elasticity and relaxation time in metal-coordinate cross-linked hydrogels. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 8306–8312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Olsen, B.D. Relaxation Processes in Supramolecular Metallogels Based on Histidine–Nickel Coordination Bonds. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 9163–9175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, H.H.; Chambon, F. Analysis of linear viscoelasticity of a crosslinking polymer at the gel point. J. Rheol. 1986, 30, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Nijenhuis, K.; Winter, H.H. Mechanical properties at the gel point of a crystallizing poly (vinyl chloride) solution. Macromolecules 1989, 22, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.G.; Mallin, D.T.; Chien, J.C.W.; Winter, H.H. Dynamic mechanical measurement of crystallization-induced gelation in thermoplastic elastomeric poly(propylene). Macromolecules 1991, 24, 850–854. [Google Scholar]
- Horst, R.H.; Winter, H.H. Stable critical gels of a crystallizing copolymer of ethene and 1-butene. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsilianis, C.; Iliopoulos, I. Viscoelastic properties of physical gels formed by associative telechelic polyelectrolytes in aqueous media. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 3662–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambon, F.; Winter, H.H. Linear viscoelasticity at the gel point of a crosslinking PDMS with imbalanced stoichiometry. J. Rheol. 1987, 31, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, H.H.; Mours, M. Rheology of polymers near liquid–solid transitions. Adv. Polym. Sci. 1997, 134, 165–234. [Google Scholar]
- Narita, T.; Indei, T. Microrheological study of physical gelation in living polymeric networks. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 4634–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Huang, C.; Weiss, R.A.; Colby, R.H. Viscoelasticity of reversible gelation for ionomers. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.E.; Adolf, D.; Wilcoxon, J.P. Viscoelasticity near the sol-gel transition. Phys. Rev. A 1989, 39, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graessley, W.W. Polymeric Liquids and Networks: Dynamics and Rheology; Polymeric Liquids and Networks, Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Muthukumar, M. Dynamics of polymeric fractals. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 83, 3161–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumar, M. Screening effect on viscoelasticity near the gel point. Macromolecules 1989, 22, 4656–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einstein, A. On the motion of small particles suspended in liquids at rest required by the molecular-kinetic theory of heat. Annalen der Physik 1905, 17, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flory, P.J. Statistical mechanics of dilute polymer solutions. J. Chem. Phys. 1949, 17, 1347–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, S.F. The theory of polymer solutions at intermediate concentration. Proc. Phys. Soc. 1966, 88, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, D.; Aharony, A. Introduction to Percolation Theory; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, T.H.; Furst, E.M. Microrheology of the liquid-solid transition during gelation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 146001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baschnagel, J.; Binder, K.; Doruker, P.; Gusev, A.A.; Hahn, O.; Kremer, K.; Mattice, W.L.; Müller-Plathe, F.; Murat, M.; Paul, W.; et al. Bridging the gap between atomistic and coarse-grained models of polymers: Status and perspectives. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2000, 41–156. [Google Scholar]
- Rouse, P.E. A theory of the linear viscoelastic properties of dilute solutions of coiling polymers. J. Chem. Phys. 1953, 21, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kestin, J.; Sokolov, M.; Wakeham, W.A. Viscosity of liquid water in the range -8 °C to 150 °C. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1978, 7, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, T.; Mayumi, K.; Ducouret, G.; Hébraud, P. Viscoelastic properties of poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels having permanent and transient cross-links studied by microrheology, classical rheometry, and dynamic light scattering. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 4174–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, M.L. Polymer molecular weights and molecular weight distributions by low-angle laser light scattering. Am. Lab. 1978, 10, 63–75. [Google Scholar]






| Hyperscaling Hypothesis Excluded-Volume Effect | Not Assumed | Assumed | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unscreened | Screened | Unscreened | Screened | |
| Fractal dimension | Equation (22) | Equation (24) | Equation (27) | Equation (28) |
| Index (used in Table 2) | (I) | (II) | (III) | (IV) |
| Hyperscaling Hypothesis Excluded-Volume Effect | Not Assumed | Assumed | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unscreened | Screened | Unscreened | Screened | |
| Index (see Table 1) | (I) | (II) | (III) | (IV) |
| Fractal dimension | 1.2 | 1.4 | 3.9 | 2.0 |
| Largest relaxed cluster size | 1.0 × 102 | 82 | 28 | 49 |
| System | PAAmVIm–Ni | PVA–borax |
|---|---|---|
| precursor polymer | PAAmVIm | PVA |
| polymer concentration () | 4 wt % | 5.5 wt % |
| weight average molecular weight () | 1.7 × 105 g mol−1 | 8.9 × 104 g/mol |
| degree of polymerization (DP) | 2.4 × 103 | 2.0 × 103 |
| radius of gyration () | 16 nm | 7.9nm |
| number of potentially cross-linkable sites per polymer chain | 2.4 × 102 | 1.0 × 103 |
| fraction of potentially cross-linkable sites | ||
| cross-linker | Ni ion (Ni2+) | borate ion (B(OH)−4) |
| cross-linker concentration at the gel point () | 1.1 mM | 3.4 mM |
| correlation length () | 6 nm | 14 nm |
| activation energy | 86 kJ mol−1 | 42 kJ mol−1 |
| System | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAAmVIm–Ni | 1.5 × 102 | 7.4 × 10−5 | 2.69 | 0.5 | 9 | 2.7 × 10−2 | 1.2 × 10−2 |
| PVA–borax | 1.7 × 103 | 5.9 × 10−7 | 1.95 | 0.59 | 550 | 1.3 × 10−1 | 1.3 × 10−2 |
| Hyperscaling Hypothesis Excluded-Volume Effect | Not Assumed | Assumed | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| System | Unscreened | Screened | Unscreened | Screened | |
| PAAmVIm–Ni | 1.2 | 1.4 | 3.9 | 2.0 | |
| 1.0 × 102 | 82 | 28 | 49 | ||
| PVA–borax | 2.1 | 1.7 | 3.1 | 1.9 | |
| 1.6 × 102 | 3.3 × 102 | 61 | 2.2 × 102 | ||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ozaki, H.; Narita, T.; Koga, T.; Indei, T. Theoretical Analysis of Critical Flowable Physical Gel Cross-Linked by Metal Ions and Polyacrylamide-Derivative Associating Polymers Containing Imidazole Groups. Polymers 2017, 9, 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9070256
Ozaki H, Narita T, Koga T, Indei T. Theoretical Analysis of Critical Flowable Physical Gel Cross-Linked by Metal Ions and Polyacrylamide-Derivative Associating Polymers Containing Imidazole Groups. Polymers. 2017; 9(7):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9070256
Chicago/Turabian StyleOzaki, Hiroto, Tetsuharu Narita, Tsuyoshi Koga, and Tsutomu Indei. 2017. "Theoretical Analysis of Critical Flowable Physical Gel Cross-Linked by Metal Ions and Polyacrylamide-Derivative Associating Polymers Containing Imidazole Groups" Polymers 9, no. 7: 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9070256
APA StyleOzaki, H., Narita, T., Koga, T., & Indei, T. (2017). Theoretical Analysis of Critical Flowable Physical Gel Cross-Linked by Metal Ions and Polyacrylamide-Derivative Associating Polymers Containing Imidazole Groups. Polymers, 9(7), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9070256