The Effect of Cover Crops on the Biodiversity and Abundance of Ground-Dwelling Arthropods in a Mediterranean Pear Orchard
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Data Analysis
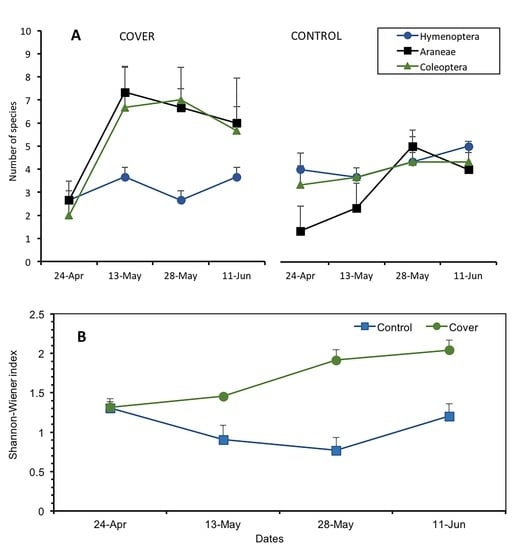
3. Results
3.1. Ground Cover and Diversity of Ground-Dwelling Arthropods
3.2. Structure of the Assemblages of Ground-Dwelling Arthropods in Pear Orchards
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, J.S. The biodiversity crisis: A multifaceted review. Curr. Sci. 2002, 82, 638–647. [Google Scholar]
- Rosengrant, M.; Cai, X. World Water and Food to 2025; International Food Policy Research Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; ISBN 0896296466. [Google Scholar]
- Foley, J.A.; DeFries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K.; et al. Global consequences of land use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Myers, N. Biodiversity and the Precautionary Principle. Ambio 1993, 22, 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, M.; Gibbs, J. Fundamentals of Conservation Biology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, R.F. Identifying Keystone Threats to Biological Diversity. In Landscape-Scale Conservation Planning; Trombulak, S.C., Baldwin, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 17–32. ISBN 9789048195749. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, R.A.; Sutherland, W.J. Post-war changes in arable farming and biodiversity in Great Britain. J. Appl. Ecol. 2002, 39, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bianchi, F.J.J.A.; Booij, C.J.H.; Tscharntke, T. Sustainable pest regulation in agricultural landscapes: A review on landscape composition, biodiversity and natural pest control. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 273, 1715–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bommarco, R.; Kleijn, D.; Potts, S.G. Ecological intensification: Harnessing ecosystem services for food security. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matson, P.A.; Parton, W.J.; Power, A.G.; Swift, M.J. Agricultural Intensification and Ecosystem Properties. Science 1997, 277, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tilman, D.; Fargione, J.; Wolff, B.; D’Antonio, C.; Dobson, A.; Howarth, R.; Schindler, D.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Simberloff, D.; Swackhamer, D. Forecasting Agriculturally Driven Global Environmental Change. Science 2001, 292, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tscharntke, T.; Klein, A.M.; Kruess, A.; Steffan-Dewenter, I.; Thies, C. Landscape perspectives on agricultural intensification and biodiversity—Ecosystem service management. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 857–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolters, V. Biodiversity of soil animals and its function. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2001, 37, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Decaëns, T.; Jiménez, J.J.; Gioia, C.; Measey, G.J.; Lavelle, P. The values of soil animals for conservation biology. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2006, 42, S23–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briones, M.J.I. Soil fauna and soil functions: A jigsaw puzzle. Front. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Culliney, T.W. Role of arthropods in maintaining soil fertility. Agriculture 2013, 3, 629–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbott, I.; Parker, C.A.; Sills, I.D. Changes in the Abundance of Large Soil Animals and Physical Properties of Soils Following Cultivation. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1979, 17, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simão, F.C.P.; Carretero, M.A.; do Amaral, M.J.A.; Soares, A.M.V.d.M.; Mateos, E. Composition and seasonal variation of epigeic arthropods in field margins of NW Portugal. Turk. J. Zool. 2015, 39, 404–411. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, H.; Moldenke, A. Response of Ground-Dwelling Arthropods to Different Thinning Intensities in Young Douglas Fir Forests of Western Oregon. Environ. Entomol. 2005, 34, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.B.; Ruberson, J.R. Abundance and diversity of ground-dwelling arthropods of pest management importance in commercial Bt and non-Bt cotton fields. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2007, 150, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, W.M.; Eble, J.A.; Franklin, K.; McManus, R.B.; Brantley, S.L.; Henkel, J.; Marek, P.E.; Hall, W.E.; Olson, C.A.; McInroy, R.; et al. Ground-Dwelling Arthropod Communities of a Sky Island Mountain Range in Southeastern Arizona, USA: Obtaining a Baseline for Assessing the Effects of Climate Change. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jabbour, R.; Pisani-Gareau, T.; Smith, R.G.; Mullen, C.; Barbercheck, M. Cover crop and tillage intensities alter ground-dwelling arthropod communities during the transition to organic production. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2016, 31, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stefani, V.; Pires, T.L.; Torezan-Silingardi, H.M.; Del-Claro, K.; Ballhorn, D. Beneficial effects of ants and spiders on the reproductive value of Eriotheca gracilipes (Malvaceae) in a tropical savanna. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, N.J. Factors influencing top-down control of insect pest populations in biological control systems. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2001, 332, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Fenollosa, E.; Ibáñez-Gual, M.V.; Pascual-Ruiz, S.; Hurtado, M.; Jacas, J.A. Effect of ground-cover management on spider mites and their phytoseiid natural enemies in clementine mandarin orchards (II): Top-down regulation mechanisms. Biol. Control 2011, 59, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnadass, A.; Fernandes, P.; Avelino, J.; Habib, R. Plant species diversity for sustainable management of crop pests and diseases in agroecosystems: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 32, 273–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snyder, W.E.; Wise, D.H. Predator Interference and the Establishment of Generalist Predator Populations for Biocontrol. Biol. Control 1999, 15, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lang, A. Intraguild interference and biocontrol effects of generalist predators in a winter wheat field. Oecologia 2003, 134, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, J.S.; Vaughan, I.P.; Andrew King, R.; Bell, J.R.; Bohan, D.A.; Bruford, M.W.; Holland, J.M.; Symondson, W.O.C. Intraguild predation in winter wheat: Prey choice by a common epigeal carabid consuming spiders. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 50, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lundgren, J.G.; Shaw, J.T.; Zaborski, E.R.; Eastman, C.E. The influence of organic transition systems on beneficial ground-dwelling arthropods and predation of insects and weed seeds. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2006, 21, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pullaro, T.C.; Marino, P.C.; Jackson, D.M.; Harrison, H.F.; Keinath, A.P. Effects of killed cover crop mulch on weeds, weed seeds, and herbivores. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 115, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Aquino, A.M.; Ferreira da Silva, R.; Mercante, F.M.; Fernandes Correia, M.E.; de Fátima Guimarães, M.; Lavelle, P. Invertebrate soil macrofauna under different ground cover plants in the no-till system in the Cerrado. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2008, 44, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearin, A.F.; Chris Reberg-Horton, S.; Gallandt, E.R. Cover Crop Effects on the Activity-Density of the Weed Seed Predator Harpalus rufipes (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Weed Sci. 2008, 56, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, D.A.; Wratten, S.D.; Gurr, G.M. Habitat Management to Conserve Natural Enemies of Arthropod Pests in Agriculture. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2000, 45, 175–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; Ramankutty, N.; Brauman, K.A.; Cassidy, E.S.; Gerber, J.S.; Johnston, M.; Mueller, N.D.; O’Connell, C.; Ray, D.K.; West, P.C.; et al. Solutions for a cultivated planet. Nature 2011, 478, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hooper, D.U.; Chapin, F.S.; Ewel, J.J.; Hector, A.; Inchausti, P.; Lavorel, S.; Lawton, J.H.; Lodge, D.M.; Loreau, M.; Naeem, S.; et al. Effects of biodiversity on ecosystem functioning: A consensus of current knowledge. Ecol. Monogr. 2005, 75, 3–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overpeck, J.; Garfin, G.; Jardine, A.; Busch, D.E.; Cayan, D.; Dettinger, M.; Fleishman, E.; Gershunov, A.; MacDonald, G.; Redmond, K.T.; et al. Summary for Decision Makers; Island Press: Washington DC, USA, 2013; ISBN 9781610914840. [Google Scholar]
- Thies, C.; Tscharntke, T. Landscape structure and biological control in agroecosystems. Science 1999, 285, 893–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, E.B.; Franco, J.C.; Vasconcelos, T.; Branco, M. Effect of ground cover vegetation on the abundance and diversity of beneficial arthropods in citrus orchards. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2010, 100, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugg, R.L.; Pickett, C.H. Introduction: Enhancing biological control-habitat management to promote natural enemies of agricultural pests. In Enhancing Biological Control; Pickett, C.H., Bugg, R.L., Eds.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1998; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson, M.; Wratten, S.D.; Landis, D.A.; Gurr, G.M. Recent advances in conservation biological control of arthropods by arthropods. Biol. Control 2008, 45, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurostat. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/data/database (accessed on 20 February 2020).
- Aguilar-Fenollosa, E.; Ibáñez-Gual, M.V.; Pascual-Ruiz, S.; Hurtado, M.; Jacas, J.A. Effect of ground-cover management on spider mites and their phytoseiid natural enemies in clementine mandarin orchards (I): Bottom-up regulation mechanisms. Biol. Control 2011, 59, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Marco, F.; Urbaneja, A.; Tena, A. A sown grass cover enriched with wild forb plants improves the biological control of aphids in citrus. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2016, 17, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommaggio, D.; Peretti, E.; Burgio, G. The effect of cover plants management on soil invertebrate fauna in vineyard in Northern Italy. BioControl 2018, 63, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrada, S.; Fournier, D.; Cuany, A.; Nguyen, T. Identification of Resistance Mechanisms in a Selected Laboratory Strain of Cacopsylla pyri (Homoptera: Psyllidae): Altered Acetylcholinesterase and Detoxifying Oxidases. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 1994, 48, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bues, R.; Boudinhon, L.; Toubon, J. Resistance of pear psylla (Cacopsylla pyri L.; Hom., Psyllidae) to deltamethrin and synergism with piperonyl butoxide. J. Appl. Entomol. 2003, 127, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civolani, S.; Cassanelli, S.; Rivi, M.; Manicardi, G.C.; Peretto, R.; Chicca, M.; Pasqualini, E.; Leis, M. Survey of Susceptibility to Abamectin of Pear Psylla (Hemiptera: Psyllidae ) in Northern Italy. J. Econ. Entomol. 2010, 103, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogya, S.; Marko, V.; Szinetár, C. Comparison of pome fruit orchard inhabiting spider assemblages at different geographical scales. Agric. For. Entomol. 1999, 1, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, M.G.; Cross, J.V.; Fitzgerald, J.D.; Campbell, C.A.M.; Jolly, R.L.; Olszak, R.W.; Niemczyk, E.; Vogt, H. Biocontrol of pests of apples and pears in northern and central Europe—3. Predators. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2000, 10, 91–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.A.; Ortín-Angulo, M.C. Abundance and population dynamics of Cacopsylla pyri (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) and its potential natural enemies in pear orchards in southern Spain. Crop Prot. 2012, 32, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.A.; López-Gallego, E.; La-Spina, M. The impact of ant mutualistic and antagonistic interactions on the population dynamics of sap-sucking hemipterans in pear orchards. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 76, 1422–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.A.; Carrasco-Ortiz, A.; López-Gallego, E.; La-Spina, M. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) reduce the density of Cacopsylla pyri (Linnaeus, 1761) in Mediterranean pear orchards. Myrmecol. News 2020, 30, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Marcos, M.; López-Gallego, E.; Ramírez-Soria, M.J.; Sanchez, J. Key parameters for the management and design of field margins aiming to the conservation of beneficial insects. Landsc. Manag. Funct. Biodivers. IOBC-WPRS Bull. 2017, 122, 151–155. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, J.A.; Carrasco, A.; La Spina, M.; Pérez-Marcos, M.; Ortiz-Sánchez, F.J. How bees respond differently to field margins of shrubby and herbaceous plants in intensive agricultural crops of the Mediterranean area. Insects 2020, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derraik, J.G.B.; Early, J.W.; Closs, G.P.; Dickinson, K.J.M. Morphospecies and taxonomic species comparison for Hymenoptera. J. Insect Sci. 2010, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez, M.D.; Acosta, F.J.; Ruiz, E. Claves Pra la Identificación de la Fauna Española. Las Subfamilias y Géneros de las Hormigas Ibéricas; Universidad Complutense: Madrid, Spain, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Goulet, H.; Huber, J.T. Hymenoptera of the World: An Identification Guide to Families; Goulet, H., Huber, J.T., Eds.; Canada Communication Group: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1993; ISBN 0660149338. [Google Scholar]
- Nentwig, W.; Blick, T.; Bosmans, R.; Gloor, D.; Hänggi, A.; Kropf, C. Araneae Version 09.2019. Available online: https://www.araneae.nmbe.ch (accessed on 9 September 2019).
- Salgado, J.; Outerello, R.; Gamarra, P.; Blas, M.; Vazquez, X.; Otero, J.C. Coleópteros. In Curso Práctico de Entomología; Barrientos, J.A., Ed.; Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Servei de Publicacions: Barcelona, Spain, 2004; pp. 741–811. ISBN 84-490-2383-1. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.M.; Walker, S.C. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R-Development-Core-Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cárdenas, M.; Castro, J.; Campos, M. Short-Term Response of Soil Spiders to Cover-Crop Removal in an Organic Olive Orchard in a Mediterranean Setting. J. Insect Sci. 2012, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rieux, R.; Simon, S.; Defrance, H. Role of hedgerows and ground cover management on arthropod populations in pear orchards. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1999, 73, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolwine, A.E.; Reagan, T.E. Potential of Winter Cover Crops to Increase Abundance of Solenopsis invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) and Other Arthropods in Sugarcane. Environ. Entomol. 2001, 30, 1017–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tillman, G.; Schomberg, H.; Phatak, S.; Mullinix, B.; Lachnicht, S.; Timper, P.; Olson, D. Influence of cover crops on insect pests and predators in conservation tillage cotton. J. Econ. Entomol. 2004, 97, 1217–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, G.; Lentini, A.; Verdinelli, M.; Delrio, G. Effects of cover crop management on grape pests in a Mediterranean environment. IOBC/WPRS Bull. 2006, 29, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Sáenz-Romo, M.G.; Veas-Bernal, A.; Martínez-García, H.; Campos-Herrera, R.; Ibáñez-Pascual, S.; Martínez-Villar, E.; Pérez-Moreno, I.; Marco-Mancebón, V.S. Ground cover management in a Mediterranean vineyard: Impact on insect abundance and diversity. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 283, 106571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, S.L.; Carolina, N. Using Ant Species as a biological indicator of Agroecosystem Condition. Environ. Entomol. 1998, 27, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchholz, J.; Querner, P.; Paredes, D.; Bauer, T.; Strauss, P.; Guernion, M.; Scimia, J.; Cluzeau, D.; Burel, F.; Kratschmer, S.; et al. Soil biota in vineyards are more influenced by plants and soil quality than by tillage intensity or the surrounding landscape. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carmona, D.M.; Landis, D.A. Influence of refuge habitats and cover crops on seasonal activity-density of ground beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) in field crops. Environ. Entomol. 1999, 28, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáenz-Romo, M.G.; Veas-Bernal, A.; Martínez-García, H.; Ibáñez-Pascual, S.; Martínez-Villar, E.; Campos-Herrera, R.; Marco-Mancebón, V.S.; Pérez-Moreno, I. Effects of ground cover management on insect predators and pests in a mediterranean vineyard. Insects 2019, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Altieri, M.A.; Schmidt, L.L. Cover Crop Manipulation in Northern California Orchards and Vineyards: Effects on Arthropod Communities. Biol. Agric. Hortic. 1985, 3, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markó, V.; Keresztes, B. Flowers for better pest control? Ground cover plants enhance apple orchard spiders (Araneae), but not necessarily their impact on pests. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2014, 24, 574–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgio, G.; Marchesini, E.; Reggiani, N.; Montepaone, G.; Schiatti, P.; Sommaggio, D. Habitat management of organic vineyard in Northern Italy: The role of cover plants management on arthropod functional biodiversity. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2016, 106, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danne, A.; Thomson, L.J.; Sharley, D.J.; Penfold, C.M.; Hoffmann, A.A. Effects of Native Grass Cover Crops on Beneficial and Pest Invertebrates in Australian Vineyards. Environ. Entomol. 2010, 39, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, E.; González, B.; Campos, M. Natural enemies associated with cereal cover crops in olive groves. Bull. Insectol. 2012, 65, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Sunderland, K.D.; Samu, F. Effects of agricultural diversification on the abundance, distribution, and pest control potential of spiders: A review. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2000, 95, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.H.; Roschewitz, I.; Thies, C.; Tscharntke, T. Differential effects of landscape and management on diversity and density of ground-dwelling farmland spiders. J. Appl. Ecol. 2005, 42, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, T. Beetles which use a setal trap to hunt springtails: The hunting strategy and apparatus of Leistus (Coleoptera, Carabidae). Pedobiologia (Jena) 1985, 28, 275–287. [Google Scholar]
- Agustí, N.; Shayler, S.P.; Harwood, J.D.; Vaughan, I.P.; Sunderland, K.D.; Symondson, W.O.C. Collembola as alternative prey sustaining spiders in arable ecosystems: Prey detection within predators using molecular markers. Mol. Ecol. 2003, 12, 3467–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIver, J.D.; Stonedahl, G. Myrmecomorphy: Morphological and behavioral mimicry of ants. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1993, 38, 351–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekár, S. Predatory characteristics of ant-eating Zodarion spiders (Araneae: Zodariidae): Potential biological control agents. Biol. Control 2005, 34, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugg, R.L.; Waddington, C. Using cover crops to manage arthropod pests of orchards: A review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1994, 50, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, A.F.; Kim, T.N.; Bahlai, C.A.; Woltz, J.M.; Gratton, C.; Landis, D.A. Cover crops have neutral effects on predator communities and biological control services in annual cellulosic bioenergy cropping systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 232, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nyffeler, M. Prey selection of spiders in the field. J. Acharol. 1999, 27, 317–324. [Google Scholar]
- Axelsen, J.A.; Kristensen, K.T. Collembola and mites in plots fertilised with different types of green manure. Pedobiologia (Jena) 2000, 44, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, L.M.; Cobb, V.A. Occurrence of Parasitoid wasps, Baeus sp. and Gelis sp., in the egg sacs of the wolf spiders Pardosa moesta and Pardosa sternalis (Araneae, Lycosidae) in Southeastern Idaho. Can. Field-Nat. 2004, 118, 122–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Honek, A. The Effect of Plant Cover and Weather on the Activity Density of Ground Surface Arthropods in a Fallow Field. Entomol. Res. Org. Agric. 1997, 15, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, E.; Wolters, V.; Birkhofer, K. Arable weeds in organically managed wheat fields foster carabid beetles by resource- and structure-mediated effects. Arthropod Plant Interact. 2012, 6, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemela, J.; Spence, J.R.; Spence, D.H. Habitat associations and seasonal activity of ground-beetles (Coleoptera, Carabidae) in Central Alberta. Can. Entomol. 1992, 124, 521–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamps, W.T.; Nelson, E.A.; Linit, M.J. Survey of Diversity and Abundance of Ground-Dwelling Arthropods in a Black Walnut-Forage Alley-Cropped System in the Mid-Western United States. J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 2009, 82, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipanski, M.E.; Barbercheck, M.; Douglas, M.R.; Finney, D.M.; Haider, K.; Kaye, J.P.; Kemanian, A.R.; Mortensen, D.A.; Ryan, M.R.; Tooker, J.; et al. A framework for evaluating ecosystem services provided by cover crops in agroecosystems. Agric. Syst. 2014, 125, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finney, D.M.; Kaye, J.P. Functional diversity in cover crop polycultures increases multifunctionality of an agricultural system. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 54, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, A. The importance of movement in the response of natural enemies to habitat manipulation. In Enhancing Biological Control: Habitat Management to Promote Natural Enemies of Agricultural Pests; Pickett, C.H., Bugg, R.L., Eds.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1998; pp. 25–48. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, M.G. Cover Crops and Conservation Biocontrol: Can the Impacts of Trichogramma (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) Be Magnified? Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2019, 112, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, D.R.; Jones, V.P.; Unruh, T.R. Use of a new immunomarking method to assess movement by generalist predators between a cover crop and tree canopy in a pear orchard. Am. Entomol. 2009, 55, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, A.S.; Hill, J.D.; Chase, C.A.; Johanns, A.M.; Liebman, M. Increasing Cropping System Diversity Balances Productivity, Profitability and Environmental Health. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haley, S.; Hogue, E. Ground cover influence on apple aphid, Aphis pomi DeGeer (Homoptera: Aphididae), and its predators in a young apple orchard. Crop Prot. 1990, 9, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, M.J.; France, C.M.; Wratten, S.D.; Frampton, C. Enhancing biological control of leafrollers (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) by sowing buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum) in an orchard. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 1998, 8, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fye, R.E. Cover Crop Manipulation for Building Pear Psylla (Homoptera: Psyllidae) Predator Populations in Pear Orchards. J. Econ. Entomol. 1983, 76, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekár, S. Predatory Behavior of Two European Ant-Eating Spiders (Araneae, Zodariidae). J. Arachnol. 2004, 32, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Order | Family | Coefficient | χ2 | df | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hymenoptera | Formicidae | −0.664 | 24.032 | 1 | <0.001 |
| Scelionidae | 0.710 | 5.161 | 1 | 0.023 | |
| Araneae | Gnaphosidae | −0.227 | 0.720 | 1 | 0.396 |
| Linyphiidae | 0.674 | 9.705 | 1 | 0.002 | |
| Lycosidae | 1.799 | 67.751 | 1 | <0.001 | |
| Zodariidae | −0.010 | 0.002 | 1 | 0.970 | |
| Coleoptera | Anthicidae | 0.144 | 0.336 | 1 | 0.562 |
| Carabidae | 2.058 | 43.180 | 1 | <0.001 | |
| Staphylinidae | 0.806 | 6.008 | 1 | 0.014 | |
| Tenebrionidae | 0.097 | 0.071 | 1 | 0.790 | |
| Collembola | - | −0.650 | 10.063 | 1 | 0.002 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Pedro, L.; Perera-Fernández, L.G.; López-Gallego, E.; Pérez-Marcos, M.; Sanchez, J.A. The Effect of Cover Crops on the Biodiversity and Abundance of Ground-Dwelling Arthropods in a Mediterranean Pear Orchard. Agronomy 2020, 10, 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10040580
de Pedro L, Perera-Fernández LG, López-Gallego E, Pérez-Marcos M, Sanchez JA. The Effect of Cover Crops on the Biodiversity and Abundance of Ground-Dwelling Arthropods in a Mediterranean Pear Orchard. Agronomy. 2020; 10(4):580. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10040580
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Pedro, Luis, Luis Gabriel Perera-Fernández, Elena López-Gallego, María Pérez-Marcos, and Juan Antonio Sanchez. 2020. "The Effect of Cover Crops on the Biodiversity and Abundance of Ground-Dwelling Arthropods in a Mediterranean Pear Orchard" Agronomy 10, no. 4: 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10040580
APA Stylede Pedro, L., Perera-Fernández, L. G., López-Gallego, E., Pérez-Marcos, M., & Sanchez, J. A. (2020). The Effect of Cover Crops on the Biodiversity and Abundance of Ground-Dwelling Arthropods in a Mediterranean Pear Orchard. Agronomy, 10(4), 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10040580