Long-Term Fertilization and Lime-Induced Soil pH Changes Affect Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Grain Yields in Acidic Soil under Wheat-Maize Rotation
Abstract
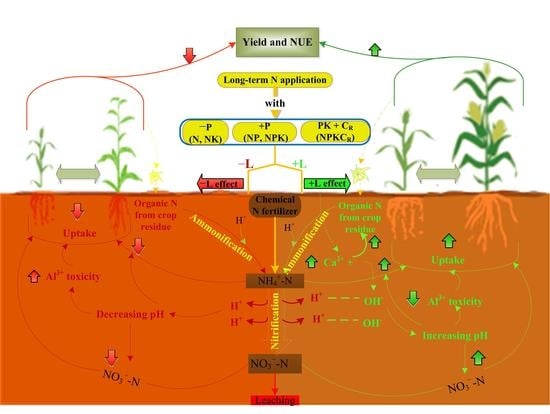
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Site
2.2. Experimental Design and Procedures
2.3. Soil Sampling and Analysis
2.4. Plant Sampling
2.5. Calculations
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Chemical Properties
3.1.1. Dynamics of Soil pH Change
3.1.2. Relationship between Soil pH, Exchangeable Soil Cations, and Years after Liming
3.2. Wheat and Maize Grain Yields (GY)
3.3. Correlation between Soil Chemical Properties, GY, and NUE Indices
3.4. Crop N Content and N Uptake
3.5. Nitrogen Use Efficiency
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Chemical Properties
4.2. Grain Yield, N Content, N Uptake, and N Use Efficiency
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ray, D.K.; Ramankutty, N.; Mueller, N.D.; West, P.C.; Foley, J.A. Recent patterns of crop yield growth and stagnation. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Cui, Z.; Fan, M.; Vitousek, P.; Zhao, M.; Ma, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yan, X.; Yang, J.; et al. Producing more grain with lower environmental costs. Nature 2014, 514, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q.; Ling, N.; Feng, X.; Yang, X.; Wu, P.; Zou, J.; Shen, Q.; Guo, S. Soil fertility and its significance to crop productivity and sustainability in typical agroecosystem: A summary of long-term fertilizer experiments in China. Plant Soil 2014, 381, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Niu, S. A global analysis of soil acidification caused by nitrogen addition. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 024019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Wang, B.; Xu, M.; Zhang, H.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; Gao, S. Intensified soil acidification from chemical N fertilization and prevention by manure in an 18-year field experiment in the red soil of southern China. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Vitousek, P.M.; Zhang, F.S. Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iturri, L.A.; Buschiazzo, D.E. Light acidification in N-fertilized loess soils along a climosequence affected chemical and mineralogical properties in the short-term. Catena 2016, 139, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Bo-Ren, W.A.N.G.; Ming-Gang, X.U.; Ting−Lu, F.A.N. Crop yield and soil responses to long-term fertilization on a red soil in southern China. Pedosphere 2009, 19, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Sun, B.H.; Zhang, S.L. Trends of yield and soil fertility in a long-term wheat-maize system. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, A.E. The value of long-term field experiments in agricultural, ecological, and environmental research. Adv. Agron. 1997, 59, 291–333. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.; Liu, X.; Song, L.; Lin, X.; Zhang, H.; Shen, C.; Chu, H. Nitrogen fertilization directly affects soil bacterial diversity and indirectly affects bacterial community composition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 92, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, K.C.; Herman, J.S. Acidification of Earth: An assessment across mechanisms and scales. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhalnina, K.; Dias, R.; de Quadros, P.D.; Davis-Richardson, A.; Camargo, F.A.; Clark, I.M.; McGrath, S.P.; Hirsch, P.R.; Triplett, E.W. Soil pH determines microbial diversity and composition in the park grass experiment. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 69, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neina, D. The role of soil pH in plant nutrition and soil remediation. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2019, 2019, 5794869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cui, S.; Chang, S.X.; Zhang, Q. Liming effects on soil pH and crop yield depend on lime material type, application method and rate, and crop species: A global meta-analysis. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 1393–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, A.; Jones, C.; Jacobsen, J. Soil pH and organic matter. Nutr. Manag. Modul. 2009, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Fageria, N.K.; Baligar, V.C. Ameliorating soil acidity of tropical Oxisols by liming for sustainable crop production. Adv. Agron. 2008, 99, 345–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.E.; Bennett, A.E.; Newton, A.C.; White, P.J.; McKenzie, B.M.; George, T.S.; Pakeman, R.J.; Bailey, J.S.; Fornara, D.A.; Hayes, R.C. Liming impacts on soils, crops and biodiversity in the UK: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.S.; Adriano, D.C.; Curtin, D. Soil acidification and liming interactions with nutrient and heavy metal transformation and bioavailability. Adv. Agron. 2003, 78, 5–272. [Google Scholar]
- Nduwumuremyi, A.; Ruganzu, V.; Mugwe, J.N.; Rusanganwa, C.A. Effects of unburned lime on soil pH and base cations in acidic soil. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2013, 2013, 707569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunhikrishnan, A.; Thangarajan, R.; Bolan, N.S.; Xu, Y.; Mandal, S.; Gleeson, D.B.; Seshadri, B.; Zaman, M.; Barton, L.; Tang, C.; et al. Functional relationships of soil acidification, liming, and greenhouse gas flux. Adv. Agron. 2016, 139, 1–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulding, K.W.T. Soil acidification and the importance of liming agricultural soils with particular reference to the United Kingdom. Soil Use Manag. 2016, 32, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.C.; Pathan, S.; Easton, J.; Hall, D.J.; Sharma, R. Short-and Long-Term Effects of Lime and Gypsum Applications on Acid Soils in a Water−Limited Environment: 1. Grain Yield Response and Nutr. Concentration. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.C.; Pathan, S.; Easton, J.; Hall, D.J.; Sharma, R. Short-and Long-Term Effects of Lime and Gypsum Applications on Acid Soils in a Water−Limited Environment: 2. Soil Chemical Properties. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, X.; Wei, T.; Yang, Z.; Jia, Z.; Yang, B.; Han, Q.; Ren, X. Effects of straw incorporation on the soil nutrient contents, enzyme activities, and crop yield in a semiarid region of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 160, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Zhang, P.; Wang, K.; Ding, R.; Yang, B.; Nie, J.; Jia, Z.; Han, Q. Effects of wheat straw incorporation on the availability of soil nutrients and enzyme activities in semiarid areas. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 0120994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akhtar, K.; Wang, W.; Ren, G.; Khan, A.; Feng, Y.; Yang, G. Changes in soil enzymes, soil properties, and maize crop productivity under wheat straw mulching in Guanzhong, China. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 182, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, B.B.; Madramootoo, C.A.; Mehuys, G.R. Yield and nitrogen content of corn under different tillage practices. Agron. J. 1999, 91, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fageria, N.K.; Baligar, V.C. Enhancing nitrogen use efficiency in crop plants. Adv. Agron. 2005, 88, 97–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Xu, J.; Tang, C.; Zhang, J.; Brookes, P.C. Differences in carbon and nitrogen mineralization in soils of differing initial pH induced by electrokinesis and receiving crop residue amendments. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 67, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Müller, C.; Cai, Z. Temporal variations of crop residue effects on soil N transformation depend on soil properties as well as residue qualities. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2018, 54, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulakh, M.S.; Walters, D.T.; Doran, J.W.; Francis, D.D.; Mosier, A.R. Crop residue type and placement effects on denitrification and mineralization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1991, 55, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobermann, A.; Cassman, K.G. Cereal area and nitrogen use efficiency are drivers of future nitrogen fertilizer consumption. Sci. China Ser. C Life Sci. 2005, 48, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladha, J.K.; Pathak, H.; Krupnik, T.J.; Six, J.; van Kessel, C. Efficiency of fertilizer nitrogen in cereal production: Retrospects and prospects. Adv. Agron. 2005, 87, 85–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoa, R.; Loomis, R.S. Nitrogen and plant production. Plant. Soil 1981, 58, 177–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F. Current nitrogen management status and measures to improve the intensive wheat–maize system in China. Ambio 2010, 39, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duan, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, B.; Yang, X.; Huang, S.; Gao, S. Long-term evaluation of manure application on maize yield and nitrogen use efficiency in China. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 1562–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, L.; Li, W.; Sheng, L. Effects of long-term application of organic fertilizer on improving organic matter content and retarding acidity in red soil from China. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Xue-Yun, Y.A.N.G.; Xin-Hua, H.E.; Ming-Gang, X.U.; Huang, S.M.; Hua, L.I.U.; Bo-Ren, W.A.N.G. Effect of long-term potassium fertilization on crop yield and potassium efficiency and balance under wheat-maize rotation in China. Pedosphere 2011, 21, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, A.; Xu, M.; Wang, B.; Zhang, W.; Liang, G.; Hou, E.; Luo, Y. Manure acts as a better fertilizer for increasing crop yields than synthetic fertilizer does by improving soil fertility. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 189, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, A.; Zhang, W.; Xu, M.; Wang, B.; Wen, S.; Shah, S.A.A. Soil fertility and crop yield after manure addition to acidic soils in South China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2018, 111, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Cai, A.; Liu, K.; Huang, J.; Wang, B.; Li, D.; Qaswar, M.; Feng, G.; Zhang, H. The links between potassium availability and soil exchangeable calcium, magnesium, and aluminum are mediated by lime in acidic soil. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaswar, M.; Dongchu, L.; Jing, H.; Tianfu, H.; Ahmed, W.; Abbas, M.; Lu, Z.; Jiangxue, D.; Khan, Z.H.; Ullah, S.; et al. Interaction of liming and long-term fertilization increased crop yield and phosphorus use efficiency (PUE) through mediating exchangeable cations in acidic soil under wheat–maize cropping system. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjos, L.; Gaistardo, C.; Deckers, J.; Dondeyne, S.; Eberhardt, E.; Gerasimova, M.; Harms, B.; Jones, A.; Krasilnikov, P.; Reinsch, T.; et al. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014 International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2015; JRC91947. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, K.A.; Gomez, A.A. Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, S.R. Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1954.
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L. Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Soil Science Society of America Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 539–579. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J.M. Determination of nitrogen in soil by the Kjeldahl method. J. Agric. Sci. 1960, 55, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motsara, M.R.; Roy, R.N. Guide to Laboratory Establishment for Plant Nutrient Analysis; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2008; Volume 19. [Google Scholar]
- Moll, R.H.; Kamprath, E.J.; Jackson, W.A. Analysis and interpretation of factors which contribute to efficiency of nitrogen utilization. Agron. J. 1982, 74, 562–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-MonasterioR, J.I.; Sayre, K.D. Rajaram, S.; McMahon, M. Genetic progress in wheat yield and nitrogen use efficiency under four nitrogen rates. Crop. Sci. 1997, 37, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VSN International Genstat for Windows, 19th ed.; VSN International: Hemel Hempstead, UK, 2019; Available online: https://www.vsni.co.uk/software/genstat/ (accessed on 22 June 2020).
- Li, W.X.; Wang, C.; Zheng, M.M.; Cai, Z.J.; Wang, B.R.; Shen, R.F. Fertilization strategies affect soil properties and abundance of N-cycling functional genes in an acidic agricultural soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 156, 103704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.Y.; Li, J.Y.; Deng, K.Y.; Xu, R.K.; Shen, R.F. Four-year effects of soil acidity amelioration on the yields of canola seeds and sweet potato and N fertilizer efficiency in an ultisol. Field Crops Res. 2019, 237, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Xu, R.K.; Li, J.Y. Amelioration of an acid ultisol by agricultural by-products. Land Degrad. Dev. 2011, 22, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, D.N. Acid soil tolerance in legumes and rhizobia. Adv. Plant. Nutr. 1986, 2, 63–91. [Google Scholar]
- Sumner, M.E.; Fey, M.V.; Noble, A.D. Nutrient status and toxicity problems in acid soils. In Soil Acidity; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991; pp. 149–182. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J. Changes in the efficiency of fertiliser use in China. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 1006–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moir, J.; Jordan, P.; Moot, D.; Lucas, R. Phosphorus response and optimum pH ranges of twelve pasture legumes grown in an acid upland New Zealand soil under glasshouse conditions. J. Soil Sci. Plant. Nutr. 2016, 16, 438–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qaswar, M.; Chai, R.; Ahmed, W.; Jing, H.; Han, T.; Liu, K.; Ye, X.; Xu, Y.; Anthonio, C.K.; Zhang, H. Partial substitution of chemical fertilizers with organic amendments increased rice yield by changing phosphorus fractions and improving phosphatase activities in fluvo-aquic soil. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 1285–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, J.; Li, G.; Shen, J.; Bergström, L.; Zhang, F. Past, present, and future use of phosphorus in Chinese agriculture and its influence on phosphorus losses. Ambio 2015, 44, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holland, J.E.; White, P.J.; Glendining, M.J.; Goulding, K.W.T.; McGrath, S.P. Yield responses of arable crops to liming–An evaluation of relationships between yields and soil pH from a long-term liming experiment. Eur. J. Agron. 2019, 105, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Gao, W.; Ren, S. Long-term effects of combined application of chemical nitrogen with organic materials on crop yields, soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in fluvo-aquic soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 151, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Xu, M.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L.; Wen, S.; Gao, S. Effectiveness of crop straws, and swine manure in ameliorating acidic red soils: A laboratory study. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 2893–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.I.; Hossain, M.B.; Schmidhalter, U. Carbon and nitrogen mineralization in different upland soils of the subtropics treated with organic materials. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 1507–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gál, A.; Vyn, T.J.; Michéli, E.; Kladivko, E.J.; McFee, W.W. Soil carbon and nitrogen accumulation with long-term no-till versus moldboard plowing overestimated with tilled-zone sampling depths. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 96, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, J.L.; Zhang, H.; Girma, K.; Raun, W.R.; Penn, C.J.; Payton, M.E. Soil acidification from long-term use of nitrogen fertilizers on winter wheat. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.; Bell, R. Wheat grain-yield response to lime application: Relationships with soil pH and aluminium in Western Australia. Crop. Pasture Sci. 2019, 70, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, H.M.; Sharma, R.P.; Sankhyan, N.K.; Sepehya, S. Effect of continuous application of fertilizers, farmyard manure and lime on soil fertility and productivity of the maize-wheat system in an acid alfisol. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant. Anal. 2017, 48, 1552–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, M.; Eşitken, A.; Pirlak, L. The effects of lime doses on some morphological and fruit characteristics of some strawberry (fragaria x ananassa duch.) cul-tivars. In IX International Scientific Agriculture Symposium “AGROSYM 2018”, Jahorina, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 4–7 October 2018, Book of Proceedings 575–582; University of East Sarajevo, Faculty of Agriculture: Lukavica, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Ma, B. Integrated nutrient management (INM) for sustaining crop productivity and reducing environmental impact: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.M.; Tang, C.; Chen, Z.L. The role of plant residues in pH change of acid soils differing in initial pH. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Huang, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, B.; Li, X.; Ma, Y. Nitrogen efficiency in long-term wheat–maize cropping systems under diverse field sites in China. Field Crops Res. 2010, 118, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Konijn, N.T. Fertilizer requirements for wheat and maize in China: The QUEFTS approach. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2006, 74, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egan, G.; McKenzie, P.; Crawley, M.; Fornara, D.A. Effects of grassland management on plant nitrogen use efficiency (NUE): Evidence from a long-term experiment. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2019, 41, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibb, D.W.; Thompson, W.R., Jr. Interaction of potassium with other nutrients. In Potassium in Agriculture; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1985; pp. 515–533. [Google Scholar]
- Vance, C.P.; Uhde-Stone, C.; Allan, D.L. Phosphorus acquisition and use: Critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource. New Phytol. 2003, 157, 423–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, T.T.; Koenig, R.T.; Huggins, D.R.; Harsh, J.B.; Rossi, R.E. Lime effects on soil acidity, crop yield, and aluminum chemistry in direct-seeded cropping systems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2008, 72, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caires, E.F.; Haliski, A.; Bini, A.R.; Scharr, D.A. Surface liming and nitrogen fertilization for crop grain production under no-till management in Brazil. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 66, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raun, W.R.; Dhillon, J.; Aula, L.; Eickhoff, E.; Weymeyer, G.; Figueirdeo, B.; Fornah, A. Unpredictable nature of the environment on nitrogen supply and demand. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 2786–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhakal, C.; Lange, K.; Parajulee, M.N.; Segarra, E. Dynamic optimization of nitrogen in plateau cotton yield functions with nitrogen carryover considerations. J. Agric. Appl. Econ. 2019, 51, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Fertilizer | pH | AK (mg kg−1) | POlsen (mg kg−1) | NO3−-N (mg kg−1) | NH4+-N (mg kg−1) | SOM (g kg−1) | TN (g kg−1) | C:N Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 5.7 a | 60.0 b | 0.7 b | 4.4 a | 0.5 c | 14.7 a | 1.1 a | 12.8 a |
| N | 4.7 a | 59.9 b | 0.6 b | 3.6 a | 3.1 a | 19.0 a | 1.3 a | 9.4 a |
| NP | 4.9 a | 64.0 b | 109.4 a | 4.6 a | 1.6 b | 22.0 a | 1.4 a | 10.6 a |
| NK | 4.7 a | 256.9 a | 0.7 b | 4.3 a | 1.7 b | 20.9 a | 1.4 a | 11.2 a |
| NPK | 5.0 a | 283.2 a | 116.4 a | 4.5 a | 1.6 b | 20.8 a | 1.5 a | 11.7 a |
| NPKCR | 5.1 a | 276.7 a | 121.8 a | 4.5 a | 1.6 b | 24.7 a | 1.5 a | 11.8 a |
| LSD (p ≤ 0.05) | ns | 46.83 | 20.34 | ns | 0.51 | ns | ns | ns |
| Treatment | pH | AK (mg kg−1) | POlsen (mg kg−1) | NO3−-N (mg kg−1) | NH4+-N (mg kg−1) | SOM (g kg−1) | TN (g kg−1) | C:N Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lime | Fertilizer | ||||||||
| Without lime (−L) | C | 5.8 a | 45.3 d | 0.6 d | 4.1 de | 0.5 g | 16.1 e | 0.99 c | 11.8 b |
| N | 4.3 e | 45.6 d | 0.5 d | 3.3 f | 3.8 a | 11.4 f | 0.99 c | 8.6 g | |
| NP | 4.5 de | 53.6 d | 62.4 c | 4.2 de | 1.8 cd | 17.4 de | 1.05 c | 9.1 fg | |
| NK | 4.3 e | 220.9 c | 0.6 d | 3.9 e | 2.5 b | 16.3 e | 0.98 c | 9.9 ef | |
| NPK | 4.5 de | 239.3 b | 77.5 a | 4.3 cde | 1.7 de | 20.1 bc | 1.04 c | 10.3 de | |
| NPKCR | 4.6 de | 236.6 b | 79.1 a | 4.3 cde | 1.6 def | 18.2 d | 1.06 bc | 11.3 bc | |
| With lime (+L) | N | 4.8 cd | 56.1 d | 0.7 d | 4.4 bcd | 1.9 c | 16.4 e | 1.18 a | 10.0 def |
| NP | 5.2 bc | 57.1 d | 70.1 b | 4.7 ab | 1.6 ef | 18.9 cd | 1.16 ab | 10.6 cde | |
| NK | 4.8 cd | 239.4 b | 0.7 d | 4.4 bcd | 1.6 def | 18.6 cd | 1.18 a | 10.4 cde | |
| NPK | 5.3 b | 262.1 a | 80.5 a | 4.6 abc | 1.6 ef | 21.9 a | 1.19 a | 11.0 bcd | |
| NPKCR | 5.3 b | 274.4 a | 82.2 a | 4.8 a | 1.5 f | 20.8 ab | 1.24 a | 13.9 a | |
| LSD (p ≤ 0.05) | 0.44 | 15.26 | 4.79 | 0.39 | 0.18 | 1.61 | 0.10 | 0.99 | |
| Item | Crop | Plant Part | Treatment | LSD (p ≤ 0.05) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | N | NP | NK | NPK | NPKCR | ||||
| N content (%) | Wheat | Grain | 1.07 d | 1.63 c | 1.98 ab | 1.90 b | 1.95 ab | 2.12 a | 0.19 |
| Straw | 0.45 c | 0.44 c | 0.60 b | 0.67 a | 0.64 ab | 0.63 ab | 0.06 | ||
| Maize | Grain | 1.10 a | 1.00 a | 1.22 a | 1.08 a | 1.15 a | 1.14 a | ns | |
| Straw | 0.87 a | 0.49 b | 1.02 a | 0.92 a | 0.99 a | 0.98 a | 0.31 | ||
| N uptake (kg ha−1) | Wheat | Grain | 4.76 d | 15.04 c | 28.01 b | 17.33 c | 40.32 a | 39.54 a | 6.11 |
| Straw | 3.54 f | 9.38 e | 16.88 c | 12.30 d | 26.82 b | 30.38 a | 2.18 | ||
| Total | 8.30 d | 24.91 cd | 44.90 b | 29.63 c | 67.14 a | 69.93 a | 8.89 | ||
| Maize | Grain | 7.42 f | 11.11 e | 25.56 c | 17.09 d | 33.79 b | 38.25 a | 2.30 | |
| Straw | 9.53 c | 8.87 c | 20.65 b | 13.73 c | 24.60 ab | 27.55 a | 6.09 | ||
| Total | 16.95 e | 19.98 e | 46.21 c | 30.82 d | 58.39 b | 65.80 a | 5.87 | ||
| Item | Crop | Plant Part | Treatment | LSD | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lime | C | N | NP | NK | NPK | NPKCR | (p ≤ 0.05) | |||
| N content (%) | Wheat | Grain | −L | 1.01 f | * | 1.69 d | * | 1.76 cd | 1.89 bc | 0.19 |
| +L | - | 1.49 e | 2.72 a | 1.46 e | 2.79 a | 2.90 a | ||||
| Straw | −L | 0.29 f | * | 0.37 e | * | 0.45 d | 0.43 d | 0.05 | ||
| +L | - | 0.61 ab | 0.65 a | 0.58 b | 0.63 ab | 0.64 a | ||||
| Maize | Grain | −L | 0.90 f | * | 0.87 f | * | 0.84 f | 0.86 f | 0.10 | |
| +L | - | 1.16 de | 1.37 b | 1.25 cd | 1.35 bc | 1.48 a | ||||
| Straw | −L | 0.44 d | * | 0.73 c | * | 0.78 c | 0.80 c | 0.09 | ||
| +L | - | 0.89 b | 1.17 a | 0.93 b | 1.15 a | 1.19 a | ||||
| N uptake (kg ha−1) | Wheat | Grain | −L | 2.67 h | * | 8.10 g | * | 9.36 fg | 14.63 e | 5.12 |
| +L | - | 11.53 efg | 39.43 c | 13.38 ef | 51.88 b | 57.07 a | ||||
| Straw | −L | 2.34 i | * | 3.75 h | * | 9.07 ef | 8.70 f | 1.12 | ||
| +L | - | 7.57 g | 14.30 c | 9.96 de | 17.63 b | 18.88 a | ||||
| Total | −L | 5.01 g | * | 11.85 f | * | 18.43 e | 23.33 e | 6.21 | ||
| +L | - | 19.10 e | 53.72 c | 23.34 e | 69.50 b | 75.95 a | ||||
| Maize | Grain | −L | 2.16 f | * | 4.96 f | * | 9.25 e | 10.14 e | 2.99 | |
| +L | - | 11.68 e | 26.11 c | 16.40 d | 37.72 b | 43.60 a | ||||
| Straw | −L | 4.91 j | * | 7.13 f | * | 10.25 e | 11.63 d | 1.08 | ||
| +L | - | 13.63 c | 16.13 b | 15.13 b | 19.25 a | 19.75 a | ||||
| Total | −L | 7.07 h | * | 12.09 g | * | 19.50 f | 21.77 ef | 4.06 | ||
| +L | - | 25.31 e | 42.23 c | 31.52 d | 56.72 b | 63.35 a | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daba, N.A.; Li, D.; Huang, J.; Han, T.; Zhang, L.; Ali, S.; Khan, M.N.; Du, J.; Liu, S.; Legesse, T.G.; et al. Long-Term Fertilization and Lime-Induced Soil pH Changes Affect Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Grain Yields in Acidic Soil under Wheat-Maize Rotation. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11102069
Daba NA, Li D, Huang J, Han T, Zhang L, Ali S, Khan MN, Du J, Liu S, Legesse TG, et al. Long-Term Fertilization and Lime-Induced Soil pH Changes Affect Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Grain Yields in Acidic Soil under Wheat-Maize Rotation. Agronomy. 2021; 11(10):2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11102069
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaba, Nano Alemu, Dongchu Li, Jing Huang, Tianfu Han, Lu Zhang, Sehrish Ali, Muhammad Numan Khan, Jiangxue Du, Shujun Liu, Tsegaye Gemechu Legesse, and et al. 2021. "Long-Term Fertilization and Lime-Induced Soil pH Changes Affect Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Grain Yields in Acidic Soil under Wheat-Maize Rotation" Agronomy 11, no. 10: 2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11102069
APA StyleDaba, N. A., Li, D., Huang, J., Han, T., Zhang, L., Ali, S., Khan, M. N., Du, J., Liu, S., Legesse, T. G., Liu, L., Xu, Y., Zhang, H., & Wang, B. (2021). Long-Term Fertilization and Lime-Induced Soil pH Changes Affect Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Grain Yields in Acidic Soil under Wheat-Maize Rotation. Agronomy, 11(10), 2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11102069