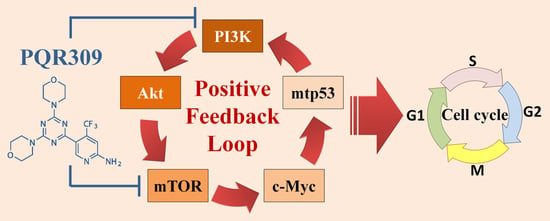
Suppression of PI3K/Akt/mTOR/c-Myc/mtp53 Positive Feedback Loop Induces Cell Cycle Arrest by Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor PQR309 in Endometrial Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Chemicals
2.2. Cell Viability Assay
2.3. Autophagosome Detection by CYTO-ID® Autophagy Detection Kit 2.0
2.4. Western Blot Assay
2.5. 3 Dimension (3D) Tumor Spheroid Formation Assay
2.6. Cancer Stem Cell Sphere Formation Assay
2.7. Flow Cytometry
2.8. VSV-G Pseudotyped Lentivirus–shRNA Production and Infection
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor PQR309 Reduces Cell Viability in Endometrial Cancer Cell Lines
3.2. Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor PQR309 Inhibits Tumor Spheroid Formation of Endometrial Cancer Cell Lines
3.3. Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor PQR309 Inhibits Cancer Stem Cell Sphere Growth of Endometrial Cancer Cell Lines
3.4. Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor PQR309 Induces Cell Cycle Arrest in Endometrial Cancer Cell Lines
3.5. Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor PQR309 Inhibits Mutant p53 and c-Myc in Endometrial Cancer Cell Lines
3.6. p53 Knockdown Decreases Cell Proliferation and Akt/mTOR Activity
3.7. p53 Knockdown Enhances PQR309-Inhibited Cell Viability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bafligil, C.; Thompson, D.J.; Lophatananon, A.; Smith, M.J.; Ryan, N.; Naqvi, A.; Evans, D.G.; Crosbie, E.J. Association between genetic polymorphisms and endometrial cancer risk: A systematic review. J. Med. Genet. 2020, 57, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzur, T.; Kessous, R.; Weintraub, A.Y. Current strategies in the diagnosis of endometrial cancer. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2017, 296, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, M.A.; Devesa, S.S.; Harvey, S.V.; Wentzensen, N. Hysterectomy-Corrected Uterine Corpus Cancer Incidence Trends and Differences in Relative Survival Reveal Racial Disparities and Rising Rates of Nonendometrioid Cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1895–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urick, M.E.; Bell, D.W. Clinical actionability of molecular targets in endometrial cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, M.; Yang, J.-X.; Cao, D.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.-M.; Yuan, Z.; Shen, K. Genomic Comparison of Endometrioid Endometrial Carcinoma and Its Precancerous Lesions in Chinese Patients by High-Depth Next Generation Sequencing. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janku, F.; Yap, T.A.; Meric-Bernstam, F. Targeting the PI3K pathway in cancer: Are we making headway? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicki, A.; Brown, N.; Xyrafas, A.; Bize, V.; Hawle, H.; Berardi, S.; Cmiljanović, N.; Cmiljanović, V.; Stumm, M.; Dimitrijević, S.; et al. First-in human, phase 1, dose-escalation pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the oral dual PI3K and mTORC1/2 inhibitor PQR309 in patients with advanced solid tumors (SAKK 67/13). Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 96, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaufils, F.; Cmiljanovic, N.; Cmiljanovic, V.; Bohnacker, T.; Melone, A.; Marone, R.; Jackson, E.; Zhang, X.; Sele, A.; Borsari, C.; et al. 5-(4,6-Dimorpholino-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-amine (PQR309), a Potent, Brain-Penetrant, Orally Bioavailable, Pan-Class I PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor as Clinical Candidate in Oncology. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 7524–7538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarantelli, C.; Gaudio, E.; Arribas, A.J.; Kwee, I.; Hillmann, P.; Rinaldi, A.; Cascione, L.; Spriano, F.; Bernasconi, E.; Guidetti, F.; et al. PQR309 Is a Novel Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor with Preclinical Antitumor Activity in Lymphomas as a Single Agent and in Combination Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 24, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, K.; Tang, X.J.; Xu, F.F.; Liu, J.H.; Tan, Y.Q.; Gao, L.; Sun, Q.; Ding, X.; Liu, B.H.; Chen, Q.X. PI3K/mTORC1/2 inhibitor PQR309 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in human glioblastoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 43, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsin, I.-L.; Hsu, J.-C.; Wu, W.-J.; Lu, H.-J.; Wu, M.-F.; Ko, J.-L. GMI, a fungal immunomodulatory protein from Ganoderma microsporum, induce apoptosis via β-catenin suppression in lung cancer cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2018, 33, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, L.-Y.; Hsin, I.-L.; Tsai, J.-N.; Chen, C.-J.; Ou, C.-C.; Wu, W.-J.; Sheu, G.-T.; Ko, J.-L. Combination treatment of Src inhibitor Saracatinib with GMI, a Ganoderma microsporum immunomodulatory protein, induce synthetic lethality via autophagy and apoptosis in lung cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsin, I.-L.; Chiu, L.-Y.; Ou, C.-C.; Wu, W.-J.; Sheu, G.-T.; Ko, J.-L. CD133 inhibition via autophagic degradation in pemetrexed-resistant lung cancer cells by GMI, a fungal immunomodulatory protein from Ganoderma microsporum. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 123, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsin, I.-L.; Chou, Y.-H.; Hung, W.-L.; Ko, J.-L.; Wang, P.-H. The Application of Arsenic Trioxide in Ameliorating ABT-737 Target Therapy on Uterine Cervical Cancer Cells through Unique Pathways in Cell Death. Cancers 2019, 12, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, Y.-T.; Hsu, W.-C.; Ou, C.-C.; Tai, H.-C.; Hsu, H.-T.; Yeh, K.-T.; Ko, J.-L. Metformin Mitigates Nickel-Elicited Angiopoietin-Like Protein 4 Expression via HIF-1α for Lung Tumorigenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sivalingam, V.; Latif, A.; Kitson, S.; McVey, R.; Finegan, K.; Marshall, K.; Lisanti, M.; Sotgia, F.; Stratford, I.J.; Crosbie, E.J. Hypoxia and hyperglycaemia determine why some endometrial tumours fail to respond to metformin. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 122, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klionsky, D.J.; Abdel-Aziz, A.K.; Abdelfatah, S.; Abdellatif, M.; Abdoli, A.; Abel, S.; Abeliovich, H.; Abildgaard, M.H.; Abudu, Y.P.; Acevedo-Arozena, A.; et al. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (4th edition)(1). Autophagy 2021, 17, 1–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Lu, L.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Jiang, P.; Chan, L.K.Y.; Zhang, T.; Yu, J.; Kwong, J.; et al. A novel miR-193a-5p-YY1-APC regulatory axis in human endometrioid endometrial adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3432–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, J.; Abisoye-Ogunniyan, A.; Metcalf, K.J.; Werb, Z. Concepts of extracellular matrix remodelling in tumour progression and metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peitzsch, C.; Tyutyunnykova, A.; Pantel, K.; Dubrovska, A. Cancer stem cells: The root of tumor recurrence and metastases. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2017, 44, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, B.; Beamon, J.; Balint, E.; Reisman, D. Transactivation of the human p53 tumor suppressor gene by c-Myc/Max contributes to elevated mutant p53 expression in some tumors. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 14, 7805–7815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pampalakis, G.; Sotiropoulou, G. Multiple mechanisms underlie the aberrant expression of the human kallikrein 6 gene in breast cancer. Biol. Chem. 2006, 387, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgrave, N.; Hill, A.D.K.; Young, L.S. Growth factor-dependent regulation of survivin by c-myc in human breast cancer. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 37, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, M.; Obata, T.; Daikoku, T.; Fujiwara, H. The Association and Significance of p53 in Gynecologic Cancers: The Potential of Targeted Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schultheis, A.M.; Martelotto, L.G.; De Filippo, M.R.; Piscuglio, S.; Ng, C.K.Y.; Hussein, Y.R.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Soslow, R.A.; Weigelt, B. TP53 Mutational Spectrum in Endometrioid and Serous Endometrial Cancers. Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 2016, 35, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weigelt, B.; Warne, P.H.; Lambros, M.B.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Downward, J. PI3K Pathway Dependencies in Endometrioid Endometrial Cancer Cell Lines. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 3533–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shoji, K.; Oda, K.; Kashiyama, T.; Ikeda, Y.; Nakagawa, S.; Sone, K.; Miyamoto, Y.; Hiraike, H.; Tanikawa, M.; Miyasaka, A.; et al. Genotype-Dependent Efficacy of a Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor, NVP-BEZ235, and an mTOR Inhibitor, RAD001, in Endometrial Carcinomas. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Wang, J.; Lee, K.Y.; Franco, H.L.; Broaddus, R.R.; Lydon, J.P.; Jeong, J.-W.; DeMayo, F.J. Effect of Conditional Pten Loss and Oncogenic K-ras Mutation on Endometrial Cancer Development Occurs via Decreased Progesterone Receptor Action. J. Oncol. 2009, 2010, 139087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Remmerie, M.; Janssens, V. Targeted Therapies in Type II Endometrial Cancers: Too Little, but Not Too Late. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ugi, S.; Imamura, T.; Maegawa, H.; Egawa, K.; Yoshizaki, T.; Shi, K.; Obata, T.; Ebina, Y.; Kashiwagi, A.; Olefsky, J.M. Protein Phosphatase 2A Negatively Regulates Insulin’s Metabolic Signaling Pathway by Inhibiting Akt (Protein Kinase B) Activity in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 8778–8789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, Y.-C.; Huang, K.-Y.; Yang, C.-H.; Yang, Y.-S.; Lee, W.-Y.; Chiang, C.-W. Regulation of phosphorylation of Thr-308 of Akt, cell proliferation, and survival by the B55α regulatory subunit targeting of the protein phosphatase 2A Holoenzyme to Akt. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 1882–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dikic, I.; Elazar, Z. Mechanism and medical implications of mammalian autophagy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayob, A.Z.; Ramasamy, T.S. Cancer stem cells as key drivers of tumour progression. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, P.; Xu, X.-Y. PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in cancer stem cells: From basic research to clinical application. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 1602–1609. [Google Scholar]
- Walcher, L.; Kistenmacher, A.-K.; Suo, H.; Kitte, R.; Dluczek, S.; Strauß, A.; Blaudszun, A.-R.; Yevsa, T.; Fricke, S.; Kossatz-Boehlert, U. Cancer Stem Cells—Origins and Biomarkers: Perspectives for Targeted Personalized Therapies. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zou, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, N.; Xu, W.; Cui, C.; Xing, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Activation of PI3K/Akt pathway by CD133-p85 interaction promotes tumorigenic capacity of glioma stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6829–6834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manoranjan, B.; Chokshi, C.; Venugopal, C.; Subapanditha, M.; Savage, N.; Tatari, N.; Provias, J.P.; Murty, N.K.; Moffat, J.; Doble, B.W.; et al. A CD133-AKT-Wnt signaling axis drives glioblastoma brain tumor-initiating cells. Oncogene 2020, 39, 1590–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herishanu, Y.; Gibellini, F.; Njuguna, N.; Hazan-Halevy, I.; Farooqui, M.; Bern, S.; Keyvanfar, K.; Lee, E.; Wilson, W.H.; Wiestner, A. Activation of CD44, a receptor for extracellular matrix components, protects chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells from spontaneous and drug induced apoptosis through MCL-1. Leuk. Lymphoma 2011, 52, 1758–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Sheng, Y.; Shi, X.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhang, G.; Gao, F. CD44/HA signaling mediates acquired resistance to a PI3Kα inhibitor. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Liu, H.; Qing, G. Targeting oncogenic Myc as a strategy for cancer treatment. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2018, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Fang, C.; Xu, H.; Xi, X. SALL4 as an Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Drug Resistance Inducer through the Regulation of c-Myc in Endometrial Cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muranen, T.; Selfors, L.; Hwang, J.; Gallegos, L.L.; Coloff, J.L.; Thoreen, C.C.; Kang, S.A.; Sabatini, D.M.; Mills, G.B.; Brugge, J.S. ERK and p38 MAPK Activities Determine Sensitivity to PI3K/mTOR Inhibition via Regulation of MYC and YAP. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 7168–7180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, J.; Yu, Q. Molecular mechanisms of tumor resistance to PI3K-mTOR-targeted therapy. Chin. J. Cancer 2013, 32, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alvarado-Ortiz, E.; de la Cruz-López, K.G.; Becerril-Rico, J.; Sarabia-Sánchez, M.A.; Ortiz-Sánchez, E.; García-Carrancá, A. Mutant p53 Gain-of-Function: Role in Cancer Development, Progression, and Therapeutic Approaches. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentino, E.; Bellazzo, A.; Di Minin, G.; Sicari, D.; Apollonio, M.; Scognamiglio, G.; Di Bonito, M.; Botti, G.; Del Sal, G.; Collavin, L. Mutant p53 potentiates the oncogenic effects of insulin by inhibiting the tumor suppressor DAB2IP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 7623–7628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yue, X.; Wu, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Boateng, M.; Mandava, K.; Zhang, C.; Feng, Z.; Gao, J.; Hu, W. Gain of function mutant p53 protein activates AKT through the Rac1 signaling to promote tumorigenesis. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 1338–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsin, I.-L.; Shen, H.-P.; Chang, H.-Y.; Ko, J.-L.; Wang, P.-H. Suppression of PI3K/Akt/mTOR/c-Myc/mtp53 Positive Feedback Loop Induces Cell Cycle Arrest by Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor PQR309 in Endometrial Cancer Cell Lines. Cells 2021, 10, 2916. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10112916
Hsin I-L, Shen H-P, Chang H-Y, Ko J-L, Wang P-H. Suppression of PI3K/Akt/mTOR/c-Myc/mtp53 Positive Feedback Loop Induces Cell Cycle Arrest by Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor PQR309 in Endometrial Cancer Cell Lines. Cells. 2021; 10(11):2916. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10112916
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsin, I-Lun, Huang-Pin Shen, Hui-Yi Chang, Jiunn-Liang Ko, and Po-Hui Wang. 2021. "Suppression of PI3K/Akt/mTOR/c-Myc/mtp53 Positive Feedback Loop Induces Cell Cycle Arrest by Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor PQR309 in Endometrial Cancer Cell Lines" Cells 10, no. 11: 2916. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10112916
APA StyleHsin, I. -L., Shen, H. -P., Chang, H. -Y., Ko, J. -L., & Wang, P. -H. (2021). Suppression of PI3K/Akt/mTOR/c-Myc/mtp53 Positive Feedback Loop Induces Cell Cycle Arrest by Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor PQR309 in Endometrial Cancer Cell Lines. Cells, 10(11), 2916. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10112916