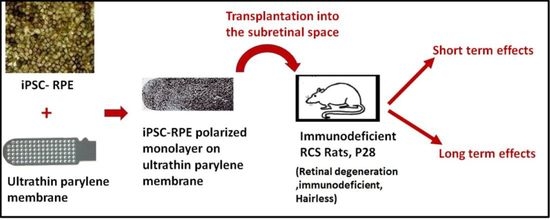
Long-Term Transplant Effects of iPSC-RPE Monolayer in Immunodeficient RCS Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Generated from iPSCs
2.2. Preparation of Polarized hESC-RPE Implant on Parylene Membranes
2.3. Immunostaining of iPSC-RPE on Parylene Membrane
2.4. Animals
2.5. Surgical Procedure
2.6. Histopathology
2.7. Superior Colliculus Electrophysiology
2.8. Optokinetic Testing
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Human iPSC-RPE Cells Can Grow as a Polarized Monolayer over Ultrathin Parylene Membrane and Demonstrate High-Purity and RPE Marker Expression
3.2. iPSC-RPE Implant Survival and Functionality Assessed by Short-Term in Vivo Experiments in Immunodeficient RCS Rats (1- and 4-Month Study)
3.3. In Vivo Assessment of Long-Term Transplant Effects in Immunodeficient RCS Rats (11 Month Study)
3.4. Preservation of Low Light Level Visual Responses in the Superior Colliculus (SC) of iPSC-RPE-Implanted Rats at 11-Month Post-Implantation
3.5. Optokinetic (OKN) Responses in iPSC-RPE-Implanted Rats
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foltz, L.P.; Clegg, D.O. Rapid, Directed Differentiation of Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells from Human Embryonic or Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2017, 128, e56274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klimanskaya, I.; Hipp, J.; Rezai, K.A.; West, M.; Atala, A.; Lanza, R. Derivation and Comparative Assessment of Retinal Pigment Epithelium from Human Embryonic Stem Cells Using Transcriptomics. Cloning Stem Cells 2004, 6, 217–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, R.D.; Wang, S.; Klimanskaya, I.; Holmes, T.; Ramos-Kelsey, R.; Lu, B.; Girman, S.; Bischoff, N.; Sauvé, Y.; Lanza, R. Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Cells Rescue Visual Function in Dystrophic RCS Rats. Cloning Stem Cells 2006, 8, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Idelson, M.; Alper, R.; Obolensky, A.; Ben-Shushan, E.; Hemo, I.; Yachimovich-Cohen, N.; Khaner, H.; Smith, Y.; Wiser, O.; Gropp, M.; et al. Directed Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells into Functional Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 5, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rowland, T.J.; Blaschke, A.J.; Buchholz, D.E.; Hikita, S.T.; Johnson, L.V.; Clegg, D.O. Differentiation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells to Retinal Pigmented Epithelium in Defined Conditions Using Purified Extracellular Matrix Proteins. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2013, 7, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazim, R.A.; Karumbayaram, S.; Jiang, M.; Dimashkie, A.; Lopes, V.S.; Li, D.; Burgess, B.L.; Vijayaraj, P.; Alva-Ornelas, J.A.; Zack, J.A.; et al. Differentiation of RPE Cells from Integration-Free IPS Cells and Their Cell Biological Characterization. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Antonio-Chronowska, A.; D’Antonio, M.; Frazer, K.A. In Vitro Differentiation of Human IPSC-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells (IPSC-RPE). Bio-Protocol 2019, 9, e3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, D.E.; Hikita, S.T.; Rowland, T.J.; Friedrich, A.M.; Hinman, C.R.; Johnson, L.V.; Clegg, D.O. Derivation of Functional Retinal Pigmented Epithelium from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 2427–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Khristov, V.; Rising, A.; Jha, B.S.; Dejene, R.; Hotaling, N.; Li, Y.; Stoddard, J.; Stankewicz, C.; Wan, Q.; et al. Clinical-Grade Stem Cell-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelium Patch Rescues Retinal Degeneration in Rodents and Pigs. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, S.D.; Tan, G.; Hosseini, H.; Nagiel, A. Subretinal Transplantation of Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelium for the Treatment of Macular Degeneration: An Assessment at 4 Years. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, ORSFc1–ORSFc9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, S.D.; Hubschman, J.-P.; Heilwell, G.; Franco-Cardenas, V.; Pan, C.K.; Ostrick, R.M.; Mickunas, E.; Gay, R.; Klimanskaya, I.; Lanza, R. Embryonic Stem Cell Trials for Macular Degeneration: A Preliminary Report. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2012, 379, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashani, A.H.; Lebkowski, J.S.; Rahhal, F.M.; Avery, R.L.; Salehi-Had, H.; Dang, W.; Lin, C.-M.; Mitra, D.; Zhu, D.; Thomas, B.B.; et al. A Bioengineered Retinal Pigment Epithelial Monolayer for Advanced, Dry Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Da Cruz, L.; Fynes, K.; Georgiadis, O.; Kerby, J.; Luo, Y.H.; Ahmado, A.; Vernon, A.; Daniels, J.T.; Nommiste, B.; Hasan, S.M.; et al. Phase 1 Clinical Study of an Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelium Patch in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mandai, M.; Watanabe, A.; Kurimoto, Y.; Hirami, Y.; Morinaga, C.; Daimon, T.; Fujihara, M.; Akimaru, H.; Sakai, N.; Shibata, Y.; et al. Autologous Induced Stem-Cell–Derived Retinal Cells for Macular Degeneration. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, B.; Thomas, P.; Thomas, B.; Ribeiro, R.; Hu, Y.; Brant, R.; Ahuja, A.; Zhu, D.; Liu, L.; Koss, M.; et al. Subretinal Implantation of Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells Derived from Human Embryonic Stem Cells: Improved Survival When Implanted as a Monolayer. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 5087–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, L.; Lu, B.; Zhu, D.; Ribeiro, R.; Diniz, B.; Thomas, P.B.; Ahuja, A.K.; Hinton, D.R.; Tai, Y.-C.; et al. A Novel Approach for Subretinal Implantation of Ultrathin Substrates Containing Stem Cell-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelium Monolayer. Ophthalmic Res. 2012, 48, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.B.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, L.; Thomas, P.B.; Hu, Y.; Nazari, H.; Stefanini, F.; Falabella, P.; Clegg, D.O.; Hinton, D.R.; et al. Survival and Functionality of HESC-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells Cultured as a Monolayer on Polymer Substrates Transplanted in RCS Rats. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 2877–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takagi, S.; Mandai, M.; Gocho, K.; Hirami, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Fujihara, M.; Sugita, S.; Kurimoto, Y.; Takahashi, M. Evaluation of Transplanted Autologous Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelium in Exudative Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmol. Retina 2019, 3, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugita, S.; Mandai, M.; Hirami, Y.; Takagi, S.; Maeda, T.; Fujihara, M.; Matsuzaki, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Iseki, K.; Hayashi, N.; et al. HLA-Matched Allogeneic IPS Cells-Derived RPE Transplantation for Macular Degeneration. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugita, S.; Iwasaki, Y.; Makabe, K.; Kamao, H.; Mandai, M.; Shiina, T.; Ogasawara, K.; Hirami, Y.; Kurimoto, Y.; Takahashi, M. Successful Transplantation of Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells from MHC Homozygote IPSCs in MHC-Matched Models. Stem Cell Rep. 2016, 7, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garber, K. RIKEN Suspends First Clinical Trial Involving Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 890–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanemura, H.; Go, M.J.; Shikamura, M.; Nishishita, N.; Sakai, N.; Kamao, H.; Mandai, M.; Morinaga, C.; Takahashi, M.; Kawamata, S. Tumorigenicity Studies of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (IPSC)-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) for the Treatment of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Su, B.; Jiao, L.; Xu, Z.-H.; Zhang, C.-J.; Nie, J.; Gao, M.-L.; Zhang, Y.V.; Jin, Z.-B. Transplantation of GMP-Grade Human IPSC-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells in Rodent Model: The First Pre-Clinical Study for Safety and Efficacy in China. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, E.; Jiao, C.; Kaalberg, E.; Cranston, C.; Mullins, R.; Stone, E.; Tucker, B. Allogenic IPSC-Derived RPE Cell Transplants Induce Immune Response in Pigs: A Pilot Study. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Westenskow, P.D.; Bucher, F.; Bravo, S.; Kurihara, T.; Feitelberg, D.; Paris, L.P.; Aguilar, E.; Lin, J.H.; Friedlander, M. IPSC-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelium Allografts Do Not Elicit Detrimental Effects in Rats: A Follow-Up Study. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Priore, L.V.D.; Ishida, O.; Johnson, E.W.; Sheng, Y.; Jacoby, D.B.; Geng, L.; Tezel, T.H.; Kaplan, H.J. Triple Immune Suppression Increases Short-Term Survival of Porcine Fetal Retinal Pigment Epithelium Xenografts. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 4044–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cooper, A.E.; Cho, J.-H.; Menges, S.; Masood, S.; Xie, J.; Yang, J.; Klassen, H. Immunosuppressive Treatment Can Alter Visual Performance in the Royal College of Surgeons Rat. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. Off. J. Assoc. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 32, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.B.; Zhu, D.; Lin, T.-C.; Kim, Y.C.; Seiler, M.J.; Martinez-Camarillo, J.C.; Lin, B.; Shad, Y.; Hinton, D.R.; Humayun, M.S. A New Immunodeficient Retinal Dystrophic Rat Model for Transplantation Studies Using Human-Derived Cells. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2018, 256, 2113–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maruotti, J.; Sripathi, S.R.; Bharti, K.; Fuller, J.; Wahlin, K.J.; Ranganathan, V.; Sluch, V.M.; Berlinicke, C.A.; Davis, J.; Kim, C.; et al. 30-Molecule–Directed, Efficient Generation of Retinal Pigment Epithelium from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 10950–10955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miyagishima, K.J.; Wan, Q.; Corneo, B.; Sharma, R.; Lotfi, M.R.; Boles, N.C.; Hua, F.; Maminishkis, A.; Zhang, C.; Blenkinsop, T.; et al. In Pursuit of Authenticity: Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelium for Clinical Applications. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 1562–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May-Simera, H.L.; Wan, Q.; Jha, B.S.; Hartford, J.; Khristov, V.; Dejene, R.; Chang, J.; Patnaik, S.; Lu, Q.; Banerjee, P.; et al. Primary Cilium-Mediated Retinal Pigment Epithelium Maturation Is Disrupted in Ciliopathy Patient Cells. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siminoff, R.; Schwassmann, H.O.; Kruger, L. An Electrophysiological Study of the Visual Projection to the Superior Colliculus of the Rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1966, 127, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koss, M.J.; Falabella, P.; Stefanini, F.R.; Pfister, M.; Thomas, B.B.; Kashani, A.H.; Brant, R.; Zhu, D.; Clegg, D.O.; Hinton, D.R.; et al. Subretinal Implantation of a Monolayer of Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelium: A Feasibility and Safety Study in Yucatán Minipigs. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch. Klin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2016, 254, 1553–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Xie, M.; Gademann, F.; Cao, J.; Wang, P.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Su, T.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J. Protective Effects of Human IPS-Derived Retinal Pigmented Epithelial Cells on Retinal Degenerative Disease. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujii, S.; Sugita, S.; Futatsugi, Y.; Ishida, M.; Edo, A.; Makabe, K.; Kamao, H.; Iwasaki, Y.; Sakaguchi, H.; Hirami, Y.; et al. A Strategy for Personalized Treatment of IPS-Retinal Immune Rejections Assessed in Cynomolgus Monkey Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, A.-J.; Vugler, A.A.; Hikita, S.T.; Lawrence, J.M.; Gias, C.; Chen, L.L.; Buchholz, D.E.; Ahmado, A.; Semo, M.; Smart, M.J.K.; et al. Protective Effects of Human IPS-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cell Transplantation in the Retinal Dystrophic Rat. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGill, T.J.; Stoddard, J.; Renner, L.M.; Messaoudi, I.; Bharti, K.; Mitalipov, S.; Lauer, A.; Wilson, D.J.; Neuringer, M. Allogeneic IPSC-Derived RPE Cell Graft Failure Following Transplantation into the Subretinal Space in Nonhuman Primates. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 1374–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ilmarinen, T.; Hiidenmaa, H.; Kööbi, P.; Nymark, S.; Sorkio, A.; Wang, J.-H.; Stanzel, B.V.; Thieltges, F.; Alajuuma, P.; Oksala, O.; et al. Ultrathin Polyimide Membrane as Cell Carrier for Subretinal Transplantation of Human Embryonic Stem Cell Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelium. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlstetter, M.; Scholz, R.; Rutar, M.; Wong, W.T.; Provis, J.M.; Langmann, T. Retinal Microglia: Just Bystander or Target for Therapy? Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2015, 45, 30–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekström, P.; Sanyal, S.; Narfström, K.; Chader, G.; Veen, T. Accumulation of Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein in Muller Radial Glia during Retinal Degeneration. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1988, 29, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar]
- Di Pierdomenico, J.; García-Ayuso, D.; Pinilla, I.; Cuenca, N.; Vidal-Sanz, M.; Agudo-Barriuso, M.; Villegas-Pérez, M.P. Early Events in Retinal Degeneration Caused by Rhodopsin Mutation or Pigment Epithelium Malfunction: Differences and Similarities. Front. Neuroanat. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Algvere, P.V.; Gouras, P.; Dafgård Kopp, E. Long-Term Outcome of RPE Allografts in Non-Immunosuppressed Patients with AMD. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 1999, 9, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, C.M.; Mason, S.; Pattwell, D.M.; Kent, D.; Grierson, I.; Williams, R. Replacement of the RPE Monolayer. Eye 2009, 23, 1910–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carlsson, E.; Supharattanasitthi, W.; Jackson, M.; Paraoan, L. Increased Rate of Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cell Migration and Pro-Angiogenic Potential Ensuing From Reduced Cystatin C Expression. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.; DiStefano, T.; Olabisi, R. The Influence of Substrate Modulus on Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2017, 105, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular Mechanisms of Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrer-vaquer, A.; Viotti, M.; Hadjantonakis, A.-K. Transitions between Epithelial and Mesenchymal States and the Morphogenesis of the Early Mouse Embryo. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2010, 4, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamiya, S.; Kaplan, H.J. Role of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy. Exp. Eye Res. 2016, 142, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Shang, P.; Terasaki, H.; Stepicheva, N.; Hose, S.; Yazdankhah, M.; Weiss, J.; Sakamoto, T.; Bhutto, I.A.; Xia, S.; et al. A Role for ΒA3/A1-Crystallin in Type 2 EMT of RPE Cells Occurring in Dry Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, AMD104–AMD113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, H.; Shan, C.; Ma, L.; Liu, J.; Yang, N.; Zhao, J. Polarity and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells in Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, D.Y.; Butcher, E.; Saint-Geniez, M. EMT and EndMT: Emerging Roles in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Geathers, J.S.; Grillo, S.L.; Weber, S.R.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Sundstrom, J.M. Role of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Retinal Pigment Epithelium Dysfunction. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Antibodies | Purpose | Manufacturer | Catalog No | Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRA-1-85 | Human marker | R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA | MAB3195 | 1:100 |
| RPE65 | RPE marker | Abcam | Ab231782 | 1:200 |
| Rhodopsin | Rods | Abcam | Ab3267 | 1:100 |
| CD68 | Microglia | Abcam | ab201340 | 1:300 |
| Vimentin | Mesenchymal marker | Abcam | ab137321 | 1:300 |
| GFAP | Reactive glial cells | Invitrogen | MA5-12023 | 1:500 |
| α Smooth muscle actin | Mesenchymal marker | Abcam | ab5694 | 1:250 |
| Goat anti-mouse IgG conjugated with Rhodamine | Secondary antibody | Jackson Immuno Research, West Grove, PA, USA | 115-025-146 | 1:500 |
| Goat anti-rabbit IgG conjugated with FITC | Secondary antibody | Abcam | Ab150081 | 1:500 |
| Ki67 | Proliferation marker | Abcam | Ab16667 | 1:500 |
| Donkey Anti-Mouse lgG H&L | Secondary Antibody | Abcam | Ab7003 | 1:500 |
| Donkey Anti-Rabbit lgG H&L | Secondary Antibody | Abcam | Ab150063 | 1:500 |
| iPSC-RPE Implant Status | RPE65 | Phagocytosis | Fibrosis/inflammation | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No cells or cells died | Presence of intact monolayer | Cells developed into clumps, no intact monolayer | ++ | + | − | ++ | + | − | ++ | + | − |
| 8 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 9 | 0 | 4 | 11 | 2 | 4 | 9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajendran Nair, D.S.; Zhu, D.; Sharma, R.; Martinez Camarillo, J.C.; Bharti, K.; Hinton, D.R.; Humayun, M.S.; Thomas, B.B. Long-Term Transplant Effects of iPSC-RPE Monolayer in Immunodeficient RCS Rats. Cells 2021, 10, 2951. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10112951
Rajendran Nair DS, Zhu D, Sharma R, Martinez Camarillo JC, Bharti K, Hinton DR, Humayun MS, Thomas BB. Long-Term Transplant Effects of iPSC-RPE Monolayer in Immunodeficient RCS Rats. Cells. 2021; 10(11):2951. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10112951
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajendran Nair, Deepthi S., Danhong Zhu, Ruchi Sharma, Juan Carlos Martinez Camarillo, Kapil Bharti, David R. Hinton, Mark S. Humayun, and Biju B. Thomas. 2021. "Long-Term Transplant Effects of iPSC-RPE Monolayer in Immunodeficient RCS Rats" Cells 10, no. 11: 2951. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10112951
APA StyleRajendran Nair, D. S., Zhu, D., Sharma, R., Martinez Camarillo, J. C., Bharti, K., Hinton, D. R., Humayun, M. S., & Thomas, B. B. (2021). Long-Term Transplant Effects of iPSC-RPE Monolayer in Immunodeficient RCS Rats. Cells, 10(11), 2951. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10112951