Progression of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPN): Diagnostic and Therapeutic Perspectives
Abstract
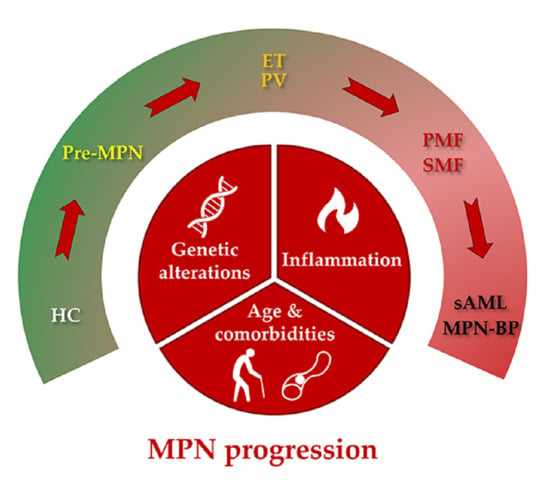
:1. Introduction
2. Types of MPN Progression
2.1. Clinically Evident Types of MPN Progression
2.2. Subclinical Types of MPN Progression
3. Etiology of MPN Progression
3.1. Genetic Risk Factors for MPN Progression
3.2. Inflammation
3.3. Age and Comorbidities
4. Clinical Risk Scores
5. Current MPN Diagnostic Landscape and New Directions
6. Novel Therapeutics Targeting MPN Progression
7. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kralovics, R.; Passamonti, F.; Buser, A.S.; Teo, S.-S.; Tiedt, R.; Passweg, J.R.; Tichelli, A.; Cazzola, M.; Skoda, R.C. A Gain-of-Function Mutation of JAK2 in Myeloproliferative Disorders. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1779–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pikman, Y.; Lee, B.H.; Mercher, T.; McDowell, E.; Ebert, B.L.; Gozo, M.; Cuker, A.; Wernig, G.; Moore, S.; Galinsky, I.; et al. MPLW515L Is a Novel Somatic Activating Mutation in Myelofibrosis with Myeloid Metaplasia. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, 1140–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klampfl, T.; Gisslinger, H.; Harutyunyan, A.S.; Nivarthi, H.; Rumi, E.; Milosevic, J.D.; Them, N.C.; Berg, T.; Gisslinger, B.; Pietra, D.; et al. Somatic Mutations of Calreticulin in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 2379–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vainchenker, W.; Kralovics, R. Genetic Basis and Molecular Pathophysiology of Classical Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Blood 2016, 129, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tefferi, A.; Vaidya, R.; Caramazza, D.; Finke, C.; Lasho, T.; Pardanani, A. Circulating Interleukin (IL)-8, IL-2R, IL-12, and IL-15 Levels Are Independently Prognostic in Primary Myelofibrosis: A Comprehensive Cytokine Profiling Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1356–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischman, A.G.; Aichberger, K.J.; Luty, S.B.; Bumm, T.G.; Petersen, C.L.; Doratotaj, S.; Vasudevan, K.B.; LaTocha, D.H.; Yang, F.; Press, R.D.; et al. TNFα Facilitates Clonal Expansion of JAK2V617F Positive Cells in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Blood 2011, 118, 6392–6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guy, A.; Gourdou-Latyszenok, V.; le Lay, N.; Peghaire, C.; Kilani, B.; Dias, J.V.; Duplaa, C.; Renault, M.A.; Denis, C.; Villeval, J.L.; et al. Vascular Endothelial Cell Expression of JAK2V617F Is Sufficient to Promote a Pro-Thrombotic State Due to Increased P-Selectin Expression. Haematologica 2019, 104, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guadall, A.; Lesteven, E.; Letort, G.; Toor, S.A.; Delord, M.; Pognant, D.; Brusson, M.; Verger, E.; Maslah, N.; Giraudier, S.; et al. Endothelial Cells Harbouring the JAK2 V617F Mutation Display Pro-Adherent and Pro-Thrombotic Features. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 1586–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gecht, J.; Tsoukakis, I.; Kricheldorf, K.; Stegelmann, F.; Klausmann, M.; Griesshammer, M.; Schulz, H.; Hollburg, W.; Göthert, J.R.; Sockel, K.; et al. Kidney Dysfunction Is Associated with Thrombosis and Disease Severity in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: Implications from the German Study Group for Mpn Bioregistry. Cancers 2021, 13, 4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, A.J.; Rampal, R.K.; Levine, R. Leukemia Secondary to Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Blood 2020, 136, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefferi, A.; Mudireddy, M.; Mannelli, F.; Begna, K.H.; Patnaik, M.M.; Hanson, C.A.; Ketterling, R.P.; Gangat, N.; Yogarajah, M.; de Stefano, V.; et al. Blast Phase Myeloproliferative Neoplasm: Mayo-AGIMM Study of 410 Patients from Two Separate Cohorts. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1200–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iurlo, A.; Cattaneo, D.; Gianelli, U. Blast Transformation in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: Risk Factors, Biological Findings, and Targeted Therapeutic Options. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cervantes, F.; Dupriez, B.; Pereira, A.; Passamonti, F.; Reilly, J.T.; Morra, E.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Mesa, R.A.; Demory, J.L.; Barosi, G.; et al. New Prognostic Scoring System for Primary Myelofibrosis Based on a Study of the International Working Group for Myelofibrosis Research and Treatment. Blood 2009, 113, 2895–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmelli, P.; Lasho, T.L.; Rotunno, G.; Mudireddy, M.; Mannarelli, C.; Nicolosi, M.; Pacilli, A.; Pardanani, A.; Rumi, E.; Rosti, V.; et al. MIPSS70: Mutation-Enhanced International Prognostic Score System for Transplantation-Age Patients with Primary Myelofibrosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbui, T.; Thiele, J.; Carobbio, A.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Tefferi, A. The Rate of Transformation from JAK2-Mutated et to PV Is Influenced by an Accurate WHO-Defined Clinico-Morphological Diagnosis. Leukemia 2015, 29, 992–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefferi, A.; Barbui, T. Polycythemia Vera and Essential Thrombocythemia: 2019 Update on Diagnosis, Risk-Stratification and Management. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carobbio, A.; Guglielmelli, P.; Rumi, E.; Cavalloni, C.; de Stefano, V.; Betti, S.; Rambaldi, A.; Finazzi, M.C.; Thiele, J.; Vannucchi, A.M.; et al. A Multistate Model of Survival Prediction and Event Monitoring in Prefibrotic Myelofibrosis. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraco, D.; Cerquozzi, S.; Gangat, N.; Patnaik, M.M.; Lasho, T.; Finke, C.; Hanson, C.A.; Ketterling, R.P.; Pardanani, A.; Tefferi, A. Monocytosis in Polycythemia Vera: Clinical and Molecular Correlates. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boiocchi, L.; Gianelli, U.; Iurlo, A.; Fend, F.; Bonzheim, I.; Cattaneo, D.; Knowles, D.M.; Orazi, A. Neutrophilic Leukocytosis in Advanced Stage Polycythemia Vera: Hematopathologic Features and Prognostic Implications. Mod. Pathol. 2015, 28, 1448–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tefferi, A.; Dingli, D.; Li, C.Y.; Dewald, G.W. Prognostic Diversity among Cytogenetic Abnormalities in Myelofibrosis with Myeloid Metaplasia. Cancer 2005, 104, 1656–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrieux, J.; Demory, J.L.; Caulier, M.T.; Agape, P.; Wetterwald, M.; Bauters, F.; Laï, J.L. Karyotypic Abnormalities in Myelofibrosis Following Polycythemia Vera. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2003, 140, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.S.; Nussenzveig, R.M.; Popat, U.; Bueso-Ramos, C.E.; Thomas, D.A.; Cortes, J.A.; Champlin, R.E.; Ciurea, S.E.; Manshouri, T.; Pierce, S.M.; et al. The Natural History and Treatment Outcome of Blast Phase BCR-ABL—Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Blood 2008, 112, 1628–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdulkarim, K.; Girodon, F.; Johansson, P.; Maynadié, M.; Kutti, J.; Carli, P.M.; Bovet, E.; Andréasson, B. AML Transformation in 56 Patients with Ph- MPD in Two Well Defined Populations. Eur. J. Haematol. 2009, 82, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucchi, A.M.; Pieri, L.; Guglielmelli, P. JAK2 Allele Burden in the Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: Effects on Phenotype, Prognosis and Change with Treatment. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2011, 2, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Passamonti, F.; Rumi, E.; Pietra, D.; Elena, C.; Boveri, E.; Arcaini, L.; Roncoroni, E.; Astori, C.; Merli, M.; Boggi, S.; et al. A Prospective Study of 338 Patients with Polycythemia Vera: The Impact of JAK2 (V617F) Allele Burden and Leukocytosis on Fibrotic or Leukemic Disease Transformation and Vascular Complications. Leukemia 2010, 24, 1574–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grinfeld, J.; Nangalia, J.; Green, A.R. Molecular Determinants of Pathogenesis and Clinical Phenotype in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Haematologica 2017, 102, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rampal, R.; Ahn, J.; Abdel-Wahaba, O.; Nahas, M.; Wang, K.; Lipson, D.; Otto, G.A.; Yelensky, R.; Hricik, T.; McKenney, A.S.; et al. Genomic and Functional Analysis of Leukemic Transformation of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E5401–E5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tefferi, A.; Lasho, T.L.; Finke, C.M.; Elala, Y.; Hanson, C.A.; Ketterling, R.P.; Gangat, N.; Pardanani, A. Targeted Deep Sequencing in Primary Myelofibrosis. Blood Adv. 2016, 1, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McNamara, C.J.; Panzarella, T.; Kennedy, J.A.; Arruda, A.; Claudio, J.O.; Daher-Reyes, G.; Ho, J.; Siddiq, N.; Devlin, R.; Tsui, H.; et al. The Mutational Landscape of Accelerated- and Blast-Phase Myeloproliferative Neoplasms Impacts Patient Outcomes. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 2658–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guglielmelli, P.; Lasho, T.L.; Rotunno, G.; Score, J.; Mannarelli, C.; Pancrazzi, A.; Biamonte, F.; Pardanani, A.; Zoi, K.; Reiter, A.; et al. The Number of Prognostically Detrimental Mutations and Prognosis in Primary Myelofibrosis: An International Study of 797 Patients. Leukemia 2014, 28, 1804–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinfeld, J.; Nangalia, J.; Baxter, E.J.; Wedge, D.C.; Angelopoulos, N.; Cantrill, R.; Godfrey, A.L.; Papaemmanuil, E.; Gundem, G.; MacLean, C.; et al. Classification and Personalized Prognosis in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1416–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefferi, A.; Guglielmelli, P.; Nicolosi, M.; Mannelli, F.; Mudireddy, M.; Bartalucci, N.; Finke, C.M.; Lasho, T.L.; Hanson, C.A.; Ketterling, R.P.; et al. GIPSS: Genetically Inspired Prognostic Scoring System for Primary Myelofibrosis. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1631–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cordua, S.; Kjaer, L.; Skov, V.; Pallisgaard, N.; Hasselbalch, H.C.; Ellervik, C. Prevalence and Phenotypes of JAK2 V617F and Calreticulin Mutations in a Danish General Population. Blood 2019, 134, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, N.; Lee, J.; Moore, L.; Baxter, E.J.; Hewinson, J.; Dawson, K.J.; Menzies, A.; Godfrey, A.L.; Green, A.R.; Campbell, P.J.; et al. Phylogenetic Reconstruction of Myeloproliferative Neoplasm Reveals Very Early Origins and Lifelong Evolution. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barosi, G.; Tefferi, A.; Besses, C.; Birgegard, G.; Cervantes, F.; Finazzi, G.; Gisslinger, H.; Griesshammer, M.; Harrison, C.; Hehlmann, R.; et al. Clinical End Points for Drug Treatment Trials in BCR-ABL1-Negative Classic Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: Consensus Statements from European LeukemiaNET (ELN) and Internation Working Group-Myeloproliferative Neoplasms Research and Treatment (IWG-MRT). Leukemia 2015, 29, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tefferi, A.; Guglielmelli, P.; Larson, D.R.; Finke, C.; Wassie, E.A.; Pieri, L.; Gangat, N.; Fjerza, R.; Belachew, A.A.; Lasho, T.L.; et al. Long-Term Survival and Blast Transformation in Molecularly Annotated Essential Thrombocythemia, Polycythemia Vera, and Myelofibrosis. Blood 2014, 124, 2507–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venney, D.; Mohd-Sarip, A.; Mills, K.I. The Impact of Epigenetic Modifications in Myeloid Malignancies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucchi, A.M.; Lasho, T.L.; Guglielmelli, P.; Biamonte, F.; Pardanani, A.; Pereira, A.; Finke, C.; Score, J.; Gangat, N.; Mannarelli, C.; et al. Mutations and Prognosis in Primary Myelofibrosis. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, S.; Faisal, M.; Büsche, G.; Schlue, J.; Hasemeier, B.; Schipper, E.; Vogtmann, J.; Westphal, L.; Lehmann, U.; Kreipe, H. Mutations Associated with Age-Related Clonal Hematopoiesis in PMF Patients with Rapid Progression to Myelofibrosis. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klampfl, T.; Harutyunyan, A.; Berg, T.; Gisslinger, B.; Schalling, M.; Bagienski, K.; Olcaydu, D.; Passamonti, F.; Rumi, E.; Pietra, D.; et al. Genome Integrity of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms in Chronic Phase and during Disease Progression. Blood 2011, 118, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatain, N.; Koschmieder, S.; Jost, E. Role of Inflammatory Factors during Disease Pathogenesis and Stem Cell Transplantation in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Cancers 2020, 12, 2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zuo, X. Cytokines Frequently Implicated in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Cytokine X 2019, 1, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allain-Maillet, S.; Bosseboeuf, A.; Mennesson, N.; Bostoën, M.; Dufeu, L.; Choi, E.H.; Cleyrat, C.; Mansier, O.; Lippert, E.; Le Bris, Y.; et al. Anti-Glucosylsphingosine Autoimmunity, JAK2V617F-Dependent Interleukin-1β and JAK2V617F-Independent Cytokines in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Cancers 2020, 12, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øbro, N.F.; Grinfeld, J.; Belmonte, M.; Irvine, M.; Shepherd, M.S.; Rao, T.N.; Karow, A.; Riedel, L.M.; Harris, O.B.; Baxter, E.J.; et al. Longitudinal Cytokine Profiling Identifies GRO-α and EGF as Potential Biomarkers of Disease Progression in Essential Thrombocythemia. HemaSphere 2020, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermouet, S.; Bigot-Corbel, E.; Gardie, B. Pathogenesis of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: Role and Mechanisms of Chronic Inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm 2015, 2015, 145293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hasselbalch, H.C.; Bjørn, M.E. MPNs as Inflammatory Diseases: The Evidence, Consequences, and Perspectives. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 102476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kleppe, M.; Kwak, M.; Koppikar, P.; Riester, M.; Keller, M.; Bastian, L.; Hricik, T.; Bhagwat, N.; McKenney, A.S.; Papalexi, E.; et al. JAK-STAT Pathway Activation in Malignant and Nonmalignant Cells Contributes to MPN Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Response. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vener, C.; Novembrino, C.; Bamonti Catena, F.; Fracchiolla, N.S.; Gianelli, U.; Savi, F.; Radaelli, F.; Fermo, E.; Cortelezzi, A.; Lonati, S.; et al. Oxidative Stress Is Increased in Primary and Post-Polycythemia Vera Myelofibrosis. Exp. Hematol. 2010, 38, 1058–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty, C.; Lacout, C.; Droin, N.; le Couédic, J.-P.; Ribrag, V.; Solary, E.; Vainchenker, W.; Villeval, J.-L.; Plo, I. A Role for Reactive Oxygen Species in JAK2 V617F Myeloproliferative Neoplasm Progression. Leukemia 2013, 27, 2187–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nieborowska-Skorska, M.; Maifrede, S.; Dasgupta, Y.; Sullivan, K.; Flis, S.; Le, B.V.; Solecka, M.; Belyaeva, E.A.; Kubovcakova, L.; Nawrocki, M.; et al. Ruxolitinib-Induced Defects in DNA Repair Cause Sensitivity to PARP Inhibitors in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Blood 2017, 130, 2848–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rai, S.; Hansen, N.; Hao-Shen, H.; Dirnhofer, S.; Tata, N.R.; Skoda, R.C. IL-1β Secreted from Mutant Cells Carrying JAK2-V617Ffavors Early Clonal Expansion and Promotes MPN Disease Initiation and Progression. Blood 2019, 134, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arranz, L.; del Mar Arriero, M.; Villatoro, A. Interleukin-1β as Emerging Therapeutic Target in Hematological Malignancies and Potentially in Their Complications. Blood Rev. 2017, 31, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaifie, A.; Kirschner, M.; Wolf, D.; Maintz, C.; Hänel, M.; Gattermann, N.; Gökkurt, E.; Platzbecker, U.; Hollburg, W.; Göthert, J.R.; et al. Bleeding, Thrombosis, and Anticoagulation in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPN): Analysis from the German SAL-MPN-Registry. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fowles, J.S.; How, J.; Allen, M.J.; Oh, S.T. Young versus Old Age at Diagnosis Confers Distinct Genomic Profiles in Patients with Polycythemia Vera. Leukemia 2019, 33, 1522–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, B.L.; Saraf, S.; Sobol, U.; Halpern, A.; Shammo, J.; Rondelli, D.; Michaelis, L.; Odenike, O.; Rademaker, A.; Zakarija, A.; et al. Age-Related Differences in Disease Characteristics and Clinical Outcomes in Polycythemia Vera. Leuk. Lymphoma 2013, 54, 1989–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, E.K.; Chung, K.W.; Chung, S.; Lee, B.; Seo, A.Y.; Chung, J.H.; Jung, Y.S.; Im, E.; et al. Redefining Chronic Inflammation in Aging and Age-Related Diseases: Proposal of the Senoinflammation Concept. Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Christensen, A.S.; Møller, J.B.; Hasselbalch, H.C. Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with the Philadelphia-Negative Chronic Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Leuk. Res. 2014, 38, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucijanic, M.; Galusic, D.; Krecak, I.; Sedinic, M.; Holik, H.; Perisa, V.; Moric Peric, M.; Zekanovic, I.; Stoos-Veic, T.; Kusec, R. Reduced Renal Function Strongly Affects Survival and Thrombosis in Patients with Myelofibrosis. Ann. Hematol. 2020, 99, 2779–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benevolo, G.; Elli, E.M.; Bartoletti, D.; Latagliata, R.; Tiribelli, M.; Heidel, F.H.; Cavazzini, F.; Bonifacio, M.; Crugnola, M.; Binotto, G.; et al. Impact of Comorbidities and Body Mass Index on the Outcome of Polycythemia Vera Patients. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, T.N.; Hansen, N.; Hilfiker, J.; Rai, S.; Majewska, J.M.; Leković, D.; Gezer, D.; Andina, N.; Galli, S.; Cassel, T.; et al. JAK2-Mutant Hematopoietic Cells Display Metabolic Alterations That Can Be Targeted to Treat Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Blood 2019, 134, 1832–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbui, T.; Barosi, G.; Birgegard, G.; Cervantes, F.; Finazzi, G.; Griesshammer, M.; Harrison, C.; Hasselbalch, H.C.; Hehlmann, R.; Hoffman, R.; et al. Philadelphia-Negative Classical Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: Critical Concepts and Management Recommendations from European LeukemiaNet. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Passamonti, F.; Thiele, J.; Girodon, F.; Rumi, E.; Carobbio, A.; Gisslinger, H.; Kvasnicka, H.M.; Ruggeri, M.; Randi, M.L.; Gangat, N.; et al. A Prognostic Model to Predict Survival in 867 World Health Organization-Defined Essential Thrombocythemia at Diagnosis: A Study by the International Working Group on Myelofibrosis Research and Treatment. Blood 2012, 120, 1197–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbui, T.; Finazzi, G.; Carobbio, A.; Thiele, J.; Passamonti, F.; Rumi, E.; Ruggeri, M.; Rodeghiero, F.; Randi, M.L.; Bertozzi, I.; et al. Development and Validation of an International Prognostic Score of Thrombosis in World Health Organization-Essential Thrombocythemia (IPSET-Thrombosis). Blood 2012, 120, 5128–5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tefferi, A.; Guglielmelli, P.; Lasho, T.L.; Coltro, G.; Finke, C.M.; Loscocco, G.G.; Sordi, B.; Szuber, N.; Rotunno, G.; Pacilli, A.; et al. Mutation-Enhanced International Prognostic Systems for Essential Thrombocythaemia and Polycythaemia Vera. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tefferi, A.; Rumi, E.; Finazzi, G.; Gisslinger, H.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Rodeghiero, F.; Randi, M.L.; Vaidya, R.; Cazzola, M.; Rambaldi, A.; et al. Survival and Prognosis among 1545 Patients with Contemporary Polycythemia Vera: An International Study. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1874–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Passamonti, F.; Cervantes, F.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Morra, E.; Rumi, E.; Cazzola, M.; Tefferi, A. Dynamic International Prognostic Scoring System (DIPSS) Predicts Progression to Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Primary Myelofibrosis. Blood 2010, 116, 2857–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gangat, N.; Caramazza, D.; Vaidya, R.; George, G.; Begna, K.; Schwager, S.; van Dyke, D.; Hanson, C.; Wu, W.; Pardanani, A.; et al. DIPSS plus: A Refined Dynamic International Prognostic Scoring System for Primary Myelofibrosis That Incorporates Prognostic Information from Karyotype, Platelet Count, and Transfusion Status. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tefferi, A.; Guglielmelli, P.; Lasho, T.L.; Gangat, N.; Ketterling, R.P.; Pardanani, A.; Vannucchi, A.M. MIPSS70+ Version 2.0: Mutation and Karyotype-Enhanced International Prognostic Scoring System for Primary Myelofibrosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1769–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palandri, F.; Palumbo, G.A.; Iurlo, A.; Polverelli, N.; Benevolo, G.; Breccia, M.; Abruzzese, E.; Tiribelli, M.; Bonifacio, M.; Tieghi, A.; et al. Differences in Presenting Features, Outcome and Prognostic Models in Patients with Primary Myelofibrosis and Post-Polycythemia Vera and/or Post-Essential Thrombocythemia Myelofibrosis Treated with Ruxolitinib. New Perspective of the MYSEC-PM in a Large Mu. Semin. Hematol. 2018, 55, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagelmann, N.; Ditschkowski, M.; Bogdanov, R.; Bredin, S.; Robin, M.; Cassinat, B.; Shahswar, R.; Thol, F.; Heuser, M.; Socié, G.; et al. Comprehensive Clinical-Molecular Transplant Scoring System for Myelofibrosis Undergoing Stem Cell Transplantation. Blood 2019, 133, 2233–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, A.L.; Hasselbalch, H.C. Antecedent Cardiovascular Disease and Autoimmunity in Philadelphia-Negative Chronic Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Leuk. Res. 2016, 41, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enblom, A.; Lindskog, E.; Hasselbalch, H.; Hersby, D.; Bak, M.; Tetu, J.; Girodon, F.; Andréasson, B. High Rate of Abnormal Blood Values and Vascular Complications before Diagnosis of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 26, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordua, S.; Kjaer, L.; Skov, V.; Pallisgaard, N.; Kefala, M.; Gjerdrum, L.M.R.; Hasselbalch, H.C.; Ellervik, C. Early Detection of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms in a Danish General Population Study. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2706–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magome, T.; Froelich, J.; Holtan, S.G.; Takahashi, Y.; Verneris, M.R.; Brown, K.; Dusenbery, K.; Wong, J.; Hui, S.K. Whole-Body Distribution of Leukemia and Functional Total Marrow Irradiation Based on FLT-PET and Dual-Energy CT. Mol. Imaging 2017, 16, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slot, S.; van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; Otten, R.H.J.; Boden, B.J.H.; Zijlstra, J.; Raijmakers, P.G.H.M.; Zweegman, S. The Value of Bone Marrow, Liver, and Spleen Imaging in Diagnosis, Prognostication, and Follow-up Monitoring of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: A Systematic Review. Cancer Imaging 2021, 21, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofias, A.M.; de Lorenzi, F.; Peña, Q.; Azadkhah Shalmani, A.; Vucur, M.; Wang, J.-W.; Kiessling, F.; Shi, Y.; Consolino, L.; Storm, G.; et al. Therapeutic and Diagnostic Targeting of Fibrosis in Metabolic, Proliferative and Viral Disorders. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 113831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derlin, T.; Alchalby, H.; Bannas, P.; Veldhoen, S.; Apostolova, I.; Triviai, I.; Bengel, F.M.; Kröger, N. Assessment of Bone Marrow Inflammation in Patients with Myelofibrosis: An 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT Study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 42, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vercellino, L.; Ouvrier, M.J.; Barré, E.; Cassinat, B.; de Beco, V.; Dosquet, C.; Chevret, S.; Meignin, V.; Chomienne, C.; Toubert, M.E.; et al. Assessing Bone Marrow Activity in Patients with Myelofibrosis: Results of a Pilot Study of 18F-FLT PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, A.; Hofman, M.; Hicks, R. Clinical Impact of Haematopoiesis Imaging with 18F-Fluorothymidine (FLT) PET/CT in Patients with Hematologic Disorders or Bone Marrow Compartment Involvement. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58 (Suppl. 1), 186. [Google Scholar]
- Nishida, Y.; Matsue, Y.; Suehara, Y.; Fukumoto, K.; Fujisawa, M.; Takeuchi, M.; Ouchi, E.; Matsue, K. Clinical and Prognostic Significance of Bone Marrow Abnormalities in the Appendicular Skeleton Detected by Low-Dose Whole-Body Multidetector Computed Tomography in Patients with Multiple Myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2015, 5, e329–e339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buhl, E.M.; Djudjaj, S.; Klinkhammer, B.M.; Ermert, K.; Puelles, V.G.; Lindenmeyer, M.T.; Cohen, C.D.; He, C.; Borkham-Kamphorst, E.; Weiskirchen, R.; et al. Dysregulated Mesenchymal PDGFR-β Drives Kidney Fibrosis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2020, 12, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polasek, M.; Yang, Y.; Schühle, D.T.; Yaseen, M.A.; Kim, Y.R.; Sung, Y.S.; Guimaraes, A.R.; Caravan, P. Molecular MR Imaging of Fibrosis in a Mouse Model of Pancreatic Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrison, C.; Kiladjian, J.-J.; Al-Ali, H.K.; Gisslinger, H.; Waltzman, R.; Stalbovskaya, V.; McQuitty, M.; Hunter, D.S.; Levy, R.; Knoops, L.; et al. JAK Inhibition with Ruxolitinib versus Best Available Therapy for Myelofibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.E. Disease Modifying Agents of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: A Review. Blood Res. 2021, 56, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masarova, L.; Yin, C.C.; Cortes, J.E.; Konopleva, M.; Borthakur, G.; Newberry, K.J.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Bueso-Ramos, C.E.; Verstovsek, S. Histomorphological Responses after Therapy with Pegylated Interferon α-2a in Patients with Essential Thrombocythemia (ET) and Polycythemia Vera (PV). Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiladjian, J.J.; Cassinat, B.; Chevret, S.; Turlure, P.; Cambier, N.; Roussel, M.; Bellucci, S.; Grandchamp, B.; Chomienne, C.; Fenaux, P. Pegylated Interferon-Alfa-2a Induces Complete Hematologic and Molecular Responses with Low Toxicity in Polycythemia Vera. Blood 2008, 112, 3065–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintás-Cardama, A.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Manshouri, T.; Kilpivaara, O.; Cortes, J.; Roupie, A.L.; Zhang, S.J.; Harris, D.; Estrov, Z.; Kantarjian, H.; et al. Molecular Analysis of Patients with Polycythemia Vera or Essential Thrombocythemia Receiving Pegylated Interferon α-2a. Blood 2013, 122, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Austin, R.J.; Straube, J.; Bruedigam, C.; Pali, G.; Jacquelin, S.; Vu, T.; Green, J.; Gräsel, J.; Lansink, L.; Cooper, L.; et al. Distinct Effects of Ruxolitinib and Interferon-Alpha on Murine JAK2V617F Myeloproliferative Neoplasm Hematopoietic Stem Cell Populations. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1075–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.Y.; Won, J.H. The Clinical Role of Interferon Alpha in Philadelphia-Negative Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Blood Res. 2021, 56, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, A.L.; Mikkelsen, S.U.; Knudsen, T.A.; Bjørn, M.E.; Andersen, C.L.; Bjerrum, O.W.; Brochmann, N.; Patel, D.A.; Rahbek Gjerdrum, L.M.; Fassi, D.; et al. Ruxolitinib and Interferon-A2 Combination Therapy for Patients with Polycythemia Vera or Myelofibrosis: A Phase II Study. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2262–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiladjian, J.-J.; Soret-Dulphy, J.; Resche-Rigon, M.; Boyer-Perrard, F.; Barraco, F.; Rolland-Neyret, V.; Capron, C.; Chevret, S.; Giraudier, S.; Cassinat, B. Ruxopeg, a Multi-Center Bayesian Phase 1/2 Adaptive Randomized Trial of the Combination of Ruxolitinib and Pegylated Interferon Alpha 2a in Patients with Myeloproliferative Neoplasm (MPN)-Associated Myelofibrosis. Blood 2018, 132, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jutzi, J.S.; Kleppe, M.; Dias, J.; Staehle, H.F.; Shank, K.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Gambheer, S.M.M.; Dierks, C.; Rienhoff, H.Y.; Levine, R.L.; et al. LSD1 Inhibition Prolongs Survival in Mouse Models of Mpn by Selectively Targeting the Disease Clone. HemaSphere 2018, 2, e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Liao, G.; Yu, B. LSD1/KDM1A Inhibitors in Clinical Trials: Advances and Prospects. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baumeister, J.; Maié, T.; Chatain, N.; Gan, L.; Weinbergerova, B.; de Toledo, M.A.S.; Eschweiler, J.; Maurer, A.; Mayer, J.; Kubesova, B.; et al. Early and Late Stage MPN Patients Show Distinct Gene Expression Profiles in CD34+ Cells. Ann. Hematol. 2021, 100, 2943–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascarenhas, J.; Harrison, C.; Luptakova, K.; Christo, J.; Wang, J.; Mertz, J.A.; Colak, G.; Shao, J.; Bobba, S.; Trojer, P.; et al. MANIFEST-2, a Global, Phase 3, Randomized, Double-Blind, Active-Control Study of CPI-0610 and Ruxolitinib vs. Placebo and Ruxolitinib in JAK-Inhibitor-Naive Myelofibrosis Patients. Blood 2020, 136, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Jia, Y.-N.; Yu, B.; Liu, H.-M. Medicinal Chemistry Strategies for the Development of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase SHP2 Inhibitors and PROTAC Degraders. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 204, 112657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handlos Grauslund, J.; Holmström, M.O.; Jørgensen, N.G.; Klausen, U.; Weis-Banke, S.E.; el Fassi, D.; Schöllkopf, C.; Clausen, M.B.; Gjerdrum, L.M.R.; Breinholt, M.F.; et al. Therapeutic Cancer Vaccination With a Peptide Derived From the Calreticulin Exon 9 Mutations Induces Strong Cellular Immune Responses in Patients With CALR-Mutant Chronic Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, L.M.; Zeiser, R. Immunotherapy in Myeloproliferative Diseases. Cells 2020, 9, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.; Chen, C.; Kundra, A.; Kodali, S.; Pandey, A.; Wong, C.; Cheung, T.; Gotlieb, V.; Joseph, G.; Tribie, S. Programmed Cell Death Receptor (PD-1) Ligand (PD-L1) Expression in Philadelphia Chromosome-Negative Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Leuk. Res. 2019, 79, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proia, D.A.; Kaufmann, G.F. Targeting Heat-Shock Protein 90 (HSP90) as a Complementary Strategy to Immune Checkpoint Blockade for Cancer Therapy. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mbofung, R.M.; McKenzie, J.A.; Malu, S.; Zhang, M.; Peng, W.; Liu, C.; Kuiatse, I.; Tieu, T.; Williams, L.; Devi, S.; et al. HSP90 Inhibition Enhances Cancer Immunotherapy by Upregulating Interferon Response Genes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Zhao, L.; Loos, F.; Marty, C.; Xie, W.; Martins, I.; Lachkar, S.; Qu, B.; Waeckel-Énée, E.; Plo, I.; et al. Immunosuppression by Mutated Calreticulin Released from Malignant Cells. Mol. Cell 2020, 77, 748–760.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancet, J.E.; Uy, G.L.; Cortes, J.E.; Newell, L.F.; Lin, T.L.; Ritchie, E.K.; Stuart, R.K.; Strickland, S.A.; Hogge, D.; Solomon, S.R.; et al. Cpx-351 (Cytarabine and Daunorubicin) Liposome for Injection versus Conventional Cytarabine plus Daunorubicin in Older Patients with Newly Diagnosed Secondary Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2684–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrone, C.K.; Blydt-Hansen, M.; Rauh, M.J. Age-Associated TET2 Mutations: Common Drivers of Myeloid Dysfunction, Cancer and Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Egeren, D.; Escabi, J.; Nguyen, M.; Liu, S.; Reilly, C.R.; Patel, S.; Kamaz, B.; Kalyva, M.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Galinsky, I.; et al. Reconstructing the Lineage Histories and Differentiation Trajectories of Individual Cancer Cells in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28, 514–523.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kröger, N.M.; Deeg, J.H.; Olavarria, E.; Niederwieser, D.; Bacigalupo, A.; Barbui, T.; Rambaldi, A.; Mesa, R.; Tefferi, A.; Griesshammer, M.; et al. Indication and Management of Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation in Primary Myelofibrosis: A Consensus Process by an EBMT/ELN International Working Group. Leukemia 2015, 29, 2126–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinaccio, C.; Suraneni, P.; Celik, H.; Volk, A.; Wen, Q.J.; Ling, T.; Bulic, M.; Lasho, T.; Koche, R.P.; Famulare, C.A.; et al. Lkb1/Stk11 Is a Tumor Suppressor in the Progression of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 1398–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| MPN subtype ⇨ | ET | PV | PMF/SMF | ||||||||||||||
| Risk score ⇨ Parameter ⇩ | Conventional/ELN [61] | IPSET [62] | IPSET-thrombosis [63] | MIPSS-ET [64] | Conventional/ELN [61] | IPSS for PV [65] | MIPSS-PV [64] | IPSS [13] | DIPSS [66] | DIPSS+ [67] | MIPSS70 [14] | MIPSS70+ [14] | MIPSS70+ v2 [68] | GIPSS [32] | MYSEC (→ sMF) [69] | MTSS (→ transplant) [70] | |
| Age | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Sex | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Clinical | Leukocytes | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||
| Hemoglobin/RBC | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||
| Blasts in peripheral blood | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||
| Platelets | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||
| Constitutional symptoms | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||
| Transfusion demand | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Thrombosis history | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||
| Cardiovascular risk factors | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Bone marrow fibrosis | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| HLA-mismatched unrelated donor | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Karnofsky performance status | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| (Cyto-) Genetic | JAK2V617F present or MPL/CALR absent | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||
| Adverse/HMR mutations | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||
| Unfavorable karyotype | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||
| VHR karyotype | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Cytogenetic risk variable | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Time of creation (from early to recent): |  |  |  | * | ** | ||||||||||||
| Type | Inhibitor | MPN Subtype | Phase | NCT Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kinase inhibitors | Fedratinib | MF | 3 | NCT03755518 |
| Pacritinib | MF | 3 | NCT03165734 | |
| Parsaclisib+Ruxolitinib | MF | 3 | NCT04551066 | |
| Ruxolitinib Phosphate | MF | 2 | NCT01787487 | |
| Ruxolitinib plus Enasidenib | MF | 2 | NCT04281498 | |
| TL-895 | MF | 2 | NCT04655118 | |
| Itacitinib | MF | 2 | NCT04629508 | |
| Fostamatinib | MF | 2 | NCT04543279 | |
| LNK01002 | MF | 1 | NCT04896112 | |
| Ruxolitinib | PV | 2 | NCT04644211 | |
| Ruxolitinib | ET | 2 | NCT04644211 | |
| Ruxolitinib | ET/PV | 2 | NCT02577926 | |
| PI3K inhibitors | Parsaclisib plus Ruxolitinib | MF | 3 | NCT04551066 |
| Parsaclisib plus Ruxolitinib | MF | 3 | NCT04551053 | |
| BCL2 inhibitors | Navitoclax | MF | 3 | NCT04472598 |
| Navitoclax | MF | 3 | NCT04468984 | |
| Navitoclax | MF | 2 | NCT03222609 | |
| Palcitoclax | MF | 1/2 | NCT04354727 | |
| BET inhibitors | Pelabresib | MF | 3 | NCT04603495 |
| Pelabresib | MF | 2 | NCT02158858 | |
| ABBV-744 | MF | 1 | NCT04454658 | |
| INCB057643 | MF | 1 | NCT04279847 | |
| INCB057643 | MF | 1 | NCT04279847 | |
| Telomerase inhibitors | Imetelstat | MF | 3 | NCT04576156 |
| SMAD inhibitors | Luspatercept | MF | 3 | NCT04717414 |
| Luspatercept | MF | 3 | NCT04064060 | |
| Luspatercept | MF | 2 | NCT03194542 | |
| MDM2 inhibitor | Navtemadlin (KRT-232) | MF | 3 | NCT03662126 |
| Navtemadlin (KRT-232) or TL-895 | MF | 2 | NCT04878003 | |
| Navtemadlin (KRT-232) or TL-895 | MF | 1/2 | NCT04640532 | |
| Navtemadlin (KRT-232) or TL-895 | MF | 1/2 | NCT04485260 | |
| Immune modulators | Thalidomide plus Ruxolitinib | MF | 2 | NCT03069326 |
| Fusion proteins | Tagraxofusp | MF | 2 | NCT02268253 |
| XPO inhibitors | Selinexor | MF | 2 | NCT04562870 |
| Selinexor | MF | 1/2 | NCT04562389 | |
| Antibodies | Elotuzumab | MF | 2 | NCT04517851 |
| GSK3 inhibitors | 9-ING-41 | MF | 2 | NCT04218071 |
| LOXL2 inhibitors | GB2064 | MF | 2 | NCT04679870 |
| Cytostatics | Decitabine | MF | 2 | NCT04282187 |
| Selumetinib/Azacitidine | MF | 1 | NCT03326310 | |
| Interferons | Ropeginterferon | MF | 2 | NCT02370329 |
| Ropeginterferon | ET | 3 | NCT04285086 | |
| Liposomal drugs | CPX-351 plus Ruxolitinib | MF | 1/2 | NCT03878199 |
| ALK2 inhibitors | INCB000928 | MF | 1/2 | NCT04455841 |
| HSP90 inhibitors | PU-H71 | MF | 1 | NCT03935555 |
| PIM inhibitors | TP-3654 | MF | 1 | NCT04176198 |
| LSD1 inhibitors | Bomedemstat | PV | 2 | NCT04262141 |
| Bomedemstat | ET | 2 | NCT04254978 | |
| Bomedemstat | ET | 2 | NCT04081220 | |
| Bomedemstat | ET | 2 | NCT04262141 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baumeister, J.; Chatain, N.; Sofias, A.M.; Lammers, T.; Koschmieder, S. Progression of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPN): Diagnostic and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cells 2021, 10, 3551. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123551
Baumeister J, Chatain N, Sofias AM, Lammers T, Koschmieder S. Progression of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPN): Diagnostic and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cells. 2021; 10(12):3551. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123551
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaumeister, Julian, Nicolas Chatain, Alexandros Marios Sofias, Twan Lammers, and Steffen Koschmieder. 2021. "Progression of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPN): Diagnostic and Therapeutic Perspectives" Cells 10, no. 12: 3551. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123551
APA StyleBaumeister, J., Chatain, N., Sofias, A. M., Lammers, T., & Koschmieder, S. (2021). Progression of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPN): Diagnostic and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cells, 10(12), 3551. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123551