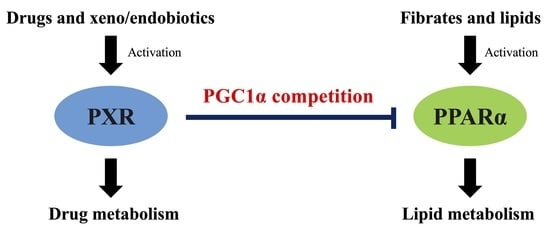
PXR Suppresses PPARα-Dependent HMGCS2 Gene Transcription by Inhibiting the Interaction between PPARα and PGC1α
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Plasmid Preparation
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. qRT-PCR
2.5. Reporter Assays
2.6. Mammalian Two-Hybrid Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. PXR Ligand Treatment Downregulates PPARα Target Gene Expression
3.2. PXR Suppresses the PPARα-Dependent Gene Transcription
3.3. PXR Competes with PPARα for PGC1α Binding
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Timsit, Y.E.; Negishi, M. CAR and PXR: The xenobiotic-sensing receptors. Steroids 2007, 72, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.-M.; Ong, S.S.; Chai, S.C.; Chen, T. Role of CAR and PXR in xenobiotic sensing and metabolism. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2012, 8, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shizu, R.; Otsuka, Y.; Ezaki, K.; Ishii, C.; Arakawa, S.; Amaike, Y.; Abe, T.; Hosaka, T.; Sasaki, T.; Kanno, Y.; et al. Antiepileptic drug-activated constitutive androstane receptor inhibits peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1alpha-dependent gene expression to increase blood triglyceride levels. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 98, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougarne, N.; Weyers, B.; Desmet, S.J.; Deckers, J.; Ray, D.W.; Staels, B.; De Bosscher, K. Molecular actions of PPARα in lipid metabolism and inflammation. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 760–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berger, J.; Moller, D.E. The Mechanisms of Action of PPARs. Annu. Rev. Med. 2002, 53, 409–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okamura, M.; Shizu, R.; Hosaka, T.; Sasaki, T.; Yoshinari, K. Possible involvement of the competition for the transcriptional coactivator glucocorticoid receptor-interacting protein 1 in the inflammatory signal-dependent suppression of PXR-mediated CYP3A induction in vitro. Drug Metab. Pharm. 2019, 34, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barretto, S.A.; Lasserre, F.; Fougerat, A.; Smith, L.; Fougeray, T.; Lukowicz, C.; Polizzi, A.; Smati, S.; Regnier, M.; Naylies, C.; et al. Gene expression profiling reveals that PXR activation inhibits hepatic PPARalpha activity and decreases FGF21 secretion in male C57Bl6/J mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, K.; Moore, R.; Negishi, M.; Sueyoshi, T. Nuclear pregnane X receptor cross-talk with FoxA2 to mediate drug-induced regulation of lipid metabolism in fasting mouse liver. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 9768–9776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shizu, R.; Nishiguchi, H.; Tashiro, S.; Sato, T.; Sugawara, A.; Kanno, Y.; Hosaka, T.; Sasaki, T.; Yoshinari, K. Helix 12 stabilization contributes to basal transcriptional activity of PXR. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 100978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, S.; Ozalp, C.; Fang, S.; Xiang, L.; Kemper, J.K. Ligand-activated pregnane X receptor interferes with HNF-4 signaling by targeting a common coactivator PGC-1alpha. Functional implications in hepatic cholesterol and glucose metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 45139–45147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Chiang, J.Y. Mechanism of rifampicin and pregnane X receptor inhibition of human cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase gene transcription. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005, 288, G74–G84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miao, J.; Fang, S.; Bae, Y.; Kemper, J.K. Functional inhibitory cross-talk between constitutive androstane receptor and hepatic nuclear factor-4 in hepatic lipid/glucose metabolism is mediated by competition for binding to the DR1 motif and to the common coactivators, GRIP-1 and PGC-1alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 14537–14546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orans, J.; Teotico, D.G.; Redinbo, M.R. The nuclear xenobiotic receptor pregnane X receptor: Recent insights and new challenges. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 19, 2891–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyrsova, L.; Smutny, T.; Carazo, A.; Moravcik, S.; Mandikova, J.; Trejtnar, F.; Gerbal-Chaloin, S.; Pavek, P. The pregnane X receptor down-regulates organic cation transporter 1 (SLC22A1) in human hepatocytes by competing for (“squelching”) SRC-1 coactivator. Br. J. Pharm. 2016, 173, 1703–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saini, S.P.S.; Mu, Y.; Gong, H.; Toma, D.; Uppal, H.; Ren, S.; Li, S.; Poloyac, S.M.; Xie, W. Dual role of orphan nuclear receptor pregnane X receptor in bilirubin detoxification in mice. Hepatology 2005, 41, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlak, M.; Lefebvre, P.; Staels, B. Molecular mechanism of PPARα action and its impact on lipid metabolism, inflammation and fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 720–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kassam, A.; Winrow, C.J.; Fernandez-Rachubinski, F.; Capone, J.P.; Rachubinski, R.A. The peroxisome proliferator response element of the gene encoding the peroxisomal beta-oxidation enzyme enoyl-CoA hydratase/3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase is a target for constitutive androstane receptor beta/9-cis-retinoic acid receptor-mediated transactivation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 4345–4350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moore, J.T.; Moore, L.B.; Maglich, J.M.; Kliewer, S.A. Functional and structural comparison of PXR and CAR. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1619, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouabdi, S.; Gibson, G.; Plant, N. Transcriptional regulation of the PXR gene: Identification and characterization of a functional peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha binding site within the proximal promoter of PXR. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2006, 34, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buler, M.; Aatsinki, S.M.; Skoumal, R.; Hakkola, J. Energy sensing factors PGC-1alpha and SIRT1 modulate PXR expression and function. Biochem. Pharm. 2011, 82, 2008–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Burk, O.; Klumpp, B.; Kandel, B.A.; Damm, G.; Weiss, T.S.; Klein, K.; Schwab, M.; Zanger, U.M. Direct transcriptional regulation of human hepatic cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα). Mol. Pharmacol. 2013, 83, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.; Winter, S.; Klumpp, B.; Turpeinen, M.; Klein, K.; Schwab, M.; Zanger, U.M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha, PPARα, directly regulates transcription of cytochrome P450 CYP2C8. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Zhai, Y.; Mu, Y.; Gong, H.; Uppal, H.; Toma, D.; Ren, S.; Evans, R.M.; Xie, W. A Novel pregnane X receptor-mediated and sterol regulatory element-binding protein-independent lipogenic pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 15013–15020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Gao, J.; Xu, M.; Ren, S.; Stefanovic-Racic, M.; O’Doherty, R.M.; Xie, W. PXR ablation alleviates diet-induced and genetic obesity and insulin resistance in mice. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1876–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Hu, B.; Huang, M.; Xie, W.; Zhai, Y. Activation of human stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase 1 contributes to the lipogenic effect of PXR in HepG2 cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khogali, A.M.; Chazan, B.I.; Metcalf, V.J.; Ramsay, J.H.R. Hyperlipidaemia as a complication of rifampicin treatment. Tubercle 1974, 55, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnhaus, E.E.; Kirchhof, B.; Peheim, E. Effect of enzyme induction on plasma lipids using antipyrine, phenobarbital, and rifampicin. Clin. Pharm. 1979, 25, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, J.C.; Kothari, H.V.; Genthe, T.M.; Lee, W.H.; Poirier, K.J.; Sawyer, W.K.; Mugrage, B.; Traxler, P.; Veenstra, S.; Grim, M.; et al. Effect of a novel series of macrocyclic hypolipidemic agents on plasma lipid and lipoprotein levels of four non-primate species. Atherosclerosis 1992, 96, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shizu, R.; Ezaki, K.; Sato, T.; Sugawara, A.; Hosaka, T.; Sasaki, T.; Yoshinari, K. PXR Suppresses PPARα-Dependent HMGCS2 Gene Transcription by Inhibiting the Interaction between PPARα and PGC1α. Cells 2021, 10, 3550. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123550
Shizu R, Ezaki K, Sato T, Sugawara A, Hosaka T, Sasaki T, Yoshinari K. PXR Suppresses PPARα-Dependent HMGCS2 Gene Transcription by Inhibiting the Interaction between PPARα and PGC1α. Cells. 2021; 10(12):3550. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123550
Chicago/Turabian StyleShizu, Ryota, Kanako Ezaki, Takumi Sato, Ayaka Sugawara, Takuomi Hosaka, Takamitsu Sasaki, and Kouichi Yoshinari. 2021. "PXR Suppresses PPARα-Dependent HMGCS2 Gene Transcription by Inhibiting the Interaction between PPARα and PGC1α" Cells 10, no. 12: 3550. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123550
APA StyleShizu, R., Ezaki, K., Sato, T., Sugawara, A., Hosaka, T., Sasaki, T., & Yoshinari, K. (2021). PXR Suppresses PPARα-Dependent HMGCS2 Gene Transcription by Inhibiting the Interaction between PPARα and PGC1α. Cells, 10(12), 3550. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123550