Orphan Nuclear Receptor Nur77 Mediates the Lethal Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Therapeutic Efficacy of Cryptomeridiol in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
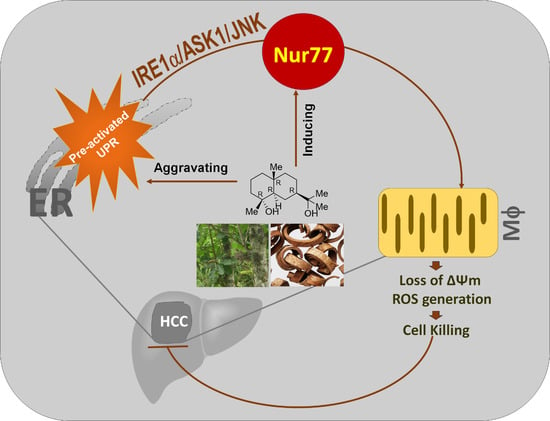
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Antibodies
2.2. Isolation and Identification of Cryptomeridiol (Bkh126)
2.3. Cell Culture and Transfection
2.4. Crispr/Cas9-Mediated Gene Knockout
2.5. Cell Apoptosis Assays
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Immunohistochemistry
2.8. Co-Immunoprecipitation Assays
2.9. Measurement of Intracellular ROS Levels
2.10. Measurement of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP) with Fluorescent JC-1
2.11. Animal Experiments
2.12. Ethics Statement
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bkh126 Induces HCC Cell Apoptosis Dependent on Nur77 Induction
3.2. Bkh126-Induced Apoptosis Is Associated with Its Activation of IRE1α and ASK1
3.3. Bkh126 Induces Nur77-Mediated ROS Production and Mitochondrial Dysfunction
3.4. Bkh126 Induces ASK1-JNK-Dependent Nur77 Mitochondrial Translocation
3.5. Bkh126 Induces Bax Activation and Mitochondrial Dysfunction
3.6. Anti-HCC Activity of Bkh126 In Vivo
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, P.; Chandra, V.; Rastinejad, F. Structural overview of the nuclear receptor superfamily: Insights into physiology and therapeutics. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72, 247–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- To, S.K.; Zeng, J.Z.; Wong, A.S. Nur77: A potential therapeutic target in cancer. Expert Opin. Targets 2012, 16, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Z.; Wen, Q.; Wang, W.J.; He, J.P.; Wu, Q. The orphan nuclear receptor TR3/Nur77 regulates ER stress and induces apoptosis via interaction with TRAPgamma. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 1600–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Huang, J.; Liu, J.; He, F.; Wen, F.; Yang, C.; Wang, W.; Wu, T.; Zhao, T.; Yao, J.; et al. Discovery of a Nur77-mediated cytoplasmic vacuolation and paraptosis inducer (4-PQBH) for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 121, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.K. Targeting Nur77 translocation. Expert Opin. Targets 2007, 11, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kolluri, S.K.; Gu, J.; Dawson, M.I.; Cao, X.; Hobbs, P.D.; Lin, B.; Chen, G.; Lu, J.; Lin, F.; et al. Cytochrome c release and apoptosis induced by mitochondrial targeting of nuclear orphan receptor TR3. Science 2000, 289, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fumoto, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Hirose, F.; Osumi, T. Orphan nuclear receptor Nur77 accelerates the initial phase of adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells by promoting mitotic clonal expansion. J. Biochem. 2007, 141, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Qin, L.; Zhao, D.; Tan, X.; Manseau, E.J.; Van Hoang, M.; Senger, D.R.; Brown, L.F.; Nagy, J.A.; Dvorak, H.F. Orphan nuclear receptor TR3/Nur77 regulates VEGF-A–induced angiogenesis through its transcriptional activity. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Lopez-Moyado, I.F.; Seo, H.; Lio, C.J.; Hempleman, L.J.; Sekiya, T.; Yoshimura, A.; Scott-Browne, J.P.; Rao, A. NR4A transcription factors limit CAR T cell function in solid tumours. Nature 2019, 567, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crean, D.; Murphy, E.P. Targeting NR4A Nuclear Receptors to Control Stromal Cell Inflammation, Metabolism, Angiogenesis, and Tumorigenesis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 589770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Calvo, R.; Tajes, M.; Vazquez-Carrera, M. The NR4A subfamily of nuclear receptors: Potential new therapeutic targets for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Expert Opin. Targets 2017, 21, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Cao, X.; Jiang, M.M.; Qiu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Chen, L.; Qin, B.; Wu, H.; Jiang, F.; Chen, J.; et al. Inhibition of beta-catenin signaling by nongenomic action of orphan nuclear receptor Nur77. Oncogene 2012, 31, 2653–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, S.S.; Sun, Z.; Lin, B.; Lang, Y.Y.; He, J.Y.; Cao, X.; Yan, T.; Wang, L.; et al. Modulation of orphan nuclear receptor Nur77-mediated apoptotic pathway by acetylshikonin and analogues. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8871–8880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hetz, C.; Papa, F.R. The Unfolded Protein Response and Cell Fate Control. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hetz, C.; Zhang, K.; Kaufman, R.J. Mechanisms, regulation and functions of the unfolded protein response. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urra, H.; Dufey, E.; Avril, T.; Chevet, E.; Hetz, C. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and the Hallmarks of Cancer. Trends Cancer 2016, 2, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Qiao, S.; Xiang, Y.; Cui, M.; Yao, X.; Lin, R.; Zhang, X. Endoplasmic reticulum stress: Multiple regulatory roles in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed Pharm. 2021, 142, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.W.; Wang, Z.M.; Sun, S.M.; Su, Y.; Li, Z.H.; Shao, J.J.; Tan, S.Z.; Chen, A.P.; Wang, S.J.; Zhang, Z.L.; et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and protein degradation in chronic liver disease. Pharm. Res. 2020, 161, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flessa, C.M.; Kyrou, I.; Nasiri-Ansari, N.; Kaltsas, G.; Papavassiliou, A.G.; Kassi, E.; Randeva, H.S. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Autophagy in the Pathogenesis of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Current Evidence and Perspectives. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2021, 10, 134–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Fang, D. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Signaling and the Pathogenesis of Hepatocarcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wu, H.; Yu, X.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y.; Fan, J.; Tang, L.; Wang, Z. A review of the phytochemistry and pharmacological activities of Magnoliae officinalis cortex. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 236, 412–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Lee, Y.M.; Lee, C.-K.; Jung, J.K.; Han, S.B.; Hong, J.T. Therapeutic applications of compounds in the Magnolia family. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 130, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Hamid, N.M.; Abass, S.A.; Mohamed, A.A.; Hamid, D.M. Herbal management of hepatocellular carcinoma through cutting the pathways of the common risk factors. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 1246–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.R.; Qiu, H.C.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.T. Herbal medicine offered as an initiative therapeutic option for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, V.U.; Farooqui, T.A.; Fiw, K.; Sultana, A.U.; Khatoon, R. Three new eudesmane sesquiterpenes from Pluchea arguta. J. Nat. Prod. 1992, 55, 730–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, N.; Calitz, C.; Thanapirom, K.; Mazza, G.; Rombouts, K.; Gerwins, P.; Heindryckx, F. Inhibiting IRE1alpha-endonuclease activity decreases tumor burden in a mouse model for hepatocellular carcinoma. eLife 2020, 9, e55865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Xiang, L.; Huang, S.; Jin, L.; Zhou, G.; Zhuge, L.; Li, J.; Fan, H.; Zhou, L.; Pan, C.; et al. IRE1alpha-XBP1 signaling pathway regulates IL-6 expression and promotes progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 4729–4736. [Google Scholar]
- Sumida, Y.; Yoneda, M. Current and future pharmacological therapies for NAFLD/NASH. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 362–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrison, S.A.; Wong, V.W.; Okanoue, T.; Bzowej, N.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Younes, Z.; Kohli, A.; Sarin, S.; Caldwell, S.H.; Alkhouri, N.; et al. Selonsertib for patients with bridging fibrosis or compensated cirrhosis due to NASH: Results from randomized phase III STELLAR trials. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Würthner, F.; Kaiser, T.E.; Saha-Möller, C.R. J-aggregates: From serendipitous discovery to supramolecular engineering of functional dye materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3376–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wu, J.F.; Zhan, Y.Y.; Chen, H.Z.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wu, Q. Regulation of the orphan receptor TR3 nuclear functions by c-Jun N terminal kinase phosphorylation. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.; Kolluri, S.K.; Lin, F.; Liu, W.; Han, Y.H.; Cao, X.; Dawson, M.I.; Reed, J.C.; Zhang, X.K. Conversion of Bcl-2 from protector to killer by interaction with nuclear orphan receptor Nur77/TR3. Cell 2004, 116, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forner, A.; Reig, M.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2018, 391, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haber, P.K.; Puigvehi, M.; Castet, F.; Lourdusamy, V.; Montal, R.; Tabrizian, P.; Buckstein, M.; Kim, E.; Villanueva, A.; Schwartz, M.; et al. Evidence-Based Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials (2002–2020). Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 879–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.F.; Liu, Z.P.; Wang, F.P. Natural sesquiterpenoids as cytotoxic anticancer agents. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imarisio, C.; Alchera, E.; Bangalore Revanna, C.; Valente, G.; Follenzi, A.; Trisolini, E.; Boldorini, R.; Carini, R. Oxidative and ER stress-dependent ASK1 activation in steatotic hepatocytes and Kupffer cells sensitizes mice fatty liver to ischemia/reperfusion injury. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 112, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.C.; Zhao, Z.B.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Y.B.; Qiu, C.; Mao, L.H.; Hu, J.J.; Cai, D.; Liu, Y.; Gong, J.P.; et al. Epigenetic silencing of GCH1promotes hepatocellular carcinoma growth by activating superoxide anion-mediated ASK1/p38 signaling via inhibiting tetrahydrobiopterin de novo biosynthesis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 168, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, S.B.; Skytte, D.M.; Denmeade, S.R.; Dionne, C.; Moller, J.V.; Nissen, P.; Isaacs, J.T. A Trojan horse in drug development: Targeting of thapsigargins towards prostate cancer cells. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 276–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ni, Z.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; Nie, Y.; Fan, D. Tunicamycin specifically aggravates ER stress and overcomes chemoresistance in multidrug-resistant gastric cancer cells by inhibiting N-glycosylation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boudreau, M.W.; Duraki, D.; Wang, L.; Mao, C.; Kim, J.E.; Henn, M.A.; Tang, B.; Fanning, S.W.; Kiefer, J.; Tarasow, T.M.; et al. A small-molecule activator of the unfolded protein response eradicates human breast tumors in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabf1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.-L.; Chen, H.-Z.; Yang, P.-B.; Li, Y.-P.; Zhang, F.-N.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Wang, W.-J.; Zhao, W.-X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Q.-T. Nur77 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma via switching glucose metabolism toward gluconeogenesis through attenuating phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase sumoylation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Song, X.; Liu, G.; Li, R.; Xie, J.; Xiao, L.; Du, M.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, X.; Gan, X. Involvement of TR3/Nur77 translocation to the endoplasmic reticulum in ER stress-induced apoptosis. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 2833–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, A.A.; Elrod, J.W. Mediating ER-mitochondrial cross-talk. Science 2017, 358, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Hou, L.; Sun, J.; Wang, W.; Li, H.; Yang, W.; Rong, P.; Nan, T.; Kang, L.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and metabolites of glycosides and lignans of the stem bark of Magnolia officinalis in functional dyspepsia and normal rats using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2022, 45, 3663–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Xie, Q.; Wang, J.; Huang, L.; Guo, X.; Fan, Y. Combination of urine and faeces metabolomics to reveal the intervention mechanism of Polygala tenuifolia compatibility with Magnolia officinalis on gastrointestinal motility disorders. J. Pharm. Pharm. 2021, 73, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J.; Lai, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhen, T.; Hu, H.; Gao, X.; Wong, A.S.T.; Zeng, J.-Z. Orphan Nuclear Receptor Nur77 Mediates the Lethal Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Therapeutic Efficacy of Cryptomeridiol in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells 2022, 11, 3870. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11233870
Li X, Chen Q, Liu J, Lai S, Zhang M, Zhen T, Hu H, Gao X, Wong AST, Zeng J-Z. Orphan Nuclear Receptor Nur77 Mediates the Lethal Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Therapeutic Efficacy of Cryptomeridiol in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells. 2022; 11(23):3870. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11233870
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xudan, Quancheng Chen, Jie Liu, Shenjin Lai, Minda Zhang, Tidong Zhen, Hongyu Hu, Xiang Gao, Alice S. T. Wong, and Jin-Zhang Zeng. 2022. "Orphan Nuclear Receptor Nur77 Mediates the Lethal Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Therapeutic Efficacy of Cryptomeridiol in Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Cells 11, no. 23: 3870. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11233870
APA StyleLi, X., Chen, Q., Liu, J., Lai, S., Zhang, M., Zhen, T., Hu, H., Gao, X., Wong, A. S. T., & Zeng, J. -Z. (2022). Orphan Nuclear Receptor Nur77 Mediates the Lethal Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Therapeutic Efficacy of Cryptomeridiol in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells, 11(23), 3870. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11233870