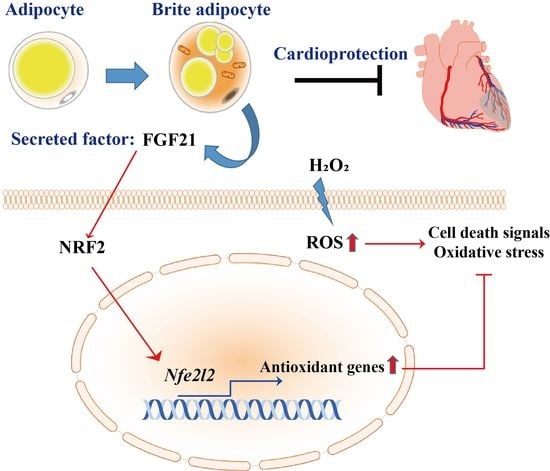
Brite Adipocyte FGF21 Attenuates Cardiac Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rat Hearts by Modulating NRF2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Experiments
2.2. RNA Sequencing and Data Analysis
2.3. H9c2 Cell Culture and ROS Induction
2.4. Transient Nrf2 Knockdown
2.5. Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity Assays
2.6. Adipocyte Differentiation and CM Preparation
2.7. Oil Red O (ORO) Staining
2.8. Adipokine Array
2.9. Nuclear Extraction
2.10. Western Blot Analysis
2.11. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) and Cell Death PathFinder RT2 ProfilerTM PCR Expression Array
2.12. Flow Cytometry
2.13. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.14. TUNEL Staining
2.15. Immunohistochemical Staining
2.16. Heart Function Assessment
2.17. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Transcriptome Analysis of Myocardial IR Injury in Rat Hearts
3.2. HBAC Differentiation for IR Rat Heart Therapy
3.3. Effects of Beige Adipocyte Secretions on Cardiomyocytes under Oxidative Stress
3.4. Regulation of Multiple Cell Death Signals by Beige Adipocyte Secretions in Cardiomyocytes under Oxidative Stress
3.5. Identification of Adipocyte Secretion Factors and Regulation of Cardiomyocytes after Injury
3.6. Effect of Treatment with the Beige Adipocyte Secretion Factor FGF21 on Cardiomyocytes under Oxidative Stress
3.7. Effect of Beige Adipocyte Secretions on IR Rat Hearts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yellon, D.M.; Hausenloy, D.J. Myocardial reperfusion injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1121–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibanez, B.; Heusch, G.; Ovize, M.; Van de Werf, F. Evolving therapies for myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 1454–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abbate, A.; Bussani, R.; Amin, M.S.; Vetrovec, G.W.; Baldi, A. Acute myocardial infarction and heart failure: Role of apoptosis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 38, 1834–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buja, L.M. Myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2005, 14, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zweier, J.L.; Talukder, M.A. The role of oxidants and free radicals in reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 70, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cadenas, S. ROS and redox signaling in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and cardioprotection. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 117, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.; Lu, Y.; Xin, L.; Gao, J.; Shang, C.; Jiang, Z.; Lin, H.; Fang, X.; Qu, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Role of Oxidative Stress in Reperfusion following Myocardial Ischemia and Its Treatments. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6614009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsumata, Y.; Shinmura, K.; Sugiura, Y.; Tohyama, S.; Matsuhashi, T.; Ito, H.; Yan, X.; Ito, K.; Yuasa, S.; Ieda, M.; et al. Endogenous prostaglandin D2 and its metabolites protect the heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury by activating Nrf2. Hypertension 2014, 63, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kensler, T.W.; Wakabayashi, N.; Biswal, S. Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007, 47, 89–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q. Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dodson, M.; de la Vega, M.R.; Cholanians, A.B.; Schmidlin, C.J.; Chapman, E.; Zhang, D.D. Modulating NRF2 in Disease: Timing Is Everything. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 59, 555–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, Z.; Wang, X.; Sun, C.; Kang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Hui, Y. Adipose-derived stem cells: Sources, potency, and implications for regenerative therapies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 114, 108765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ma, T.; Sun, J.; Shen, M.; Xue, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z. Harnessing the secretome of adipose-derived stem cells in the treatment of ischemic heart diseases. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautiainen, S.; Laaksonen, T.; Koivuniemi, R. Angiogenic Effects and Crosstalk of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells and Their Extracellular Vesicles with Endothelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceicao, G.; Matos, J.; Miranda-Silva, D.; Goncalves, N.; Sousa-Mendes, C.; Goncalves, A.; Ferreira, R.; Leite-Moreira, A.F.; Vitorino, R.; Falcao-Pires, I. Fat Quality Matters: Distinct Proteomic Signatures Between Lean and Obese Cardiac Visceral Adipose Tissue Underlie its Differential Myocardial Impact. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 54, 384–400. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Gao, E.; Xu, X.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. Adiponectin determines farnesoid X receptor agonism-mediated cardioprotection against post-infarction remodelling and dysfunction. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 1335–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.S.; Zhu, B.; Luo, A.L.; Yang, L.; Yang, C. The Role of Cardiokines in Heart Diseases: Beneficial or Detrimental? BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8207058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Senesi, P.; Luzi, L.; Terruzzi, I. Adipokines, Myokines, and Cardiokines: The Role of Nutritional Interventions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Leung, P.S. Fibroblast growth factor 21: A regulator of metabolic disease and health span. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 313, E292–E302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Jia, W.; Man, K.; Lo, C.M.; Wang, Y.; Lam, K.S.; Xu, A. Fibroblast growth factor 21 protects against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by potentiating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor coactivator protein-1alpha-mediated antioxidant capacity in mice. Hepatology 2014, 60, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Bai, F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Zou, D.; Qu, S.; Tian, G.; Song, L.; Zhang, T.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF21) protects mouse liver against D-galactose-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis via activating Nrf2 and PI3K/Akt pathways. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 403, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Zhang, C.; Xin, Y.; Huang, Z.; Tan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Feng, W.; Li, X.; Li, W.; et al. Protective effect of FGF21 on type 1 diabetes-induced testicular apoptotic cell death probably via both mitochondrial- and endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent pathways in the mouse model. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 219, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planavila, A.; Redondo-Angulo, I.; Ribas, F.; Garrabou, G.; Casademont, J.; Giralt, M.; Villarroya, F. Fibroblast growth factor 21 protects the heart from oxidative stress. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 106, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cong, W.T.; Ling, J.; Tian, H.S.; Ling, R.; Wang, Y.; Huang, B.B.; Zhao, T.; Duan, Y.M.; Jin, L.T.; Li, X.K. Proteomic study on the protective mechanism of fibroblast growth factor 21 to ischemia-reperfusion injury. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2013, 91, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hondares, E.; Iglesias, R.; Giralt, A.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Giralt, M.; Mampel, T.; Villarroya, F. Thermogenic activation induces FGF21 expression and release in brown adipose tissue. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 12983–12990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quesada-Lopez, T.; Cereijo, R.; Turatsinze, J.V.; Planavila, A.; Cairo, M.; Gavalda-Navarro, A.; Peyrou, M.; Moure, R.; Iglesias, R.; Giralt, M.; et al. The lipid sensor GPR120 promotes brown fat activation and FGF21 release from adipocytes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moon, H.; Choi, J.W.; Song, B.W.; Kim, I.K.; Lim, S.; Lee, S.; Hwang, K.C.; Kim, S.W. Isoliquiritigenin Enhances the Beige Adipocyte Potential of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells by JNK Inhibition. Molecules 2020, 25, 5660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Pachter, L.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat: Discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinten-Johansen, J.; Jiang, R.; Reeves, J.G.; Mykytenko, J.; Deneve, J.; Jobe, L.J. Inflammation, proinflammatory mediators and myocardial ischemia-reperfusion Injury. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North Am. 2007, 21, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Feng, A.; Lin, S.; Yu, L.; Lin, X.; Yan, X.; Lu, X.; Zhang, C. Fibroblast growth factor-21 prevents diabetic cardiomyopathy via AMPK-mediated antioxidation and lipid-lowering effects in the heart. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; He, J.; Li, S.; Song, L.; Guo, X.; Yao, W.; Zou, D.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y.; Bai, F.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) inhibits macrophage-mediated inflammation by activating Nrf2 and suppressing the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 38, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Liu, J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Cui, Z.; Yao, D.; Huang, Z.; Xu, M.; Chen, M.; et al. FGF21 attenuates hypoxiainduced dysfunction and apoptosis in HPAECs through alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 1684–1694. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moscoso, I.; Cebro-Marquez, M.; Rodriguez-Manero, M.; Gonzalez-Juanatey, J.R.; Lage, R. FNDC5/Irisin counteracts lipotoxic-induced apoptosis in hypoxic H9c2 cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2019, 63, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarroya, F.; Cereijo, R.; Villarroya, J.; Giralt, M. Brown adipose tissue as a secretory organ. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Ramos, D.; Mehta, R.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 and Browning of White Adipose Tissue. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hua, L.; Zhuo, Y.; Jiang, D.; Li, J.; Huang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Z.; Yan, L.; Jin, C.; Jiang, X.; et al. Identification of hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 as a mediator in 17beta-estradiol-induced white adipose tissue browning. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 5602–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chartoumpekis, D.V.; Habeos, I.G.; Ziros, P.G.; Psyrogiannis, A.I.; Kyriazopoulou, V.E.; Papavassiliou, A.G. Brown adipose tissue responds to cold and adrenergic stimulation by induction of FGF21. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.M.; Neves, K.B.; Tostes, R.C.; Lobato, N.S. Perivascular Adipose Tissue as a Relevant Fat Depot for Cardiovascular Risk in Obesity. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldiss, P.; Davies, G.; Woods, R.; Budge, H.; Sacks, H.S.; Symonds, M.E. ‘Browning’ the cardiac and peri-vascular adipose tissues to modulate cardiovascular risk. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 228, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vomund, S.; Schafer, A.; Parnham, M.J.; Brune, B.; von Knethen, A. Nrf2, the Master Regulator of Anti-Oxidative Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.M.; Maltagliati, A.J. Nrf2 at the heart of oxidative stress and cardiac protection. Physiol. Genom. 2018, 50, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Lei, H.; Cai, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhu, P.; He, Q.; Zhao, M. The Nrf-2/HO-1 Signaling Axis: A Ray of Hope in Cardiovascular Diseases. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2020, 5695723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mata, A.; Cadenas, S. The Antioxidant Transcription Factor Nrf2 in Cardiac Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, A.; Dai, W.; Jang, M.J.; Medrano, L.; Li, Z.; Zhao, H.; Shao, M.; Tan, J.; Li, A.; Ning, T.; et al. Low- and high-thermogenic brown adipocyte subpopulations coexist in murine adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, W.; Dong, H.; Balaz, M.; Slyper, M.; Drokhlyansky, E.; Colleluori, G.; Giordano, A.; Kovanicova, Z.; Stefanicka, P.; Balazova, L.; et al. snRNA-seq reveals a subpopulation of adipocytes that regulates thermogenesis. Nature 2020, 587, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Alloush, J.; Beck, E.; Weisleder, N. A murine model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through ligation of the left anterior descending artery. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 10, 51329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Gene | Forward Sequence | Reverse Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Ucp1 | ACAAATAGCCCTGGTGGCTG | AACTCACCATCTTGGCTCGG |
| Prdm16 | CCTAACAACGTGCTCAGGGT | CTCTCTGCACGAAGTCAGCA |
| Pparg | GGAGATCTCCAGTGATATCGACCA | ACGGCTTCTACGGATCGAAACT |
| Cidea | GACCCAGCTTTCACGCAAT | TCTGCCTCCTTTCTCTTGCG |
| Cebpb | AATCCGGATCAAACGTGGCT | CCCCGCAGGAACATCTTTAAGT |
| Pargc1a | TTCAGGAGCTGGATGGCTTG | AGATCTGGGCAAAGAGGCTG |
| Fabp4 | GTCCTGGTACATGTGCAGAA | CTCTTGTAGAAGTCACGCCT |
| Fgf21 | TCCAGTTTGGGGGTCAAGTC | GACTTTCTGGACTGCGGTGT |
| Nfe2l2 | TTTGTAGATGACCATGAGTCGC | ATGTCCTGCTGTATGCTGCTT |
| Nqo1 | AGCCCTGATTGTATTGGCCC | GATTCGACCACCTCCCATCC |
| Cat | GCTCCGCAATCCTACACCAT | GTGGTCAGGACATCGGGTTT |
| Sens2 | TACCTTAGCAGCTTCTGGCG | AGGTAAGAACACTGGTGGCG |
| Sod1 | TTTTGCTCTCCCAGGTTCCG | TCGAAGTGAATGACGCCCTG |
| Sod2 | ACCGAGGAGAAGTACCACGA | TGGGTTCTCCACCACCCTTA |
| Hmax1 | ACATGGCCTTCTGGTATGGG | ATGAGTACCTCCCACCTCGT |
| Gapdh | AGTGCCAGCCTCGTCTCATA | GAAGGGGTCGTTGATGGCAA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moon, H.; Choi, J.-W.; Song, B.-W.; Kim, I.-K.; Lim, S.; Lee, S.; Han, G.; Hwang, K.-C.; Kim, S.W. Brite Adipocyte FGF21 Attenuates Cardiac Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rat Hearts by Modulating NRF2. Cells 2022, 11, 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030567
Moon H, Choi J-W, Song B-W, Kim I-K, Lim S, Lee S, Han G, Hwang K-C, Kim SW. Brite Adipocyte FGF21 Attenuates Cardiac Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rat Hearts by Modulating NRF2. Cells. 2022; 11(3):567. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030567
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoon, Hanbyeol, Jung-Won Choi, Byeong-Wook Song, Il-Kwon Kim, Soyeon Lim, Seahyoung Lee, Gyoonhee Han, Ki-Chul Hwang, and Sang Woo Kim. 2022. "Brite Adipocyte FGF21 Attenuates Cardiac Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rat Hearts by Modulating NRF2" Cells 11, no. 3: 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030567
APA StyleMoon, H., Choi, J. -W., Song, B. -W., Kim, I. -K., Lim, S., Lee, S., Han, G., Hwang, K. -C., & Kim, S. W. (2022). Brite Adipocyte FGF21 Attenuates Cardiac Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rat Hearts by Modulating NRF2. Cells, 11(3), 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030567