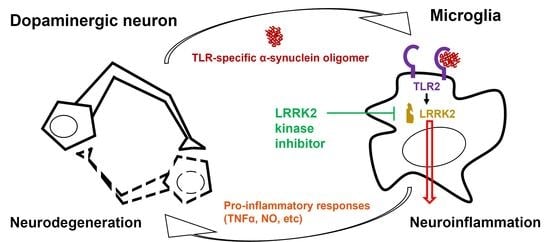
LRRK2 Inhibition Mitigates the Neuroinflammation Caused by TLR2-Specific α-Synuclein and Alleviates Neuroinflammation-Derived Dopaminergic Neuronal Loss
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.2. Generation and Isolation of Oligomeric αSyn
2.3. Western Blot and Dot-Blot Analyses
2.4. Human TLR2 Activity Test
2.5. Isolation and Culture of Rat Primary Microglia
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immune Sorbent Assay (ELISA) of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine
2.7. Immunofluorescence
2.8. Co-Culture of C20 with dSH
2.9. Mouse Handling and Post-Injection Behavioral Testing
2.10. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Immunocytochemistry (ICC)
2.11. Human Substantia Nigra Tissue Extraction
2.12. Data Analysis and Presentation
3. Results
3.1. Upregulation of LRRK2 Activity Is Promoted by TLR2 Activation via the αSyn Oligomer
3.2. Activation of TLR2 by Neuron-Released αSyn Is Responsible for the Increase in LRRK2 Activity
3.3. Activation of Microglia by Dopaminergic Neuronal Cells Expressing αSyn Leads to Neurodegeneration Due to the Neuroinflammatory Response
3.4. LRRK2 Inhibitor Ameliorated the Neuroinflammation and Degeneration of Dopaminergic Neurons Triggered by Neuron-Released αSyn In Vivo
3.5. Association between the Upregulation of LRRK2 Activity and Increases in TLR2 and αSyn Oligomer Levels in the Human SN
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Griffiths, M.; Neal, J.W.; Gasque, P. Innate immunity and protective neuroinflammation: New emphasis on the role of neuroimmune regulatory proteins. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2007, 82, 29–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ising, C.; Heneka, M.T. Functional and structural damage of neurons by innate immune mechanisms during neurodegeneration. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhard, A.; Pavese, N.; Hotton, G.; Turkheimer, F.; Es, M.; Hammers, A.; Eggert, K.; Oertel, W.; Banati, R.B.; Brooks, D.J. In vivo imaging of microglial activation with [11C](R)-PK11195 PET in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2006, 21, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.; Janelidze, S.; Surova, Y.; Widner, H.; Zetterberg, H.; Hansson, O. Cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of inflammatory markers in Parkinson’s disease and atypical parkinsonian disorders. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miliukhina, I.V.; Usenko, T.S.; Senkevich, K.A.; Nikolaev, M.A.; Timofeeva, A.A.; Agapova, E.A.; Semenov, A.V.; Lubimova, N.E.; Totolyan, A.A.; Pchelina, S.N. Plasma Cytokines Profile in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease Associated with Mutations in GBA Gene. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 168, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Béraud, D.; Maguire-Zeiss, K.A. Misfolded α-synuclein and Toll-like receptors: Therapeutic targets for Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2012, 18 (Suppl. S1), S17–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, X.; Maguire-Zeiss, K.A.; Giuliano, R.; Prifti, L.; Venkatesh, K.; Federoff, H.J. Synuclein activates microglia in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2008, 29, 1690–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, T.; Hoekstra, J.; Heng, X.; Kang, W.; Ding, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J. P2X7 receptor is critical in α-synuclein--mediated microglial NADPH oxidase activation. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 2304–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingelsson, M. Alpha-Synuclein Oligomers-Neurotoxic Molecules in Parkinson’s Disease and Other Lewy Body Disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallings, R.L.; Tansey, M.G. LRRK2 regulation of immune-pathways and inflammatory disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2019, 47, 1581–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, P.N.; Chen, S.G.; Wilson-Delfosse, A.L. Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2): A key player in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 1283–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dzamko, N.; Inesta-Vaquera, F.; Zhang, J.; Xie, C.; Cai, H.; Arthur, S.; Tan, L.; Choi, H.; Gray, N.; Cohen, P.; et al. The IkappaB kinase family phosphorylates the Parkinson’s disease kinase LRRK2 at Ser935 and Ser910 during Toll-like receptor signaling. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, D.H.; Lee, H.; Son, I.; Seol, W. G2019s LRRK2 promotes mitochondrial fission and increases TNFα-mediated neuroinflammation responses. Anim. Cells Syst. 2019, 23, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.; Ho, D.H.; Suk, J.E.; You, S.; Michael, S.; Kang, J.; Joong Lee, S.; Masliah, E.; Hwang, D.; Lee, H.J.; et al. Neuron-released oligomeric α-synuclein is an endogenous agonist of TLR2 for paracrine activation of microglia. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daniele, S.G.; Béraud, D.; Davenport, C.; Cheng, K.; Yin, H.; Maguire-Zeiss, K.A. Activation of MyD88-dependent TLR1/2 signaling by misfolded α-synuclein, a protein linked to neurodegenerative disorders. Sci. Signal. 2015, 8, ra45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nam, D.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, M.; Kim, J.; Seol, W.; Son, I.; Ho, D.H. Detection and Assessment of α-Synuclein Oligomers in the Urine of Parkinson’s Disease Patients. J. Parkinson’s Dis. 2020, 10, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.H.; Seol, W.; Son, I. Upregulation of the p53-p21 pathway by G2019S LRRK2 contributes to the cellular senescence and accumulation of α-synuclein. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, D.H.; Je, A.R.; Lee, H.; Son, I.; Kweon, H.S.; Kim, H.G.; Seol, W. LRRK2 Kinase Activity Induces Mitochondrial Fission in Microglia via Drp1 and Modulates Neuroinflammation. Exp. Neurobiol. 2018, 27, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, D.; Kim, A.; Han, S.J.; Lee, S.I.; Park, S.H.; Seol, W.; Son, I.; Ho, D.H. Analysis of α-synuclein levels related to LRRK2 kinase activity: From substantia nigra to urine of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Anim. Cells Syst. 2021, 25, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansey, M.G.; Goldberg, M.S. Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: Its role in neuronal death and implications for therapeutic intervention. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maekawa, T.; Sasaoka, T.; Azuma, S.; Ichikawa, T.; Melrose, H.L.; Farrer, M.J.; Obata, F. Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) regulates α-synuclein clearance in microglia. BMC Neurosci. 2016, 17, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Novello, S.; Arcuri, L.; Dovero, S.; Dutheil, N.; Shimshek, D.R.; Bezard, E.; Morari, M. G2019S LRRK2 mutation facilitates α-synuclein neuropathology in aged mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 120, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpicelli-Daley, L.A.; Abdelmotilib, H.; Liu, Z.; Stoyka, L.; Daher, J.P.; Milnerwood, A.J.; Unni, V.K.; Hirst, W.D.; Yue, Z.; Zhao, H.T.; et al. G2019S-LRRK2 Expression Augments α-Synuclein Sequestration into Inclusions in Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 7415–7427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loria, F.; Vargas, J.Y.; Bousset, L.; Syan, S.; Salles, A.; Melki, R.; Zurzolo, C. α-Synuclein transfer between neurons and astrocytes indicates that astrocytes play a role in degradation rather than in spreading. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 134, 789–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kam, T.-I.; Hinkle, J.T.; Dawson, T.M.; Dawson, V.L. Microglia and astrocyte dysfunction in parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 144, 105028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codolo, G.; Plotegher, N.; Pozzobon, T.; Brucale, M.; Tessari, I.; Bubacco, L.; de Bernard, M. Triggering of inflammasome by aggregated α-synuclein, an inflammatory response in synucleinopathies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, I.; Zhang, Y.; Seegobin, S.P.; Pruvost, M.; Wang, Q.; Purtell, K.; Zhang, B.; Yue, Z. Microglia clear neuron-released α-synuclein via selective autophagy and prevent neurodegeneration. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.; Beilina, A.; Smith, N.; Li, Y.; Kim, M.; Kumaran, R.; Kaganovich, A.; Mamais, A.; Adame, A.; Iba, M.; et al. LRRK2 mediates microglial neurotoxicity via NFATc2 in rodent models of synucleinopathies. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaay0399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, E.-J.; Lee, H.-J.; Rockenstein, E.; Ho, D.-H.; Park, E.-B.; Yang, N.-Y.; Desplats, P.; Masliah, E.; Lee, S.-J. Antibody-aided clearance of extracellular α-synuclein prevents cell-to-cell aggregate transmission. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 13454–13469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.T.; Chung, C.H.-Y.; Iba, M.; Zhang, B.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Luk, K.C.; Lee, V.M.Y. A-synuclein immunotherapy blocks uptake and templated propagation of misfolded α-synuclein and neurodegeneration. Cell Rep. 2014, 7, 2054–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brundin, P.; Dave, K.D.; Kordower, J.H. Therapeutic approaches to target alpha-synuclein pathology. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 298 Pt B, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, D.-H.; Nam, D.; Seo, M.; Park, S.-W.; Seol, W.; Son, I. LRRK2 Inhibition Mitigates the Neuroinflammation Caused by TLR2-Specific α-Synuclein and Alleviates Neuroinflammation-Derived Dopaminergic Neuronal Loss. Cells 2022, 11, 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11050861
Ho D-H, Nam D, Seo M, Park S-W, Seol W, Son I. LRRK2 Inhibition Mitigates the Neuroinflammation Caused by TLR2-Specific α-Synuclein and Alleviates Neuroinflammation-Derived Dopaminergic Neuronal Loss. Cells. 2022; 11(5):861. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11050861
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Dong-Hwan, Daleum Nam, Mikyoung Seo, Sung-Woo Park, Wongi Seol, and Ilhong Son. 2022. "LRRK2 Inhibition Mitigates the Neuroinflammation Caused by TLR2-Specific α-Synuclein and Alleviates Neuroinflammation-Derived Dopaminergic Neuronal Loss" Cells 11, no. 5: 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11050861
APA StyleHo, D. -H., Nam, D., Seo, M., Park, S. -W., Seol, W., & Son, I. (2022). LRRK2 Inhibition Mitigates the Neuroinflammation Caused by TLR2-Specific α-Synuclein and Alleviates Neuroinflammation-Derived Dopaminergic Neuronal Loss. Cells, 11(5), 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11050861