Crocin Inhibits Angiogenesis and Metastasis in Colon Cancer via TNF-α/NF-kB/VEGF Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Cell Line Culture
2.3. Preparation of Drug Stock Solution
2.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.5. Colony-Forming Assay
2.6. Cell Migration Assay
2.7. Cell Invasion Assay
2.8. Tube Formation Assay
2.9. Effect of Crocin on Colon Carcinoma Cell VEGF and NF-kB Downregulation
2.10. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) for VEGF and Phosphorylated NF-KB p65 Subunit
2.11. In Vivo Angiogenesis Model for Colon Cancer
Animals
2.12. Densitometry and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Crocin Significantly Reduces the Viability of Human Colon Carcinoma and Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells, but Was Not Toxic to Normal Human Colonic Epithelial Cells
3.2. Crocin Significantly Reduces Colon Carcinoma Cell Colony Formation
3.3. Crocin Significantly Inhibits Cell Migration and Invasion in Colon Carcinoma Cells in a Concentration-Dependent Manner
3.4. Crocin Demonstrates Marked Anti-Angiogenic Activity in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
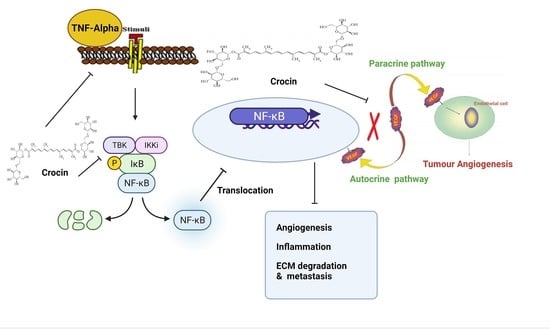
3.5. Crocin May Inhibit Colon Carcinoma Induced Angiogenesis through the TNF-α/NF-kB/VEGF Pathways
3.6. Crocin Can Inhibit the Growth and Angiogenesis of Colon Tumours in Male Athymic Nude Mice (NCR nu/nu)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fitzmaurice, C.; Allen, C.; Barber, R.M.; Barregard, L.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Brenner, H.; Dicker, D.J.; Chimed-Orchir, O.; Dandona, R.; Dandona, L.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived with Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-years for 32 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 524–548. [Google Scholar]
- Nishida, N.; Yano, H.; Nishida, T.; Kamura, T.; Kojiro, M. Angiogenesis in cancer. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2006, 2, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Møller, B. Predicting the future burden of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Shan, Y.; Li, C.; Sun, Y.; Su, P.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Pan, X.; Zhang, J. Discovery of novel anti-angiogenesis agents. Part 6: Multi-targeted RTK inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 127, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folkman, J. Angiogenesis. Annu. Rev. Med. 2006, 57, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, J.; Hurwitz, H.I.; Sandler, A.B.; Miles, D.; Coleman, R.L.; Deurloo, R.; Chinot, O.L. Bevacizumab (Avastin®) in cancer treatment: A review of 15 years of clinical experience and future outlook. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2020, 86, 102017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettinger, D.S.; Aisner, D.L.; Wood, D.E.; Akerley, W.; Bauman, J.; Chang, J.Y.; Chirieac, L.R.; D’Amico, T.A.; Dilling, T.J.; Dobelbower, M.; et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 5.2018. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2018, 16, 807–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cardoso, F.; Senkus, E.; Costa, A.; Papadopoulos, E.; Aapro, M.; André, F.; Harbeck, N.; Aguilar Lopez, B.; Barrios, C.H.; Bergh, J.; et al. 4th ESO-ESMO International Consensus Guidelines for Advanced Breast Cancer (ABC 4). Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1634–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baichwal, V.R.; Baeuerle, P.A. Apoptosis: Activate NF-κB or die? Curr. Biol. 1997, 7, R94–R96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beg, A.A.; Baltimore, D. An essential role for NF-κB in preventing TNF-α-induced cell death. Science 1996, 274, 782–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, I.M.; Stevenson, J. IκB kinase: Beginning, not the end. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 11758–11760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.J.; Parent, L.; Maniatis, T. Site-specific phosphorylation of IκBα by a novel ubiquitination-dependent protein kinase activity. Cell 1996, 84, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shishodia, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Nuclear factor-κB activation: A question of life or death. BMB Rep. 2002, 35, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.X.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, N.; Gong, W.; Huang, S. Constitutive NFκB activity regulates the expression of VEGF and IL8 and tumorangiogenesis of human glioblastoma. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 23, 725–732. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Z.B.; Meng, F.R.; Fang, Y.X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, C.W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, G.Q.; Feng, F.B.; Qiu, H.Y. Inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway induces apoptosis and suppresses proliferation and angiogenesis of human fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Medicine 2018, 97, e10920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Boyle, D.L.; Manning, A.M.; Firestein, G.S. AP-1 and NF-κB regulation in rheumatoid arthritis and murine collagen induced arthritis. Autoimmunity 1998, 28, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabruyn, S.P.; Griffioen, A.W. NF-κB: A new player in angiostatic therapy. Angiogenesis 2008, 11, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dudics, S.; Langan, D.; Meka, R.R.; Venkatesha, S.H.; Berman, B.M.; Che, C.-T.; Moudgil, K.D. Natural Products for the Treatment of Autoimmune Arthritis: Their Mechanisms of Action, Targeted Delivery, and Interplay with the Host Microbiome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, P.; Cecchi, L.; Bellumori, M.; Balli, D.; Giovannelli, L.; Huang, L.; Mulinacci, N. Phenolic Compounds and Triterpenes in Different Olive Tissues and Olive Oil By-Products, and Cytotoxicity on Human Colorectal Cancer Cells: The Case of Frantoio, Moraiolo and Leccino Cultivars (Olea europaea L.). Foods 2021, 10, 2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antognelli, C.; Frosini, R.; Santolla, M.F.; Peirce, M.J.; Talesa, V.N. Oleuropein-Induced Apoptosis Is Mediated by Mitochondrial Glyoxalase 2 in NSCLC A549 Cells: A Mechanistic Inside and a Possible Novel Nonenzymatic Role for an Ancient Enzyme. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 8576961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cárdeno, A.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M.; Rosillo, M.A.; Alarcón de la Lastra, C. Oleuropein, a secoiridoid derived from olive tree, inhibits the proliferation of human colorectal cancer cell through downregulation of HIF-1α. Nutr. Cancer 2013, 65, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Natural Toxins in Food. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/natural-toxins-in-food (accessed on 9 May 2018).
- Ashktorab, H.; Soleimani, A.; Singh, G.; Amin, A.; Tabtabaei, S.; Latella, G.; Stein, U.; Akhondzadeh, S.; Solanki, N.; Gondré-Lewis, M.C.; et al. Saffron: The Golden Spice with Therapeutic Properties on Digestive Diseases. Nutrients 2019, 11, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khorasany, A.R.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Therapeutic effects of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) in digestive disorders: A review. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2016, 19, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Kharrag, R.; Amin, A.; Hisaindee, S.; Greish, Y.; Karam, S.M. Development of a therapeutic model of precancerous liver using crocin-coated magnetite nanoparticles. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdalla, A.; Murali, C.; Amin, A. Safranal Inhibits Angiogenesis via Targeting HIF-1α/VEGF Machinery: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Insights. Front. Oncol. 2022, 11, 789172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rameshrad, M.; Razavi, B.M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Saffron and its derivatives, crocin, crocetin and safranal: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2018, 28, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Jin, S.; Liu, C. Effects of crocin on inflammatory activities in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes and collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Immunol. Res. 2018, 66, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, H.A.; Hakkim, F.L.; Sam, S. Molecular mechanism of crocin induced Caspase mediated MCF-7 cell death: In Vivo toxicity profiling and Ex Vivo macrophage activation. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 17, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakshi, H.; Sam, S.; Rozati, R.; Sultan, P.; Islam, T.; Rathore, B.; Lone, Z.; Sharma, M.; Triphati, J.; Saxena, R.C. DNA fragmentation and cell cycle arrest: A hallmark of apoptosis induced by crocin from Kashmiri saffron in a human pancreatic cancer cell line. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2010, 11, 675–679. [Google Scholar]
- Bakshi, H.A.; Zoubi, M.S.A.; Faruck, H.L.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Rabi, F.A.; Hafiz, A.A.; Al-Batanyeh, K.M.; Al-Trad, B.; Ansari, P.; Nasef, M.M.; et al. Dietary Crocin is Protective in Pancreatic Cancer while Reducing Radiation-Induced Hepatic Oxidative Damage. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, H.; Sam, S.; Feroz, A.; Ravesh, Z.; Shah, G.; Sharma, M. Crocin from Kashmiri Saffron (Crocus sativus) induces in vitro and in vivo Xenograft Growth inhibition of Dalton’s lymphoma. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2009, 10, 887–890. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bakshi, H.A.; Hakkim, F.L.; Sam, S.; Javid, F.; Rashan, L. Dietary crocin reverses melanoma metastasis. J. Biomed. Res. 2018, 32, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Bakshi, H.; Hakkim, F.; Sam, S.; Javid, F. Role of Dietary Crocin in In Vivo Melanoma Tumor Remission. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2017, 18, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.-L.; Hsing, H.-W.; Lai, T.-C.; Chen, Y.-W.; Lee, T.-R.; Chan, H.-T.; Lyu, P.-C.; Wu, C.-L.; Lu, Y.-C.; Lin, S.-T.; et al. Trypsin-induced proteome alteration during cell subculture in mammalian cells. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 17, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vali, F.; Changizi, V.; Safa, M. Synergistic Apoptotic Effect of Crocin and Paclitaxel or Crocin and Radiation on MCF-7 Cells, a Type of Breast Cancer Cell Line. Int. J. Breast Cancer 2015, 2015, 139349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiangbing, H.; Yankai, Z.; Ming, L.; Yong, L.; Yu, Z.; Huiyong, Z.; Yingying, C.; Jing, H.; Yun, X.; Liang, J.; et al. The fusion protein of HSP65 with tandem repeats of β-hCG acting as a potent tumor vaccine in suppressing hepatocarcinoma. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2010, 10, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bogenrieder, T.; Herlyn, M. Axis of evil: Molecular mechanisms of cancer metastasis. Oncogene 2003, 22, 6524–6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sagar, S.M.; Yance, D.; Wong, R.K. Natural health products that inhibit angiogenesis: A potential source for investigational new agents to treat cancer—Part 1. Curr. Oncol. 2006, 13, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinkhani, Z.; Norooznezhad, F.; Rastegari-Pouyani, M.; Mansouri, K. Medicinal Plants Extracts with Antiangiogenic Activity: Where Is the Link? Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 10, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, H.A.; Hakkim, F.L.; Sam, S. Assessment of in vitro cytotoxicity of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) on cervical cancer cells (HEp-2) and their in vivo pre-clinical toxicity in normal swiss albino mice. Int. J. Herbal Med. 2016, 4, 80–83. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, M.K.; Qin, R.-Y. Mechanism and its regulation of tumor-induced angiogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 9, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Schootbrugge, C.; Bussink, J.; Span, P.N.; Sweep, F.C.; Grénman, R.; Stegeman, H.; Pruijn, G.J.; Kaanders, J.H.; Boelens, W.C. αB-crystallin stimulates VEGF secretion and tumor cell migration and correlates with enhanced distant metastasis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Qi, Y.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, T.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Han, M. Primary tumor-secreted VEGF induces vascular hyperpermeability in premetastatic lung via the occludin phosphorylation/ubiquitination pathway. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 2316–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.H.; Wu, Y.J.; Chang, C.Y.; Tien, T.Y.; Tseng, S.W.; Tsai, C.H.; Bettinger, T.; Tsai, C.H.; Yeh, H.I. The increase of VEGF secretion from endothelial progenitor cells post ultrasonic VEGF gene delivery enhances the proliferation and migration of endothelial cells. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2013, 39, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melincovici, C.S.; Boşca, A.B.; Şuşman, S.; Mărginean, M.; Mihu, C.; Istrate, M.; Moldovan, I.M.; Roman, A.L.; Mihu, C.M. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)—Key factor in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2018, 59, 455–467. [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak, H.F. Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor: A critical cytokine in tumor angiogenesis and a potential target for diagnosis and therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 4368–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-Y.; Zeng, Q.-H.; Cao, P.-G.; Xie, D.; Chen, X.; Yang, F.; He, L.-Y.; Dai, Y.-B.; Li, J.-J.; Liu, X.-M.; et al. RIPK4 promotes bladder urothelial carcinoma cell aggressiveness by upregulating VEGF-A through the NF-κB pathway. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 1617–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, S.; Hao, J.; Bi, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, W.; Wang, D. The Protection of Crocin against Ulcerative Colitis and Colorectal Cancer via Suppression of NF-κB-Mediated Inflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 639458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahi, A.; Abedini, M.R.; Javdani, H.; Arzi, L.; Chamani, E.; Farhoudi, R.; Talebloo, N.; Hoshyar, R. Crocin and Metformin suppress metastatic breast cancer progression via VEGF and MMP9 downregulations: In vitro and in vivo studies. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 476, 3341–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F. TNF-α in promotion and progression of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006, 25, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Huang, Y.; Dai, K.; Zhang, X. TNF-α-induced LRG1 promotes angiogenesis and mesenchymal stem cell migration in the subchondral bone during osteoarthritis. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remels, A.H.V.; Gosker, H.R.; Verhees, K.J.P.; Langen, R.C.J.; Schols, A.M.W.J. TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation stimulates skeletal muscle glycolytic metabolism through activation of HIF-1α. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 1770–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Jung, K.; Kim, I.-S.; Lee, I.-S.; Ko, Y.; Shin, J.E.; Park, K.I. TNF-α induces human neural progenitor cell survival after oxygen-glucose deprivation by activating the NF-κB pathway. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bakshi, H.A.; Quinn, G.A.; Nasef, M.M.; Mishra, V.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; El-Tanani, M.; Serrano-Aroca, Á.; Webba Da Silva, M.; McCarron, P.A.; Tambuwala, M.M. Crocin Inhibits Angiogenesis and Metastasis in Colon Cancer via TNF-α/NF-kB/VEGF Pathways. Cells 2022, 11, 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11091502
Bakshi HA, Quinn GA, Nasef MM, Mishra V, Aljabali AAA, El-Tanani M, Serrano-Aroca Á, Webba Da Silva M, McCarron PA, Tambuwala MM. Crocin Inhibits Angiogenesis and Metastasis in Colon Cancer via TNF-α/NF-kB/VEGF Pathways. Cells. 2022; 11(9):1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11091502
Chicago/Turabian StyleBakshi, Hamid A., Gerry A. Quinn, Mohamed M. Nasef, Vijay Mishra, Alaa A. A. Aljabali, Mohamed El-Tanani, Ángel Serrano-Aroca, Mateus Webba Da Silva, Paul A. McCarron, and Murtaza M. Tambuwala. 2022. "Crocin Inhibits Angiogenesis and Metastasis in Colon Cancer via TNF-α/NF-kB/VEGF Pathways" Cells 11, no. 9: 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11091502
APA StyleBakshi, H. A., Quinn, G. A., Nasef, M. M., Mishra, V., Aljabali, A. A. A., El-Tanani, M., Serrano-Aroca, Á., Webba Da Silva, M., McCarron, P. A., & Tambuwala, M. M. (2022). Crocin Inhibits Angiogenesis and Metastasis in Colon Cancer via TNF-α/NF-kB/VEGF Pathways. Cells, 11(9), 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11091502