Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Ameliorated Diabetic Nephropathy by Autophagy Induction through the mTOR Signaling Pathway
Abstract
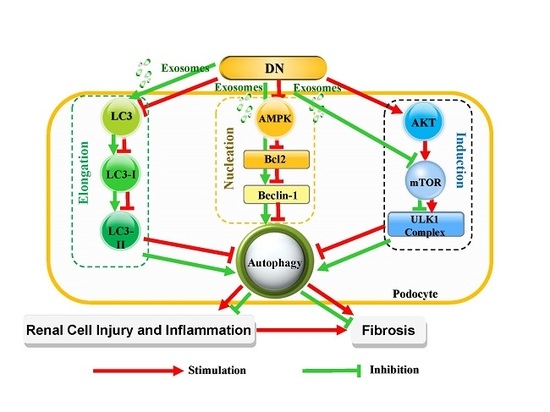
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. Preparation of MSC-Derived Exosomes
2.3. Characterization of MSC-Derived Exosomes
Exosome Labeling with PKH-26
2.4. Western Blot for Characterization of Exosomes
2.5. Experimental Chemicals
2.6. Induction of DN
2.7. Experimental Design and Treatment Protocol
2.8. Sampling
2.9. Histological Analysis
2.9.1. Light Microscopy Study
2.9.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy Study
2.10. Morphometric Study
2.10.1. Determination of the Expressions of LC3, mTOR, and Beclin-1 Genes by qPCR
Total RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription
Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.11. Western Blot
3. Results
3.1. Exosome Characterization
3.2. Biochemical Analysis
3.3. Histological Examination
3.3.1. Light Microscope Examination
Hematoxylin and Eosin
Masson’s Trichrome Stain
3.4. Immunohistochemical Study
3.5. Morphometric Analysis
3.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy Study
3.7. Gene Expression Results of LC3-II, mTOR, and Beclin-1 Genes in All Experimental Groups
3.8. mTOR, LC3-I, LC3-II, S6K1, p62, Fibronectin, TGF-β, and β-Actin Detection by Western Blotting
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Authors Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Martínez-Castelao, A.; Navarro-González, J.F.; Górriz, J.L.; de Alvaro, F. The concept and the epidemiology of diabetic nephropathy have changed in recent years. J. Clin. Med. 2015, 4, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saran, R.; Robinson, B.; Abbott, K.C.; Agodoa, L.Y.; Albertus, P.; Ayanian, J.; Balkrishnan, R.; Bragg-Gresham, J.; Cao, J.; Chen, J.L.; et al. US renal data system 2016 annual data report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 69, A7–A8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, J.M.; Coughlan, M.T.; Cooper, M.E. Oxidative stress as a major culprit in kidney disease in diabetes. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzen, J.M.; Haller, H.; Thum, T. MicroRNAs as mediators and therapeutic targets in chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 7, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Fernandez, B.; Ortiz, A.; Gomez-Guerrero, C.; Egido, J. Therapeutic approaches to diabetic nephropathy—Beyond the RAS. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, J. Management of diabetic nephropathy: Recent progress and future perspective. Diabetes Metab. Syndrome 2015, 9, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satirapoj, B.; Adler, S.G. Comprehensive approach to diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 33, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tögel, F.; Weiss, K.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, P.; Westenfelder, C. Vasculotropic, paracrine actions of infused mesenchymal stem cells are important to the recovery from acute kidney injury. Am. J. Physiol. 2007, 292, F1626–F1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ullah, I.; Subbarao, R.B.; Rho, G.J. Human mesenchymal stem cells-current trends and future prospective. Biosci. Rep. 2015, 35, e00191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuda, T.; Kosaka, N.; Takeshita, F.; Ochiya, T. The therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Proteomics 2013, 13, 1637–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Hochberg, F.H.; Jones, P.S. Extracellular vesicles: the growth as diagnostics and therapeutics; a survey. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeagy, B.A.; Cherqui, S. Kidney repair and stem cells: a complex and controversial process. Pediatric Nephrol. 2011, 26, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarjou, A.; Kim, J.; Traylor, A.M.; Sanders, P.W.; Balla, J.; Agarwal, A.; Curtis, L.M. Paracrine effects of mesenchymal stem cells in cisplatin-induced renal injury require heme oxygenase-1. Am. J. Physiol. 2011, 300, F254–F262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Qian, H.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, X.; Yan, Y.; Ye, S.; Peng, X.; Li, W.; Xu, W. Hepatocyte growth factor modification promotes the amelioration effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on rat acute kidney injury. Stem Cells Dev. 2010, 20, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, T.; Lamark, T. Selective autophagy mediated by autophagic adapter proteins. Autophagy 2011, 7, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Rechter, S.; Decuypere, J.-P.; Ivanova, E.; van den Heuvel, L.P.; De Smedt, H.; Levtchenko, E.; Mekahli, D. Autophagy in renal diseases. Pediatric Nephrol. 2016, 31, 737–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Choi, M.E. Autophagy in diabetic nephropathy. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 224, R15–R30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deng, X.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, A. Advance of autophagy in chronic kidney diseases. Renal Fail. 2017, 39, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zoncu, R.; Efeyan, A.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR: From growth signal integration to cancer, diabetes and ageing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lloberas, N.; Cruzado, J.M.; Franquesa, M.; Herrero-Fresneda, I.; Torras, J.; Alperovich, G.; Rama, I.; Vidal, A.; Grinyó, J.M. Mammalian target of rapamycin pathway blockade slows progression of diabetic kidney disease in rats. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, H.; Inoki, K.; Masutani, K.; Wakabayashi, Y.; Komai, K.; Nakagawa, R.; Guan, K.-L.; Yoshimura, A. The mTOR pathway is highly activated in diabetic nephropathy and rapamycin has a strong therapeutic potential. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 384, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gödel, M.; Hartleben, B.; Herbach, N.; Liu, S.; Zschiedrich, S.; Lu, S.; Debreczeni-Mór, A.; Lindenmeyer, M.T.; Rastaldi, M.-P.; Hartleben, G.; et al. Role of mTOR in podocyte function and diabetic nephropathy in humans and mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121, 2197–2209. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Bruno, S.; Grange, C.; Collino, F.; Deregibus, M.C.; Cantaluppi, V.; Biancone, L.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Microvesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells enhance survival in a lethal model of acute kidney injury. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatti, S.; Bruno, S.; Deregibus, M.C.; Sordi, A.; Cantaluppi, V.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Microvesicles derived from human adult mesenchymal stem cells protect against ischaemia–Reperfusion-induced acute and chronic kidney injury. Nephrol. Dialysis Transplantation 2011, 26, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liu, X.-X.; Fan, H.; Tang, Q.; Shou, Z.-X.; Zuo, D-.M.; Zou, Z.; Xu, M.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Peng, Y.; et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protect against experimental colitis via attenuating colon inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange-Consiglio, A.; Perrini, C.; Albini, G.; Modina, S.; Lodde, V.; Orsini, E.; Esposti, P.; Cremonesi, F. Oviductal microvesicles and their effect on in vitro maturation of canine oocytes. Reproduction 2017, 154, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesch, G.H.; Allen, T.J. Rodent models of streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy (Methods in Renal Research). Nephrology 2007, 12, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Cai, Q.-H.; Wang, Y.-J.; Fan, S.-H.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Xiao, M.-Q.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Wu, D.-M.; Lu, J.; Zheng, Y.-L. Protective effect of autophagy on endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis of alveolar epithelial cells in rat models of COPD. Biosci. Rep. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, M.A. Principles and techniques of electron microscopy. In Biological Applications; Edward Arnold: London, UK, 1981; Volume I, p. 412. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; El Nahas, A.M.; Thomas, G.L.; Haylor, J.L.; Watson, P.F.; Wagner, B.; Johnson, T.S. Caspase-3 and apoptosis in experimental chronic renal scarring. Kidney Int. 2001, 60, 1765–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiame, I.; Remy, S.; Swennen, R.; Sagi, L. Irreversible heat inactivation of DNase I without RNA degradation. BioTechniques 2000, 29, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helming, L.; Winter, J.; Gordon, S. The scavenger receptor CD36 plays a role in cytokine-induced macrophage fusion. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fleige, S.; Pfaffl, M.W. RNA integrity and the effect on the real-time qRT-PCR performance. Mol. Aspects Med. 2006, 27, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.T.; Zhao, X.; Yaster, M.; Tao, Y.X. Expression and distribution of mTOR, p70S6K, 4E-BP1, and their phosphorylated counterparts in rat dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord dorsal horn. Brain Res. 2010, 1336, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, G.; Liu, C.; Wei, R.; Zhu, S.; Xu, Y.; Wu, M.; Miao, Q. Acanthopanax versus 3-methyladenine ameliorates sodium taurocholate-induced severe acute pancreatitis by inhibiting the autophagic pathway in rats. Mediators Inflammation 2016, 2016, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Li, X.; Fu, Z.; Yang, M.; Bian, W.; Wang, S.; Song, Y.; Tang, J.; et al. Cathelicidin-OA1, a novel antioxidant peptide identified from an amphibian, accelerates skin wound healing. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magalhaes, J.; Gegg, M.; Migdalska-Richards, A.; Schapira, A. Effects of ambroxol on the autophagy-lysosome pathway and mitochondria in primary cortical neurons. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, G.; Liu, D.; Hu, J.; Gan, F.; Hou, L.; Zhai, N.; Chen, X.; Huang, K. SeMet attenuates OTA-induced PCV2 replication promotion by inhibiting autophagy by activating the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Veterinary Res. 2018, 49, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Bu, Z.; Zhao, F.; Xiao, D. Increased T-helper 17 cell differentiation mediated by exosome-mediated micro RNA-451 redistribution in gastric cancer infiltrated T cells. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Zhao, X.; Hu, Y.; Sun, H.; Gong, G.; Huang, X.; Chen, X.; Xia, M.; Sun, C.; Huang, Q.; et al. Autophagy regulates the degeneration of the auditory cortex through the AMPK-mTOR-ULK1 signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 41, 2086–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kitada, M.; Takeda, A.; Nagai, T.; Ito, H.; Kanasaki, K.; Koya, D. Dietary restriction ameliorates diabetic nephropathy through anti-inflammatory effects and regulation of the autophagy via restoration of Sirt1 in diabetic Wistar fatty (fa/fa) rats: a model of type 2 diabetes. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.C.; Cooper, M.E.; Zimmet, P. Changing epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and associated chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokdad, A.H.; Ford, E.S.; Bowman, B.A.; Dietz, W.H.; Vinicor, F.; Bales, V.S.; Marks, J.S. Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. Jama 2003, 289, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Kume, S.; Kitada, M.; Kanasaki, K.; Uzu, T.; Maegawa, H.; Koya, D. Autophagy as a therapeutic target in diabetic nephropathy. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matboli, M.; Eissa, S.; Ibrahim, D.; Hegazy, M.G.; Imam, S.S.; Habib, E.K. Caffeic acid attenuates diabetic kidney disease via modulation of autophagy in a high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Hany, H.O.; Atef, H.; Said, E.; Elkashef, H.A.; Salem, H.A. Crocin mediated amelioration of oxidative burden and inflammatory cascade suppresses diabetic nephropathy progression in diabetic rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 284, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, P.; Hu, C.; Quan, C.; Yu, T.; Huang, W.; Chen, W.; Tang, S.; Shi, Y.; Martin, F.L.; Yang, K. 4-Nonylphenol induces autophagy and attenuates mTOR-p70S6K/4EBP1 signaling by modulating AMPK activation in Sertoli cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 267, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, C.-Y.; Miaw, C.-L.; Hsieh, C.-C.; Tseng, H.-C.; Yang, Y.-H.; Yen, C.-H. Effects of chronic 4-n-nonylphenol treatment on aortic vasoconstriction and vasorelaxation in rats. Arch. Toxicol. 2009, 83, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A.; Mehmood, M.H.; Channa, H.; Akhtar, M.S.; Gilani, A.-H. Pharmacological basis for the medicinal use of polyherbal formulation and its ingredients in cardiovascular disorders using rodents. BMC Complementary Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kriz, W.; LemLey, K.V. Mechanical challenges to the glomerular filtration barrier: adaptations and pathway to sclerosis. Pediatric Nephrol. 2017, 32, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiatecka-Urban, A. Endocytic trafficking at the mature podocyte slit diaphragm. Front. Pediatrics 2017, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cara-Fuentes, G.; Clapp, W.L.; Johnson, R.J.; Garin, E.H. Pathogenesis of proteinuria in idiopathic minimal change disease: Molecular mechanisms. Pediatric Nephrol. 2016, 31, 2179–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenoir, O.; Jasiek, M.; Hénique, C.; Guyonnet, L.; Hartleben, B.; Bork, T.; Chipont, A.; Flosseau, K.; Bensaada, I.; Schmitt, A. Endothelial cell and podocyte autophagy synergistically protect from diabetes-induced glomerulosclerosis. Autophagy 2015, 11, 1130–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, R.; Zeh, H.; Lotze, M.; Tang, D. The Beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klionsky, D.J.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Abe, A.; Abedin, M.J.; Abeliovich, H.; Arozena, A.A.; Adachi, H.; Adams, C.M.; Adams, P.D.; Adeli, K.; et al. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Autophagy 2016, 12, 1–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, H.; Wen, P.; Jiang, L.; He, W.; Dai, C.; Yang, J. Autophagy attenuates diabetic glomerular damage through protection of hyperglycemia-induced podocyte injury. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.J.; Huang, W.F.; Ye, L.; Chen, R.H.; Yang, C.; Wu, H.L.; Pan, Q.J.; Liu, H.F. The activity and role of autophagy in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 3182–3189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-H.; Inoki, K.; Guan, K.-L. mTOR pathway as a target in tissue hypertrophy. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007, 47, 443–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-K.; Chen, J.; Neilson, E.G.; Harris, R.C. Role of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in compensatory renal hypertrophy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Qin, L.; Shou, Z.; Zhao, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J. Rapamycin prevents early steps of the development of diabetic nephropathy in rats. Am. J. Nephrol. 2007, 27, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoki, K.; Mori, H.; Wang, J.; Suzuki, T.; Hong, S.; Yoshida, S.; Blattner, S.M.; Ikenoue, T.; Rüegg, M.A.; Hall, M.N.; et al. mTORC1 activation in podocytes is a critical step in the development of diabetic nephropathy in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121, 2181–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, C.D.; Lee, M.-S.; Marchetti, P.; Pietropaolo, M.; Towns, R.; Vaccaro, M.I.; Watada, H.; Wiley, J.W. The emerging role of autophagy in the pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus. Autophagy 2011, 7, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamahara, K.; Kume, S.; Koya, D.; Tanaka, Y.; Morita, Y.; Chin-Kanasaki, M.; Araki, H.; Isshiki, K.; Araki, S.-I.; Haneda, M.; et al. Obesity-mediated autophagy insufficiency exacerbates proteinuria-induced tubulointerstitial lesions. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 1769–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, K.Y.; Horng, L.Y.; Sung, H.C.; Huang, H.C.; Wu, R.T. Hepatocyte growth factor has a role in the amelioration of diabetic vascular complications via autophagic clearance of advanced glycation end products: Dispo85E, an HGF inducer, as a potential botanical drug. Metabolism 2011, 60, 888–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosokawa, N.; Hara, T.; Kaizuka, T.; Kishi, C.; Takamura, A.; Miura, Y.; Iemura, S.-I.; Natsume, T.; Takehana, K.; Yamada, N.; et al. Nutrient-dependent mTORC1 association with the ULK1–Atg13–FIP200 complex required for autophagy. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 1981–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushima, N. The role of the Atg1/ULK1 complex in autophagy regulation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 22, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaishi, K.; Mizue, Y.; Chikenji, T.; Otani, M.; Nakano, M.; Konari, N.; Fujimiya, M. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy ameliorates diabetic nephropathy via the paracrine effect of renal trophic factors including exosomes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nassar, W.; El-Ansary, M.; Sabry, D.; Mostafa, M.A.; Fayad, T.; Kotb, E.; Temraz, M.; Saad, A.N.; Essa, W.; Adel, H. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells derived extracellular vesicles can safely ameliorate the progression of chronic kidney diseases. Biomater. Res. 2016, 20, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, M.; Ichimura, Y. Physiological significance of selective degradation of p62 by autophagy. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 1374–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Jin, X.; Hu, C.F.; Li, R.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, C.X. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells rescue myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury by inducing cardiomyocyte autophagy via AMPK and Akt pathways. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Y.; Yan, W.J.; Yin, T.L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, J. Diet-induced obesity impairs spermatogenesis: A potential role for autophagy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.T.; Tan, H.L.; Shui, G.; Bauvy, C.; Huang, Q.; Wenk, M.R.; Ong, C.N.; Codogno, P.; Shen, H.M. Dual role of 3-methyladenine in modulation of autophagy via different temporal patterns of inhibition on class I and III phosphoinositide 3-kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 10850–10861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verschooten, L.; Barrette, K.; Van Kelst, S.; Rubio Romero, N.; Proby, C.; De Vos, R.; Agostinis, P.; Garmyn, M. Autophagy inhibitor chloroquine enhanced the cell death inducing effect of the flavonoid luteolin in metastatic squamous cell carcinoma cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ebrahim, N.; Ahmed, I.A.; Hussien, N.I.; Dessouky, A.A.; Farid, A.S.; Elshazly, A.M.; Mostafa, O.; Gazzar, W.B.E.; Sorour, S.M.; Seleem, Y.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Ameliorated Diabetic Nephropathy by Autophagy Induction through the mTOR Signaling Pathway. Cells 2018, 7, 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7120226
Ebrahim N, Ahmed IA, Hussien NI, Dessouky AA, Farid AS, Elshazly AM, Mostafa O, Gazzar WBE, Sorour SM, Seleem Y, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Ameliorated Diabetic Nephropathy by Autophagy Induction through the mTOR Signaling Pathway. Cells. 2018; 7(12):226. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7120226
Chicago/Turabian StyleEbrahim, Nesrine, Inas A. Ahmed, Noha I. Hussien, Arigue A. Dessouky, Ayman Samir Farid, Amal M. Elshazly, Ola Mostafa, Walaa Bayoumie El Gazzar, Safwa M. Sorour, Yasmin Seleem, and et al. 2018. "Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Ameliorated Diabetic Nephropathy by Autophagy Induction through the mTOR Signaling Pathway" Cells 7, no. 12: 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7120226
APA StyleEbrahim, N., Ahmed, I. A., Hussien, N. I., Dessouky, A. A., Farid, A. S., Elshazly, A. M., Mostafa, O., Gazzar, W. B. E., Sorour, S. M., Seleem, Y., Hussein, A. M., & Sabry, D. (2018). Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Ameliorated Diabetic Nephropathy by Autophagy Induction through the mTOR Signaling Pathway. Cells, 7(12), 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7120226