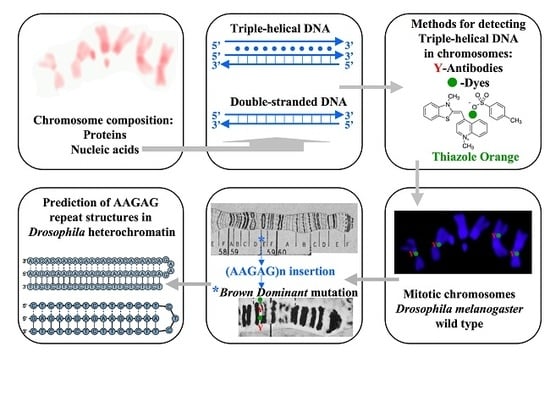
Triple-Helical DNA in Drosophila Heterochromatin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Preparation of Chromosome Spreads
2.3. Immunological Detection of Triple-Helical DNA
2.4. Thiazole Orange (TO) Staining
2.5. In Situ Hybridization
2.6. Triplex DNA Search Algorithm
3. Results
3.1. Triplex DNA is Immunologically Detected in Centromeric Regions of Drosophila Chromosomes
3.2. Triplex-Forming Sequences are Identified by Exploiting Immunocytochemical Detection and Drosophila Mutants
3.3. Conceptual Intra-Molecular Triplex DNA Assembled with AAGAG Repeats
3.4. A Structural Mark of Triple-Helical DNA is Detected by In Situ Hybridization
3.5. Thiazole Orange and Antibodies to Triplex DNA Simultaneously Bind to Satellite Repeats
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riley, M.; Maling, B.; Chamberlin, M.J. Physical and chemical characterization of two- and three-stranded adenine-thymine and adenine-uracil homopolymer complexes. J. Mol. Biol. 1966, 20, 359–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank-Kamenetskii, M.D.; Mirkin, S.M. Triplex DNA structures. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1995, 64, 65–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsenfeld, G.; Davies, D.R.; Rich, A. Formation of a three-stranded polynucleotide molecule. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1957, 79, 2023–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyne, P.R.; Edwards, L.M.; Viari, A.; Maher, L.J. Searching genomes for sequences with the potential to form intra-strand triple helices. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 302, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-García, E.; Vaquero, A.; Espinás, M.L.; Soliva, R.; Orozco, M.; Bernués, J.; Azorín, F. The GAGA factor of Drosophila binds triple-stranded DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 24640–24648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Hundseth, K.; Ding, H.; Vidhyasagar, V.; Inoue, A.; Nguyen, C.H.; Zain, R.; Lee, J.S.; Wu, Y. A distinct triplex DNA unwinding activity of ChlR1 helicase. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 5174–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Burkholder, G.D.; Latimer, L.J.P.; Haug, B.L.; Braun, R.P. A monoclonal antibody to triplex DNA binds to eucaryotic chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987, 15, 1047–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burkholder, G.D.; Latimer, L.J.P.; Lee, J.S. Immunofluorescent staining of mammalian nuclei and chromosomes with a monoclonal antibody to triplex DNA. Chromosoma 1988, 97, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkholder, G.D.; Latimer, L.J.P.; Lee, J.S. Immunofluorescent localization of triplex DNA in polytene chromosomes of Chironomus and Drosophila. Chromosoma 1991, 101, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agazie, Y.M.; Lee, J.S.; Burkholder, G.D. Characterization of a new monoclonal antibody to triplex DNA and immunofluorescent staining of mammalian chromosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 7019–7023. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agazie, Y.M.; Burkholder, G.D.; Lee, J.S. Triplex DNA in the nucleus: Direct binding of triplex-specific antibodies and their effect on transcription, replication and cell growth. Biochem. J. 1996, 316, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, M.; Fukagawa, T.; Lee, J.S.; Ikemura, T. Triplex-forming DNAs in the human interphase nucleus visualized in situ by polypurine/polypyrimidine DNA probes and anti-triplex antibodies. Chromosoma 2002, 111, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Černá, A.; López-Fernández, C.; Fernández, J.L.; de la Espina, S.M.D.; De la Torre, C.; Gosálvez, J. Triplex configuration in the nick-free DNAs that constitute the chromosomal scaffolds in grasshopper spermatids. Chromosoma 2008, 117, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Piergentili, R.; Mencarelli, C. Drosophila melanogaster kl-3 and kl-5 Y-loops harbor triple-stranded nucleic acids. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorab, E.; Amabis, J.M.; Stocker, A.J.; Drummond, L.; Stollar, B.D. Potential sites of triple-helical nucleic acid formation in chromosomes of Rhynchosciara (Diptera: Sciaridae) and Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosome Res. 2009, 17, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadloun, A.; Le Gras, S.; Jost, B.; Ziegler-Birling, C.; Takahashi, H.; Gorab, E.; Carninci, P.; Torres-Padilla, M.-E. Chromatin signatures and retrotransposon profiling in mouse embryos reveal regulation of LINE-1 by RNA. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, T.; Subhash, S.; Vaid, R.; Enroth, S.; Uday, S.; Reinius, B.; Mitra, S.; Mohammed, A.; James, A.R.; Hoberg, E.; et al. MEG long noncoding RNA regulates TGF-fl pathway genes through formation of RNA-DNA triplex structures. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavan, S.C.; Chastain, P.; Lee, J.S.; Hegde, B.G.; Houston, S.; Langen, R.; Hsieh, C.L.; Haworth, I.S.; Lieber, M.R. Evidence for a triplex DNA conformation at the bcl-2 major breakpoint region of the t(14;18) translocation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 22749–22756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergquist, H.; Rocha, C.S.; Álvarez-Asencio, R.; Nguyen, C.H.; Rutland, M.W.; Smith, C.I.; Good, L.; Nielsen, P.E.; Zain, R. Disruption of higher order DNA structures in Freidreich’s Ataxia (GAA)n repeats by PNA or LNA targeting. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorab, E.; Pearson, P.L. Thiazole orange as an alternative to antibody binding for detecting triple-helical DNA in heterochromatin of Drosophila and Rhynchosciara. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2018, 66, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roiha, H.; Miller, J.R.; Woods, L.C.; Glover, D.M. Arrangement and rearrangements of sequences flanking the two types of rDNA insertion in D. melanogaster. Nature 1981, 290, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hon, J.; Martínek, T.; Rajdl, K.; Lexa, M. Triplex: An R/Bioconductor package for identification and visualization of potential intramolecular triplex patterns in DNA sequences. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1900–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csink, A.K.; Henikoff, S. Genetic modification of heterochromatic association and nuclear organization in Drosophila. Nature 1996, 381, 529–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridges, C. Salivary chromosome maps with a key to the banding of chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. J. Hered. 1935, 26, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudkin, G.T. The relative mutabilities of DNA regions of the X chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 1965, 52, 665–681. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zain, R.; Sun, J.-S. Do natural DNA triple-helical structures occur and function in vivo? Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2003, 60, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, V.; Lacroix, L.; Gautier, T.; Takasugi, M.; Mergny, J.-L.; Lacoste, J. Triple helix formation with Drosophila satellite repeats. Unexpected stabilization by copper ions. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 11196–11205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, C.; Geinguenaud, F.; Gouyette, C.; Liquier, J.; Lacoste, J. Mechanism of copper mediated triple helix formation at neutral pH in Drosophila satellite repeats. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 2498–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohe, A.R.; Hiliker, A.J.; Roberts, P.A. Mapping simple repeated DNA sequences in heterochromatin of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 1993, 134, 1149–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisha, P.; Plank, J.L.; Csink, A.K. Analysis of chromatin structure of genes silenced by heterochromatin in trans. Genetics 2008, 179, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beisel, C.; Paro, R. Silencing chromatin: Comparing modes and mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piacentini, L.; Fanti, L.; Berloco, M.; Perrini, B.; Pimpinelli, S. Heterochromatin protein 1(HP1) is associated with induced gene expression in Drosophila euchromatin. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 161, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henikoff, S.; Furuyama, T. The unconventional structure of centromeric nucleosomes. Chromosoma 2012, 121, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Espinás, M.L.; Jiménez-García, E.; Martínez-Balbás, Á.; Azorín, F. Formation of triple-stranded DNA at d(GA_TC)n sequences prevents nucleosome assembly and is hindered by nucleosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 31801–31812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.; Wang, Y.H. Friedreich’s ataxia GAA.TTC duplex and GAA.GAA.TTC triplex structures exclude nucleosome assembly. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 383, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gorab, E. Triple-Helical DNA in Drosophila Heterochromatin. Cells 2018, 7, 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7120227
Gorab E. Triple-Helical DNA in Drosophila Heterochromatin. Cells. 2018; 7(12):227. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7120227
Chicago/Turabian StyleGorab, Eduardo. 2018. "Triple-Helical DNA in Drosophila Heterochromatin" Cells 7, no. 12: 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7120227
APA StyleGorab, E. (2018). Triple-Helical DNA in Drosophila Heterochromatin. Cells, 7(12), 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7120227