RAC1B: A Rho GTPase with Versatile Functions in Malignant Transformation and Tumor Progression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. RAC1B in the Evolution of Ras-like GTPases
3. General Structure and Tissue Expression of RAC1B
4. Biochemical Properties, Generation and Degradation of RAC1B
4.1. Biochemical Properties
4.2. Regulation of RAC1B Splicing
4.3. Regulation of RAC1B Protein Stability
4.4. Regulation of RAC1B Biological Activity by Subcellular Localization
4.5. Binding Partners and Downstream Effectors
5. Biological Functions of RAC1B
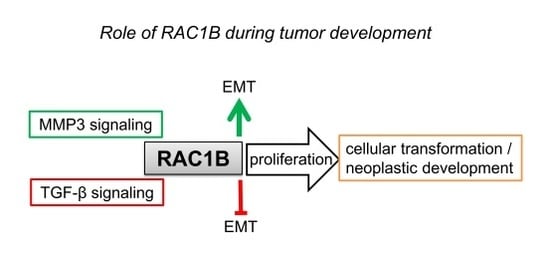
5.1. Cancer Progression/Cellular Transformation
5.2. Inflammation and Regeneration
5.3. Stromal Control of RAC1B by MMP3
5.4. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT)
5.5. Adhesion and Cell-Cell Interactions
5.6. Cell Motility and Migration
5.7. Proliferation/Cell Cycle Regulation
5.8. Cellular Senescence
5.9. Survival/Anti-Apoptosis
5.10. Neurogenic Stem Cell Differentiation
5.11. Mutual Negative Regulation of RAC1 and RAC1B
6. Regulation of Signaling Pathways by RAC1B
6.1. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases (MAPKs)
6.2. NFκB
6.3. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
6.4. Wnt/β-Catenin
6.5. TGF-β/SMAD
6.6. Inhibitors
7. RAC1B as a Prognostic Marker in Cancer
7.1. Breast Cancer
7.2. Colorectal Cancer (CRC)
7.3. Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
7.4. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
7.5. Pancreatic Cancer and Chronic Pancreatitis
7.6. Thyroid Cancer
8. Conclusions and Perspectives
8.1. Is RAC1B Really the Bad Brother of RAC1 in Cancer?
- by upstream activators that affect its generation and subcellular localization. For instance, PI3-kinase/AKT signaling promotes RAC1B expression via alternative splicing while Wnt signaling inhibits it.
- by an increase in RAC1B activation levels due to altered regulation by GEFs and GAPs.
- by functional interactions with factors that promote malignant progression such as oncogenes (BRAF, KRAS) and tumor suppressor genes (APC), or environmental clues such as MMPs.
- by shifting the balance of pro- to antitumorigenic signaling pathways. For instance, RAC1B activates tumor-promoting NFκB and KRAS signaling but inhibits tumor-suppressive TGF-β signaling.
- by stimulating cancer-promoting processes such as carcinogen/acute inflammation or protecting against cancer such as early mucosal repair, depending on the tissue.
- by promoting early mucosal healing after resolution of intestinal inflammation.
- by antagonizing TGF-β signaling under conditions where TGF-β promotes malignant progression, i.e., in advanced stages of many carcinomas.
8.2. Potential Prognostic and Therapeutic Use of RAC1B
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boureux, A.; Vignal, E.; Faure, S.; Fort, P. Evolution of the rho family of ras-like gtpases in eukaryotes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, P.; Skaug, J.; Marques, B.; Beck, S.; Veríssimo, F.; Gespach, C.; Boavida, M.G.; Scherer, S.W.; Jordan, P. Small gtpase rac1: Structure, localization, and expression of the human gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 277, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnelzer, A.; Prechtel, D.; Knaus, U.; Dehne, K.; Gerhard, M.; Graeff, H.; Harbeck, N.; Schmitt, M.; Lengyel, E. Rac1 in human breast cancer: Overexpression, mutation analysis, and characterization of a new isoform, rac1b. Oncogene 2000, 19, 3013–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiegen, D. Alternative splicing of rac1 generates rac1b, a self-activating gtpase. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 4743–4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeusler, L.C.; Hemsath, L.; Fiegen, D.; Blumenstein, L.; Herbrand, U.; Stege, P.; Dvorsky, R.; Ahmadian, M.R. Purification and biochemical properties of rac1, 2, 3 and the splice variant rac1b. Methods Enzymol. 2006, 406, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.J.; Ha, B.H.; Holman, E.C.; Halaban, R.; Schlessinger, J.; Boggon, T.J. Rac1p29s is a spontaneously activating cancer-associated gtpase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Karnoub, A.E.; Palmby, T.R.; Lengyel, E.; Sondek, J.; Der, C.J. Rac1b, a tumor associated, constitutively active rac1 splice variant, promotes cellular transformation. Oncogene 2004, 23, 9369–9380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, P.; Collard, J.G.; Jordan, P. Tumor-related alternatively spliced rac1b is not regulated by rho-gdp dissociation inhibitors and exhibits selective downstream signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 50442–50448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, V.; Matos, P.; Jordan, P. Antagonistic sr proteins regulate alternative splicing of tumor-related rac1b downstream of the pi3-kinase and wnt pathways. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 3696–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordonaro, M. Crosstalk between wnt signaling and rna processing in colorectal cancer. J. Cancer 2013, 4, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, V.; Henriques, A.; Pereira, J.; Neves Costa, A.; Moyer, M.P.; Moita, L.F.; Gama-Carvalho, M.; Matos, P.; Jordan, P. Phosphorylation of srsf1 by srpk1 regulates alternative splicing of tumor-related rac1b in colorectal cells. RNA 2014, 20, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelisch, F.; Khauv, D.; Risso, G.; Stallings-Mann, M.; Blaustein, M.; Quadrana, L.; Radisky, D.C.; Srebrow, A. Involvement of hnrnp a1 in the matrix metalloprotease-3-dependent regulation of rac1 pre-mrna splicing. J. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 113, 2319–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Fu, X.; Chen, P.; Wu, P.; Fan, X.; Li, N.; Zhu, H.; Jia, T.T.; Ji, H.; Wang, Z.; et al. SPSB1-mediated HnRNP A1 ubiquitylation regulates alternative splicing and cell migration in EGF signaling. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 540–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ishii, H.; Saitoh, M.; Sakamoto, K.; Kondo, T.; Katoh, R.; Tanaka, S.; Motizuki, M.; Masuyama, K.; Miyazawa, K. Epithelial splicing regulatory proteins 1 (esrp1) and 2 (esrp2) suppress cancer cell motility via different mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 27386–27399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esufali, S.; Charames, G.S.; Bapat, B. Suppression of nuclear wnt signaling leads to stabilization of rac1 isoforms. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 4850–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visvikis, O.; Lorès, P.; Boyer, L.; Chardin, P.; Lemichez, E.; Gacon, G. Activated rac1, but not the tumorigenic variant rac1b, is ubiquitinated on Lys 147 through a jnk-regulated process. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Chen, Q.K.; Lui, C.; Cichon, M.A.; Radisky, D.C.; Nelson, C.M. Matrix compliance regulates rac1b localization, nadph oxidase assembly, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 4097–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.K.; Lee, K.; Radisky, D.C.; Nelson, C.M. Extracellular matrix proteins regulate epithelial–mesenchymal transition in mammary epithelial cells. Differentiation 2013, 86, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehner, C.; Miller, E.; Khauv, D.; Nassar, A.; Oberg, A.L.; Bamlet, W.R.; Zhang, L.; Waldmann, J.; Radisky, E.S.; Crawford, H.C.; et al. Tumor cell-derived mmp3 orchestrates rac1b and tissue alterations that promote pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esufali, S.; Charames, G.S.; Pethe, V.V.; Buongiorno, P.; Bapat, B. Activation of tumor-specific splice variant rac1b by dishevelled promotes canonical wnt signaling and decreased adhesion of colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2469–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlichenko, L.; Geyer, R.; Yanagisawa, M.; Khauv, D.; Radisky, E.S.; Anastasiadis, P.Z.; Radisky, D.C. The 19-amino acid insertion in the tumor-associated splice isoform rac1b confers specific binding to p120 catenin. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 19153–19161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, B.; Zhang, X.; Shang, R.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Dou, K. Blockade of ARHGAP11A reverses malignant progress via inactivating Rac1B in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 16, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallings-Mann, M.L.; Waldmann, J.; Zhang, Y.; Miller, E.; Gauthier, M.L.; Visscher, D.W.; Downey, G.P.; Radisky, E.S.; Fields, A.P.; Radisky, D.C. Matrix metalloproteinase induction of rac1b, a key effector of lung cancer progression. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Licciulli, S.; Avila, J.L.; Cho, M.; Troutman, S.; Jiang, P.; Kossenkov, A.V.; Showe, L.C.; Liu, Q.; Vachani, A.; et al. The rac1 splice form rac1b promotes k-ras-induced lung tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2013, 32, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotelevets, L.; Walker, F.; Mamadou, G.; Lehy, T.; Jordan, P.; Chastre, E. The Rac1 splice form Rac1b favors mouse colonic mucosa regeneration and contributes to intestinal cancer progression. Oncogene 2018, 37, 6054–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, M.; Matos, P.; Pereira, T.; Cabrera, R.; Cardoso, B.A.; Bugalho, M.J.; Silva, A.L. Rac1b overexpression stimulates proliferation and nf-kb-mediated anti-apoptotic signaling in thyroid cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, P.; Kotelevets, L.; Goncalves, V.; Henriques, A.F.; Zerbib, P.; Moyer, M.P.; Chastre, E.; Jordan, P. Ibuprofen inhibits colitis-induced overexpression of tumor-related Rac1b. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radisky, D.C.; Levy, D.D.; Littlepage, L.E.; Liu, H.; Nelson, C.M.; Fata, J.E.; Leake, D.; Godden, E.L.; Albertson, D.G.; Angela Nieto, M.; et al. Rac1b and reactive oxygen species mediate mmp-3-induced emt and genomic instability. Nature 2005, 436, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.R.; Durrans, A.; Lee, S.; Sheng, J.; Li, F.; Wong, S.T.C.; Choi, H.; El Rayes, T.; Ryu, S.; Troeger, J.; et al. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is not required for lung metastasis but contributes to chemoresistance. Nature 2015, 527, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, X.; Carstens, J.L.; Kim, J.; Scheible, M.; Kaye, J.; Sugimoto, H.; Wu, C.-C.; LeBleu, V.S.; Kalluri, R. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is dispensable for metastasis but induces chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Nature 2015, 527, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stallings-Mann, M.; Radisky, D. Matrix metalloproteinase-induced malignancy in mammary epithelial cells. Cells Tissues Organs 2007, 185, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, C.M.; Khauv, D.; Bissell, M.J.; Radisky, D.C. Change in cell shape is required for matrix metalloproteinase-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of mammary epithelial cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 105, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cichon, M.A.; Nelson, C.M.; Radisky, D.C. Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells by cell contact and adhesion. Cancer Inform. 2015, 14 (Suppl. 3), 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoni, E.; Bianchini, F.; Calorini, L.; Chiarugi, P. Cancer associated fibroblasts exploit reactive oxygen species through a proinflammatory signature leading to epithelial mesenchymal transition and stemness. Antioxid. Redox 2011, 14, 2361–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witte, D.; Otterbein, H.; Forster, M.; Giehl, K.; Zeiser, R.; Lehnert, H.; Ungefroren, H. Negative regulation of TGF-beta1-induced MKK6-p38 and MEK-ERK signalling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by Rac1b. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chartier, N.T. Laminin-5-integrin interaction signals through pi 3-kinase and rac1b to promote assembly of adherens junctions in ht-29 cells. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, E.; Frasa, M.A.M.; Smolarczyk, K.; Knaus, U.G.; Braga, V.M.M. Pak is required for the disruption of e-cadherin adhesion by the small gtpase rac. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Larribere, L.; Sun, Q.; Novak, D.; Sachindra, S.; Granados, K.; Umansky, V.; Utikal, J. Loss of neural crest-associated gene FOXD1 impairs melanoma invasion and migration via RAC1B downregulation. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 2962–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzer, C.; Hass, R.; von der Ohe, J.; Lehnert, H.; Ungefroren, H. The role of TGF-beta and its crosstalk with RAC1/RAC1b signaling in breast and pancreas carcinoma. Cell Commun. Signal. 2017, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungefroren, H.; Sebens, S.; Giehl, K.; Helm, O.; Groth, S.; Fandrich, F.; Rocken, C.; Sipos, B.; Lehnert, H.; Gieseler, F. Rac1b negatively regulates TGF-beta1-induced cell motility in pancreatic ductal epithelial cells by suppressing Smad signalling. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, P.; Jordan, P. Expression of rac1b stimulates nf-κb-mediated cell survival and g1/s progression. Exp. Cell Res. 2005, 305, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, P.; Jordan, P. Increased rac1b expression sustains colorectal tumor cell survival. Mol. Cancer Res. 2008, 6, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Ying, L.; Wang, H.; Wei, S.S.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.H.; Xu, W.P.; Jie, Q.Q.; Zhou, Q.; Li, Y.G.; et al. Rac1b enhances cell survival through activation of the JNK2/c-JUN/Cyclin-D1 and AKT2/MCL1 pathways. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 17970–17985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Curtis, K.M.; Gomez, L.A.; Schiller, P.C. Rac1b regulates nt3-stimulated mek-erk signaling, directing marrow-isolated adult multilineage inducible (miami) cells toward an early neuronal phenotype. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2012, 49, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, P.; Oliveira, C.; Velho, S.; Gonçalves, V.; da Costa, L.T.; Moyer, M.P.; Seruca, R.; Jordan, P. B-rafv600e cooperates with alternative spliced rac1b to sustain colorectal cancer cell survival. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melzer, C.; von der Ohe, J.; Hass, R.; Ungefroren, H. TGF-beta-Dependent Growth Arrest and Cell Migration in Benign and Malignant Breast Epithelial Cells Are Antagonistically Controlled by Rac1 and Rac1b. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, Y.; Yagi, S.; Sakurai, A.; Matsuda, M.; Kiyokawa, E. Insufficient ability of rac1b to perturb cystogenesis. Small GTPases 2013, 4, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, A.F.A.; Barros, P.; Moyer, M.P.; Matos, P.; Jordan, P. Expression of tumor-related rac1b antagonizes b-raf-induced senescence in colorectal cells. Cancer Lett. 2015, 369, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, C.; Hass, R. Mmp-7 is involved in the aging of primary human mammary epithelial cells (hmec). Exp. Gerontol. 2008, 43, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, C.; Hass, R. Cellular responses to reactive oxygen species-induced DNA damage and aging. Biol. Chem. 2008, 389, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, C.; Hass, R. Cellular senescence of human mammary epithelial cells (hmec) is associated with an altered mmp-7/hb-egf signaling and increased formation of elastin-like structures. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2009, 130, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayachandra, K.; Higgins, W.; Lee, J.; Glick, A. Induction of p16ink4aand p19arfby tgfβ1 contributes to growth arrest and senescence response in mouse keratinocytes. Mol. Carcinog. 2009, 48, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.W.; Nikpay, M.; Silva, A.; Lau, P.; Martinuk, A.; Linseman, T.A.; Soubeyrand, S.; McPherson, R. Functional interaction between col4a1/col4a2 and smad3 risk loci for coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 2015, 242, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiercinska, E.; Naber, H.P.H.; Pardali, E.; van der Pluijm, G.; van Dam, H.; ten Dijke, P. The tgf-β/smad pathway induces breast cancer cell invasion through the up-regulation of matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 in a spheroid invasion model system. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 128, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugioka, K.; Kodama, A.; Okada, K.; Iwata, M.; Yoshida, K.; Kusaka, S.; Matsumoto, C.; Kaji, H.; Shimomura, Y. Tgf-β2 promotes rpe cell invasion into a collagen gel by mediating urokinase-type plasminogen activator (upa) expression. Exp. Eye Res. 2013, 115, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Hass, R. Extracellular signals in young and aging breast epithelial cells and possible connections to age-associated breast cancer development. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2011, 132, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipriano, R.; Kan, C.E.; Graham, J.; Danielpour, D.; Stampfer, M.; Jackson, M.W. Tgf-beta signaling engages an atm-chk2-p53-independent ras-induced senescence and prevents malignant transformation in human mammary epithelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8668–8673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, L.; Li, G.; Wei, S.; Wang, H.; An, P.; Wang, X.; Guo, K.; Luo, X.; Gao, J.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Sanguinarine inhibits rac1b-rendered cell survival enhancement by promoting apoptosis and blocking proliferation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimnual, A.S.; Taylor, L.J.; Nyako, M.; Jeng, H.-H.; Bar-Sagi, D. Perturbation of cytoskeleton dynamics by the opposing effects of rac1 and rac1b. Small GTPases 2010, 1, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lee, W.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Jhunjhunwala, S.; Haverty, P.M.; Gnad, F.; Guan, Y.; Gilbert, H.N.; Stinson, J.; et al. Genome and transcriptome sequencing of lung cancers reveal diverse mutational and splicing events. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 2315–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matos, P.; Jordan, P. Rac1, but not rac1b, stimulates relb-mediated gene transcription in colorectal cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 13724–13732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, P.; Jordan, P.; Matos, P. Rac1 signaling modulates bcl-6-mediated repression of gene transcription. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 4156–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.T.; Park, J.T.; Choi, K.; Choi, H.J.C.; Jung, C.W.; Kim, G.R.; Lee, Y.S.; Park, S.C. Chemical screening identifies ROCK as a target for recovering mitochondrial function in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. Aging Cell 2017, 16, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pethe, V.V.; Charames, G.S.; Bapat, B. Rac1b recruits Dishevelled and beta-catenin to Wnt target gene promoters independent of Wnt3A stimulation. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 39, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shutes, A.; Onesto, C.; Picard, V.; Leblond, B.; Schweighoffer, F.; Der, C.J. Specificity and mechanism of action of eht 1864, a novel small molecule inhibitor of rac family small gtpases. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 35666–35678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Dickerson, J.B.; Guo, F.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, Y. Rational design and characterization of a rac gtpase-specific small molecule inhibitor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 7618–7623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beausoleil, E.; Chauvignac, C.; Taverne, T.; Lacombe, S.; Pognante, L.; Leblond, B.; Pallares, D.; Oliveira, C.D.; Bachelot, F.; Carton, R.; et al. Structure–activity relationship of isoform selective inhibitors of rac1/1b gtpase nucleotide binding. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 5594–5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehner, C.; Miller, E.; Nassar, A.; Bamlet, W.R.; Radisky, E.S.; Radisky, D.C. Tumor cell expression of MMP3 as a prognostic factor for poor survival in pancreatic, pulmonary, and mammary carcinoma. Genes Cancer 2015, 6, 480–489. [Google Scholar]
- Guinney, J.; Dienstmann, R.; Wang, X.; de Reyniès, A.; Schlicker, A.; Soneson, C.; Marisa, L.; Roepman, P.; Nyamundanda, G.; Angelino, P.; et al. The consensus molecular subtypes of colorectal cancer. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1350–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alonso-Espinaco, V.; Cuatrecasas, M.; Alonso, V.; Escudero, P.; Marmol, M.; Horndler, C.; Ortego, J.; Gallego, R.; Codony-Servat, J.; Garcia-Albeniz, X.; et al. Rac1b overexpression correlates with poor prognosis in kras/braf wt metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with first-line folfox/xelox chemotherapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, V.; Gupta, A.; Kumar, R.; Gupta, T.; Mohan, A.; Dey, S. Quantification of rac1 and rac1b in serum of non small cell lung cancer by label free real time assay. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 460, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, M.; Capinha, L.; Simões-Pereira, J.; Bugalho, M.J.; Silva, A.L. Extending the impact of rac1b overexpression to follicular thyroid carcinomas. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.L.; Carmo, F.; Bugalho, M.J. Rac1b overexpression in papillary thyroid carcinoma: A role to unravel. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 168, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carl, C.; Flindt, A.; Hartmann, J.; Dahlke, M.; Rades, D.; Dunst, J.; Lehnert, H.; Gieseler, F.; Ungefroren, H. Ionizing radiation induces a motile phenotype in human carcinoma cells in vitro through hyperactivation of the TGF-beta signaling pathway. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heid, I.; Lubeseder–Martellato, C.; Sipos, B.; Mazur, P.K.; Lesina, M.; Schmid, R.M.; Siveke, J.T. Early requirement of rac1 in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Melzer, C.; Hass, R.; Lehnert, H.; Ungefroren, H. RAC1B: A Rho GTPase with Versatile Functions in Malignant Transformation and Tumor Progression. Cells 2019, 8, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8010021
Melzer C, Hass R, Lehnert H, Ungefroren H. RAC1B: A Rho GTPase with Versatile Functions in Malignant Transformation and Tumor Progression. Cells. 2019; 8(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleMelzer, Catharina, Ralf Hass, Hendrik Lehnert, and Hendrik Ungefroren. 2019. "RAC1B: A Rho GTPase with Versatile Functions in Malignant Transformation and Tumor Progression" Cells 8, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8010021
APA StyleMelzer, C., Hass, R., Lehnert, H., & Ungefroren, H. (2019). RAC1B: A Rho GTPase with Versatile Functions in Malignant Transformation and Tumor Progression. Cells, 8(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8010021