Dendritic Cells Expressing MyD88 Molecule Are Necessary and Sufficient for CpG-Mediated Inhibition of IgE Production In Vivo
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Alum Gel Preparation
2.3. Experimental Protocol
2.4. Generation of Bone Marrow Derived Dendritic Cells
2.5. ELISA for Antibody Determinations
2.6. Active Cutaneous Anaphylaxis (ACA) Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. CpG Regulates Lung Allergic Inflammation and Immunoglobulin Production
3.2. MyD88 Expression on B Cells Is Not Essential for CpG-Mediated Regulation of IgE and IgG2c Isotype Production In Vivo
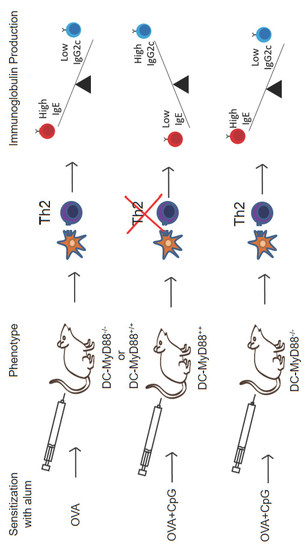
3.3. CD11c-Positive Dendritic Cells Expressing MyD88 Molecule Are Necessary and Sufficient for CpG-Induced Inhibition of IgE and Augmented IgG2c Production
3.4. CpG-Induced Inhibition of IgE and Augment IgG2a Production Is Independent of Type I or Type II Interferon Receptors
3.5. MyD88 Expression on OVA-primed Dendritic Cells Is Essential for Inhibition IgE Production by CpG
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, L.C.; Zarrin, A.A. The production and regulation of IgE by the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirakawa, T.; Enomoto, T.; Shimazu, S.I.; Hopkin, J.M. The Inverse Association Between Tuberculin Responses and Atopic Disorder. Science 1997, 275, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strachan, D.P. Family size, infection and atopy: The first decade of the ‘hygiene hypothesis’. Thorax 2000, 55, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.C.; Scheerens, H. Targeting IgE production in mice and humans. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 31, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coffman, R.L.; Seymour, B.W.P.; Lebman, D.A.; Hiraki, D.D.; Christiansen, J.A.; Shrader, B.; Cherwinski, H.M.; Savelkoul, H.F.J.; Finkelman, F.D.; Bond, M.W.; et al. The Role of Helper T Cell Products in Mouse B Cell Differentiation and Isotype Regulation. Immunol. Rev. 1988, 102, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrack, P.; McKee, A.S.; Munks, M.W. Towards an understanding of the adjuvant action of aluminium. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pasquale, A.; Preiss, S.; Silva, F.; Garçon, N. Vaccine Adjuvants: From 1920 to 2015 and Beyond. Vaccines 2015, 3, 320–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolatto, J.; Mirotti, L.; Rodriguez, D.; Gomes, E.; Russo, M. Adsorption of Toll-Like Receptor 4 Agonist to Alum-Based Tetanus Toxoid Vaccine Dampens Pro-T Helper 2 Activities and Enhances Antibody Responses. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirotti, L.C.; Custódio, R.W.A.; Gomes, E.; Rammauro, F.; De Araujo, E.F.; Calich, V.L.G.; Russo, M. CpG-ODN Shapes Alum Adjuvant Activity Signaling via MyD88 and IL-10. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhagen, F.; Kinjo, T.; Bode, C.; Klinman, D.M. TLR-based immune adjuvants. Vaccine 2011, 29, 3341–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, N.; Ohnishi, N.; Ni, L.; Akira, S.; Bacon, K.B. CpG directly induces T-bet expression and inhibits IgG1 and IgE switching in B cells. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caton, M.L.; Smith-Raska, M.R.; Reizis, B. Notch–RBP-J signaling controls the homeostasis of CD8−dendritic cells in the spleen. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, J.; Wu, K.; Azhati, B.; Rexiati, M. Culture and Identification of Mouse Bone Marrow-Derived Dendritic Cells and Their Capability to Induce T Lymphocyte Proliferation. Med Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radu, M.; Chernoff, J. An in vivo Assay to Test Blood Vessel Permeability. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 16, e50062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasare, C.; Medzhitov, R. Control of B-cell responses by Toll-like receptors. Nature 2005, 438, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retter, I.; Chevillard, C.; Scharfe, M.; Conrad, A.; Hafner, M.; Im, T.-H.; Ludewig, M.; Nordsiek, G.; Severitt, S.; Thies, S.; et al. Sequence and Characterization of the Ig Heavy Chain Constant and Partial Variable Region of the Mouse Strain 129S1. J. Immunol. 2014, 179, 2419–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasare, C.; Medzhitov, R. Immunology: Toll-like receptors and antibody responses (reply). Nature 2006, 438, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavin, A.L.; Hoebe, K.; Duong, B.; Ota, T.; Martin, C.; Beutler, B.; Nemazee, D. Adjutant-enhanced antibody responses in the absence of toll-like receptor signaling. Science 2006, 314, 1936–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, M.L.; Yildirim, A.Ö.; Sonar, S.S.; Kiliç, A.; Sudowe, S.; Lunow, M.; Teich, R.; Renz, H.; Garn, H. Comparison of adjuvant and adjuvant-free murine experimental asthma models. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2009, 39, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krieg, A.M.; Yi, A.K.; Matson, S.; Waldschmidt, T.J.; Bishop, G.A.; Teasdale, R.; Koretzky, G.A.; Klinman, D.M. CpG motifs in bacterial DNA trigger direct B-cell activation. Nature 1995, 374, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeredjian-Ding, I.; Jego, G. Toll-like receptors–sentries in the B-cell response. Immunology 2009, 128, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Gerth, A.J.; Peng, S.L. CpG DNA redirects class-switching towards “Th1-like” Ig isotype production via TLR9 and MyD88. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 1483–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Goldschmidt, T.; Salter, H. Possible allelic structure of IgG2a and IgG2c in mice. Mol. Immunol. 2012, 50, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinton, M.; Kopf, M.F.; Bachmann, A.; Jegerlehner, P.; Maurer, J.; Bessa, H.J.; Jegerlehner, A.; Maurer, P.; Bessa, J.; Hinton, H.J.; et al. Switch Recombination to IgG2a TLR9 Signaling in B Cells Determines Class TLR9 Signaling in B Cells Determines Class Switch Recombination to IgG2a. J. Immunol. Ref. J. Immunol. 2016, 178, 2415–2420. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, B.; Reizis, B.; DeFranco, A.L. Toll-like receptors activate innate and adaptive immunity by using dendritic cell-intrinsic and -extrinsic mechanisms. Immunity 2008, 29, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, B.; Saudan, P.; Ott, G.; Wheeler, M.L.; Ji, M.; Kuzmich, L.; Lee, L.M.; Coffman, R.L.; Bachmann, M.F.; DeFranco, A.L. Selective utilization of Toll-like receptor and MyD88 signaling in B cells for enhancement of the antiviral germinal center response. Immunity 2011, 34, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutelier, J.P.; van der Logt, J.T.; Heessen, F.W.; Warnier, G.; Van Snick, J. IgG2a restriction of murine antibodies elicited by viral infections. J. Exp. Med. 1987, 165, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jegerlehner, A.; Maurer, P.; Bessa, J.; Hinton, H.J.; Kopf, M.; Bachmann, M.F. TLR9 signaling in B cells determines class switch recombination to IgG2a. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 2415–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kline, J.N.; Waldschmidt, T.J.; Businga, T.R.; Lemish, J.E.; Weinstock, J.V.; Thorne, P.S.; Krieg, A.M. Modulation of airway inflammation by CpG oligodeoxynucleotides in a murine model of asthma. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 2555–2559. [Google Scholar]
- Markine-Goriaynoff, D.; Van Der Logt, J.T.M.; Truyens, C.; Nguyen, T.D.; Heessen, F.W.A.; Bigaignon, G.; Carlier, Y.; Coutelier, J.P. IFN-γ-independent IgG2a production in mice infected with viruses and parasites. Int. Immunol. 2000, 12, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, M.M.; Bizzarro, B.; Sá-Nunes, A.; Rios, F.J.; Jancar, S. Boosting Adaptive Immunity: A New Role for PAFR Antagonists. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DeVries, A.; Vercelli, D. Epigenetics in allergic diseases. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2015, 27, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Potaczek, D.P.; Harb, H.; Michel, S.; Alhamwe, B.A.; Renz, H.; Tost, J. Epigenetics and allergy: From basic mechanisms to clinical applications. Epigenomics 2017, 9, 539–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowthaman, U.; Chen, J.S.; Zhang, B.; Flynn, W.F.; Lu, Y.; Song, W.; Joseph, J.; Gertie, J.A.; Xu, L.; Collet, M.A.; et al. Identification of a T follicular helper cell subset that drives anaphylactic IgE. Science 2019, 365, 6433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, H.; Dolpady, J.; Wabl, M.; Curotto de Lafaille, M.A.; Lafaille, J.J. Sequential class switching is required for the generation of high affinity IgE antibodies. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alberca Custodio, R.W.; Mirotti, L.; Gomes, E.; Nunes, F.P.B.; S. Vieira, R.; Graça, L.; R. Almeida, R.; S. Câmara, N.O.; Russo, M. Dendritic Cells Expressing MyD88 Molecule Are Necessary and Sufficient for CpG-Mediated Inhibition of IgE Production In Vivo. Cells 2019, 8, 1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101165
Alberca Custodio RW, Mirotti L, Gomes E, Nunes FPB, S. Vieira R, Graça L, R. Almeida R, S. Câmara NO, Russo M. Dendritic Cells Expressing MyD88 Molecule Are Necessary and Sufficient for CpG-Mediated Inhibition of IgE Production In Vivo. Cells. 2019; 8(10):1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101165
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlberca Custodio, Ricardo W., Luciana Mirotti, Eliane Gomes, Fernanda P.B. Nunes, Raquel S. Vieira, Luís Graça, Rafael R. Almeida, Niels O. S. Câmara, and Momtchilo Russo. 2019. "Dendritic Cells Expressing MyD88 Molecule Are Necessary and Sufficient for CpG-Mediated Inhibition of IgE Production In Vivo" Cells 8, no. 10: 1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101165
APA StyleAlberca Custodio, R. W., Mirotti, L., Gomes, E., Nunes, F. P. B., S. Vieira, R., Graça, L., R. Almeida, R., S. Câmara, N. O., & Russo, M. (2019). Dendritic Cells Expressing MyD88 Molecule Are Necessary and Sufficient for CpG-Mediated Inhibition of IgE Production In Vivo. Cells, 8(10), 1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101165