Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Kidney Regeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Extracellular Vesicles
EV Composition and Biogenesis
3. MSC-EVs and Tissue Regeneration
4. MSC-EVs and Acute Kidney Injury
5. Conditioning of the Kidney Transplant
6. MSC-EVs and Chronic Kidney Disease
7. MSC-EVs and Clinical Trials
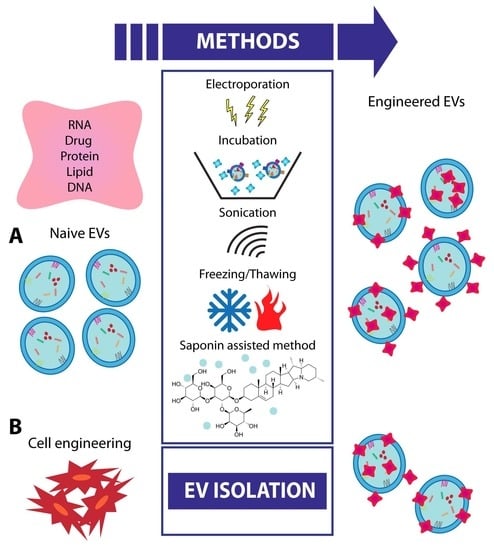
8. EV Engineering and Future Strategies
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.S.; Li, B. Renal Injury Repair: How About the Role of Stem Cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1165, 661–670. [Google Scholar]
- Pozzoli, S.; Simonini, M.; Manunta, P. Predicting acute kidney injury: Current status and future challenges. J. Nephrol. 2017, 31, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rewa, O.; Bagshaw, S.M. Acute Kidney injury-epidemiology, outcomes and economics. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grange, C.; Iampietro, C.; Bussolati, B. Stem cell extracellular vesicles and kidney injury. Stem Cell Investig. 2017, 4, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetta, C.; Weiss, S.; Grange, C.; Camussi, G. Adult Stem Cells and Extracellular Vesicles in Acute and Chronic Kidney Injury. Curr. Regen. Med. 2016, 6, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, N.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Ohlrogge, A.W.; Malanda, B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abecassis, M.; Bartlett, S.T.; Collins, A.J.; Davis, C.L.; Delmonico, F.L.; Friedewald, J.J.; Hays, R.; Howard, A.; Jones, E.; Leichtman, A.B.; et al. Kidney Transplantation as Primary Therapy for End-Stage Renal Disease: A National Kidney Foundation/Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (NKF/KDOQITM) Conference. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 3, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grange, C.; Tritta, S.; Tapparo, M.; Cedrino, M.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G.; Brizzi, M.F. Stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles inhibit and revert fibrosis progression in a mouse model of diabetic nephropathy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, S.; Chiabotto, G.; Favaro, E.; Deregibus, M.C.; Camussi, G. Role of extracellular vesicles in stem cell biology. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2019, 317, C303–C313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, R.C.; Yeo, R.W.; Lim, S.K. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2015, 40, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, M.Z.; Kucia, M.; Jadczyk, T.; Greco, N.J.; Wojakowski, W.; Tendera, M.; Ratajczak, J. Pivotal role of paracrine effects in stem cell therapies in regenerative medicine: Can we translate stem cell-secreted paracrine factors and microvesicles into better therapeutic strategies? Leukemia 2012, 26, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratajczak, M.Z.; Ratajczak, J. Extracellular Microvesicles as Game Changers in Better Understanding the Complexity of Cellular Interactions-From Bench to Clinical Applications. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 354, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendt, M.; Rezvani, K.; Shpall, E. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for clinical use. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019, 54, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grange, C.; Tapparo, M.; Kholia, S.; Bussolati, B.; Camussi, G. The Distinct Role of Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Normal and Cancer Stem Cells. Current Stem Cell Reports 2017, 3, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgovan, T.; Crawford, L.; Nwizu, C.; Quesenberry, P. Stem cells and extracellular vesicles: Biological regulators of physiology and disease. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 317, C155–C166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesenberry, P.; Goldberg, L.R. A New Stem Cell Biology: Transplantation and Baseline, Cell Cycle and Exosomes. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1056, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Chargaff, E.; West, R. The biological significance of the thromboplastic protein of blood. J. Biol. Chem. 1946, 166, 189–197. [Google Scholar]
- Janowska-Wieczorek, A.; Majka, M.; Kijowski, J.; Baj-Krzyworzeka, M.; Reca, R.; Turner, A.R.; Ratajczak, J.; Emerson, S.G.; Kowalska, M.A.; Ratajczak, M.Z. Platelet-derived microparticles bind to hematopoietic progenitor cells and enhance their engraftment. Blood 2001, 98, 3143–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deregibus, M.C.; Cantaluppi, V.; Calogero, R.; Lo Iacono, M.; Tetta, C.; Biancone, L.; Bruno, S.; Bussolati, B.; Camussi, G. Endothelial progenitor cell derived microvesicles activate an angiogenic program in endothelial cells by a horizontal transfer of mRNA. Blood 2007, 110, 2440–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, J.; Miekus, K.; Kucia, M.; Zhang, J.; Reca, R.; Dvorak, P.; Ratajczak, M.Z. Embrionic stem cell-derived microvesicles reprogram hematopoietic progenitors: Evidence for horizontal transfer of mRNA and protein delivery. Leukemia 2006, 20, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ratajczak, M.Z.; Ratajczak, J. Horizontal transfer of RNA and proteins between cells by extracellular microvesicles: 14 years later. Clin. Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keller, S.; Ridinger, J.; Rupp, A.K.; Janssen, J.W.; Altevogt, P. Body fluid derived exosomes as a novel template for clinical diagnostics. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- György, B.; Szabó, T.G.; Pásztói, M.; Pál, Z.; Misják, P.; Aradi, B.; László, V.; Pállinger, E.; Pap, E.; Kittel, A.; et al. Membrane vesicles, current state-of-the-art: Emerging role of extracellular vesicles. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 2667–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lener, T.; Gimona, M.; Aigner, L.; Börger, V.; Buzas, E.; Camussi, G.; Chaput, N.; Chatterjee, D.; Court, F.A.; Del Portillo, H.A.; et al. Applying extracellular vesicles based therapeutics in clinical trials —an ISEV position paper. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2015, 4, 30087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotvall, J.; Hill, A.F.; Hochberg, F.; Buzás, E.I.; Di Vizio, D.; Gardiner, C.; Gho, J.S.; Kurochkin, I.V.; Mathivanan, S.; Quesenberry, P.; et al. Minimal experimental requirements for definition of extracellular vesicles and their functions: A position statement from the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 22, 26913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, S.J.; Raposo, G. As we wait: Coping with an imperfect nomenclature for extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathivanan, S.; Ji, H.; Simpson, R.J. Exosomes: Extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J. Proteomics 2010, 73, 1907–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Pol, E.; Böing, A.N.; Harrison, P.; Sturk, A.; Nieuwland, R. Classification, functions, and clinical relevance of extracellular vesicles. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 676–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Ostrowski, M.; Segura, E. Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobarrez, F.; Sjövik, C.; Soop, A.; Hållström, L.; Frostell, C.; Pisetsky, D.S.; Wallén, H. CD40L expression in plasma of volunteers following LPS administration: A comparison between assay of CD40L on platelet microvesicles and soluble CD40L. Platelets 2015, 26, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, D.K.; Fenix, A.M.; Franklin, J.L.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Zhang, Q.; Zimmerman, L.J.; Liebler, D.C.; Ping, J.; Liu, Q.; Evans, R.; et al. Reassessment of Exosome Composition. Cell 2019, 177, 428–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, L.C.; Marfell, B.J.; Scott, A.P.; Waterhouse, N.J. Quantitation of Apoptosis and Necrosis by Annexin V Binding, Propidium Iodide Uptake, and Flow Cytometry. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2016, 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Record, M.; Subra, C.; Silvente-Poirot, S.; Poirot, M. Exosomes as intercellular signalosomes and pharmacological effectors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 81, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batagov, A.O.; Kurochkin, I.V. Exosomes secreted by human cells transport largely mRNA fragments that are enriched in the 3′-untranslated regions’. Biology Direct. 2013, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leva, G.; Garofalo, M.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2014, 9, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trionfini, P.; Benigni, A.; Remuzzi, G. MicroRNAs in kidney physiology and disease. Nature Reviews Nephrology 2015, 11, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplan, A.I.; Dennis, J.E. Mesenchymal stem cells as trophic mediators. J. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 98, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, B.D.; Bonventre, J.V. Mesenchymal stem cells in acute kidney injury. Annu. Rev. Med. 2008, 59, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, F.M.; Farwell, D.G.; Nolta, J.A.; Anderson, J.D. Concise Review: Preclinical Translation of Exosomes Derived from Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells. Stem Cells 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, O.G.; Van Balkom, B.W.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Bouten, C.V.; Verhaar, M.C. Extracellular vesicles: Potential roles in regenerative medicine. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, B.; Schmitt, R.; Israilova, M.; Nishio, H.; Cantley, L.G. Stromal cells protect against acute tubular injury via an endocrine effect. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 2486–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heldring, N.; Mäger, I.; Wood, M.J.; Le Blanc, K.; Andaloussi, S.E. Therapeutic Potential of Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Their Extracellular Vesicles. Hum. Gene Ther. 2015, 26, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.R.; Teixeira, G.Q.; Santos, S.G.; Barbosa, M.A.; Almeida-Porada, G.; Gonçalves, R.M. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Secretome: Influencing Therapeutic Potential by Cellular Pre conditioning. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, S.; Tapparo, M.; Collino, F.; Chiabotto, G.; Deregibus, M.C.; Soares Lindoso, R.; Neri, F.; Kholia, S.; Giunti, S.; Wen, S.; et al. Renal Regenerative Potential of Different Extracellular Vesicle Populations Derived from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Tissue Eng. Part. A 2017, 23, 21–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, G.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, M.; Liu, Y. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a new therapeutic strategy for liver diseases. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börger, V.; Bremer, M.; Ferrer-Tur, R.; Gockeln, L.; Stambouli, O.; Becic, A.; Giebel, B. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles and their potential as novel immunomodulatory therapeutic agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, R.C.; Tan, S.S.; Teh, B.J.; Sze, S.K.; Arslan, F.; de Kleijn, D.P.; Choo, A.; Lim, S.K. Proteolytic potential of the MSC exosome proteome: Implications for an exosome-mediated delivery of therapeutic proteasome. Int. J. Proteom. 2012, 2012, 971907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.E.; de Jong, O.G.; Brouwer, M.; Wood, M.J.; Lavieu, G.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Vader, P. Extracellular vesicle-based therapeutics: Natural versus engineered targeting and trafficking. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooijmans, S.A.A.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Zarovni, N.; Vago, R. Modulation of tissue tropism and biological activity of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles: New nanotools for cancer treatment. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantaluppi, V.; Biancone, L.; Quercia, A.; Deregibus, M.C.; Segoloni, G.; Camussi, G. Rationale of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in kidney injury. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2013, 61, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyman, S.N.; Rosenberger, C.; Rosen, S. Acute kidney injury: Lessons from experimental models. Contrib. Nephrol. 2011, 169, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bruno, S.; Grange, C.; Deregibus, M.C.; Calogero, R.A.; Saviozzi, S.; Collino, F.; Morando, L.; Busca, A.; Falda, M.; Bussolati, B.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles protect against acute tubular injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1053–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hu, C.; Zhang, P.; Jiang, H.; Chen, J. Genetic communication by extracellular vesicles is an important mechanism underlying stem cell-based therapy-mediated protection against acute kidney injury. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Hong, Q.; Zhang, C.Y.; Yang, Y.J.; Cai, G.Y.; Chen, X.M. miRNAs in stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles for acute kidney injury treatment: Comprehensive review of preclinical studies. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collino, F.; Bruno, S.; Incarnato, D.; Dettori, D.; Neri, F.; Provero, P.; Pomatto, M.; Oliviero, S.; Tetta, C.; Quesenberry, P.J.; et al. AKI recovery induced by mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles carrying microRNA. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 2349–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasoni, S.; Longaretti, L.; Rota, C.; Morigi, M.; Conti, S.; Gotti, E.; Capelli, C.; Introna, M.; Remuzzi, G.; Benigni, A. Transfer of growth factor receptor mRNA via exosomes unravels the regenerative effect of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, S.; Grange, C.; Collino, F.; Deregibus, M.C.; Cantaluppi, V.; Biancone, L.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Microvesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells enhance survival in a lethal model of acute kidney injury. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, L.A.; Borges, F.T.; Simões, M.J.; Borges, A.A.; Sinigaglia-Coimbra, R.; Schor, N. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells repaired but did not prevent gentamicin-induced acute kidney injury through paracrine effects in rats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, S.; Bruno, S.; Deregibus, M.C.; Sordi, A.; Cantaluppi, V.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Microvesicles derived from human adult mesenchymal stem cells protect against ischaemia-reperfusion-induced acute and chronic kidney injury. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2011, 26, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Qiu, J.; Fan, Y. CCR2 Positive Exosome Released by Mesenchymal Stem Cells Suppresses Macrophage Functions and Alleviates Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Renal Injury. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 1240301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, H.; Xu, W.; Wang, B.; Wu, H.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, M.; Mao, F.; Yan, Y.; et al. Exosomes released by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells protect against cisplatin-induced renal oxidative stress and apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2013, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.; Zhang, G.; Cheng, Z.; Yin, D.; Du, T.; Ju, G.; Miao, S.; Liu, G.; Lu, M.; Zhu, Y. Microvesicles derived from human Wharton’s Jelly mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by suppressing CX3CL1. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2014, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, G.Q.; Cheng, J.; Zhong, L.; Wu, S.; Zou, X.Y.; Zhang, G.Y.; Gu, D.; Miao, S.; Zhu, Y.J.; Sun, J.; et al. Microvesicles derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells facilitate tubular epithelial cell dedifferentiation and growth via hepatocyte growth factor induction. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Zou, X.; Ju, G.; Zhang, G.; Bao, E.; Zhu, Y. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Derived. Extracellular Vesicles Ameliorate Acute Renal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury by Inhibition of Mitochondrial Fission through miR-30. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 2093940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranghino, A.; Bruno, S.; Bussolati, B.; Moggio, A.; Dimuccio, V.; Tapparo, M.; Biancone, L.; Gontero, P.; Frea, B.; Camussi, G. The effects of glomerular and tubular renal progenitors and derived extracellular vesicles on recovery from acute kidney injury. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.Y.; Moon, S.J.; Ratliff, B.B.; Ahn, S.H.; Jung, A.; Lee, M.; Lee, S.; Lim, B.J.; Kim, B.S.; Plotkin, M.D.; et al. Microparticles from kidney-derived mesenchymal stem cells act as carriers of proangiogenic signals and contribute to recovery from acute kidney injury. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera Sanchez, M.B.; Bruno, S.; Grange, C.; Tapparo, M.; Cantaluppi, V.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Human liver stem cells and derived extracellular vesicles improve recovery in a murine model of acute kidney injury. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2014, 5, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bank, J.R.; Rabelink, T.J.; de Fijter, J.W.; Reinders, M.E. Safety and Efficacy Endpoints for Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapy in Renal Transplant Recipients. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 391797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorini, M.; Corradetti, V.; Pattonieri, E.F.; Rocca, C.; Milanesi, S.; Peloso, A.; Canevari, S.; De Cecco, L.; Dugo, M.; Avanzini, M.A.; et al. Perfusion of isolated rat kidney with Mesenchymal Stromal Cells/Extracellular Vesicles prevents ischaemic injury. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 3381–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pini, A.; Grange, C.; Veglia, E.; Argenziano, M.; Cavalli, R.; Guasti, D.; Calosi, L.; Ghè, C.; Solarino, R.; Thurmond, R.L.; et al. Histamine (H4) receptor antagonism prevents the progression of diabetic nephropathy in male DBA2/J mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 128, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonson, M.S. Phenotypic transitions and fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, A.K. Diabetic nephropathy—complications and treatment. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2014, 7, 361–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.Z.; Liu, Y.M.; Niu, X.; Yin, J.Y.; Hu, B.; Guo, S.C.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, N.S. Exosomes secreted by human urine-derived stem cells could prevent kidney complications from type I diabetes in rats. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2016, 7, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaishi, K.; Mizue, Y.; Chikenji, T.; Otani, M.; Nakano, M.; Konari, N.; Fujimiya, M. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy ameliorates diabetic nephropathy via the paracrine effect of renal trophic factors including exosomes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34842–34858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholia, S.; Herrera Sanchez, M.B.; Cedrino, M.; Papadimitriou, E.; Tapparo, M.; Deregibus, M.C.; Brizzi, M.F.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Human Liver Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Prevent Aristolochic Acid-Induced Kidney Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heuer, J.G.; Harlan, S.M.; Yang, D.D.; Jaqua, D.L.; Boyles, J.S.; Wilson, J.M.; Heinz-Taheny, K.M.; Sullivan, J.M.; Wei, T.; Qian, H.R.; et al. Role of TGF-alpha in the progression of diabetic kidney disease. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2017, 312, F951–F962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Yu, M.; Wang, C.; Pei, X.; Zhu, B.; Wu, J.; Zhao, W. Bone marrow stem cells-derived microvesicles protect against renal injury in the mouse remnant kidney model. Nephrology Carlton 2012, 17, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhu, B.; Pei, X.; Wu, J.; Zhao, W. Micro-vesicles derived from bone marrow stem cells protect the kidney both in vivo and in vitro by microRNA-dependent repairing. Nephrology Carlton 2015, 20, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Koppen, A.; Verhaar, M.C.; Bongartz, L.G.; Joles, J.A. 5/6th nephrectomy in combination with high salt diet and nitric oxide synthase inhibition to inducechronic kidney disease in the Lewis rat. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 77, e50398. [Google Scholar]
- Eirin, A.; Zhu, X.Y.; Puranik, A.S.; Tang, H.; McGurren, K.A.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Lerman, A.; Lerman, L.O. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate kidney inflammation. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassar, W.; El-Ansary, M.; Sabry, D.; Mostafa, M.A.; Fayad, T.; Kotb, E.; Temraz, M.; Saad, A.N.; Essa, W.; Adel, H. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells derived extracellular vesicles can safely ameliorate the progression of chronic kidney diseases. Biomater. Res. 2016, 20, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiklander, O.P.B.; Brennan, M.Á.; Lötvall, J.; Breakefield, X.O.; El Andaloussi, S. Advances in therapeutic applications of extracellular vesicles. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, O.G.; Kooijmans, S.A.A.; Murphy, D.E.; Jiang, L.; Evers, M.J.W.; Sluijter, J.P.G.; Vader, P.; Schiffelers, R.M. Drug Delivery with Extracellular Vesicles: From Imagination to Innovation. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 1761–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hung, M.E.; Leonard, J.N. A platform for actively loading cargo RNA to elucidate limiting steps in EV-mediated delivery. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2016, 5, 31027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meel, R.; Fens, M.H.; Vader, P.; van Solinge, W.W.; Eniola-Adefeso, O.; Schiffelers, R.M. Extracellular vesicles as drug delivery systems: Lessons from the liposome field. J. Control. Release 2014, 195, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, A.D.; Dowdy, S.F. GalNAc-siRNA conjugates: Leading the way for delivery of RNAi therapeutics. Nucleic Acid. Ther. 2018, 28, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, G.; Serio, A.; Mazo, M.; Nair, R.; Stevens, M.M. Active loading into extracellular vesicles significantly improves the cellular uptake and photodynamic effect of porphyrins. J. Control. Release 2015, 205, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, S.; Takanashi, M.; Sudo, K.; Ueda, S.; Ishikawa, A.; Matsuyama, N.; Fujita, K.; Mizutani, T.; Ohgi, T.; Ochiya, T.; et al. Systemically injected exosomes targeted to EGFR deliver antitumor microRNA to breast cancer cells. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zhuang, X.; Xiang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Barnes, S.; Grizzle, W.; Miller, D.; Zhang, H.G. A novel nanoparticle drug delivery system: The anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin is enhanced when encapsulated in exosomes. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 1606–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomatto, M.A.C.; Bussolati, B.; D’Antico, S.; Ghiotto, S.; Tetta, C.; Brizzi, M.F.; Camussi, G. Improved Loading of Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles to Encapsulate Antitumor miRNAs. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2019, 13, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tao, S.C.; Rui, B.Y.; Wang, Q.Y.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, S.C. Extracellular vesicle-mimetic nanovesicles transport LncRNA-H19 as competing endogenous RNA for the treatment of diabetic wounds. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haney, M.J.; Klyachko, N.L.; Harrison, E.B.; Zhao, Y.; Kabanov, A.V.; Batrakova, E.V. TPP1 Delivery to Lysosomes with Extracellular Vesicles and their Enhanced Brain Distribution in the Animal Model of Batten Disease. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, e1801271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haney, M.J.; Klyachko, N.L.; Zhao, Y.; Gupta, R.; Plotnikova, E.G.; He, Z.; Patel, T.; Piroyan, A.; Sokolsky, M.; Kabanov, A.V.; et al. Exosomes as drug delivery vehicles for Parkinson’s disease therapy. J. Control. Release 2015, 207, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lainšček, D.; Kadunc, L.; Keber, M.M.; Bratkovič, I.H.; Romih, R.; Jerala, R. Delivery of an Artificial Transcription Regulator dCas9-VPR by Extracellular Vesicles for Therapeutic Gene Activation. ACS Synth. Biol. 2018, 7, 2715–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yao, K.; Huuskes, B.M.; Shen, H.H.; Zhuang, J.; Godson, C.; Brennan, E.P.; Wilkinson-Berka, J.L.; Wise, A.F.; Ricardo, S.D. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Deliver Exogenous MicroRNA-let7c via Exosomes to Attenuate Renal Fibrosis. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tapparo, M.; Bruno, S.; Collino, F.; Togliatto, G.; Deregibus, M.C.; Provero, P.; Wen, S.; Quesenberry, P.J.; Camussi, G. Renal Regenerative Potential of Extracellular Vesicles Derived from miRNA-Engineered Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| MSC Origin | In vivo Models | Type of Injury | Injection | Administration | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bone Marrow | Glycerol | AKI | Single: 15 μg Single: 2.2 × 108 | Intravenously | Bruno et al. [54] Collino et al. [57] |
| IRI | AKI | Single: 30 μg | Intravenously | Gatti et al. [61] | |
| Cisplatin | AKI | Single: 100 μg | Intravenously | Bruno et al. [59] | |
| Gentamicin | AKI | Multiple: 100 μg | Intravenously | Reis et al. [60] | |
| IRI | AKI | Single:200 μg | Into renal capsule | Shen B et al. [62] | |
| IRI | CKD | Single: 30 μg | Intravenously | Gatti et al. [61] | |
| Cisplatin | CKD | Multiple: 100 μg followed by 50 μg every 4 days | Intravenously | Bruno et al. [59] | |
| Remnant kidney | CKD | Single: 30 μg | Caudal vein | He et al. [79] | |
| Type 1 diabetes | CKD | Single: 5.3 × 10 exosomes | Renal subcapsular | Nagaishi et al. [76] | |
| Unilateral ureteral obstruction | CKD | Single: 30 μg | Caudal vein | He et al. [80] | |
| Type 1 diabetes | CKD | Multiple: 1 × 1010/dose | Intravenously | Grange et al. [8] | |
| Cord blood | Cisplatin | AKI | Single: 200 μg | Caudal vein | Zhou et al. [63] |
| IRI | AKI | Single: 30 μg | Caudal vein | Ju et al. [65] | |
| Warton Jelly | IRI | AKI | Single:100 μg | Caudal vein Caudal vein | Zou et al. [64] Gu et al. [66] |
| Renal | IRI | AKI | Single: 2 × 107 | Intravenously | Choi et al. [68] |
| IRI | AKI | Single: 400 × 106 | Intravenously | Ranghino et al. [67] | |
| Liver | Glycerol | AKI | Single:1.88 ± 0.6 × 109 Single: 5.53 ± 2.1 × 109 | Intravenously Intravenously | Herrera Sanchez et al. [69] |
| Aristolochic acid nephropathy | CKD | Multiple | Intravenously | Kholia et al. [77] | |
| Type 1 diabetes | CKD | Multiple: 1 × 1010/dose | Intravenously | Grange et al. [9] | |
| Urine | Type 1 diabetes | CKD | Multiple: 100 μg weekly 12 times | Intravenously | Jiang et al. [75] |
| Embryonic | Remnant kidney and specic diet L-NG–nitroarginine and 6% NaCl | CKD | Multiple: 7 μg twice daily for 4 consecutive days | Intravenously | Van Koppen et al. [81] |
| Adipose tissue | Porcine model of metabolic syndrome and renal artery stenosis | CKD | Single: 1 × 1010 | Intra renal | Eirin et al. [82] |
| Disease | Intervention | N. Pats | Follow Up | State | Location | Number/Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 | Two doses of MSC-EVs | 20 | 3 months | Unknown | Sahel Teaching Hospital Sahel, Cairo, Egypt | NCT02138331 |
| Chronic kidney disease | Two doses of umbilical cord MSC-EVs (100 μg/kg/dose) | 20 | 1 year | Concluded | Sahel Teaching Hospital Sahel, Cairo, Egypt | Nassar et al. [83] |
| Macular degeneration | 20–50 mg of cord tissue MSC-EVs injected directly around macular hole | 44 | 24 weeks | Recruiting | Tianjin Medical University Hospital Tianjin, China | NCT03437759 |
| Cerebrovascular disorders acute ischemic stroke | Allogenic MSC-EVs enriched by miR-124 | 5 | 12 months | Not yet recruiting | Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Teheran Iran | NCT03384433 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grange, C.; Skovronova, R.; Marabese, F.; Bussolati, B. Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Kidney Regeneration. Cells 2019, 8, 1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101240
Grange C, Skovronova R, Marabese F, Bussolati B. Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Kidney Regeneration. Cells. 2019; 8(10):1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101240
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrange, Cristina, Renata Skovronova, Federica Marabese, and Benedetta Bussolati. 2019. "Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Kidney Regeneration" Cells 8, no. 10: 1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101240
APA StyleGrange, C., Skovronova, R., Marabese, F., & Bussolati, B. (2019). Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Kidney Regeneration. Cells, 8(10), 1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101240