The Oncogenic Signaling Pathways in BRAF-Mutant Melanoma Cells Are Modulated by Naphthalene Diimide-Like G-Quadruplex Ligands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and General Procedures
2.2. Cell Lines
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Gene Expression Analysis
2.5. Circular Dichroism
2.6. Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer
2.7. Taq Polymerase Stop Assay
2.8. Western Immunoblotting
2.9. Analysis of Cell Cycle Phase Distribution
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Screening of the Anticancer Activity of c-exNDIs in Melanoma Cells
3.3. C-exNDI 1 Induces a Global Down-Regulation of Gene Expression in BRAFV600E-Mutant Melanoma Cells
3.4. Melanoma-Relevant Genes as Possible G4 Targets of c-exNDI 1
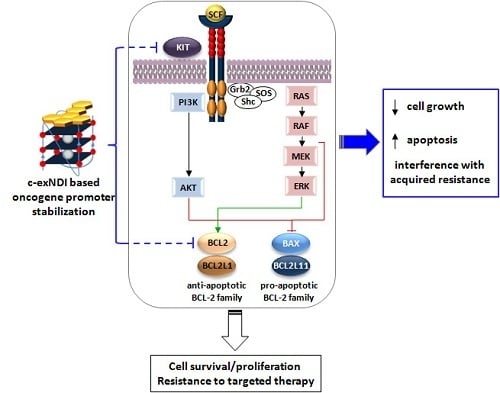
3.5. The Exposure of BRAFV600E Melanoma Cells to c-exNDI 1 Results in KIT and BCL-2 Protein Down-Regulation, Inhibition of MAPK and PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathways, and Apoptosis Induction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kozar, I.; Margue, C.; Rothengatter, S.; Haan, C.; Kreis, S. Many ways to resistance: How melanoma cells evade targeted therapies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Rev. Cancer 2019, 1871, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najem, A.; Krayem, M.; Perdrix, A.; Kerger, J.; Awada, A.; Journe, F.; Ghanem, G. New drug combination strategies in melanoma: Current status and future directions. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 5941–5953. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kunz, M.; Hölzel, M. The impact of melanoma genetics on treatment response and resistance in clinical and experimental studies. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017, 36, 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunz, M. The genetic basis of new treatment modalities in melanoma. Curr. Drug Targets 2015, 16, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollag, G.; Tsai, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Ibrahim, P.; Nolop, K.; Hirth, P. Vemurafenib: The first drug approved for BRAF-mutant cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Collado, A.X.; Knott, J.; Jazirehi, A.R. Reversal of resistance in targeted therapy of metastatic melanoma: Lessons learned from Vemurafenib (BRAFV600E-specific inhibitor). Cancers 2018, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, B.C.; Esteve-Puig, R. Targeting activated KIT signaling for melanoma therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3288–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iams, W.T.; Sosman, J.A.; Chandra, S. Novel targeted therapies for metastatic melanoma. Cancer J. 2017, 23, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, N.; Schwan, J.V.; Fujita, M.; Norris, D.A.; Shellman, Y.G. Alternative treatments for melanoma: Targeting BCL-2 family members to de-bulk and kill cancer stem cells. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 2155–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aird, D.; Teng, T.; Huang, C.-L.; Pazolli, E.; Banka, D.; Cheung-Ong, K.; Eifert, C.; Furman, C.; Wu, Z.J.; Seiler, M.; et al. Sensitivity to splicing modulation of BCL2 family genes defines cancer therapeutic strategies for splicing modulators. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavendra, N.M.; Pingili, D.; Kadasi, S.; Mettu, A.; Prasad, S.V.U.M. Dual or multi-targeting inhibitors: The next generation anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 143, 1277–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppert, J.L. Structure, location and interactions of G-quadruplexes. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 3452–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, N.H.; Neidle, S. G-quadruplexes and metal ions. Met. Ions Life Sci. 2012, 10, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burge, S.; Parkinson, G.N.; Hazel, P.; Todd, A.K.; Neidle, S. Quadruplex DNA: Sequence, topology and structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 5402–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, D.; Lipps, H.J. G-quadruplexes and their regulatory roles in biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 8627–8637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, Y.-J.; Kumarasamy, V.; Camacho, D.; Sun, D. Involvement of G-quadruplex structures in regulation of human RET gene expression by small molecules in human medullary thyroid carcinoma TT cells. Oncogene 2015, 34, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Fleming, A.M.; Averill, A.M.; Burrows, C.J.; Wallace, S.S. The NEIL glycosylases remove oxidized guanine lesions from telomeric and promoter quadruplex DNA structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 4039–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berardinelli, F.; Siteni, S.; Tanzarella, C.; Stevens, M.F.; Sgura, A.; Antoccia, A. The G-quadruplex-stabilising agent RHPS4 induces telomeric dysfunction and enhances radiosensitivity in glioblastoma cells. DNA Repair 2015, 25, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, R.; Nadai, M.; Frasson, I.; Poe, J.A.; Butovskaya, E.; Smithgall, T.E.; Palumbo, M.; Palù, G.; Richter, S.N. A dynamic G-quadruplex region regulates the HIV-1 long terminal repeat promoter. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 6521–6530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paeschke, K.; Bochman, M.L.; Garcia, P.D.; Cejka, P.; Friedman, K.L.; Kowalczykowski, S.C.; Zakian, V.A. Pif1 family helicases suppress genome instability at G-quadruplex motifs. Nature 2013, 497, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahama, K.; Takada, A.; Tada, S.; Shimizu, M.; Sayama, K.; Kurokawa, R.; Oyoshi, T. Regulation of telomere length by G-quadruplex telomere DNA- and TERRA-binding protein TLS/FUS. Chem. Biol. 2013, 20, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neidle, S. Quadruplex nucleic acids as targets for anticancer therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simone, R.; Balendra, R.; Moens, T.G.; Preza, E.; Wilson, K.M.; Heslegrave, A.; Woodling, N.S.; Niccoli, T.; Gilbert-Jaramillo, J.; Abdelkarim, S.; et al. G-quadruplex-binding small molecules ameliorate C9orf72 FTD/ALS pathology in vitro and in vivo. EMBO Mol. Med. 2018, 10, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Geng, Y.; Liu, C.; Miao, H.; Ren, Y.; Xu, N.; Shi, X.; You, Y.; Lee, T.; Zhu, G. Characterizations of distinct parallel and antiparallel G-quadruplexes formed by two-repeat ALS and FTD related GGGGCC sequence. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, O.; Bourdoncle, A.; Boulé, J.-B.; Brosh, R.M.; Mergny, J.-L. G-quadruplexes and helicases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 1989–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scalabrin, M.; Frasson, I.; Ruggiero, E.; Perrone, R.; Tosoni, E.; Lago, S.; Tassinari, M.; Palù, G.; Richter, S.N. The cellular protein hnRNP A2/B1 enhances HIV-1 transcription by unfolding LTR promoter G-quadruplexes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, A.; Wu, Y.; Huang, Y.C.; Chavez, E.A.; Platt, J.; Johnson, F.B.; Brosh, R.M.; Sen, D.; Lansdorp, P.M. Detection of G-quadruplex DNA in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffi, G.; Tannahill, D.; McCafferty, J.; Balasubramanian, S. Quantitative visualization of DNA G-quadruplex structures in human cells. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänsel-Hertsch, R.; Beraldi, D.; Lensing, S.V.; Marsico, G.; Zyner, K.; Parry, A.; Di Antonio, M.; Pike, J.; Kimura, H.; Narita, M.; et al. G-quadruplex structures mark human regulatory chromatin. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.Y.; Lejault, P.; Chevrier, S.; Boidot, R.; Robertson, A.G.; Wong, J.M.Y.; Monchaud, D. Transcriptome-wide identification of transient RNA G-quadruplexes in human cells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, I.; Grandmougin, M.; Roux, A.; Yang, S.Y.; Lejault, P.; Pirrotta, M.; Wong, J.M.Y.; Monchaud, D. Small-molecule affinity capture of DNA/RNA quadruplexes and their identification in vitro and in vivo through the G4RP protocol. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neidle, S. Human telomeric G-quadruplex: The current status of telomeric G-quadruplexes as therapeutic targets in human cancer. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppert, J.L.; Balasubramanian, S. G-quadruplexes in promoters throughout the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, T.A.; Kendrick, S.; Hurley, L. Making sense of G-quadruplex and i-motif functions in oncogene promoters. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 3459–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddiqui-Jain, A.; Grand, C.L.; Bearss, D.J.; Hurley, L.H. Direct evidence for a G-quadruplex in a promoter region and its targeting with a small molecule to repress c-MYC transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11593–11598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, L.; Mazzini, S.; Rossini, A.; Castagnoli, L.; Scaglioni, L.; Artali, R.; Di Nicola, M.; Zunino, F.; Dallavalle, S. c-MYC G-quadruplex binding by the RNA polymerase I inhibitor BMH-21 and analogues revealed by a combined NMR and biochemical Approach. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hagan, M.P.; Morales, J.C.; Galan, M.C. Binding and beyond: What else can G-quadruplex ligands do? Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 2019, 4995–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Di Antonio, M.; McKinney, S.; Mathew, V.; Ho, B.; O’Neil, N.J.; Dos Santos, N.; Silvester, J.; Wei, V.; Garcia, J.; et al. CX-5461 is a DNA G-quadruplex stabilizer with selective lethality in BRCA1/2 deficient tumours. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Hurley, L.H.; Neidle, S. Targeting G-quadruplexes in gene promoters: A novel anticancer strategy? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirota, V.; Nadai, M.; Doria, F.; Richter, S. Naphthalene diimides as multimodal G-quadruplex-selective ligands. Molecules 2019, 24, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, R.; Doria, F.; Butovskaya, E.; Frasson, I.; Botti, S.; Scalabrin, M.; Lago, S.; Grande, V.; Nadai, M.; Freccero, M.; et al. Synthesis, binding and antiviral properties of potent core-extended naphthalene diimides targeting the HIV-1 long terminal repeat promoter G-quadruplexes. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 9639–9652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuffo, M.; Guédin, A.; Leriche, E.-D.; Doria, F.; Pirota, V.; Gabelica, V.; Mergny, J.-L.; Freccero, M. More is not always better: Finding the right trade-off between affinity and selectivity of a G-quadruplex ligand. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenfield, N.J. Using circular dichroism collected as a function of temperature to determine the thermodynamics of protein unfolding and binding interactions. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2527–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachwal, P.A.; Fox, K.R. Quadruplex melting. Methods 2007, 43, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doria, F.; Nadai, M.; Folini, M.; Di Antonio, M.; Germani, L.; Percivalle, C.; Sissi, C.; Zaffaroni, N.; Alcaro, S.; Artese, A.; et al. Hybrid ligand-alkylating agents targeting telomeric G-quadruplex structures. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 2798–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassinari, M.; Cimino-Reale, G.; Nadai, M.; Doria, F.; Butovskaya, E.; Recagni, M.; Freccero, M.; Zaffaroni, N.; Richter, S.N.; Folini, M. Down-regulation of the androgen receptor by G-quadruplex ligands sensitizes castration-resistant prostate cancer cells to Enzalutamide. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 8625–8638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino-Reale, G.; Zaffaroni, N.; Folini, M. Emerging role of G-quadruplex DNA as target in anticancer therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 6612–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Todd, A.K.; Zloh, M.; Gunaratnam, M.; Parkinson, G.N.; Neidle, S. Crystal structure of a promoter sequence in the B-raf gene reveals an intertwined dimer quadruplex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 19319–19329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Wu, J.; Shao, F.; Yan, J. Stability and kinetics of c- MYC promoter G-quadruplexes studied by single-molecule manipulation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 2424–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P.; Lin, C.; Mathad, R.I.; Carver, M.; Yang, D. The major G-quadruplex formed in the human BCL-2 proximal promoter adopts a parallel structure with a 13-nt loop in K + solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 1750–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, H.; Reszka, A.P.; Huppert, J.; Ladame, S.; Rankin, S.; Venkitaraman, A.R.; Neidle, S.; Balasubramanian, S. A conserved quadruplex motif located in a transcription activation site of the human c-kit oncogene. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 7854–7860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rankin, S.; Reszka, A.P.; Huppert, J.; Zloh, M.; Parkinson, G.N.; Todd, A.K.; Ladame, S.; Balasubramanian, S.; Neidle, S. Putative DNA quadruplex formation within the human c-kit oncogene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 10584–10589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neidle, S. The structures of quadruplex nucleic acids and their drug complexes. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2009, 19, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monchaud, D.; Teulade-Fichou, M.-P. A hitchhiker’s guide to G-quadruplex ligands. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2008, 6, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadai, M.; Cimino-Reale, G.; Sattin, G.; Doria, F.; Butovskaya, E.; Zaffaroni, N.; Freccero, M.; Palumbo, M.; Richter, S.N.; Folini, M. Assessment of gene promoter G-quadruplex binding and modulation by a naphthalene diimide derivative in tumor cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberle, J.; Hossini, A.M. Expression and function of bcl-2 proteins in melanoma. Curr. Genom. 2008, 9, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Compound | IC50 1 (nM) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 8 ± 1 |
| 2 | 20 ± 2 |
| 3 | 50 ± 3 |
| 4 | 74 ± 6 |
| 5 | >500 |
| 6 | >500 |
| 7 | 101 ± 11 |
| 8 | 94 ± 6 |
| 9 | >500 |
| 10 | >500 |
| 11 | 54 ± 2 |
| 12 | 104 ± 3 |
| 13 | 415 ± 36 |
| 14 | 195 ± 19 |
| Oligonucleotide | Tm Values 1 (°C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Compound | c-exNDI 1 | |||
| λ = 264 nm | λ = 290 nm | λ = 264 nm | λ = 290 nm | |
| blc-2 | 67.5 ± 1.3 | / | >90.0 | / |
| c-myc | 58.8 ± 0.7 | / | >90.0 | / |
| b-raf | >90.0 | 50.3 ± 0.3 | >90.0 | 68.7 ± 0.8 |
| c-kit 1 | 48.0 ± 0.3 | / | >90.0 | / |
| c-kit 2 | 57.0 ± 0.3 | / | >90.0 | / |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Recagni, M.; Tassinari, M.; Doria, F.; Cimino-Reale, G.; Zaffaroni, N.; Freccero, M.; Folini, M.; Richter, S.N. The Oncogenic Signaling Pathways in BRAF-Mutant Melanoma Cells Are Modulated by Naphthalene Diimide-Like G-Quadruplex Ligands. Cells 2019, 8, 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101274
Recagni M, Tassinari M, Doria F, Cimino-Reale G, Zaffaroni N, Freccero M, Folini M, Richter SN. The Oncogenic Signaling Pathways in BRAF-Mutant Melanoma Cells Are Modulated by Naphthalene Diimide-Like G-Quadruplex Ligands. Cells. 2019; 8(10):1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101274
Chicago/Turabian StyleRecagni, Marta, Martina Tassinari, Filippo Doria, Graziella Cimino-Reale, Nadia Zaffaroni, Mauro Freccero, Marco Folini, and Sara N. Richter. 2019. "The Oncogenic Signaling Pathways in BRAF-Mutant Melanoma Cells Are Modulated by Naphthalene Diimide-Like G-Quadruplex Ligands" Cells 8, no. 10: 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101274
APA StyleRecagni, M., Tassinari, M., Doria, F., Cimino-Reale, G., Zaffaroni, N., Freccero, M., Folini, M., & Richter, S. N. (2019). The Oncogenic Signaling Pathways in BRAF-Mutant Melanoma Cells Are Modulated by Naphthalene Diimide-Like G-Quadruplex Ligands. Cells, 8(10), 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101274