Membrane-Associated, Not Cytoplasmic or Nuclear, FGFR1 Induces Neuronal Differentiation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmid Construction
2.2. Cell Culture and Transfection
2.3. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
2.4. Immunogold Electron Microscopy
2.5. Stimulation and Immunoblot
2.6. Quantification of Results and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
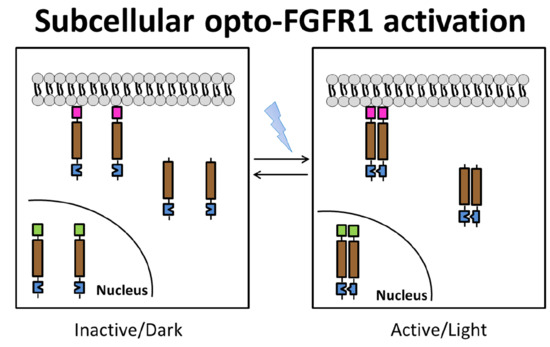
3.1. Localization of mV-opto-FGFR1s
3.2. Opto-FGFR1-Dependent Signaling Pathway Activation in HEK293 Cells
3.3. Immunocytochemistry of mV-opto-FGFR1-Transfected PC12 Cells
3.4. Neuronal Differentiation of PC12 Cells Induced by Blue Light
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, P.L.; Johnson, D.E.; Cousens, L.S.; Fried, V.A.; Williams, L.T. Purification and complementary DNA cloning of a receptor for basic fibroblast growth factor. Science 1989, 245, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.Q.; Snider, W.D. Intracellular control of developmental and regenerative axon growth. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 2006, 361, 1575–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eswarakumar, V.P.; Lax, I.; Schlessinger, J. Cellular signaling by fibroblast growth factor receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005, 16, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platta, H.W.; Stenmark, H. Endocytosis and signaling. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2011, 23, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacInnis, B.L.; Campenot, R.B. Retrograde support of neuronal survival without retrograde transport of nerve growth factor. Science 2002, 295, 1536–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausott, B.; Vallant, N.; Hochfilzer, M.; Mangger, S.; Irschick, R.; Haugsten, E.M.; Klimaschewski, L. Leupeptin enhances cell surface localization of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 in adult sensory neurons by increased recycling. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 91, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachowiak, E.K.; Maher, P.A.; Tucholski, J.; Mordechai, E.; Joy, A.; Moffett, J.; Coons, S.; Stachowiak, M.K. Nuclear accumulation of fibroblast growth factor receptors in human glial cells-association with cell proliferation. Oncogene 1997, 14, 2201–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Planque, N. Nuclear trafficking of secreted factors and cell-surface receptors: New pathways to regulate cell proliferation and differentiation, and involvement in cancers. Cell Commun. Signal. 2006, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Myers, J.; Fang, X.; Stachowiak, E.K.; Maher, P.A.; Martins, G.G.; Popescu, G.; Berezney, R.; Stachowiak, M.K. Integrative nuclear FGFR1 signaling (INFS) pathway mediates activation of the tyrosine hydroxylase gene by angiotensin II, depolarization and protein kinase C. J. Neurochem. 2002, 81, 506–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunham-Ems, S.M.; Pudavar, H.E.; Myers, J.M.; Maher, P.A.; Prasad, P.N.; Stachowiak, M.K. Factors controlling fibroblast growth factor receptor-1’s cytoplasmic trafficking and its regulation as revealed by FRAP analysis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 2223–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowiak, M.K.; Birkaya, B.; Aletta, J.M.; Narla, S.T.; Benson, C.A.; Decker, B.; Stachowiak, E.K. Nuclear FGF receptor-1 and CREB binding protein: An integrative signaling module. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 230, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.W.; Stachowiak, E.K.; Birkaya, B.; Terranova, C.; Capacchietti, M.; Claus, P.; Aletta, J.M.; Stachowiak, M.K. NGF-induced cell differentiation and gene activation is mediated by integrative nuclear FGFR1 signaling (INFS). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horbinski, C.; Stachowiak, E.K.; Chandrasekaran, V.; Miuzukoshi, E.; Higgins, D.; Stachowiak, M.K. Bone morphogenetic protein-7 stimulates initial dendritic growth in sympathetic neurons through an intracellular fibroblast growth factor signaling pathway. J. Neurochem. 2002, 80, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, C.; Xiao, J.; McKeehan, W.L.; Wang, F. Fibroblast growth factors, old kids on the new block. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 53, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grusch, M.; Schelch, K.; Riedler, R.; Reichhart, E.; Differ, C.; Berger, W.; Inglés-Prieto, Á.; Janovjak, H. Spatio-temporally precise activation of engineered receptor tyrosine kinases by light. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 1713–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tokuyasu, K.T. A technique for ultracryotomy of cell suspensions and tissues. J. Cell Biol. 1973, 57, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, W.; Geuze, H.J.; Slot, J.W. Improving structural integrity of cryosections for immunogold labeling. Histochem. Cell Biol. 1996, 106, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, M.W.; Vogel, G.F.; Yordanov, T.E.; Witting, B.; Gutleben, K.; Ebner, H.L.; de Araujo, M.E.G.; Filipek, P.A.; Huber, L.A. Combining high-pressure freezing with pre-embedding immunogold electron microscopy and tomography. Traffic 2018, 19, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Pasumarthi, K.B.; Bock, M.E.; Lytras, A.; Kardami, E.; Cattini, P.A. Cloning and expression of fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 isoforms in the mouse heart: Evidence for isoform switching during heart development. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 1994, 26, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, L.; Hope, J.M.; Guo, S.; Ong, Q.; François, A.; Kaplan, L.; Scherrer, G.; Cui, B. Optical Activation of TrkA Signaling. ACS Synth. Biol. 2018, 7, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsvetanova, N.G.; von Zastrow, M. Spatial encoding of cyclic AMP signaling specificity by GPCR endocytosis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 1061–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.Y.; Woo, D.; Jung, H.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Won, J.; Kyung, T.; Park, H.; Kim, N.; Yang, H.W.; et al. Light-inducible receptor tyrosine kinases that regulate neurotrophin signalling. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, N.; Kim, J.M.; Lee, M.; Kim, C.Y.; Chang, K.Y.; Heo, W.D. Spatiotemporal control of fibroblast growth factor receptor signals by blue light. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichhart, E.; Ingles-Prieto, A.; Tichy, A.M.; McKenzie, C.; Janovjak, H. A Phytochrome Sensory Domain Permits Receptor Activation by Red Light. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 6339–6342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haugsten, E.M.; Sørensen, V.; Brech, A.; Olsnes, S.; Wesche, J. Different intracellular trafficking of FGF1 endocytosed by the four homologous FGF receptors. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 3869–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irschick, R.; Trost, T.; Karp, G.; Hausott, B.; Auer, M.; Claus, P.; Klimaschewski, L. Sorting of the FGF receptor 1 in a human glioma cell line. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 139, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, P.A. Nuclear Translocation of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptors in response to FGF-2. J. Cell Biol. 1996, 134, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Małecki, J.; Wiedłocha, A.; Wesche, J.; Olsnes, S. Vesicle transmembrane potential is required for translocation to the cytosol of externally added FGF-1. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 4480–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reilly, J.F.; Maher, P.A. Importin beta-mediated nuclear import of fibroblast growth factor receptor: Role in cell proliferation. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 152, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowiak, M.K.; Fang, X.; Myers, J.M.; Dunham, S.M.; Berezney, R.; Maher, P.A.; Stachowiak, E.K. Integrative nuclear FGFR1 signaling (INFS) as a part of a universal “feed-forward-and-gate” signaling module that controls cell growth and differentiation. J. Cell. Biochem. 2003, 90, 662–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somanathan, S.; Stachowiak, E.K.; Siegel, A.J.; Stachowiak, M.K.; Berezney, R. Nuclear matrix bound fibroblast growth factor receptor is associated with splicing factor rich and transcriptionally active nuclear speckles. J. Cell. Biochem. 2003, 90, 856–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachowiak, M.K.; Maher, P.A.; Joy, A.; Mordechai, E.; Stachowiak, E.K. Nuclear localization of functional FGF receptor 1 in human astrocytes suggests a novel mechanism for growth factor action. Brain. Res. Mol. Brain. Res. 1996, 38, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowiak, M.K.; Maher, P.A.; Joy, A.; Mordechai, E.; Stachowiak, E.K. Nuclear accumulation of fibroblast growth factor receptors is regulated by multiple signals in adrenal medullary cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 1996, 7, 1299–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chioni, A.M.; Grose, R. FGFR1 cleavage and nuclear translocation regulates breast cancer cell behavior. J. Cell. Biol. 2012, 197, 801–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coleman, S.J.; Bruce, C.; Chioni, A.M.; Kocher, H.M.; Grose, R.P. The ins and outs of fibroblast growth factor receptor signalling. Clin. Sci. (Lond) 2014, 127, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, K.C.; Robertson, S.C.; Kanemitsu, M.Y.; Meyer, A.N.; Tynan, J.A.; Donoghue, D.J. Transformation and Stat activation by derivatives of FGFR1, FGFR3, and FGFR4. Oncogene 2000, 19, 3309–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klimaschewski, L.; Nindl, W.; Feurle, J.; Kavakebi, P.; Kostron, H. Basic fibroblast growth factor isoforms promote axonal elongation and branching of adult sensory neurons in vitro. Neuroscience 2004, 126, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausott, B.; Schlick, B.; Vallant, N.; Dorn, R.; Klimaschewski, L. Promotion of neurite outgrowth by fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 overexpression and lysosomal inhibition of receptor degradation in pheochromocytoma cells and adult sensory neurons. Neuroscience 2008, 153, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausott, B.; Rietzler, A.; Vallant, N.; Auer, M.; Haller, I.; Perkhofer, S.; Klimaschewski, L. Inhibition of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 endocytosis promotes axonal branching of adult sensory neurons. Neuroscience 2011, 188, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toettcher, J.E.; Weiner, O.D.; Lim, W.A. Using optogenetics to interrogate the dynamic control of signal transmission by the Ras/Erk module. Cell 2013, 155, 1422–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Duan, L.; Ong, Q.; Lin, Z.; Varman, P.M.; Sung, K.; Cui, B. Light-mediated kinetic control reveals the temporal effect of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in PC12 cell neurite outgrowth. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Nakayama, K.; Satoh, T.; Nishida, E. Down-regulation of the PI3-kinase/Akt pathway by ERK MAP kinase in growth factor signaling. Genes Cells 2008, 13, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hensel, N.; Baskal, S.; Walter, L.M.; Brinkmann, H.; Gernert, M.; Claus, P. ERK and ROCK functionally interact in a signaling network that is compensationally upregulated in Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2017, 108, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelastro, J.M.; Klimaschewski, L.; Tang, S.; Vitolo, O.V.; Weissman, T.A.; Donlin, L.T.; Shelanski, M.L.; Greene, L.A. Identification of diverse nerve growth factor-regulated genes by serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE) profiling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10424–10429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greene, L.A.; Tischler, A.S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 2424–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausott, B.; Klimaschewski, L. Membrane turnover and receptor trafficking in regenerating axons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2016, 43, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.J.; Stippec, S.A.; Goldsmith, E.; White, M.A.; Cobb, M.H. A constitutively active and nuclear form of the MAP kinase ERK2 is sufficient for neurite outgrowth and cell transformation. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, M.K.; Donoghue, D.J. Enhanced signaling and morphological transformation by a membrane-localized derivative of the fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 kinase domain. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 5739–5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Moffett, J.; Myers, J.; Fang, X.; Stachowiak, E.K.; Maher, P.; Kratz, E.; Hines, J.; Fluharty, S.J.; Mizukoshi, E.; et al. Novel nuclear signaling pathway mediates activation of fibroblast growth factor-2 gene by type 1 and type 2 angiotensin II receptors. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Fang, X.; Dunham, S.M.; Prada, C.; Stachowiak, E.K.; Stachowiak, M.K. 90-kDa ribosomal S6 kinase is a direct target for the nuclear fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1): Role in FGFR1 signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 29325–29335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Csanaky, K.; Hess, M.W.; Klimaschewski, L. Membrane-Associated, Not Cytoplasmic or Nuclear, FGFR1 Induces Neuronal Differentiation. Cells 2019, 8, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8030243
Csanaky K, Hess MW, Klimaschewski L. Membrane-Associated, Not Cytoplasmic or Nuclear, FGFR1 Induces Neuronal Differentiation. Cells. 2019; 8(3):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8030243
Chicago/Turabian StyleCsanaky, Katalin, Michael W. Hess, and Lars Klimaschewski. 2019. "Membrane-Associated, Not Cytoplasmic or Nuclear, FGFR1 Induces Neuronal Differentiation" Cells 8, no. 3: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8030243
APA StyleCsanaky, K., Hess, M. W., & Klimaschewski, L. (2019). Membrane-Associated, Not Cytoplasmic or Nuclear, FGFR1 Induces Neuronal Differentiation. Cells, 8(3), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8030243