Identification of Transcriptional Markers and microRNA–mRNA Regulatory Networks in Colon Cancer by Integrative Analysis of mRNA and microRNA Expression Profiles in Colon Tumor Stroma
Abstract
:1. Background
2. Methods
2.1. Datasets
2.2. Identification of DEGs and DEmiRs between CTS and Normal Stroma
2.3. Identification of Upstream Transcription Factors and Target Genes of DEmiRs
2.4. KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis of DEmiRs
2.5. Construction of Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network of DEGs
2.6. Comparisons of the Expression Levels of Hub Genes between Colon Cancer and Normal Tissue and Between Colon Tumor Stromal Fibroblast and Normal Fibroblast
2.7. Associations of the Expression Levels of the Hub Genes Targeted by DEmiRswith Survival Prognosis in Colon Cancer
2.8. Associations of the Expression Levels of the Hub Genes Targeted by DEmiRs with Immune Signature Enrichment Levels in Colon Cancer
2.9. Identification of Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-Approved Drug-Hub Gene Interaction
3. Results
3.1. Identification of DEmiRs and Their Target DEGs
3.2. Identification of Upstream TFs and Genes Significantly Associated with the DEmiRs
3.3. Identification of Pathways Significantly Associated with DEmiRs
3.4. Identification of Differentially Expressed Hub Genes Targeted by DEmiRs
3.4.1. The Hub Genes Are Negative Prognostic Factors in CRC
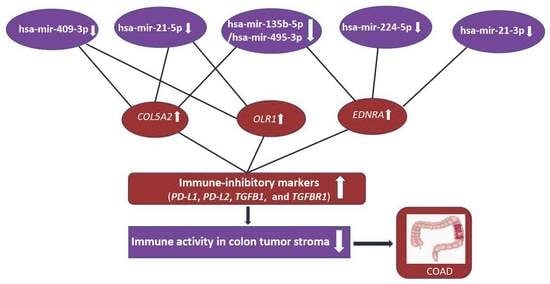
3.4.2. The Elevated Expression of Hub Genes Is Associated with the Immunosuppressive TME in Colon Cancer
3.5. Identification of Candidate Drugs Targeting Hub Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valkenburg, K.C.; de Groot, A.E.; Pienta, K.C. Targeting the tumour stroma to improve cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 366–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Coussens, L.M. Accessories to the crime: Functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calon, A.; Lonardo, E.; Berenguer-Llergo, A.; Espinet, E.; Hernando-Momblona, X.; Iglesias, M.; Sevillano, M.; Palomo-Ponce, S.; Tauriello, D.V.F.; Byrom, D.; et al. Stromal gene expression defines poor-prognosis subtypes in colorectal cancer. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Isella, C.; Terrasi, A.; Bellomo, S.E.; Petti, C.; Galatola, G.; Muratore, A.; Mellano, A.; Senetta, R.; Cassenti, A.; Sonetto, C.; et al. Stromal contribution to the colorectal cancer transcriptome. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.N.; Li, M.; Wang, X. Identification of Transcriptional Signatures of Colon Tumor Stroma by a Meta-Analysis. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 8752862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cătană, C.-S.; Pichler, M.; Giannelli, G.; Mader, R.M.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Non-coding RNAs, the Trojan horse in two-way communication between tumor and stroma in colorectal and hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 29519–29534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bullock, M.D.; Pickard, K.; Mitter, R.; Sayan, A.E.; Primrose, J.N.; Ivan, C.; Calin, G.A.; Thomas, G.J.; Packham, G.K.; Mirnezami, A.H. Stratifying risk of recurrence in stage II colorectal cancer using deregulated stromal and epithelial microRNAs. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7262–7279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hiyoshi, Y.; Schetter, A.J.; Okayama, H.; Inamura, K.; Anami, K.; Nguyen, G.H.; Horikawa, I.; Hawkes, J.E.; Bowman, E.D.; Leung, S.Y.; et al. Increased MicroRNA-34b and -34c Predominantly Expressed in Stromal Tissues Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Human Colon Cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, Y. Identification of More Feasible MicroRNA–mRNA Interactions within Multiple Cancers Using Principal Component Analysis Based Unsupervised Feature Extraction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, L.; Ma, J.; Yang, S.; Zou, C.; Yu, X. miRNA and mRNA Integration Network Construction Reveals Novel Key Regulators in Left-Sided and Right-Sided Colon Adenocarcinoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7149296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Gill, R.; Cooper, N.G.; Yoo, J.K.; Datta, S. Modeling microRNA-mRNA Interactions Using PLS Regression in Human Colon Cancer. BMC Med. Genom. 2011, 4, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.; Lakatos, P.; Hartmann, A.; Schneider-Stock, R.; Vera, J. Identification of miRNA-mRNA Modules in Colorectal Cancer Using Rough Hypercuboid Based Supervised Clustering. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sells, E.; Pandey, R.; Chen, H.; Skovan, B.A.; Cui, H.; Ignatenko, N.A. Specific microRNA–mRNA Regulatory Network of Colon Cancer Invasion Mediated by Tissue Kallikrein–Related Peptidase 6. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 396–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izadi, F.; Zamanian-Azodi, M.; Mansouri, V.; Khodadoostan, M.; Naderi, N. Exploring conserved mRNA-miRNA interactions in colon and lung cancers. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed. Bench 2017, 10, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pham, V.V.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Truong, B.; Xu, T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Li, J.; Le, T.D. Identifying miRNA-mRNA regulatory relationships in breast cancer with invariant causal prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, W.; Ding, B.; Xu, L.; Fan, W. Construction of Potential Glioblastoma Multiforme-Related miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; Siklenka, K.; Arora, S.K.; Ribeiro, P.; Kimmins, S.; Xia, J. miRNet-dissecting miRNA-target interactions and functional associations through network-based visual analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W135–W141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Gill, E.E.; Hancock, R.E.W. NetworkAnalyst for statistical, visual and network-based meta-analysis of gene expression data. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 823–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, M.; Keerthikumar, S.; Ang, C.-S.; Gangoda, L.; Quek, C.Y.J.; Williamson, N.A.; Mouradov, D.; Sieber, O.M.; Simpson, R.J.; Salim, A.; et al. FunRich: An open access standalone functional enrichment and interaction network analysis tool. Proteomics 2015, 15, 2597–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachos, I.S.; Zagganas, K.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Georgakilas, G.; Karagkouni, D.; Vergoulis, T.; Dalamagas, T.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA-miRPath v3.0: Deciphering microRNA function with experimental support. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W460–W466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, D.M.; Baek, D.; Shin, C.; Bell, G.W.; Grimson, A.; Bartel, D.P. Weak Seed-Pairing Stability and High Target-Site Abundance Decrease the Proficiency of lsy-6 and Other miRNAs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Li, C.; Kang, B.; Gao, G.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z. GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W98–W102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, H.; Kitada, K.; Nakai, K.; Sarai, A. PrognoScan: A new database for meta-analysis of the prognostic value of genes. BMC Med. Genom. 2009, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Fan, J.; Wang, B.; Traugh, N.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J.S.; Li, B.; Liu, X.S. TIMER: A Web Server for Comprehensive Analysis of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e108–e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein–protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotto, K.C.; Wagner, A.H.; Feng, Y.-Y.; Kiwala, S.; Coffman, A.C.; Spies, G.; Wollam, A.; Spies, N.C.; Griffith, O.L.; Griffith, M. DGIdb 3.0: A redesign and expansion of the drug-gene interaction database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1068–D1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abba, M.; Laufs, S.; Aghajany, M.; Korn, B.; Benner, A.; Allgayer, H. Look who’s talking: Deregulated signaling in colorectal cancer. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2012, 9, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Nishida, N.; Nagahara, M.; Sato, T.; Mimori, K.; Sudo, T.; Tanaka, F.; Shibata, K.; Ishii, H.; Sugihara, K.; Doki, Y.; et al. Microarray analysis of colorectal cancer stromal tissue reveals upregulation of two oncogenic miRNA clusters. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 3054–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.J.; Deane, N.G.; Wu, F.; Merchant, N.B.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, A.; Lu, P.; Johnson, J.C.; Schmidt, C.; Bailey, C.E.; et al. Experimentally derived metastasis gene expression profile predicts recurrence and death in patients with colon cancer. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, T.J.; Smith, J.J.; Chen, X.; Washington, M.K.; Roland, J.T.; Means, A.L.; Eschrich, S.A.; Yeatman, T.J.; Deane, N.G.; Beauchamp, R.D. Smad4-mediated signaling inhibits intestinal neoplasia by inhibiting expression of β-catenin. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 562–571.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorissen, R.N.; Gibbs, P.; Christie, M.; Prakash, S.; Lipton, L.; Desai, J.; Kerr, D.; Aaltonen, L.A.; Arango, D.; Kruhøffer, M.; et al. Metastasis-Associated Gene Expression Changes Predict Poor Outcomes in Patients with Dukes Stage B and C Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 7642–7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature 2012, 487, 330–337. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GEO Accession Viewer. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE46824 (accessed on 24 August 2019).
- Johnson, W.E.; Li, C.; Rabinovic, A. Adjusting batch effects in microarray expression data using empirical Bayes methods. Biostatistics 2007, 8, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochran, W.G. The Combination of Estimates from Different Experiments. Biometrics 1954, 10, 101–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Georgakilas, G.; Kostoulas, N.; Vlachos, I.S.; Vergoulis, T.; Reczko, M.; Filippidis, C.; Dalamagas, T.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA-microT web server v5.0: Service integration into miRNA functional analysis workflows. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W169–W173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. KEGG: New perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D353–D361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davoli, T.; Uno, H.; Wooten, E.C.; Elledge, S.J. Tumor aneuploidy correlates with markers of immune evasion and with reduced response to immunotherapy. Science 2017, 355, eaaf8399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhães, L.; Quintana, L.G.; Lopes, D.C.F.; Vidal, A.F.; Pereira, A.L.; D’Araujo Pinto, L.C.; de Jesus Viana Pinheiro, J.; Khayat, A.S.; Goulart, L.R.; Burbano, R.; et al. APC gene is modulated by hsa-miR-135b-5p in both diffuse and intestinal gastric cancer subtypes. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullany, L.E.; Wolff, R.K.; Herrick, J.S.; Buas, M.F.; Slattery, M.L. SNP Regulation of microRNA Expression and Subsequent Colon Cancer Risk. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-M.; Chen, H.-C.; Chen, S.-J.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chen, P.-Y.; Wu, T.-W.E.; Feng, L.-Y.; Tsai, H.-C.; Lui, T.-N.; Hsueh, C.; et al. MicroRNA-495 inhibits proliferation of glioblastoma multiforme cells by downregulating cyclin-dependent kinase 6. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kara, M.; Yumrutas, O.; Ozcan, O.; Celik, O.I.; Bozgeyik, E.; Bozgeyik, I.; Tasdemir, S. Differential expressions of cancer-associated genes and their regulatory miRNAs in colorectal carcinoma. Gene 2015, 567, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Huang, L.; Cao, Q.; Liu, F. Identification of colorectal cancer-restricted microRNAs and their target genes based on high-throughput sequencing data. Onco-Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, W. Novel circulating microRNAs expression profile in colon cancer: A pilot study. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2017, 22, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faltejskova, P.; Svoboda, M.; Srutova, K.; Mlcochova, J.; Besse, A.; Nekvindova, J.; Radova, L.; Fabian, P.; Slaba, K.; Kiss, I.; et al. Identification and functional screening of microRNAs highly deregulated in colorectal cancer. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2012, 16, 2655–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Chen, M.; Greening, D.W.; He, W.; Rai, A.; Zhang, W.; Simpson, R.J. Deep Sequencing of RNA from Three Different Extracellular Vesicle (EV) Subtypes Released from the Human LIM1863 Colon Cancer Cell Line Uncovers Distinct Mirna-Enrichment Signatures. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heublein, S.; Albertsmeier, M.; Pfeifer, D.; Loehrs, L.; Bazhin, A.V.; Kirchner, T.; Werner, J.; Neumann, J.; Angele, M.K. Association of differential miRNA expression with hepatic vs. peritoneal metastatic spread in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellatt, D.F.; Stevens, J.R.; Wolff, R.K.; Mullany, L.E.; Herrick, J.S.; Samowitz, W.; Slattery, M.L. Expression Profiles of miRNA Subsets Distinguish Human Colorectal Carcinoma and Normal Colonic Mucosa. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2016, 7, e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takami, Y.; Russell, M.B.; Gao, C.; Mi, Z.; Guo, H.; Mantyh, C.R.; Kuo, P.C. Sp1 Regulates Osteopontin Expression in SW480 Human Colon Adenocarcinoma Cells. Surgery 2007, 142, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathi, S.; Jutooru, I.; Chadalapaka, G.; Nair, V.; Lee, S.-O.; Safe, S. Aspirin Inhibits Colon Cancer Cell and Tumor Growth and Downregulates Specificity Protein (Sp) Transcription Factors. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.-J.; Liu, R.-J.; Zeng, Z.; Alper, S.L.; Cui, H.-J.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Yan, Z.-W.; Fu, G.-H. Gastrin inhibits a novel, pathological colon cancer signaling pathway involving EGR1, AE2 and P-ERK. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 90, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Arreguín, K.; Bensard, C.; Schell, J.C.; Swanson, E.; Chen, X.; Rutter, J.; Tantin, D. Oct1/Pou2f1 is selectively required for colon regeneration and regulates colon malignancy. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1007687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniue, K.; Kurimoto, A.; Takeda, Y.; Nagashima, T.; Okada-Hatakeyama, M.; Katou, Y.; Shirahige, K.; Akiyama, T. ASBEL–TCF3 complex is required for the tumorigenicity of colorectal cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 12739–12744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Guo, Q.; Yang, J.; Chen, H.; Hu, K.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, S.; Pang, X.; Zhou, S.; Dang, Y.; et al. FOXD3 is a tumor suppressor of colon cancer by inhibiting EGFR-Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK signal pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 5048–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, M.L.; Herrick, J.S.; Lundgreen, A.; Wolff, R.K. Genetic variation in the TGF-β signaling pathway and colon and rectal cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2011, 20, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlcochova, J.; Faltejskova, P.; Nemecek, R.; Svoboda, M.; Slaby, O. MicroRNAs targeting EGFR signalling pathway in colorectal cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 139, 1615–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, E.J.; Weyers, A.; Li, G.; Gasimli, L.; Li, L.; Choi, W.J.; Lee, K.B.; Linhardt, R.J. Carbohydrate-Containing Molecules as Potential Biomarkers in Colon Cancer. OMICS 2014, 18, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Huang, X.; Liang, S.; Tang, S.; Wu, S.; Huang, T.; Mo, Z.; Wang, Q. Identifying miRNA and gene modules of colon cancer associated with pathological stage by weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Onco-Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 2815–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdocca, M.; Mango, R.; Pucci, S.; Biocca, S.; Testa, B.; Capuano, R.; Paolesse, R.; Sanchez, M.; Orlandi, A.; di Natale, C.; et al. The lectin-like oxidized LDL receptor-1: A new potential molecular target in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 14765–14780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachidi, S.M.; Qin, T.; Sun, S.; Zheng, W.J.; Li, Z. Molecular Profiling of Multiple Human Cancers Defines an Inflammatory Cancer-Associated Molecular Pattern and Uncovers KPNA2 as a Uniform Poor Prognostic Cancer Marker. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtani, H. Focus on TILs: Prognostic significance of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in human colorectal cancer. Cancer Immun. 2007, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepist, E.-I.; Gillies, H.; Smith, W.; Hao, J.; Hubert, C.; St. Claire, R.L.; Brouwer, K.R.; Ray, A.S. Evaluation of the Endothelin Receptor Antagonists Ambrisentan, Bosentan, Macitentan, and Sitaxsentan as Hepatobiliary Transporter Inhibitors and Substrates in Sandwich-Cultured Human Hepatocytes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Hanibuchi, M.; Kim, S.-J.; Yu, H.; Kim, M.S.; He, J.; Langley, R.R.; Lehembre, F.; Regenass, U.; Fidler, I.J. Treatment of experimental human breast cancer and lung cancer brain metastases in mice by macitentan, a dual antagonist of endothelin receptors, combined with paclitaxel. Neuro. Oncol. 2016, 18, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, M.S.; Choi, H.J.; He, J.; Wu, Q.; Aldape, K.; Weinberg, J.S.; Alfred Yung, W.K.; Conrad, C.A.; et al. Macitentan, a dual endothelin receptor antagonist, in combination with temozolomide leads to glioblastoma regression and long-term survival in mice. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4630–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullany, L.E.; Herrick, J.S.; Wolff, R.K.; Stevens, J.R.; Samowitz, W.; Slattery, M.L. MicroRNA-transcription factor interactions and their combined effect on target gene expression in colon cancer cases. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2018, 57, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| miRNA | Log2 FC a | FDR b | Number of Target Genes c |
|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-mir-375 | 2.52 | 0.03 | 48 |
| hsa-mir-551b-3p | 2.33 | 0.009 | NA d |
| hsa-mir-513c-5p | 2.29 | 0.005 | 2 |
| hsa-mir-192-3p | 2.10 | 0.038 | 15 |
| hsa-mir-215-5p | 2.01 | 0.01 | 27 |
| hsa-mir-192-5p | 1.96 | 0.01 | 37 |
| hsa-mir-378a-3p | 1.76 | 0.01 | 5 |
| hsa-mir-194-5p | 1.74 | 0.04 | 19 |
| hsa-mir-29c-3p | 1.61 | 0.01 | 91 |
| hsa-mir-498 | 1.52 | 0.009 | 28 |
| hsa-mir-194-3p | 1.46 | 0.03 | 8 |
| hsa-mir-29c-5p | 1.38 | 0.008 | NA |
| hsa-mir-10b-5p | 1.31 | 0.01 | 30 |
| hsa-mir-338-3p | 1.31 | 0.01 | 18 |
| hsa-mir-139-5p | 1.28 | 0.01 | 7 |
| hsa-mir-512-3p | 1.09 | 0.01 | 30 |
| hsa-miR-768-3p | 1.09 | 0.02 | NA |
| hsa-mir-135b-5p | −2.81 | 0.009 | 19 |
| hsa-mir-214-3p | −1.66 | 0.02 | 38 |
| hsa-mir-224-5p | −1.60 | 0.01 | 25 |
| hsa-mir-409-3p | −1.30 | 0.04 | 8 |
| hsa-mir-495-3p | −1.22 | 0.01 | 43 |
| hsa-mir-21-5p | −1.15 | 0.04 | 87 |
| hsa-mir-21-3p | −1.08 | 0.01 | 6 |
| Change of DEmiRs | Upstream TFs | p-Value (Hypergeometric Test) |
|---|---|---|
| Upregulated | EGR1 | 6.50 × 10−37 |
| SP1 | 5.36 × 10−29 | |
| SP4 | 6.01 × 10−26 | |
| NKX6-1 | 5.19 × 10−22 | |
| POU2F1 | 3.44 × 10−21 | |
| MEF2A | 3.64 × 10−18 | |
| RREB1 | 1.41 × 10−17 | |
| ZFP161 | 1.94 × 10−16 | |
| NFIC | 2.61 × 10−15 | |
| ONECUT1 | 1.90 × 10−14 | |
| Downregulated | SP4 | 1.30 × 10−17 |
| SP1 | 3.82 × 10−17 | |
| EGR1 | 3.85 × 10−15 | |
| HOXA5 | 1.43 × 10−8 | |
| PDX1 | 1.92 × 10−8 | |
| KLF7 | 3.18 × 10−8 | |
| RORA | 3.62 × 10−8 | |
| POU2F1 | 3.98 × 10−8 | |
| TCF3 | 9.19 × 10−8 | |
| FOXD3 | 3.27 × 10−7 |
| Immune Signature | Marker Gene | COL5A2 | EDNRA | OLR1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cor | p | cor | p | cor | p | ||
| Monocyte | CD86 | 0.629 | 7.81 × 10−52 | 0.492 | 2.47 × 10−29 | 0.78 | 8.21 × 10−95 |
| CD115 | 0.601 | <1 × 10−100 | 0.448 | <1 × 10−100 | 0.618 | 1.34 × 10−49 | |
| TAM | CCL2 | 0.645 | <1 × 10−100 | 0.593 | <1 × 10−100 | 0.686 | 6.35 × 10−65 |
| CD68 | 0.42 | <1 × 10−100 | 0.243 | 1.47 × 10−7 | 0.494 | 1.59 × 10−29 | |
| IL10 | 0.427 | 1 × 10−21 | 0.359 | 2.15 × 10−15 | 0.537 | 1.61 × 10−35 | |
| M2 Macrophage | CD163 | 0.667 | 2.9 × 10−60 | 0.481 | 6.39 × 10−28 | 0.741 | 5.84 × 10−81 |
| VSIG4 | 0.588 | <1 × 10−100 | 0.462 | <1 × 10−100 | 0.729 | 3.86 × 10−77 | |
| MS4A4A | 0.575 | 1.34 × 10−41 | 0.475 | 4.2 × 10−27 | 0.74 | 1.92 × 10−80 | |
| Th1 | T-bet | 0.321 | 2.02 × 10−12 | 0.175 | 1.73 × 10−4 | 0.369 | 3.39 × 10−16 |
| IFN-γ | 0.176 | 1.55 × 10−4 | 0.1 | 3.32 × 10−2 | 0.325 | 9.92 × 10−13 | |
| TNF-α | 0.314 | 6.3 × 10−12 | 0.248 | 7.32 × 10−8 | 0.375 | 9.92 × 10−17 | |
| Treg | FOXP3 | 0.496 | <1 × 10−100 | 0.358 | 3.57 × 10−15 | 0.468 | 2.79 × 10−26 |
| CCR8 | 0.537 | 1.61 × 10−35 | 0.406 | 1.34 × 10−19 | 0.535 | 2.51 × 10−35 | |
| TGFB1 | 0.605 | <1 × 10−100 | 0.396 | <1 × 10−100 | 0.577 | 6.38 × 10−42 | |
| T cell exhaustion | PD-1 | 0.268 | 5.8 × 10−9 | 0.106 | 2.39 × 10−2 | 0.333 | 2.6 × 10−13 |
| CTLA4 | 0.375 | 9.02 × 10−17 | 0.274 | 2.59 × 10−9 | 0.43 | 4.53 × 10−22 | |
| LAG3 | 0.258 | 2.44 × 10−8 | 0.109 | 1.99 × 10−2 | 0.359 | 2.28 × 10−15 | |
| TIM-3 | 0.625 | <1 × 10−100 | 0.469 | <1 × 10−100 | 0.788 | 3.58 × 10−98 | |
| TIGIT | 0.408 | 8.6 × 10−20 | 0.243 | 1.36 × 10−7 | 0.493 | 1.8 × 10−29 | |
| CXCL13 | 0.365 | 7.39 × 10−16 | 0.245 | 1.04 × 10−7 | 0.494 | 1.54 × 10−29 | |
| LAYN | 0.766 | 1.75 × 10−89 | 0.636 | 2.4 × 10−53 | 0.7 | 1.08 × 10−68 | |
| Drug | Target Gene | Interaction Types | Score d |
|---|---|---|---|
| ambrisentan | EDNRA | antagonist | 9 |
| aspirin | EDNRA | NA | 2 |
| guanfacine | EDNRA | antagonist | 1 |
| cefadroxil | EDNRA | antagonist | 1 |
| bosentan | EDNRA | antagonist | 11 |
| macitentan | EDNRA | antagonist | 7 |
| collagenase clostridium histolyticum | COL5A2 | NA | 1 |
| ocriplasmin | COL5A2 | NA | 1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uddin, M.N.; Li, M.; Wang, X. Identification of Transcriptional Markers and microRNA–mRNA Regulatory Networks in Colon Cancer by Integrative Analysis of mRNA and microRNA Expression Profiles in Colon Tumor Stroma. Cells 2019, 8, 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091054
Uddin MN, Li M, Wang X. Identification of Transcriptional Markers and microRNA–mRNA Regulatory Networks in Colon Cancer by Integrative Analysis of mRNA and microRNA Expression Profiles in Colon Tumor Stroma. Cells. 2019; 8(9):1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091054
Chicago/Turabian StyleUddin, Md. Nazim, Mengyuan Li, and Xiaosheng Wang. 2019. "Identification of Transcriptional Markers and microRNA–mRNA Regulatory Networks in Colon Cancer by Integrative Analysis of mRNA and microRNA Expression Profiles in Colon Tumor Stroma" Cells 8, no. 9: 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091054
APA StyleUddin, M. N., Li, M., & Wang, X. (2019). Identification of Transcriptional Markers and microRNA–mRNA Regulatory Networks in Colon Cancer by Integrative Analysis of mRNA and microRNA Expression Profiles in Colon Tumor Stroma. Cells, 8(9), 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091054