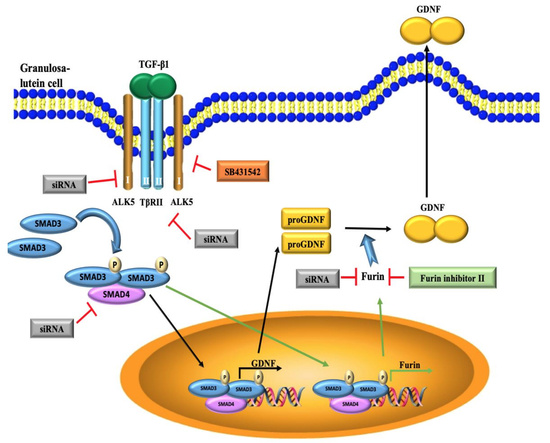
TGF-β1 Increases GDNF Production by Upregulating the Expression of GDNF and Furin in Human Granulosa-Lutein Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culture of Primary and Immortalized hGL Cells
2.2. Antibodies and Reagents
2.3. Real-Time RT-qPCR
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Small Interfering RNA Transfection
2.6. Measurement of Secreted GDNF
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. TGF-β1 Induces GDNF Expression in Immortalized and Primary hGL Cells
3.2. TGF-β1 Induces Furin Expression in Immortalized and Primary hGL Cells
3.3. The TGF-β Type II Receptor TβRII Mediates The TGF-β1-Induced Expression of GDNF and Furin in SVOG Cells
3.4. ALK5 is the Principal Type I Receptor that Mediates the Induced Expression of GDNF and Furin by TGF-β1 in SVOG Cells
3.5. The SMAD3-SMAD4 Signaling Pathway is Required for the Upregulation of GDNF and Furin by TGF-β1 in SVOG Cells
3.6. Furin Is Involved in the Increased GDNF Production by TGF-β1 in hGL Cells
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, L.F.; Doherty, D.H.; Lile, J.D.; Bektesh, S.; Collins, F. GDNF: A glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor for midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Science 1993, 260, 1130–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomac, A.; Lindqvist, E.; Lin, L.F.; Ogren, S.O.; Young, D.; Hoffer, B.J.; Olson, L. Protection and repair of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system by GDNF in vivo. Nature 1995, 373, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grondin, R.; Gash, D.M. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF): A drug candidate for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 1998, 245, P35–P42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golden, J.P.; DeMaro, J.A.; Osborne, P.A.; Milbrandt, J.; Johnson, E.M., Jr. Expression of neurturin, GDNF, and GDNF family-receptor mRNA in the developing and mature mouse. Exp. Neurol. 1999, 158, 504–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtzeborn, K.; Cebrian, C.; Kuure, S. Regulation of Renal Differentiation by Trophic Factors. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhi, J.; Ao, A.; Fisch, B.; Zhang, X.Y.; Garor, R.; Abir, R. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) and its receptors in human ovaries from fetuses, girls, and women. Fertil. Steril. 2010, 93, 2565–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dole, G.; Nilsson, E.E.; Skinner, M.K. Glial-derived neurotrophic factor promotes ovarian primordial follicle development and cell-cell interactions during folliculogenesis. Reproduction 2008, 135, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, H.M.; Wu, H.C.; Sun, Z.G.; Lian, F.; Leung, P.C.K. Neurotrophins and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in the ovary: Physiological and pathophysiological implications. Hum. Reprod. Update 2019, 25, 224–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linher, K.; Wu, D.; Li, J. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor: An intraovarian factor that enhances oocyte developmental competence in vitro. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 4292–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Fang, L.; Mao, X.; Chang, H.M.; Leung, P.C.K.; Ye, Y. GDNF-Induced Downregulation of miR-145-5p Enhances Human Oocyte Maturation and Cumulus Cell Viability. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 2510–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Qiao, J.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Yan, L.Y.; Hsueh, A.J.; Duan, E.K. Gonadotrophin-induced paracrine regulation of human oocyte maturation by BDNF and GDNF secreted by granulosa cells. Hum Reprod. 2011, 26, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawamura, K.; Ye, Y.; Kawamura, N.; Jing, L.; Groenen, P.; Gelpke, M.S.; Rauch, R.; Hsueh, A.J.; Tanaka, T. Completion of Meiosis I of preovulatory oocytes and facilitation of preimplantation embryo development by glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. Dev. Biol. 2008, 315, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sporn, M.B.; Roberts, A.B. Transforming growth factor-beta: Recent progress and new challenges. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 119, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Chang, H.M.; Cheng, J.C.; Klausen, C.; Leung, P.C.; Yang, X. Transforming growth factor-beta1 increases lysyl oxidase expression by downregulating MIR29A in human granulosa lutein cells. Reproduction 2016, 152, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juengel, J.L.; McNatty, K.P. The role of proteins of the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily in the intraovarian regulation of follicular development. Hum. Reprod. Update 2005, 11, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingman, W.V.; Robertson, S.A. Transforming growth factor-beta1 null mutation causes infertility in male mice associated with testosterone deficiency and sexual dysfunction. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 4032–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilchrist, R.B.; Morrissey, M.P.; Ritter, L.J.; Armstrong, D.T. Comparison of oocyte factors and transforming growth factor-beta in the regulation of DNA synthesis in bovine granulosa cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2003, 201, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Chang, H.M.; Cheng, J.C.; Tsai, H.D.; Wu, C.H.; Leung, P.C. Transforming growth factor-beta1 up-regulates connexin43 expression in human granulosa cells. Hum. Reprod. 2015, 30, 2190–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.C.; Chang, H.M.; Fang, L.; Sun, Y.P.; Leung, P.C. TGF-β1 Up-Regulates Connective Tissue Growth Factor Expression in Human Granulosa Cells through Smad and ERK1/2 Signaling Pathways. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Chang, H.M.; Cheng, J.C.; Leung, P.C.; Sun, Y.P. TGF-beta1 induces COX-2 expression and PGE2 production in human granulosa cells through Smad signaling pathways. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E1217–E1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, L.; Chang, H.M.; Cheng, J.C.; Leung, P.C.; Sun, Y.P. TGF-β1 downregulates StAR expression and decreases progesterone production through Smad3 and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in human granulosa cells. J Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E2234–E2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Chang, H.M.; Yi, Y.; Li, H.; Leung, P.C.K. TGF-β1 promotes hyaluronan synthesis by upregulating hyaluronan synthase 2 expression in human granulosa-lutein cells. Cell. Signal. 2019, 63, 109392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Chang, H.M.; Shi, Z.; Leung, P.C.K. ID3 mediates the TGF-β1-induced suppression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in human granulosa cells. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 4310–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artenstein, A.W.; Opal, S.M. Proprotein convertases in health and disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2507–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Ven, W.J.; Voorberg, J.; Fontijn, R.; Pannekoek, H.; van den Ouweland, A.M.; van Duijnhoven, H.L.; Roebroek, A.J.; Siezen, R.J. Furin is a subtilisin-like proprotein processing enzyme in higher eukaryotes. Mol. Biol. Rep. 1990, 14, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidah, N.G.; Prat, A. The biology and therapeutic targeting of the proprotein convertases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigenbrot, C.; Gerber, N. X-ray structure of glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor at 1.9 A resolution and implications for receptor binding. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1997, 4, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh-hashi, K.; Ito, M.; Tanaka, T.; Hirata, Y.; Kiuchi, K. Biosynthesis, processing, and secretion of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in astroglial cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 323, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonka-Nevalaita, L.; Lume, M.; Leppanen, S.; Jokitalo, E.; Peranen, J.; Saarma, M. Characterization of the intracellular localization, processing, and secretion of two glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor splice isoforms. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 11403–11413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.M.; Cheng, J.C.; Klausen, C.; Leung, P.C. Recombinant BMP4 and BMP7 increase activin A production by up-regulating inhibin βA subunit and furin expression in human granulosa-lutein cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E375–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Chang, H.M.; Zhu, H.; Liu, R.Z.; Leung, P.C.K. BMP6 increases TGF-beta1 production by up-regulating furin expression in human granulosa-lutein cells. Cell. Signal. 2019, 55, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchette, F.; Day, R.; Dong, W.; Laprise, M.H.; Dubois, C.M. TGFbeta1 regulates gene expression of its own converting enzyme furin. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 1974–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, H.M.; Fang, L.; Cheng, J.C.; Taylor, E.L.; Sun, Y.P.; Leung, P.C. Effects of growth differentiation factor 8 on steroidogenesis in human granulosa-lutein cells. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 105, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lie, B.L.; Leung, E.; Leung, P.C.; Auersperg, N. Long-term growth and steroidogenic potential of human granulosa-lutein cells immortalized with SV40 large T antigen. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1996, 120, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.M.; Klausen, C.; Leung, P.C. Antimüllerian hormone inhibits follicle-stimulating hormone-induced adenylyl cyclase activation, aromatase expression, and estradiol production in human granulosa-lutein cells. Fertil. Steril. 2013, 100, 585–592.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja-Khan, N.; Kunselman, A.R.; Demers, L.M.; Ewens, K.G.; Spielman, R.S.; Legro, R.S. A variant in the fibrillin-3 gene is associated with TGF-beta and inhibin B levels in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil. Steril. 2010, 94, 2916–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanchette, F.; Rudd, P.; Grondin, F.; Attisano, L.; Dubois, C.M. Involvement of Smads in TGFbeta1-induced furin (fur) transcription. J. Cell. Physiol. 2001, 188, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchette, F.; Rivard, N.; Rudd, P.; Grondin, F.; Attisano, L.; Dubois, C.M. Cross-talk between the p42/p44 MAP kinase and Smad pathways in transforming growth factor beta 1-induced furin gene transactivation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 33986–33994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Massagué, J. TGF-beta signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 753–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrana, J.L.; Attisano, L.; Wieser, R.; Ventura, F.; Massagué, J. Mechanism of activation of the TGF-beta receptor. Nature 1994, 370, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, H.G.; Kögel, D.; Rami, A.; Prehn, J.H. TGF-{beta}1 activates two distinct type I receptors in neurons: Implications for neuronal NF-{kappa}B signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 168, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inman, G.J.; Nicolas, F.J.; Callahan, J.F.; Harling, J.D.; Gaster, L.M.; Reith, A.D.; Laping, N.J.; Hill, C.S. SB-431542 is a potent and specific inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta superfamily type I activin receptor-like kinase (ALK) receptors ALK4, ALK5, and ALK7. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 62, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Ho, J.N.; Lewis, J.A.; Karim, K.A.; Daniels, R.N.; Gentry, P.R.; Hopkins, C.R.; Lindsley, C.W.; Hong, C.C. In vivo structure-activity relationship study of dorsomorphin analogues identifies selective VEGF and BMP inhibitors. ACS Chem. Biol. 2010, 5, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Chang, H.M.; Shi, Z.; Leung, P.C.K. SNAIL Mediates TGF-beta1-Induced Downregulation of Pentraxin 3 Expression in Human Granulosa Cells. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 1644–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilchrist, R.B.; Lane, M.; Thompson, J.G. Oocyte-secreted factors: Regulators of cumulus cell function and oocyte quality. Hum. Reprod. Update 2008, 14, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buccione, R.; Schroeder, A.C.; Eppig, J.J. Interactions between somatic cells and germ cells throughout mammalian oogenesis. Biol. Reprod. 1990, 43, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, H.M.; Qiao, J.; Leung, P.C. Oocyte-somatic cell interactions in the human ovary-novel role of bone morphogenetic proteins and growth differentiation factors. Hum. Reprod. Update 2016, 23, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.H.; Zhou, H.X.; Liu, S.J.; Zhou, C.J.; Kong, X.W.; Han, Z.; Liang, C.G. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor supplementation promotes bovine in vitro oocyte maturation and early embryo development. Theriogenology 2018, 113, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stawowy, P.; Margeta, C.; Kallisch, H.; Seidah, N.G.; Chrétien, M.; Fleck, E.; Graf, K. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase MT1-MMP/MMP-2 in cardiac fibroblasts by TGF-beta1 involves furin-convertase. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 63, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ventura, E.; Weller, M.; Burghardt, I. Cutting Edge: ERK1 Mediates the Autocrine Positive Feedback Loop of TGF-beta and Furin in Glioma-Initiating Cells. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 4569–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubois, C.M.; Blanchette, F.; Laprise, M.H.; Leduc, R.; Grondin, F.; Seidah, N.G. Evidence that furin is an authentic transforming growth factor-beta1-converting enzyme. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 158, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, R.; Sladkevicius, P.; Engmann, L.; Conway, G.S.; Payne, N.N.; Bekis, J.; Tan, S.L.; Campbell, S.; Jacobs, H.S. Serum vascular endothelial growth factor concentrations and ovarian stromal blood flow are increased in women with polycystic ovaries. Hum. Reprod. 1998, 13, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tal, R.; Seifer, D.B.; Shohat-Tal, A.; Grazi, R.V.; Malter, H.E. Transforming growth factor-beta1 and its receptor soluble endoglin are altered in polycystic ovary syndrome during controlled ovarian stimulation. Fertil. Steril. 2013, 100, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Lu, K.; Lin, J.; Wu, L.; Hildebrandt, M.A.; Chang, D.W.; Meyer, L.; Wu, X.; Liang, D. Genetic variants in TGF-β pathway are associated with ovarian cancer risk. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, A.; Heinayati, A.; Bao, D.; Liu, H.; Ding, X.; Tong, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Qin, H. Small molecule inhibitor of TGF-β signaling enables robust osteogenesis of autologous GMSCs to successfully repair minipig severe maxillofacial bone defects. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Senarath-Yapa, K.; Li, S.; Walmsley, G.G.; Zielins, E.; Paik, K.; Britto, J.A.; Grigoriadis, A.E.; Wan, D.C.; Liu, K.J.; Longaker, M.T.; et al. Small Molecule Inhibition of Transforming Growth Factor Beta Signaling Enables the Endogenous Regenerative Potential of the Mammalian Calvarium. Tissue Eng. Part A 2016, 22, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, L.; Ma, W.; Wu, L.; Xu, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Sha, W.; Li, H.; Xu, J.; Feng, R.; et al. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) mediates hepatic stellate cell activation via ALK5/Smad signalling. Gut 2019, 68, 2214–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M. The GDNF/RET signaling pathway and human diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2001, 12, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airaksinen, M.S.; Titievsky, A.; Saarma, M. GDNF family neurotrophic factor signaling: Four masters, one servant? Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 1999, 13, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterziel, H.; Unsicker, K.; Krieglstein, K. TGFbeta induces GDNF responsiveness in neurons by recruitment of GFRalpha1 to the plasma membrane. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 159, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, J.; Chang, H.-M.; Yi, Y.; Yao, Y.; Leung, P.C.K. TGF-β1 Increases GDNF Production by Upregulating the Expression of GDNF and Furin in Human Granulosa-Lutein Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010185
Yin J, Chang H-M, Yi Y, Yao Y, Leung PCK. TGF-β1 Increases GDNF Production by Upregulating the Expression of GDNF and Furin in Human Granulosa-Lutein Cells. Cells. 2020; 9(1):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010185
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Jingwen, Hsun-Ming Chang, Yuyin Yi, Yuanqing Yao, and Peter C.K. Leung. 2020. "TGF-β1 Increases GDNF Production by Upregulating the Expression of GDNF and Furin in Human Granulosa-Lutein Cells" Cells 9, no. 1: 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010185
APA StyleYin, J., Chang, H. -M., Yi, Y., Yao, Y., & Leung, P. C. K. (2020). TGF-β1 Increases GDNF Production by Upregulating the Expression of GDNF and Furin in Human Granulosa-Lutein Cells. Cells, 9(1), 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010185