Flow Cytometric Methods for the Detection of Intracellular Signaling Proteins and Transcription Factors Reveal Heterogeneity in Differentiating Human B Cell Subsets
Abstract
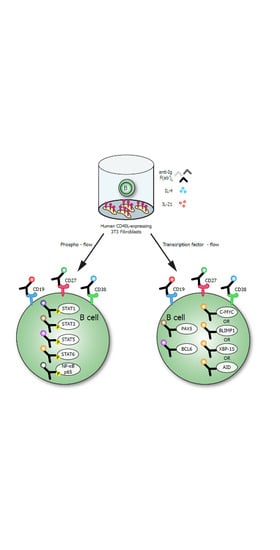
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Isolation of Peripheral Blood Mononucleated Cells and B Cells from Human Healthy Donors
2.3. In Vitro B Cell Stimulation Cultures
2.4. Phosphoflow Protocol
2.4.1. Flow Cytometry Antibodies
2.4.2. Harvesting, Fixation and Permeabilization
2.4.3. Intracellular Staining and FACS Analysis
2.5. Real-Time Semiquantitative RT-PCR
- c-MYC: F: 5′-TACAACACCCGAGCAAGGAC-3′
- R: 5′GAGGCTGCTGGTTTTCCACT-3′
- PA5: F: 5′-ACGCTGACAGGGATGGTG-3′,
- R: 5′-CCTCCAGGAGTCGTTGTACG-3′
- BCL6: F: 5′-GAGCTCTGTTGATTCTTAGAACTGG-3′
- R: 5′-GCCTTGCTTCACAGTCCAA-3′
- BLIMP1: F: 5′-AACGTGTGGGTACGACCTTG-3′
- R: 5′-ATTTTCATGGTCCCCTTGGT-3′
- XBP-1: F: 5′-CCGCAGCACTCAGACTACG-3′,
- R: 5′-TGCCCAACAGGATATCAGACT-3′
- AICDA: F: 5′-GACTTTGGTTATCTTCGCAATAAGA-3′
- R: 5′AGGTCCCAGTCCGAGATGTA-3′
- 18S-rRNA: F: 5′-CGGCTACCACATCCAAGGAA-3′
- R: 5′-GCTGGAATTACCGCGGCT-3′
2.6. TF-Flow Protocol
2.7. Multimarker Analysis Using UMAP
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. In Vitro Stimulation of B Cells
3.2. Establishment of Phosphoflow Assay Shows Differences in Phospho-Signaling Profiles within B Cell Subpopulations
3.3. Sorted Naïve and Memory B Cells Show Significant Differences in Response to Varying CD40L, IL-21 and/or IL-4 Stimuli
3.4. TF-Flow Assay Allows for a High-Resolution Analysis of TFs within Subpopulations
3.5. UMAP Analysis Unravels B Cell Subpopulation Heterogeneity
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- King, C.; Tangye, S.G.; Mackay, C.R. T Follicular Helper (T FH) Cells in Normal and Dysregulated Immune Responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 741–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhardt, R.L.; Liang, H.E.; Locksley, R.M. Cytokine-secreting follicular T cells shape the antibody repertoire. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulman, Z.; Gitlin, A.D.; Weinstein, J.S.; Lainez, B.; Esplugues, E.; Flavell, R.A.; Craft, J.E.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Dynamic signaling by T follicular helper cells during germinal center B cell selection. Science 2014, 345, 1058–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajewsky, K. Clonal selection and learning in the antibody system. Nature 1996, 381, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitlin, A.D.; Shulman, Z.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Clonal selection in the germinal centre by regulated proliferation and hypermutation. Nature 2014, 509, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McHeyzer-Williams, L.J.; Pelletier, N.; Mark, L.; Fazilleau, N.; McHeyzer-Williams, M.G. Follicular helper T cells as cognate regulators of B cell immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2009, 21, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, Y.; Dutta, P.R.; Cerasoli, D.M.; Kelsoe, G. In situ studies of the primary immune response to (4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)acetyl. v. affinity maturation develops in two stages of clonal selection. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisel, F.J.; Zuccarino-Catania, G.V.; Chikina, M.; Shlomchik, M.J. A Temporal Switch in the Germinal Center Determines Differential Output of Memory B and Plasma Cells. Immunity 2016, 44, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zotos, D.; Coquet, J.M.; Zhang, Y.; Light, A.; D’Costa, K.; Kallies, A.; Corcoran, L.M.; Godfrey, D.I.; Toellner, K.-M.; Smyth, M.J.; et al. IL-21 regulates germinal center B cell differentiation and proliferation through a B cell-intrinsic mechanism. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, B.B.; Bi, E.; Chen, H.; Yu, J.J.; Ye, B.H. IL-21 and CD40L Synergistically Promote Plasma Cell Differentiation through Upregulation of Blimp-1 in Human B Cells. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 1827–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moens, L.; Tangye, S.G. Cytokine-mediated regulation of plasma cell generation: IL-21 takes center stage. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, I.; Kageyama, R.; Monticelli, L.; Johnston, R.J.; DiToro, D.; Hansen, K.; Barnett, B.; Crotty, S. Germinal Center T Follicular Helper Cell IL-4 Production Is Dependent on Signaling Lymphocytic Activation Molecule Receptor (CD150). J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weinstein, J.S.; Herman, E.I.; Lainez, B.; Licona-Limón, P.; Esplugues, E.; Flavell, R.; Craft, J. TFH cells progressively differentiate to regulate the germinal center response. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascan, H.; Gauchat, J.F.; Roncarolo, M.G.; Yssel, H.; Spits, H.; De Vries, J.E. Human B cell clones can be induced to proliferate and to switch to IgE and IgG4 synthesis by interleukin 4 and a signal provided by activated CD4+ T cell clones. J. Exp. Med. 1991, 173, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avery, D.T.; Bryant, V.L.; Ma, C.S.; de Waal Malefyt, R.; Tangye, S.G. IL-21-Induced Isotype Switching to IgG and IgA by Human Naive B Cells Is Differentially Regulated by IL-4. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 1767–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, D.G.; Cote, C.M.; Patel, J.R.; Smith, C.B.; Zhang, Y.; Nickerson, K.M.; Zhang, T.; Kerfoot, S.M.; Haberman, A.M. Nonredundant Roles of IL-21 and IL-4 in the Phased Initiation of Germinal Center B Cells and Subsequent Self-Renewal Transitions. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 3569–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Craxton, A.; Shu, G.; Graves, J.D.; Saklatvala, J.; Krebs, E.G.; Clark, E.A. p38 MAPK is required for CD40-induced gene expression and proliferation in B lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 3225–3236. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9759836 (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Chen, D.; Ireland, S.J.; Remington, G.; Alvarez, E.; Racke, M.K.; Greenberg, B.; Frohman, E.M.; Monson, N.L. CD40-Mediated NF-κB Activation in B Cells Is Increased in Multiple Sclerosis and Modulated by Therapeutics. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 4257–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.C. The non-canonical NF-κB pathway in immunity and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, M.B.; Chang, C.-C.; Berton, M.T.; Danial, N.N.; Zhang, J.; Kuehner, D.; Ye, B.H.; Kvatyuk, M.; Pandolfi, P.P.; Cattoretti, G.; et al. Transcriptional Repression of Stat6-Dependent Interleukin-4-Induced Genes by BCL-6: Specific Regulation of Iε Transcription and Immunoglobulin E Switching. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 7264–7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wurster, A.L.; Rodgers, V.L.; White, M.F.; Rothstein, T.L.; Grusby, M.J. Interleukin-4-mediated protection of primary B cells from apoptosis through Stat6-dependent up-regulation of Bcl-xL. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 27169–27175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avery, D.T.; Ma, C.S.; Bryant, V.L.; Santner-Nanan, B.; Nanan, R.; Wong, M.; Fulcher, D.A.; Cook, M.C.; Tangye, S.G. STAT3 is required for IL-21 induced secretion of IgE from human naive B cells. Blood 2008, 112, 1784–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Avery, D.T.; Deenick, E.K.; Ma, C.S.; Suryani, S.; Simpson, N.; Chew, G.Y.; Chan, T.D.; Palendira, U.; Bustamante, J.; Boisson-Dupuis, S.; et al. B cell-intrinsic signaling through IL-21 receptor and STAT3 is required for establishing long-lived antibody responses in humans. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darnell, J.E.; Kerr, I.M.; Stark, G.R. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 1994, 264, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Ghosh, S. The NF-kappaB family of transcription factors and its regulation. In Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Suffolk County, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuijnenburg, P.; Lango Allen, H.; Burns, S.O.; Greene, D.; Jansen, M.H.; Staples, E.; Stephens, J.; Carss, K.J.; Biasci, D.; Baxendale, H.; et al. Loss-of-function nuclear factor κB subunit 1 (NFKB1) variants are the most common monogenic cause of common variable immunodeficiency in Europeans. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 1285–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Victora G, D.; Nussenzweig M, C. Germinal centers. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 429–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesin, L.; Ersching, J.; Victora, G.D. Germinal Center B Cell Dynamics. Immunity 2016, 45, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Silva, N.S.; Klein, U. Dynamics of B cells in germinal centres. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cobaleda, C.; Schebesta, A.; Delogu, A.; Busslinger, M. Pax5: The guardian of B cell identity and function. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.L.; Melchers, M.; Wang, H.; Torrey, T.A.; Slota, R.; Qi, C.F.; Ji, Y.K.; Lugar, P.; Hee, J.K.; Farrington, L.; et al. Regulation of the germinal center gene program by interferon (IFN) regulatory factor 8/IFN consensus sequence-binding protein. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Pedro Calado, D.; Sasaki, Y.; Godinho, S.A.; Pellerin, A.; Köchert, K.; Sleckman, B.P.; Moreno de Alborán, I.; Janz, M.; Rodig, S.; Rajewsky, K. MYC is essential for the formation and maintenance of germinal centers HHS Public Access. Nat. Immunol 2012, 13, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nutt, S.L.; Hodgkin, P.D.; Tarlinton, D.M.; Corcoran, L.M. The generation of antibody-secreting plasma cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkin, S.; Hartweger, H.; Oliveira, T.Y.; Kara, E.E.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Protein Amounts of the MYC Transcription Factor Determine Germinal Center B Cell Division Capacity. Immunity 2019, 51, 324–336.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellier, J.; Nutt, S.L. Plasma cells: The programming of an antibody-secreting machine. Eur. J. Immunol. 2019, 49, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, H.; Matsui, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Okada, T.; Mori, K. XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription factor. Cell 2001, 107, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bugatti, S.; Vitolo, B.; Caporali, R.; Montecucco, C.; Manzo, A. B cells in rheumatoid arthritis: From pathogenic players to disease biomarkers. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yap, D.Y.H.; Chan, T.M. B cell abnormalities in systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis—role in pathogenesis and effect of immunosuppressive treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McClure, M.; Gopaluni, S.; Jayne, D.; Jones, R. B cell therapy in ANCA-associated vasculitis: Current and emerging treatment options. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavenski, K.; Freedman, J.; Semple, J.W. HLA alloimmunization against platelet transfusions: Pathophysiology, significance, prevention and management. Tissue Antigens 2012, 79, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Barrios, O.; Meler, A.; Parra, M. MYC’s Fine Line Between B Cell Development and Malignancy. Cells 2020, 9, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaffer, A.L.; Young, R.M.; Staudt, L.M. Pathogenesis of Human B Cell Lymphomas. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 565–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamilloux, Y.; El Jammal, T.; Vuitton, L.; Gerfaud-Valentin, M.; Kerever, S.; Sève, P. JAK inhibitors for the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 102390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rip, J.; de Bruijn, M.J.W.; Kaptein, A.; Hendriks, R.W.; Corneth, O.B.J. Phosphoflow Protocol for Signaling Studies in Human and Murine B Cell Subpopulations. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 2852–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krutzik, P.O.; Clutter, M.R.; Nolan, G.P. Coordinate Analysis of Murine Immune Cell Surface Markers and Intracellular Phosphoproteins by Flow Cytometry. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 2357–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Urashima, M.; Chauhan, D.; Uchiyama, H.; Freeman, G.J.; Anderson, K.C. CD40 ligand triggered interleukin-6 secretion in multiple myeloma. Blood 1995, 85, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karonitsch, T.; Feierl, E.; Steiner, C.W.; Dalwigk, K.; Korb, A.; Binder, N.; Rapp, A.; Steiner, G.; Scheinecker, C.; Smolen, J.; et al. Activation of the interferon-gamma signaling pathway in systemic lupus erythematosus peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1463–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, N.; Liu, Y.; Bentebibel, S.E.; Munagala, I.; Bourdery, L.; Venuprasad, K.; Banchereau, J.; Ueno, H. The cytokine TGF-β 2 co-opts signaling via STAT3-STAT4 to promote the differentiation of human T FH cells. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souwer, Y.; Chamuleau, M.E.D.; van de Loosdrecht, A.A.; Tolosa, E.; Jorritsma, T.; Muris, J.J.F.; Dinnissen-van Poppel, M.J.; Snel, S.N.; van de Corput, L.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; et al. Detection of aberrant transcription of major histocompatibility complex class II antigen presentation genes in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia identifies HLA-DOA mRNA as a prognostic factor for survival. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 145, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krutzik, P.O.; Nolan, G.P. Intracellular phospho-protein staining techniques for flow cytometry: Monitoring single cell signaling events. Cytometry 2003, 55A, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huse, K.; Wogsland, C.E.; Polikowsky, H.G.; Diggins, K.E.; Smeland, E.B.; Myklebust, J.H.; Irish, J.M. Human Germinal Center B Cells Differ from Naïve and Memory B Cells in CD40 Expression and CD40L-Induced Signaling Response. Cytom. Part. A 2019, 95, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deenick, E.K.; Avery, D.T.; Chan, A.; Berglund, L.J.; Ives, M.L.; Moens, L.; Stoddard, J.L.; Bustamante, J.; Boisson-Dupuis, S.; Tsumura, M.; et al. Naive and memory human B cells have distinct requirements for STAT3 activation to differentiate into antibody-secreting plasma cells. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 2739–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheeren, F.A.; Naspetti, M.; Diehl, S.; Schotte, R.; Nagasawa, M.; Wijnands, E.; Gimeno, R.; Vyth-Dreese, F.A.; Blom, B.; Spits, H. STAT5 regulates the self-renewal capacity and differentiation of human memory B cells and controls Bcl-6 expression. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, S.A.; Schmidlin, H.; Nagasawa, M.; van Haren, S.D.; Kwakkenbos, M.J.; Yasuda, E.; Beaumont, T.; Scheeren, F.A.; Spits, H. STAT3-mediated up-regulation of BLIMP1 Is coordinated with BCL6 down-regulation to control human plasma cell differentiation. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 4805–4815. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18354204 (accessed on 28 March 2017).
- Heltemes-Harris, L.M.; Farrar, M.A. The role of STAT5 in lymphocyte development and transformation. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basso, K.; Dalla-Favera, R. Roles of BCL6 in normal and transformed germinal center B cells. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 247, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Weisel, F.; Shlomchik, M.J. B Cell Receptor and CD40 Signaling Are Rewired for Synergistic Induction of the c-Myc Transcription Factor in Germinal Center B Cells. Immunity 2018, 48, 313–326.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| Antibody Target | Conjugate | Clone | Manufacturer | Dilutions * | Cat. No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Membrane Markers | |||||
| CD19 | APC | SJ25C1 | BD | 1:400 | 345,791 |
| BV510 | SJ25C1 | BD | 1:100 | 562,947 | |
| CD27 | APC | L128 | BD | 1:50 | 337,169 |
| PE | L128 | BD | 1:50 | 340,425 | |
| BUV395 | L128 | BD | 1:100 | 563,815 | |
| BUV737 | L128 | BD | 1:100 | 612,829 | |
| CD38 | V450 | HB7 | BD | 1:100 | 646,851 |
| FITC | T16 | Beckman Coulter | 1:50 | A07778 | |
| Phosphoflow | |||||
| pSTAT1 | Percp-Cy5.5 | 4a pY701 | BD | 1:5 | 560,113 |
| pSTAT3 | PE | 4/P-STAT3 | BD | 1:5 | 612,569 |
| pSTAT5 | Pacific Blue | 47/Stat5 (pY694) | BD | 1:5 | 560,311 |
| pSTAT6 | AF647 | 18/P-Stat6 | BD | 1:5 | 612,601 |
| NF-κB p65 | PE-Cy7 | K10-895.12.50 | BD | 1:25 | 560,335 |
| Transcription Factors | |||||
| PAX5 | PE | 1H9 | Biolegend | 1:10.000 | 649,708 |
| c-MYC | AF647 | D84C12 | CST | 1:150 | 13871S |
| BCL6 | PE-Cy7 | 7D1 | Biolegend | 1:400 | 358,512 |
| BLIMP1 | AF647 | #646702 | R&D | 1:40 | IC36081R-025 |
| XBP-1s | AF647 | Q3-695 | BD | 1:40 | 562,821 |
| AID | AF647 | EK2-5G9 | BD | 1:150 | 565,785 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marsman, C.; Jorritsma, T.; ten Brinke, A.; van Ham, S.M. Flow Cytometric Methods for the Detection of Intracellular Signaling Proteins and Transcription Factors Reveal Heterogeneity in Differentiating Human B Cell Subsets. Cells 2020, 9, 2633. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122633
Marsman C, Jorritsma T, ten Brinke A, van Ham SM. Flow Cytometric Methods for the Detection of Intracellular Signaling Proteins and Transcription Factors Reveal Heterogeneity in Differentiating Human B Cell Subsets. Cells. 2020; 9(12):2633. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122633
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarsman, Casper, Tineke Jorritsma, Anja ten Brinke, and S. Marieke van Ham. 2020. "Flow Cytometric Methods for the Detection of Intracellular Signaling Proteins and Transcription Factors Reveal Heterogeneity in Differentiating Human B Cell Subsets" Cells 9, no. 12: 2633. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122633
APA StyleMarsman, C., Jorritsma, T., ten Brinke, A., & van Ham, S. M. (2020). Flow Cytometric Methods for the Detection of Intracellular Signaling Proteins and Transcription Factors Reveal Heterogeneity in Differentiating Human B Cell Subsets. Cells, 9(12), 2633. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122633