Conformational Switching in Bcl-xL: Enabling Non-Canonic Inhibition of Apoptosis Involves Multiple Intermediates and Lipid Interactions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Membrane Interactions of the Loop between α1 and α2 Helices
3.2. Secondary Structure Changes of Membrane-inserted Bcl-xL
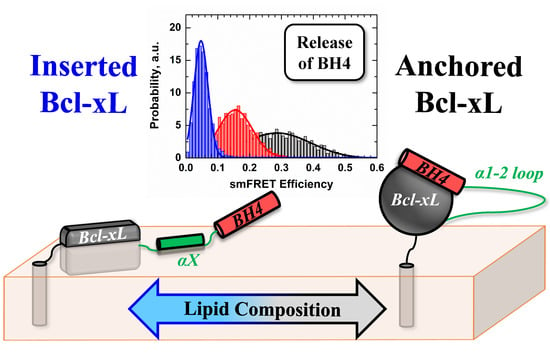
3.3. Ensemble and Single-Molecule FRET Measurements of the BH4 Domain Release in Membrane-Inserted Bcl-xL
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hardwick, J.M.; Youle, R.J. SnapShot: BCL-2 proteins. Cell 2009, 138, 404–404e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bogner, C.; Leber, B.; Andrews, D.W. Apoptosis: Embedded in membranes. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 22, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, J.; Osterlund, E.J.; Andrews, D.W. BCL-2 family proteins: Changing partners in the dance towards death. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Billen, L.P.; Kokoski, C.L.; Lovell, J.F.; Leber, B.; Andrews, D.W. Bcl-XL inhibits membrane permeabilization by competing with Bax. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldoveanu, T.; Follis, A.V.; Kriwacki, R.W.; Green, D.R. Many players in BCL-2 family affairs. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leber, B.; Lin, J.; Andrews, D.W. Embedded together: The life and death consequences of interaction of the Bcl-2 family with membranes. Apoptosis 2007, 12, 897–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, J.; Mooers, B.H.; Zhang, Z.; Kale, J.; Falcone, D.; McNichol, J.; Huang, B.; Zhang, X.C.; Xing, C.; Andrews, D.W. After embedding in membranes antiapoptotic Bcl-XL protein binds both Bcl-2 homology region 3 and helix 1 of proapoptotic Bax protein to inhibit apoptotic mitochondrial permeabilization. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 11873–11896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Subburaj, Y.; Cosentino, K.; Axmann, M.; Pedrueza-Villalmanzo, E.; Hermann, E.; Bleicken, S.; Spatz, J.; Garcia-Saez, A.J. Bax monomers form dimer units in the membrane that further self-Assemble into multiple oligomeric species. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, K.; O’Neill, K.L.; Li, J.; Zhou, W.; Han, N.; Pang, X.; Wu, W.; Struble, L.; Borgstahl, G.; Liu, Z.; et al. BH3-Only proteins target BCL-xL/MCL-1, not BAX/BAK, to initiate apoptosis. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.M. BAX and BAK become killers without a BH3 trigger. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 967–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, C.; Jayasinghe, S.; Hristova, K.; White, S.H. MPEx: A tool for exploring membrane proteins. Protein Sci. 2009, 18, 2624–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Posokhov, Y.O.; Rodnin, M.V.; Lu, L.; Ladokhin, A.S. Membrane insertion pathway of annexin B12: Thermodynamic and kinetic characterization by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and fluorescence quenching. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 5078–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasquez-Montes, V.; Vargas-Uribe, M.; Pandey, N.K.; Rodnin, M.V.; Langen, R.; Ladokhin, A.S. Lipid-Modulation of membrane insertion and refolding of the apoptotic inhibitor Bcl-xL. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2019, 1867, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchmore, S.W.; Sattler, M.; Liang, H.; Meadows, R.P.; Harlan, J.E.; Yoon, H.S.; Nettesheim, D.; Chang, B.S.; Thompson, C.B.; Wong, S.L.; et al. X-Ray and NMR structure of human Bcl-xL, an inhibitor of programmed cell death. Nature 1996, 381, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna-Vargas, M.P.; Chipuk, J.E. The deadly landscape of pro-Apoptotic BCL-2 proteins in the outer mitochondrial membrane. FEBS J. 2015, 283, 2676–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Fujimoto, L.M.; Hirshman, N.; Bobkov, A.A.; Antignani, A.; Youle, R.J.; Marassi, F.M. Conformation of BCL-XL upon membrane-Integration. J. Mol. Biol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diaz, J.L.; Oltersdorf, T.; Horne, W.; McConnell, M.; Wilson, G.; Weeks, S.; Garcia, T.; Fritz, L.C. A common binding site mediates heterodimerization and homodimerization of Bcl-2 family members. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 11350–11355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sattler, M.; Liang, H.; Nettesheim, D.; Meadows, R.P.; Harlan, J.E.; Eberstadt, M.; Yoon, H.S.; Shuker, S.B.; Chang, B.S.; Minn, A.J.; et al. Structure of Bcl-xL-Bak peptide complex: Recognition between regulators of apoptosis. Science 1997, 275, 983–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czabotar, P.E.; Westphal, D.; Dewson, G.; Ma, S.; Hockings, C.; Fairlie, W.D.; Lee, E.F.; Yao, S.; Robin, A.Y.; Smith, B.J.; et al. Bax crystal structures reveal how BH3 domains activate Bax and nucleate its oligomerization to induce apoptosis. Cell 2013, 152, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vargas-Uribe, M.; Rodnin, M.V.; Ladokhin, A.S. Comparison of membrane insertion pathways of the apoptotic regulator Bcl-xL and the diphtheria toxin translocation domain. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 7901–7909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barclay, L.A.; Wales, T.E.; Garner, T.P.; Wachter, F.; Lee, S.; Guerra, R.M.; Stewart, M.L.; Braun, C.R.; Bird, G.H.; Gavathiotis, E.; et al. Inhibition of Pro-Apoptotic BAX by a noncanonical interaction mechanism. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hope, M.J.; Bally, M.B.; Mayer, L.D.; Janoff, A.S.; Cullis, P.R. Generation of multilamellar and unilamellar phospholipid vesicles. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1986, 40, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, L.D.; Hope, M.J.; Cullis, P.R. Vesicles of variable sizes produced by a rapid extrusion procedure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1986, 858, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugland, R.P. Handbook of Fluorescent Probes and Research Chemicals, 6th ed.; Molecular Probes, Inc.: Eugene, OR, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Ladokhin, A.S. Fluorescence spectroscopy in thermodynamic and kinetic analysis of pH-dependent membrane protein insertion. Methods Enzymol. 2009, 466, 19–42. [Google Scholar]
- Posokhov, Y.O.; Ladokhin, A.S. Lifetime fluorescence method for determining membrane topology of proteins. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 348, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 1–698. [Google Scholar]
- Kyrychenko, A.; Rodnin, M.V.; Ghatak, C.; Ladokhin, A.S. Joint refinement of FRET measurements using spectroscopic and computational tools. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 522, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, T.; Schlesinger, R.; Gabba, M.; Fitter, J. Native and unfolded states of phosphoglycerate kinase studied by single-molecule FRET. Chemphyschem 2011, 12, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Yang, J.T.; Chau, K.H. Determination of the helix and beta form of proteins in aqueous solution by circular dichroism. Biochemistry 1974, 13, 3350–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardail, D.; Privat, J.-P.; Egret-Charlier, M.; Levrat, C.; Lerme, F.; Louisot, P. Mitochondrial contact sites: Lipid composition and dynamics. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 18797–18802. [Google Scholar]
- Daum, G. Lipids of mitochondria. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Rev. Biomembr. 1985, 822, 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kerr, J.F.; Wyllie, A.H.; Currie, A.R. Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-Ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br. J. Cancer 1972, 26, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsujimoto, Y.; Cossman, J.; Jaffe, E.; Croce, C.M. Involvement of the bcl-2 gene in human follicular lymphoma. Science 1985, 228, 1440–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaux, D.L.; Cory, S.; Adams, J.M. Bcl-2 gene promotes haemopoietic cell survival and cooperates with c-myc to immortalize pre-B cells. Nature 1988, 335, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strasser, A.; Cory, S.; Adams, J.M. Deciphering the rules of programmed cell death to improve therapy of cancer and other diseases. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 3667–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Youle, R.J. The role of mitochondria in apoptosis *. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2009, 43, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cosentino, K.; García-Sáez, A.J. Mitochondrial alterations in apoptosis. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2014, 181, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youle, R.J.; Strasser, A. The BCL-2 protein family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, X.; Kale, J.; Leber, B.; Andrews, D.W. Regulating cell death at, on, and in membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 2100–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crimi, M.; Esposti, M.D. Apoptosis-Induced changes in mitochondrial lipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipuk, J.E.; McStay, G.P.; Bharti, A.; Kuwana, T.; Clarke, C.J.; Siskind, L.J.; Obeid, L.M.; Green, D.R. Sphingolipid metabolism cooperates with BAK and BAX to promote the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. Cell 2012, 148, 988–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hollville, E.; Martin, S.J. Greasing the path to BAX/BAK activation. Cell 2012, 148, 845–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Renault, T.T.; Chipuk, J.E. Death upon a kiss: Mitochondrial outer membrane composition and organelle communication govern sensitivity to BAK/BAX-dependent apoptosis. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raemy, E.; Martinou, J.C. Involvement of cardiolipin in tBID-Induced activation of BAX during apoptosis. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2014, 179, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladokhin, A.S.; White, S.H. Folding of amphipathic a-helices on membranes: Energetics of helix formation by melittin. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 285, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vasquez-Montes, V.; Kyrychenko, A.; Vargas-Uribe, M.; Rodnin, M.V.; Ladokhin, A.S. Conformational Switching in Bcl-xL: Enabling Non-Canonic Inhibition of Apoptosis Involves Multiple Intermediates and Lipid Interactions. Cells 2020, 9, 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030539
Vasquez-Montes V, Kyrychenko A, Vargas-Uribe M, Rodnin MV, Ladokhin AS. Conformational Switching in Bcl-xL: Enabling Non-Canonic Inhibition of Apoptosis Involves Multiple Intermediates and Lipid Interactions. Cells. 2020; 9(3):539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030539
Chicago/Turabian StyleVasquez-Montes, Victor, Alexander Kyrychenko, Mauricio Vargas-Uribe, Mykola V. Rodnin, and Alexey S. Ladokhin. 2020. "Conformational Switching in Bcl-xL: Enabling Non-Canonic Inhibition of Apoptosis Involves Multiple Intermediates and Lipid Interactions" Cells 9, no. 3: 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030539
APA StyleVasquez-Montes, V., Kyrychenko, A., Vargas-Uribe, M., Rodnin, M. V., & Ladokhin, A. S. (2020). Conformational Switching in Bcl-xL: Enabling Non-Canonic Inhibition of Apoptosis Involves Multiple Intermediates and Lipid Interactions. Cells, 9(3), 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030539