HOXA9 Transcriptionally Promotes Apoptosis and Represses Autophagy by Targeting NF-κB in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
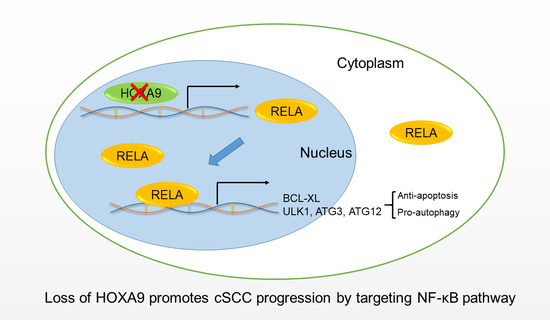
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Experiments
2.2. Cell Line and Drug Treatment
2.3. RNA Isolation and qRT-PCR
2.4. DNA Construct
2.5. RNA-Seq
2.6. Immunoblotting and Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Assays
2.7. Xenograft Mouse Model
2.8. ChIP-qPCR Analysis
2.9. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.10. Apoptosis Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
2.12. Data Availability
3. Results
3.1. HOXA9 Is Predicted to Regulate Apoptotic- and Autophagic-Genes in cSCC
3.2. HOXA9 Promotes Apoptosis While Inhibits Autophagy
3.3. HOXA9 Negatively Regulated the Expression of RELA, BCL-XL, ULK1, ATG3, and ATG12
3.4. HOXA9 Inhibits the Epigenetic Activities of NF-κB
3.5. Inhibition of RELA Decreased the Expression of BCL-XL, ULK1, ATG3, and ATG12
3.6. Loss of HOXA9 Inhibits Apoptotic geNes While Enhances Autophagic Genes In Vivo
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, J.; Yan, S. Prognostic variables in high-risk cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: A review. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2016, 43, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomas, A.; Leonardi Bee, J.; Bath Hextall, F. A systematic review of worldwide incidence of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 166, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dotto, G.P.; Rustgi, A.K. Squamous Cell Cancers: A Unified Perspective on Biology and Genetics. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 622–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.S.; Bhaduri, A.; Mah, A.; Johnson, W.L.; Ungewickell, A.; Aros, C.J.; Nguyen, C.B.; Rios, E.J.; Siprashvili, Z.; Straight, A. Recurrent point mutations in the kinetochore gene KNSTRN in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1060–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipuk, J.E.; Green, D.R. How do BCL-2 proteins induce mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization? Trends Cell Biol. 2008, 18, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabellini, C.; Trisciuoglio, D.; Bufalo, D.D.J.C. Non-canonical roles of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL proteins: Relevance of BH4 domain. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, D.T.; Korsmeyer, S.J. BCL-2 FAMILY: Regulators of Cell Death. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 16, 395–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maejima, Y.; Kyoi, S.; Zhai, P.; Liu, T.; Li, H.; Ivessa, A.; Sciarretta, S.; Del Re, D.P.; Zablocki, D.; Hsu, C.P.; et al. Mst1 inhibits autophagy by promoting the interaction between Beclin1 and Bcl-2. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chonghaile, T.N.; Sarosiek, K.A.; Vo, T.T.; Ryan, J.; Tammareddi, A.; Moore, V.D.G.; Deng, J.; Anderson, K.C.; Richardson, P.; Tai, Y.T.; et al. Pretreatment mitochondrial priming correlates with clinical response to cytotoxic chemotherapy. Science 2011, 334, 1129–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klionsky, D.J.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Abe, A.; Abedin, J.; Abeliovich, H.; Arozena, A.A.; Adachi, H.; Adams, C.M.; Adams, P.D.; Adeli, K.J.A. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy 2016, 12, 1–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.J.; Chee, C.E.; Huang, S.; Sinicrope, F.A. The Role of Autophagy in Cancer: Therapeutic Implications. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, J.M.M.; Towers, C.G.; Thorburn, A. Targeting autophagy in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 528–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikic, I.; Elazar, Z. Mechanism and medical implications of mammalian autophagy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Ding, Z.J. HOXA9 inhibits HIF-1α-mediated glycolysis through interacting with CRIP2 to repress cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma development. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, C.; Hess, J.L. Role of HOXA9 in leukemia: Dysregulation, cofactors and essential targets. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocabas, F.; Xie, L.; Xie, J.; Yu, Z.; Deberardinis, R.J.; Kimura, W.; Thet, S.; Elshamy, A.; Abouellail, H.; Muralidhar, S. Hypoxic metabolism in human hematopoietic stem cells. Cell Biosci. 2015, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loots, G.G.; Ovcharenko, I. rVISTA 2.0: Evolutionary analysis of transcription factor binding sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W217–W221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, G.; Nisosantano, M.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Kroemer, G. Self-consumption: The interplay of autophagy and apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroemer, G.; Marino, G.; Levine, B. Autophagy and the Integrated Stress Response. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faber, J.; Krivtsov, A.V.; Stubbs, M.C.; Wright, R.; Davis, T.; Van-Den-Heuvel-Eibrink, M.; Zwaan, C.; Kung, A.; Armstrong, S. HOXA9 is required for survival in human MLL-rearranged acute leukemias. Blood 2009, 113, 2375–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quéré, R.; Karlsson, G.; Hertwig, F.; Rissler, M.; Lindqvist, B.; Fioretos, T.; Vandenberghe, P.; Slovak, M.L.; Cammenga, J.; Karlsson, S. Smad4 binds Hoxa9 in the cytoplasm and protects primitive hematopoietic cells against nuclear activation by Hoxa9 and leukemia transformation. Blood 2011, 117, 5918–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, L.L.; Yeung, J.; Zeisig, B.B.; Popov, N.; Huijbers, I.; Barnes, J.; Wilson, A.J.; Taskesen, E.; Delwel, R.; Gil, J. Functional crosstalk between Bmi1 and MLL/Hoxa9 axis in establishment of normal hematopoietic and leukemic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 8, 649–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, P.M.; Mouw, J.K.; Unger, M.A.; Lakins, J.N.; Gbegnon, M.K.; Clemmer, V.B.; Benezra, M.; Licht, J.D.; Boudreau, N.J.; Tsai, K.K. HOXA9 regulates BRCA1 expression to modulate human breast tumor phenotype. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 1535–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, K.; Karin, M. NF-κB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: Coming of age. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karin, M.; Greten, F.R. NF-κB: Linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.L.; Lee, D.C.; Sohn, H.A.; Lee, S.Y.; Jeon, H.S.; Lee, J.H.; Park, C.G.; Lee, H.Y.; Yeom, Y.I.; Son, J.W.; et al. Homeobox A9 directly targeted by miR-196b regulates aggressiveness through nuclear Factor-kappaB activity in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2016, 55, 1915–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkenazi, A.; Fairbrother, W.J.; Leverson, J.D.; Souers, A.J. From basic apoptosis discoveries to advanced selective BCL-2 family inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.F.; Fairlie, W.D. The Structural Biology of Bcl-xL. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takase, O.; Minto, A.; Puri, T.; Cunningham, P.; Jacob, A.; Hayashi, M.; Quigg, R. Inhibition of NF-κB-dependent Bcl-xL expression by clusterin promotes albumin-induced tubular cell apoptosis. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.L.; Yeh, J.; Friedman, J.; Yan, B.; Yang, X.; Yeh, N.T.; Van Waes, C.; Chen, Z. A signal network involving coactivated NF-κB and STAT3 and altered p53 modulates BAX/BCL-XL expression and promotes cell survival of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 1987–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushima, N. The role of the Atg1/ULK1 complex in autophagy regulation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 22, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murrow, L.; Debnath, J. ATG12–ATG3 connects basal autophagy and late endosome function. Autophagy 2015, 11, 961–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Category | GO ID | Term | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| GOTERM_BP_DIRECT | GO:0045893 | Positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | 5.65 × 10−12 |
| GOTERM_BP_DIRECT | GO:0043065 | Positive regulation of apoptotic process | 1.58 × 10−9 |
| GOTERM_BP_DIRECT | GO:0045944 | Positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter | 2.14 × 10−8 |
| GOTERM_BP_DIRECT | GO:0051092 | Positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity | 2.19 × 10−8 |
| GOTERM_BP_DIRECT | GO:0006915 | Apoptotic process | 4.17 × 10−8 |
| GOTERM_BP_DIRECT | GO:0043123 | Positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling | 5.28 × 10−8 |
| GOTERM_BP_DIRECT | GO:0042981 | Regulation of apoptotic process | 5.16 × 10−6 |
| GOTERM_BP_DIRECT | GO:1902041 | Regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors | 1.12 × 10−4 |
| GOTERM_BP_DIRECT | GO:0043068 | Positive regulation of programmed cell death | 1.57 × 10−3 |
| GOTERM_BP_DIRECT | GO:0016236 | Macroautophagy | 1.78 × 10−2 |
| KEGG_PATHWAY | hsa05200 | Pathways in cancer | 6.91 × 10−12 |
| KEGG_PATHWAY | hsa04064 | NF-kappaB signaling pathway | 2.63 × 10−9 |
| KEGG_PATHWAY | hsa04210 | Apoptosis | 1.08 × 10−2 |
| KEGG_PATHWAY | hsa04140 | Regulation of autophagy | 4.96 × 10−2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, S.; Li, X.; Liang, X.; Zhou, L. HOXA9 Transcriptionally Promotes Apoptosis and Represses Autophagy by Targeting NF-κB in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cells 2019, 8, 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8111360
Han S, Li X, Liang X, Zhou L. HOXA9 Transcriptionally Promotes Apoptosis and Represses Autophagy by Targeting NF-κB in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cells. 2019; 8(11):1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8111360
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Shuo, Xue Li, Xiaoting Liang, and Liang Zhou. 2019. "HOXA9 Transcriptionally Promotes Apoptosis and Represses Autophagy by Targeting NF-κB in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma" Cells 8, no. 11: 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8111360
APA StyleHan, S., Li, X., Liang, X., & Zhou, L. (2019). HOXA9 Transcriptionally Promotes Apoptosis and Represses Autophagy by Targeting NF-κB in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cells, 8(11), 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8111360