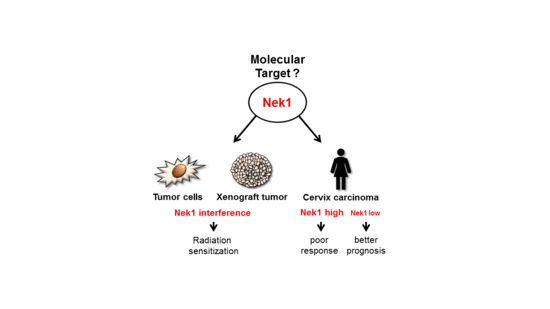
Fractionation-Dependent Radiosensitization by Molecular Targeting of Nek1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. RNA Interference-Mediated Knockdown
2.3. D Culture and in vitro Irradiation
2.4. Quantitative Nek1 Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
2.5. Immunoblotting
2.6. 3D Clonogenic Radiation Survival Assay
2.7. Cell Cycle Analysis and Apoptosis Assays
2.8. Staining and Quantification of γH2AX Foci Formation
2.9. Murine Xenograft Model and in vivo Irradiation
2.10. Patient Characteristics
2.11. Treatment and Follow-Up
2.12. Immunohistochemical Staining of Nek1 and Scoring
2.13. Cervical Cancer TCGA Dataset
2.14. Statistical Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Knockdown of Nek1 Reduces 3D Clonogenic Cell Survival
3.2. Fractionation-Dependent Radiation Sensitization by Knockdown of Nek1
3.3. Nek1 Overexpression in Cervical Cancer is Associated with Impaired Clinical Outcome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meirelles, G.V.; Perez, A.M.; De Souza, E.E.; Basei, F.L.; Papa, P.F.; Melo-Hanchuk, T.D.; Cardoso, V.B.; Kobarg, J. “Stop Ne(c)king around”: How interactomics contributes to functionally characterize Nek family kinases. World J. Boil. Chem. 2014, 5, 141–160. [Google Scholar]
- Feige, E.; Shalom, O.; Tsuriel, S.; Yissachar, N.; Motro, B. Nek1 shares structural and functional similarities with NIMA kinase. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Bioenerg. 2006, 1763, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Connell, M.J.; Krien, M.J.; Hunter, T. Never say never. The NIMA-related protein kinases in mitotic control. Trends Cell Boil. 2003, 13, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, P.-L.; Chen, C.-F.; Jiang, X.; Riley, D.J. Never-in-mitosis related kinase 1 functions in DNA damage response and checkpoint control. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 3194–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelegrini, A.L.; Moura, D.J.; Brenner, B.L.; Ledur, P.F.; Maques, G.P.; Henriques, J.A.P.; Saffi, J.; Lenz, G. Nek1 silencing slows down DNA repair and blocks DNA damage-induced cell cycle arrest. Mutagenesis 2010, 25, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polci, R.; Peng, A.; Chen, P.-L.; Riley, D.J. NIMA-Related Protein Kinase 1 Is Involved Early in the Ionizing Radiation-Induced DNA Damage Response. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 8800–8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grudzenski, S.; Raths, A.; Conrad, S.; Rübe, C.E.; Löbrich, M. Inducible response required for repair of low-dose radiation damage in human fibroblasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14205–14210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, C.-F.; Riley, D.J.; Chen, P.-L. Nek1 kinase functions in DNA damage response and checkpoint control through a pathway independent of ATM and ATR. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spies, J.; Waizenegger, A.; Barton, O.; Sürder, M.; Wright, W.D.; Heyer, W.-D.; Löbrich, M. Nek1 Regulates Rad54 to Orchestrate Homologous Recombination and Replication Fork Stability. Mol. Cell 2016, 62, 903–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, V.; Jaiswal, P.K.; Ghosh, I.; Koul, H.K.; Yu, X.; De Benedetti, A. The TLK1-Nek1 axis promotes prostate cancer progression. Cancer Lett. 2019, 453, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ho, C.K.; Ouyang, J.; Zou, L. Nek1 kinase associates with ATR–ATRIP and primes ATR for efficient DNA damage signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2175–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, C.-F.; Chiang, H.-C.; Pena, M.; Polci, R.; Wei, R.L.; Edwards, R.A.; Hansel, D.E.; Chen, P.-L.; Riley, D.J. Mutation of NIMA-related kinase 1 (NEK1) leads to chromosome instability. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fry, A.M.; O’Regan, L.; Sabir, S.; Bayliss, R. Cell cycle regulation by the NEK family of protein kinases. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 4423–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Craigen, W.J.; Riley, D.J. Nek1 regulates cell death and mitochondrial membrane permeability through phosphorylation of VDAC1. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, V.; Khalil, I.; De Benedetti, A. The TLK1/Nek1 axis contributes to mitochondrial integrity and apoptosis prevention via phosphorylation of VDAC1. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, A.P.; Issayama, L.K.; Pavan, I.B.; Silva, F.R.; Melo-Hanchuk, T.D.D.; Simabuco, F.M.M.; Kobarg, J. Checking NEKs: Overcoming a Bottleneck in Human Diseases. Molecules 2020, 25, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, C.L.; Possemato, R.; Bauerlein, E.L.; Xie, A.; Scully, R.; Hahn, W.C. Nek4 Regulates Entry into Replicative Senescence and the Response to DNA Damage in Human Fibroblasts. Mol. Cell. Boil. 2012, 32, 3963–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melo-Hanchuk, T.D.; Slepicka, P.F.; Pelegrini, A.L.; Menck, C.F.; Kobarg, J. NEK5 interacts with topoisomerase IIβ and is involved in the DNA damage response induced by etoposide. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 16853–16866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeyta, A.; Castella, M.; Jacquemont, C.; Taniguchi, T. NEK8 regulates DNA damage-induced RAD51 foci formation and replication fork protection. Cell Cycle 2016, 16, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.C.; Petrova, A.V.; Madden, M.Z.; Wang, H.; Pan, Y.; Warren, M.D.; Hardy, C.W.; Liang, N.; Liu, E.A.; Robinson, M.H.; et al. A gemcitabine sensitivity screen identifies a role for NEK9 in the replication stress response. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 11517–11527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabir, S.; Sahota, N.K.; Jones, G.; Fry, A.M. Loss of Nek11 Prevents G2/M Arrest and Promotes Cell Death in HCT116 Colorectal Cancer Cells Exposed to Therapeutic DNA Damaging Agents. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Noguchi, K.; Fukazawa, H.; Murakami, Y.; Uehara, Y. Nek11, a New Member of the NIMA Family of Kinases, Involved in DNA Replication and Genotoxic Stress Responses. J. Boil. Chem. 2002, 277, 39655–39665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Cai, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhao, W. Frequent Nek1 overexpression in human gliomas. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 476, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyrskjøt, L.; Reinert, T.; Algaba, F.; Christensen, E.; Nieboer, D.; Hermann, G.G.; Mogensen, K.; Beukers, W.; Marquez, M.; Segersten, U.; et al. Prognostic Impact of a 12-gene Progression Score in Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer: A Prospective Multicentre Validation Study. Eur. Urol. 2017, 72, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.L.; Alirezaie, N.; Connor, A.; Chan-Seng-Yue, M.; Grant, R.; Selander, I.; Bascuñana, C.; Borgida, A.; Hall, A.; Whelan, T.; et al. Candidate DNA repair susceptibility genes identified by exome sequencing in high-risk pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015, 370, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, N.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 136, 359–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehlgans, S.; Booms, P.; Güllülü, Ö.; Sader, R.; Rödel, C.; Balermpas, P.; Rödel, F.; Ghanaati, S. Radiation Sensitization of Basal Cell and Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma by the Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitor Vismodegib. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faustino, A.; Oliveira, P.A.; Pinho, J.O.; Teixeira-Guedes, C.; Soares-Maia, R.; Gil Da Costa, R.M.; Colaço, B.; Pires, M.J.; Colaço, J.; Ferreira, R.; et al. Estimation of rat mammary tumor volume using caliper and ultrasonography measurements. Lab Anim. 2013, 42, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rödel, F.; Wieland, U.; Fraunholz, I.; Kitz, J.; Rave-Fränk, M.; Wolff, H.A.; Weiss, C.; Wirtz, R.; Balermpas, P.; Fokas, E.; et al. Human papillomavirus DNA load and p16INK4aexpression predict for local control in patients with anal squamous cell carcinoma treated with chemoradiotherapy. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 136, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, P.; Florez, M.; Najafov, A.; Pan, H.; Geng, J.; Ofengeim, D.; Dziedzic, S.A.; Wang, H.; Barrett, V.J.; Ito, Y.; et al. Regulation of a distinct activated RIPK1 intermediate bridging complex I and complex II in TNFα-mediated apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E5944–E5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Gent, D.C.; Hoeijmakers, J.H.J.; Kanaar, R. Chromosomal stability and the DNA double-stranded break connection. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.M.; Carlson, D.J.; Brenner, D.J. The tumor radiobiology of SRS and SBRT: are more than the 5 Rs involved? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 88, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, E. Radiobiology for the radiologist; Lippincott Williams &Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bourhis, J.; Overgaard, J.; Audry, H.; Ang, K.K.; Saunders, M.; Bernier, J.; Horiot, J.-C.; Le Maître, A.; Pajak, T.F.; Poulsen, M.G.; et al. Hyperfractionated or accelerated radiotherapy in head and neck cancer: a meta-analysis. Lancet 2006, 368, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryankalayil, M.J.; Palayoor, S.T.; Cerna, D.; Simone, C.B.; Falduto, M.T.; Magnuson, S.R.; Coleman, C.N. Fractionated Radiation Therapy Can Induce a Molecular Profile for Therapeutic Targeting. Radiat. Res. 2010, 174, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinde, A.Y.; Eke, I.; Aryankalayil, M.J.; Ahmed, M.M.; Coleman, C.N. Exploiting Gene Expression Kinetics in Conventional Radiotherapy, Hyperfractionation, and Hypofractionation for Targeted Therapy. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 26, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, F.; Mazin, A.V. A Small Molecule Inhibitor of Human RAD51 Potentiates Breast Cancer Cell Killing by Therapeutic Agents in Mouse Xenografts. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, H.O.; Brend, T.; Payne, H.L.; Wright, A.; Ward, T.A.; Patel, K.; Egnuni, T.; Stead, L.F.; Patel, A.; Wurdak, H.; et al. RAD51 Is a Selective DNA Repair Target to Radiosensitize Glioma Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 8, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sankaranarayanan, R.; Swaminathan, R.; Jayant, K.; Brenner, H. An overview of cancer survival in Africa, Asia, the Caribbean and Central America: the case for investment in cancer health services. IARC Sci. Publ. 2011, 162, 257–291. [Google Scholar]
- Pötter, R.; Georg, P.; Dimopoulos, J.C.; Grimm, M.; Berger, D.; Nesvacil, N.; Georg, D.; Schmid, M.P.; Reinthaller, A.; Sturdza, A.; et al. Clinical outcome of protocol based image (MRI) guided adaptive brachytherapy combined with 3D conformal radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced cervical cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2011, 100, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackson, S.E.; Chester, J. Personalised cancer medicine. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 137, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biewenga, P.; Van Der Velden, J.; Mol, B.W.J.; Stalpers, L.J.; Schilthuis, M.S.; Van Der Steeg, J.W.; Burger, M.P.; Buist, M.R. Validation of existing prognostic models in patients with early-stage cervical cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2009, 115, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadducci, A.; Guerrieri, M.E.; Greco, C. Tissue biomarkers as prognostic variables of cervical cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2013, 86, 104–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo-Hanchuk, T.D.; Martins, M.B.; Cunha, L.L.; Soares, F.A.; Ward, L.S.; Vassallo, J.; Kobarg, J. Expression of the NEK family in normal and cancer tissue: an immunohistochemical study. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, C.-F.; Polci, R.; Wei, R.; Riley, D.J.; Chen, P.-L. Increased Nek1 expression in Renal Cell Carcinoma cells is associated with decreased sensitivity to DNA-damaging treatment. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 4283–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Multivariate Analyses | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95% Confidence Interval | |||||
| Univariate P-Value | Hazard Ratio (HR) | Lower | Upper | P-Value | |
| Cumulative incidence of local failure | |||||
| T-stage (T1-2/T3-4) | 0.011 | 1.07 | 0.2 | 5.7 | 0.935 |
| FIGO (Ia-IIb/IIIa-IVb) | 0.006 | 5.6 | 0.5 | 62.52 | 0.162 |
| Nek1 (WS ≤ 6/> 6) | 0.028 | 5.46 | 1.02 | 29.26 | 0.047 |
| Cumulative incidence of distant failure | |||||
| T-stage (T1-2/T3-4) | 0.011 | 2.13 | 0.45 | 10.01 | 0.336 |
| FIGO (Ia-IIb/IIIa-IVb) | 0.008 | 5.59 | 0.5 | 62.7 | 0.162 |
| Nek1 (WS ≤ 6/> 6) | 0.035 | 4.49 | 1.17 | 10.41 | 0.025 |
| Cancer-specific survival | |||||
| T-stage (T1-2/T3-4) | 0.006 | 5.58 | 0.69 | 44.67 | 0.105 |
| FIGO (Ia-IIB/IIIa-IVb) | 0.017 | 1.01 | 0.89 | 11.58 | 0.989 |
| p16INK4a (WS ≤ 6/> 6) | 0.013 | 3.44 | 1.18 | 10.04 | 0.023 |
| Nek1 (WS ≤ 6/> 6) | 0.008 | 6.31 | 2.09 | 10.01 | 0.001 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Freund, I.; Hehlgans, S.; Martin, D.; Ensminger, M.; Fokas, E.; Rödel, C.; Löbrich, M.; Rödel, F. Fractionation-Dependent Radiosensitization by Molecular Targeting of Nek1. Cells 2020, 9, 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051235
Freund I, Hehlgans S, Martin D, Ensminger M, Fokas E, Rödel C, Löbrich M, Rödel F. Fractionation-Dependent Radiosensitization by Molecular Targeting of Nek1. Cells. 2020; 9(5):1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051235
Chicago/Turabian StyleFreund, Isabel, Stephanie Hehlgans, Daniel Martin, Michael Ensminger, Emmanouil Fokas, Claus Rödel, Markus Löbrich, and Franz Rödel. 2020. "Fractionation-Dependent Radiosensitization by Molecular Targeting of Nek1" Cells 9, no. 5: 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051235
APA StyleFreund, I., Hehlgans, S., Martin, D., Ensminger, M., Fokas, E., Rödel, C., Löbrich, M., & Rödel, F. (2020). Fractionation-Dependent Radiosensitization by Molecular Targeting of Nek1. Cells, 9(5), 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051235