Anxiety and Depression Are Related to Higher Activity of Sphingolipid Metabolizing Enzymes in the Rat Brain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Elevated Plus-Maze Test (EPM)
2.4. Social Preference Test (SPT)
2.5. Novelty-Suppressed Feeding Paradigm (NSF)
2.6. Measurement of Sphingomyelinase and Ceramidase Activities
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Phenotype of HAB and LAB Females
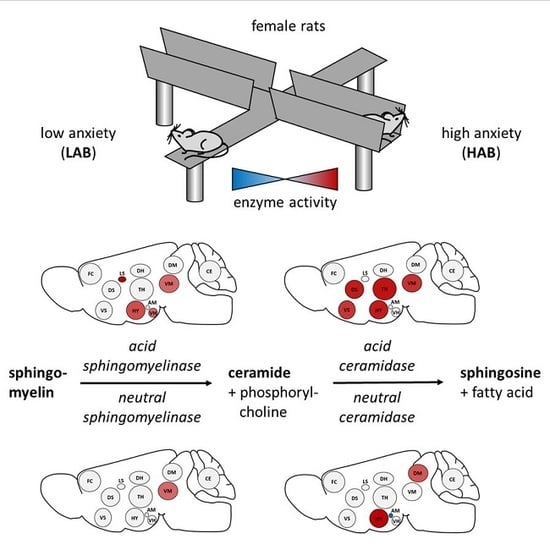
3.2. Enzyme Activities in Selected Brain Regions of HAB and LAB Females
3.3. Correlations between Behavior and Enzyme Activities in HAB and LAB Females
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders: Global Health Estimates; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lenz, B.; Rother, M.; Bouna-Pyrrou, P.; Mühle, C.; Tektas, O.Y.; Kornhuber, J. The androgen model of suicide completion. Prog. Neurobiol. 2019, 172, 84–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, C.P.; Reichel, M.; Mühle, C.; Rhein, C.; Gulbins, E.; Kornhuber, J. Brain membrane lipids in major depression and anxiety disorders. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1851, 1052–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schneider, P.B.; Kennedy, E.P. Sphingomyelinase in normal human spleens and in spleens from subjects with Niemann-Pick disease. J. Lipid Res. 1967, 8, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goni, F.M.; Alonso, A. Sphingomyelinases: Enzymology and membrane activity. FEBS Lett. 2002, 531, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinreb, N.J.; Brady, R.O.; Tappel, A.L. The lysosomal localization of sphingolipid hydrolases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1968, 159, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornhuber, J.; Rhein, C.; Müller, C.P.; Mühle, C. Secretory sphingomyelinase in health and disease. Biol. Chem. 2015, 396, 707–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.G.; Spence, M.W. Sphingomyelinase activity at pH 7.4 in human brain and a comparison to activity at pH 5.0. J. Lipid Res. 1976, 17, 506–515. [Google Scholar]
- Mühle, C.; Reichel, M.; Gulbins, E.; Kornhuber, J. Sphingolipids in psychiatric disorders and pain syndromes. Handb. Exp. Pharm. 2013, 431–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.D.; Hertervig, E.; Nyberg, L.; Hauge, T.; Sternby, B.; Lillienau, J.; Farooqi, A.; Nilsson, A. Distribution of alkaline sphingomyelinase activity in human beings and animals. Tissue and species differences. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1996, 41, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, M.; Willians, M.; Dulaney, J.T.; Moser, H.W. Ceramidase and ceramide synthesis in human kidney and cerebellum. Description of a new alkaline ceramidase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1975, 398, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornhuber, J.; Medlin, A.; Bleich, S.; Jendrossek, V.; Henkel, A.W.; Wiltfang, J.; Gulbins, E. High activity of acid sphingomyelinase in major depression. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna) 2005, 112, 1583–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mühle, C.; Wagner, C.J.; Färber, K.; Richter-Schmidinger, T.; Gulbins, E.; Lenz, B.; Kornhuber, J. Secretory acid sphingomyelinase in the serum of medicated patients predicts the prospective course of depression. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rhein, C.; Reichel, M.; Kramer, M.; Rotter, A.; Lenz, B.; Mühle, C.; Gulbins, E.; Kornhuber, J. Alternative splicing of SMPD1 coding for acid sphingomyelinase in major depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 209, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhein, C.; Tripal, P.; Seebahn, A.; Konrad, A.; Kramer, M.; Nagel, C.; Kemper, J.; Bode, J.; Mühle, C.; Gulbins, E.; et al. Functional implications of novel human acid sphingomyelinase splice variants. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gracia-Garcia, P.; Rao, V.; Haughey, N.J.; Bandaru, V.V.; Smith, G.; Rosenberg, P.B.; Lobo, A.; Lyketsos, C.G.; Mielke, M.M. Elevated plasma ceramides in depression. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 23, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunkhorst-Kanaan, N.; Klatt-Schreiner, K.; Hackel, J.; Schroter, K.; Trautmann, S.; Hahnefeld, L.; Wicker, S.; Reif, A.; Thomas, D.; Geisslinger, G.; et al. Targeted lipidomics reveal derangement of ceramides in major depression and bipolar disorder. Metabolism 2019, 95, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinoff, A.; Saleem, M.; Herrmann, N.; Mielke, M.M.; Oh, P.I.; Venkata, S.L.V.; Haughey, N.J.; Lanctot, K.L. Plasma sphingolipids and depressive symptoms in coronary artery disease. Brain Behav. 2017, 7, e00836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moaddel, R.; Shardell, M.; Khadeer, M.; Lovett, J.; Kadriu, B.; Ravichandran, S.; Morris, P.J.; Yuan, P.; Thomas, C.J.; Gould, T.D.; et al. Plasma metabolomic profiling of a ketamine and placebo crossover trial of major depressive disorder and healthy control subjects. Psychopharmacol (Berlin) 2018, 235, 3017–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, J.; Zheng, P.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, C.; Hu, C.; Hou, X.; Wang, H.; Xie, P.; Xu, G. Plasma lipidomics reveals potential lipid markers of major depressive disorder. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 6497–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkan, A.; Isaacs, A.; Ugocsai, P.; Liebisch, G.; Struchalin, M.; Rudan, I.; Wilson, J.F.; Pramstaller, P.P.; Gyllensten, U.; Campbell, H.; et al. Plasma phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin concentrations are associated with depression and anxiety symptoms in a Dutch family-based lipidomics study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2013, 47, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willner, P. The chronic mild stress (CMS) model of depression: History, evaluation and usage. Neurobiol. Stress 2017, 6, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.D.; Shi, D.D.; Zhang, Z.J. Antidepressant and anxiolytic effects of the proprietary Chinese medicine Shexiang Baoxin pill in mice with chronic unpredictable mild stress. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 27, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, T.G.; Chan, R.B.; Bravo, F.V.; Miranda, A.; Silva, R.R.; Zhou, B.; Marques, F.; Pinto, V.; Cerqueira, J.J.; Di Paolo, G.; et al. The impact of chronic stress on the rat brain lipidome. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gregus, A.; Wintink, A.J.; Davis, A.C.; Kalynchuk, L.E. Effect of repeated corticosterone injections and restraint stress on anxiety and depression-like behavior in male rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2005, 156, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, F.; Smith, D.W.; Hutson, P.H. Chronic low dose corticosterone exposure decreased hippocampal cell proliferation, volume and induced anxiety and depression like behaviours in mice. Eur. J. Pharm. 2008, 583, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, D.J.; Samuels, B.A.; Rainer, Q.; Wang, J.W.; Marsteller, D.; Mendez, I.; Drew, M.; Craig, D.A.; Guiard, B.P.; Guilloux, J.P.; et al. Neurogenesis-dependent and -independent effects of fluoxetine in an animal model of anxiety/depression. Neuron 2009, 62, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miranda, A.M.; Bravo, F.V.; Chan, R.B.; Sousa, N.; Di Paolo, G.; Oliveira, T.G. Differential lipid composition and regulation along the hippocampal longitudinal axis. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulbins, E.; Palmada, M.; Reichel, M.; Luth, A.; Bohmer, C.; Amato, D.; Muller, C.P.; Tischbirek, C.H.; Groemer, T.W.; Tabatabai, G.; et al. Acid sphingomyelinase-ceramide system mediates effects of antidepressant drugs. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 934–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zoicas, I.; Huber, S.E.; Kalinichenko, L.S.; Gulbins, E.; Müller, C.P.; Kornhuber, J. Ceramides affect alcohol consumption and depressive-like and anxiety-like behavior in a brain region- and ceramide species-specific way in male mice. Addict. Biol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zoicas, I.; Reichel, M.; Gulbins, E.; Kornhuber, J. Role of acid sphingomyelinase in the regulation of social behavior and memory. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.P.; Kalinichenko, L.S.; Tiesel, J.; Witt, M.; Stockl, T.; Sprenger, E.; Fuchser, J.; Beckmann, J.; Praetner, M.; Huber, S.E.; et al. Paradoxical antidepressant effects of alcohol are related to acid sphingomyelinase and its control of sphingolipid homeostasis. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 133, 463–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zoicas, I.; Schumacher, F.; Kleuser, B.; Reichel, M.; Gulbins, E.; Fejtova, A.; Kornhuber, J.; Rhein, C. The forebrain—Specific overexpression of acid sphingomyelinase induces depressive-like symptoms in mice. Cells 2020. accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinichenko, L.S.; Mühle, C.; Eulenburg, V.; Praetner, M.; Reichel, M.; Gulbins, E.; Kornhuber, J.; Müller, C.P. Enhanced alcohol preference and anxiolytic alcohol effects in Niemann-Pick Disease model in mice. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liebsch, G.; Montkowski, A.; Holsboer, F.; Landgraf, R. Behavioural profiles of two Wistar rat lines selectively bred for high or low anxiety-related behaviour. Behav. Brain Res. 1998, 94, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidtner, A.K.; Slattery, D.A.; Glasner, J.; Hiergeist, A.; Gryksa, K.; Malik, V.A.; Hellmann-Regen, J.; Heuser, I.; Baghai, T.C.; Gessner, A.; et al. Minocycline alters behavior, microglia and the gut microbiome in a trait-anxiety-dependent manner. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wegener, G.; Mathe, A.A.; Neumann, I.D. Selectively bred rodents as models of depression and anxiety. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2012, 12, 139–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brivio, E.; Lopez, J.P.; Chen, A. Sex differences: Transcriptional signatures of stress exposure in male and female brains. Genes Brain Behav. 2020, 19, e12643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, S.E.; Zoicas, I.; Reichel, M.; Mühle, C.; Buttner, C.; Ekici, A.B.; Eulenburg, V.; Lenz, B.; Kornhuber, J.; Müller, C.P. Prenatal androgen receptor activation determines adult alcohol and water drinking in a sex-specific way. Addict. Biol. 2018, 23, 904–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, M.; Toth, I.; Reber, S.O.; Slattery, D.A.; Veenema, A.H.; Neumann, I.D. The neuropeptide oxytocin facilitates pro-social behavior and prevents social avoidance in rats and mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 2159–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühle, C.; Kornhuber, J. Assay to measure sphingomyelinase and ceramidase activities efficiently and safely. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1481, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, T.P.; Neve, R.L.; Duman, R.S.; Russell, D.S. Antidepressant effect of the calcium-activated tyrosine kinase Pyk2 in the lateral septum. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 54, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muigg, P.; Hoelzl, U.; Palfrader, K.; Neumann, I.; Wigger, A.; Landgraf, R.; Singewald, N. Altered brain activation pattern associated with drug-induced attenuation of enhanced depression-like behavior in rats bred for high anxiety. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 782–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheehan, T.P.; Chambers, R.A.; Russell, D.S. Regulation of affect by the lateral septum: Implications for neuropsychiatry. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 2004, 46, 71–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choleris, E.; Devidze, N.; Kavaliers, M.; Pfaff, D.W. Steroidal/neuropeptide interactions in hypothalamus and amygdala related to social anxiety. Prog. Brain Res. 2008, 170, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vertes, R.P.; Linley, S.B.; Hoover, W.B. Limbic circuitry of the midline thalamus. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 54, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, B.; Luo, Q.; Qiu, L.; Wang, S. Gray matter structural alterations in social anxiety disorder: A voxel-based meta-analysis. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becker, M.P.I.; Simon, D.; Miltner, W.H.R.; Straube, T. Altered activation of the ventral striatum under performance-related observation in social anxiety disorder. Psychol. Med. 2017, 47, 2502–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.Z.; Puglia, M.H.; Morris, J.P.; Connelly, J.J. Oxytocin receptor genotype and low economic privilege reverses ventral striatum-social anxiety association. Soc. Neurosci. 2019, 14, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühle, C.; Huttner, H.B.; Walter, S.; Reichel, M.; Canneva, F.; Lewczuk, P.; Gulbins, E.; Kornhuber, J. Characterization of acid sphingomyelinase activity in human cerebrospinal fluid. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarrafpour, S.; Ormseth, C.; Chiang, A.; Arakaki, X.; Harrington, M.; Fonteh, A. Lipid metabolism in late-onset Alzheimer’s disease differs from patients presenting with other dementia phenotypes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mühle, C.; Bilbao Canalejas, R.D.; Kornhuber, J. Sphingomyelin synthases in neuropsychiatric health and disease. Neurosignals 2019, 27, 54–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zoicas, I.; Mühle, C.; Schmidtner, A.K.; Gulbins, E.; Neumann, I.D.; Kornhuber, J. Anxiety and Depression Are Related to Higher Activity of Sphingolipid Metabolizing Enzymes in the Rat Brain. Cells 2020, 9, 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051239
Zoicas I, Mühle C, Schmidtner AK, Gulbins E, Neumann ID, Kornhuber J. Anxiety and Depression Are Related to Higher Activity of Sphingolipid Metabolizing Enzymes in the Rat Brain. Cells. 2020; 9(5):1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051239
Chicago/Turabian StyleZoicas, Iulia, Christiane Mühle, Anna K. Schmidtner, Erich Gulbins, Inga D. Neumann, and Johannes Kornhuber. 2020. "Anxiety and Depression Are Related to Higher Activity of Sphingolipid Metabolizing Enzymes in the Rat Brain" Cells 9, no. 5: 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051239
APA StyleZoicas, I., Mühle, C., Schmidtner, A. K., Gulbins, E., Neumann, I. D., & Kornhuber, J. (2020). Anxiety and Depression Are Related to Higher Activity of Sphingolipid Metabolizing Enzymes in the Rat Brain. Cells, 9(5), 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051239