Targeting Nuclear NOTCH2 by Gliotoxin Recovers a Tumor-Suppressor NOTCH3 Activity in CLL
Abstract
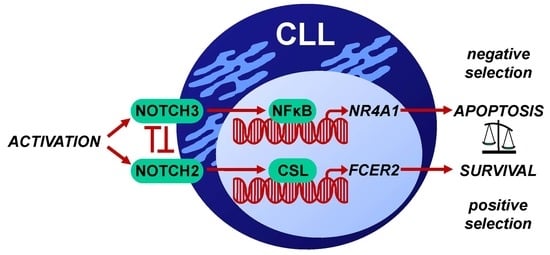
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients’ Characteristics and Sample Collection
2.2. Chemical Reagents, Compounds, and Culture
2.3. Flow Cytometry and Detection of Cell Viability
2.4. Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Analysis
2.5. Gene Silencing by RNA-Interference
2.6. ATAC-Seq
3. Results
3.1. Dose and Time-Dependent Effects of Gliotoxin and GSI on CLL Cell Viability
3.2. GSI Inhibited Spontaneous Apoptosis in Early Clinical Stage-Derived CLL Samples Expressing GSI Resistant Nuclear NOTCH2
3.3. The Inhibition of Spontaneous Apoptosis by RO4929097 is Associated with Inhibition of Recovered NOTCH3 mRNA Expression in CLL Cells
3.4. Induction of Surface NOTCH3 Expression by Gliotoxin is Associated with Downregulation of CD23 and Increased Apoptosis of CLL Cells
3.5. Targeting NOTCH3 Signaling Decreased NR4A1 mRNA Expression and Counteracted Gliotoxin Induced Apoptosis in CLL Cells
3.6. Gliotoxin Modulates Chromatin Accessibility at Gene Regulatory Elements Containing Potential NOTCH/CSL and NR4A1 Binding Sites
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chiorazzi, N.; Ferrarini, M. Cellular origin(s) of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Cautionary notes and additional considerations and possibilities. Blood 2011, 117, 1781–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, J.; Chiorazzi, N. B cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Trends Immunol. 2013, 34, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vardi, A.; Agathangelidis, A.; Sutton, L.-A.; Ghia, P.; Rosenquist, R.; Stamatopoulos, K. Immunogenetic Studies of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Revelations and Speculations about Ontogeny and Clinical Evolution. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 4211–4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Packham, G.; Krysov, S.; Allen, A.; Savelyeva, N.; Steele, A.J.; Forconi, F.; Stevenson, P.F.K. The outcome of B-cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Proliferation or anergy. Haematologica 2014, 99, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seifert, M.; Sellmann, L.; Bloehdorn, J.; Wein, F.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Dürig, J.; Küppers, R. Cellular origin and pathophysiology of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 2183–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bosch, F.; Dalla-Favera, R. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: From genetics to treatment. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 684–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubmann, R.; Schwarzmeier, J.D.; Shehata, M.; Hilgarth, M.; Duechler, M.; Dettke, M.; Berger, R. Notch2 is involved in the overexpression of CD23 in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2002, 99, 3742–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosati, E.; Sabatini, R.; Rampino, G.; Tabilio, A.; Di Ianni, M.; Fettucciari, K.; Bartoli, A.; Coaccioli, S.; Screpanti, I.; Marconi, P. Constitutively activated Notch signaling is involved in survival and apoptosis resistance of B-CLL cells. Blood 2009, 113, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, G.; Holmes, A.B.; Viganotti, M.; Scuoppo, C.; Belver, L.; Herranz, D.; Yan, X.-J.; Kieso, Y.; Rossi, D.; Gaidano, G.; et al. Common nonmutational NOTCH1 activation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E2911–E2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Falco, F.; Del Papa, B.; Baldoni, S.; Sabatini, R.; Falzetti, F.; Di Ianni, M.; Martelli, M.P.; Mezzasoma, F.; Pelullo, M.; Marconi, P.; et al. IL-4-dependent Jagged1 expression/processing is associated with survival of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells but not with Notch activation. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secchiero, P.; Melloni, E.; Di Iasio, M.G.; Tiribelli, M.; Rimondi, E.; Corallini, F.; Gattei, V.; Zauli, G. Nutlin-3 up-regulates the expression of Notch1 in both myeloid and lymphoid leukemic cells, as part of a negative feedback antiapoptotic mechanism. Blood 2009, 113, 4300–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puente, X.S.; Pinyol, M.; Quesada, V.; Conde, L.; Ordóñez, G.R.; Villamor, N.; Escaramis, G.; Jares, P.; Beà, S.; González-Díaz, M.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing identifies recurrent mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nature 2011, 475, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fabbri, G.; Rasi, S.; Rossi, D.; Trifonov, V.; Khiabanian, H.; Ma, J.; Grunn, A.; Fangazio, M.; Capello, D.; Monti, S.; et al. Analysis of the chronic lymphocytic leukemia coding genome: Role of NOTCH1 mutational activation. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 1389–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossi, D.; Rasi, S.; Fabbri, G.; Spina, V.; Fangazio, M.; Forconi, F.; Marasca, R.; Laurenti, L.; Bruscaggin, A.; Cerri, M.; et al. Mutations of NOTCH1 are an independent predictor of survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2012, 119, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weissmann, S.; Roller, A.; Jeromin, S.; Hernández, M.; Abáigar, M.; Hernández-Rivas, J.M.; Grossmann, V.; Haferlach, C.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, T.; et al. Prognostic impact and landscape of NOTCH1 mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): A study on 852 patients. Leukemia 2013, 27, 2393–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- López-Guerra, M.; Xargay-Torrent, S.; Rosich, L.; Montraveta, A.; Roldán, J.; Matas-Céspedes, A.; Villamor, N.; Aymerich, M.; Lopez-Otin, C.; Pérez-Galán, P.; et al. The γ-secretase inhibitor PF-03084014 combined with fludarabine antagonizes migration, invasion and angiogenesis in NOTCH1-mutated CLL cells. Leukemia 2014, 29, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, E.; Baldoni, S.; De Falco, F.; Del Papa, B.; Dorillo, E.; Rompietti, C.; Albi, E.; Falzetti, F.; Di Ianni, M.; Sportoletti, P. NOTCH1 Aberrations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hubmann, R.; Düchler, M.; Schnabl, S.; Hilgarth, M.; Demirtas, D.; Mitteregger, D.; Hölbl, A.; Vanura, K.; Le, T.; Look, T.; et al. NOTCH2 links protein kinase C delta to the expression of CD23 in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) cells. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 148, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artavanis-Tsakonas, S. Notch Signaling: Cell Fate Control and Signal Integration in Development. Science 1999, 284, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hori, K.; Sen, A.; Artavanis-Tsakonas, S. Notch signaling at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 2135–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ntziachristos, P.; Lim, J.S.; Sage, J.; Aifantis, I. From fly wings to targeted cancer therapies: A centennial for notch signaling. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 318–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henrique, D.; Schweisguth, F. Mechanisms of Notch signaling: A simple logic deployed in time and space. Development 2019, 146, dev172148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ayaz, F.; Osborne, B.A. Non-canonical Notch Signaling in Cancer and Immunity. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cruickshank, M.N.; Ulgiati, D. The role of notch signaling in the development of a normal B-cell repertoire. Immunol. Cell Boil. 2009, 88, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, V.; Shukla, A.; Joshi, S.S.; Lu, R. Interferon regulatory factor 4 attenuates Notch signaling to suppress the development of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 41081–41094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lobry, C.; Oh, P.; Mansour, M.R.; Look, A.T.; Aifantis, I. Notch signaling: Switching an oncogene to a tumor suppressor. Blood 2014, 123, 2451–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiu, M.-X.; Liu, Y.-M. The role of oncogenic Notch2 signaling in cancer: A novel therapeutic target. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 837–854. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Espinoza, I.; Miele, L. Notch inhibitors for cancer treatment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 139, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersson, E.R.; Lendahl, U. Therapeutic modulation of Notch signalling—Are we there yet? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 357–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, M.; Katoh, M. Precision medicine for human cancers with Notch signaling dysregulation (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 45, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobranowski, P.; Ban, F.; Cherkasov, A.; Black, P.C.; Contreras-Sanz, A. Perspectives on the discovery of NOTCH2-specific inhibitors. Chem. Boil. Drug Des. 2017, 91, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubmann, R.; Hilgarth, M.; Schnabl, S.; Ponath, E.; Reiter, M.; Demirtas, D.; Sieghart, W.; Valent, P.; Zielinski, C.; Jäger, U.; et al. Gliotoxin is a potent NOTCH2 transactivation inhibitor and efficiently induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) cells. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 160, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luistro, L.; He, W.; Smith, M.; Packman, K.; Vilenchik, M.; Carvajal, D.; Roberts, J.; Cai, J.; Berkofsky-Fessler, W.; Hilton, H.; et al. Preclinical profile of a potent gamma-secretase inhibitor targeting notch signaling with in vivo efficacy and pharmacodynamic properties. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7672–7680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buenrostro, J.D.; Giresi, P.G.; Zaba, L.C.; Chang, H.Y.; Greenleaf, W.J. Transposition of native chromatin for fast and sensitive epigenomic profiling of open chromatin, DNA-binding proteins and nucleosome position. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendeiro, A.F.; Schmidl, C.; Strefford, J.C.; Walewska, R.; Davis, Z.; Farlik, M.; Oscier, D.; Bock, C. Chromatin accessibility maps of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia identify subtype-specific epigenome signatures and transcription regulatory networks. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Boil. 2014, 15, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heinz, S.; Benner, C.; Spann, N.; Bertolino, E.; Lin, Y.; Laslo, P.; Cheng, J.X.; Murre, C.; Singh, H.; Glass, C.K. Simple Combinations of Lineage-Determining Transcription Factors Prime cis-Regulatory Elements Required for Macrophage and B Cell Identities. Mol. Cell 2010, 38, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheffield, N.C.; Bock, C. LOLA: Enrichment analysis for genomic region sets and regulatory elements in R and Bioconductor. Bioinformtics 2015, 32, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.Y.; Tan, C.M.; Kou, Y.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Meirelles, G.V.; Clark, N.R.; Ma’Ayan, A. Enrichr: Interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosati, E.; Sabatini, R.; De Falco, F.; Del Papa, B.; Falzetti, F.; Di Ianni, M.; Cavalli, L.; Fettucciari, K.; Bartoli, A.; Screpanti, I.; et al. γ-Secretase inhibitor I induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells by proteasome inhibition, endoplasmic reticulum stress increase and notch down-regulation. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 132, 1940–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herishanu, Y.; Pérez-Galán, P.; Liu, D.; Biancotto, A.; Pittaluga, S.; Vire, B.; Gibellini, F.; Njuguna, N.; Lee, E.; Stennett, L.; et al. The lymph node microenvironment promotes B-cell receptor signaling, NF-κB activation, and tumor proliferation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2011, 117, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krysov, S.; Dias, S.; Paterson, A.; Mockridge, C.I.; Potter, K.N.; Smith, K.-A.; Ashton-Key, M.; Stevenson, P.F.K.; Packham, G. Surface IgM stimulation induces MEK1/2-dependent MYC expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Blood 2012, 119, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzo, F.; Bittolo, T.; Vendramini, E.; Bomben, R.; Bulian, P.; Rossi, F.M.; Zucchetto, A.; Tissino, E.; Degan, M.; D’Arena, G.; et al. NOTCH1-mutated chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells are characterized by a MYC-related overexpression of nucleophosmin 1 and ribosome-associated components. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2407–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Papa, B.; Baldoni, S.; Dorillo, E.; De Falco, F.; Rompietti, C.; Cecchini, D.; Cantelmi, M.G.; Sorcini, D.; Nogarotto, M.; Adamo, F.M.; et al. Decreased NOTCH1 Activation Correlates with Response to Ibrutinib in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 7540–7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- López-Guerra, M.; Xargay-Torrent, S.; Fuentes, P.; Roldán, J.; González-Farré, B.; Rosich, L.; Silkenstedt, E.; García-León, M.J.; Lee-Vergés, E.; Giménez, N.; et al. Specific NOTCH1 antibody targets DLL4-induced proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis in NOTCH1-mutated CLL cells. Oncogene 2019, 39, 1185–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Asmar, B.; Giner, X.C.; Tremblay, J.J. Transcriptional cooperation between NF-κB p50 and CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β regulates Nur77 transcription in Leydig cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 42, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vacca, A.; Felli, M.P.; Palermo, R.; Di Mario, G.; Calce, A.; Di Giovine, M.; Frati, L.; Gulino, A.; Screpanti, I. Notch3 and pre-TCR interaction unveils distinct NF-κB pathways in T-cell development and leukemia. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Bianco, C.; Vedenko, A.; Choi, S.H.; Berger, M.F.; Shokri, L.; Bulyk, M.L.; Blacklow, S.C. Notch and MAML-1 Complexation Do Not Detectably Alter the DNA Binding Specificity of the Transcription Factor CSL. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lauring, A.S.; Overbaugh, J. Evidence that an IRES within the Notch2 coding region can direct expression of a nuclear form of the protein. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, I.; Craig, C.; Funahashi, Y.; Jung, K.-M.; Kim, T.-W.; Byers, R.; Weng, A.P.; Kutok, J.L.; Aster, J.C.; Kitajewski, J.; et al. Notch Oncoproteins Depend on γ-Secretase/Presenilin Activity for Processing and Function. J. Boil. Chem. 2004, 279, 30771–30780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hubmann, R.; Sieghart, W.; Schnabl, S.; Araghi, M.; Hilgarth, M.; Reiter, M.; Demirtas, D.; Valent, P.; Zielinski, C.; Jäger, U.; et al. Gliotoxin Targets Nuclear NOTCH2 in Human Solid Tumor Derived Cell Lines In Vitro and Inhibits Melanoma Growth in Xenograft Mouse Model. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Lee, K.-H.; Weidner-Glunde, M.; Osborne, B.A.; Hayward, S.D. Epstein-Barr virus EBNA2 blocks Nur77- mediated apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11878–11883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deutsch, A.; Rinner, B.; Wenzl, K.; Pichler, M.; Troppan, K.; Steinbauer, E.; Schwarzenbacher, D.; Reitter, S.; Feichtinger, J.; Tierling, S.; et al. NR4A1-mediated apoptosis suppresses lymphomagenesis and is associated with a favorable cancer-specific survival in patients with aggressive B-cell lymphomas. Blood 2014, 123, 2367–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.; Noviski, M.; Huizar, J.; Zikherman, J. Self-reactivity on a spectrum: A sliding scale of peripheral B cell tolerance. Immunol. Rev. 2019, 292, 37–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miele, L. Transcription factor RBPJ/CSL: A genome-wide look at transcriptional regulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14715–14716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimizu, K.; Chiba, S.; Saito, T.; Kumano, K.; Hamada, Y.; Hirai, H. Functional Diversity among Notch1, Notch2, and Notch3 Receptors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 291, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatus, P.; Lundkvist, J.; Oberg, C.; Lendahl, U. The notch 3 intracellular domain represses notch 1-mediated activation through Hairy/Enhancer of split (HES) promoters. Development 1999, 126, 3925–3935. [Google Scholar]
- Baeten, J.T.; Lilly, B. Differential Regulation of NOTCH2 and NOTCH3 Contribute to Their Unique Functions in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. J. Boil. Chem. 2015, 290, 16226–16237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, Q.; Dai, X.; Cai, Y. MicroRNA-16 is involved in the pathogenesis of pre-eclampsia via regulation of Notch2. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 235, 4530–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumang, J.R.; Hastings, W.D.; Bai, C.; Rothstein, T.L. Peritoneal and splenic B-1 cells are separable by phenotypic, functional, and transcriptomic characteristics. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 2158–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stache, V.; Verlaat, L.; Gätjen, M.; Heinig, K.; Westermann, J.; Rehm, A.; Höpken, U.E. The splenic marginal zone shapes the phenotype of leukemia B cells and facilitates their niche-specific retention and survival. OncoImmunology 2017, 6, e1323155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Descatoire, M.; Weller, S.; Irtan, S.; Sarnacki, S.; Feuillard, J.; Storck, S.; Guiochon-Mantel, A.; Bouligand, J.; Morali, A.; Cohen, J.; et al. Identification of a human splenic marginal zone B cell precursor with NOTCH2-dependent differentiation properties. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 987–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, S.-Q.; Fang, Z.; Zweidler-McKay, P.A.; Yang, H.; Wei, Y.; Gonzalez-Cervantes, E.A.; Boumber, Y.; Quintás, G. Epigenetic Inactivation of Notch-Hes Pathway in Human B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliveto, S.; Mancino, M.; Manfrini, N.; Biffo, S. Role of microRNAs in translation regulation and cancer. World J. Boil. Chem. 2017, 8, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu-Zhang, A.X.; Newton, A.C. Protein kinase C pharmacology: Refining the toolbox. Biochem. J. 2013, 452, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mecklenbräuker, I.; Saijo, K.; Zheng, N.-Y.; Leitges, M.; Tarakhovsky, A. Protein kinase Cδ controls self-antigen-induced B-cell tolerance. Nature 2002, 416, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringshausen, I.; Schneller, F.; Bogner, C.; Hipp, S.; Duyster, J.; Peschel, C.; Decker, T. Constitutively activated phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI-3K) is involved in the defect of apoptosis in B-CLL: Association with protein kinase Cδ. Blood 2002, 100, 3741–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Sweetwyne, M.T.; Hankenson, K. PKCδ Is Required for Jagged-1 Induction of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Osteogenic Differentiation. Stem Cells 2013, 31, 1181–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, K.; Peluso, M.; Fu, M.; Rosin, N.Y.; A Burger, J.; Wierda, W.G.; Keating, M.J.; Faia, K.; O’Brien, S.; Kutok, J.L.; et al. The phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K)-delta and gamma inhibitor, IPI-145 (Duvelisib), overcomes signals from the PI3K/AKT/S6 pathway and promotes apoptosis in CLL. Leukemia 2015, 29, 1811–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Pat. ID | Age | Gender | Rai/Binet Stage | IGHV Status | Cytogenetic Alterations | NOTCH1 Mutations | NOTCH2 GSI-R/S* | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLL1 | 76 | male | II/B | U, VH2-5 | normal | N1ΔCT | GSI-S | no |
| CLL2 | 69 | male | II/B | U, VH1-69 | normal | N1ΔCT | GSI-R | no |
| CLL3 | 70 | male | IV/C | M, VH4-34 | Tri12 | wt | ND | no |
| CLL4 | 64 | male | II/B | M, VH3-23 | 13q-, 17p- | wt | ND | no |
| CLL5 | 51 | female | IV/C | U, VH1-69 | normal | wt | ND | no |
| CLL6 | 56 | male | IV/C | M, VH3-21 | 13q-, 11q- | wt | GSI-S | no |
| CLL7 | 68 | male | II/B | M, VH3-48 | 13q-, 11q- | wt | GSI-R | no |
| CLL8 | 84 | male | I/A | NA | normal | wt | GSI-R | no |
| CLL9 | 81 | female | I/A | M, VH3-15 | 13q- | wt | GSI-R | no |
| CLL10 | 73 | female | IV/C | M, VH3-23 | normal | wt | GSI-S | no |
| CLL11 | 66 | female | I/A | M, VH3-48 | 13q- | wt | GSI-R | no |
| CLL12 | 70 | male | I/A | M, VH1-8 | 13q- | wt | GSI-R | no |
| CLL13 | 66 | female | II/B | M, VH3-23 | 13q- | wt | GSI-R | no |
| CLL14 | 75 | female | IV/C | NA | 13q- | wt | GSI-S | no |
| CLL15 | 65 | male | I/A | U, VH1-69 | 14q32- | wt | GSI-R | no |
| CLL16 | 52 | male | IV/C | U, VH1-69 | normal | wt | GSI-S | no |
| CLL17 | 55 | male | II/B | U, VH3-11 | 13q-, 11q- | wt | GSI-R | Ibrutinib |
| CLL18 | 40 | female | I/A | U, VH3-20 | normal | wt | GSI-S | no |
| CLL19 | 68 | female | III/B | U, VH1-2 | 13q- | N1ΔCT | GSI-S | no |
| CLL20 | 60 | male | IV/C | U, VH1-46 | 13q-, 11q- | N1ΔCT | GSI-S | no |
| CLL21 | 52 | male | II/B | NA | 13q- | ND | GSI-R | no |
| CLL22 | 70 | female | II/B | M, VH3-13 | 13q- | ND | GSI-S | no |
| CLL23 | 54 | male | I/A | U, VH3-53 | normal | ND | ND | no |
| CLL24 | 77 | female | IV/C | NA | 17p- | ND | ND | no |
| CLL25 | 54 | male | I/A | U, VH4-39 | 11q- | ND | ND | Duvelisib |
| CLL26 | 69 | male | II/B | U, VH3-21 | 13q- | ND | ND | Ibrutinib |
| CLL27 | 70 | male | II/B | M, VH3-13 | 13q- | ND | ND | no |
| CLL28 | 61 | female | I/A | M, VH3-7 | normal | ND | ND | no |
| CLL29 | 77 | female | II/B | M, VH3-74 | normal | ND | ND | no |
| CLL30 | 87 | female | IV/C | M, VH3-11 | 13q- | ND | ND | Idealisib |
| CLL31 | 68 | female | II/B | M, VH3-48 | 13q- | ND | ND | no |
| CLL32 | 83 | female | II/B | M, VH4-59 | 13q- | ND | ND | Ibrutinib |
| CLL33 | 60 | male | II/B | U, VH1-69 | 13q-/11q- | ND | ND | Idealisib |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hubmann, R.; Schnabl, S.; Araghi, M.; Schmidl, C.; Rendeiro, A.F.; Hilgarth, M.; Demirtas, D.; Ali, F.; Staber, P.B.; Valent, P.; et al. Targeting Nuclear NOTCH2 by Gliotoxin Recovers a Tumor-Suppressor NOTCH3 Activity in CLL. Cells 2020, 9, 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061484
Hubmann R, Schnabl S, Araghi M, Schmidl C, Rendeiro AF, Hilgarth M, Demirtas D, Ali F, Staber PB, Valent P, et al. Targeting Nuclear NOTCH2 by Gliotoxin Recovers a Tumor-Suppressor NOTCH3 Activity in CLL. Cells. 2020; 9(6):1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061484
Chicago/Turabian StyleHubmann, Rainer, Susanne Schnabl, Mohammad Araghi, Christian Schmidl, André F. Rendeiro, Martin Hilgarth, Dita Demirtas, Farghaly Ali, Philipp B. Staber, Peter Valent, and et al. 2020. "Targeting Nuclear NOTCH2 by Gliotoxin Recovers a Tumor-Suppressor NOTCH3 Activity in CLL" Cells 9, no. 6: 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061484
APA StyleHubmann, R., Schnabl, S., Araghi, M., Schmidl, C., Rendeiro, A. F., Hilgarth, M., Demirtas, D., Ali, F., Staber, P. B., Valent, P., Zielinski, C., Jäger, U., & Shehata, M. (2020). Targeting Nuclear NOTCH2 by Gliotoxin Recovers a Tumor-Suppressor NOTCH3 Activity in CLL. Cells, 9(6), 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061484