Waves Out of the Korean Peninsula and Inter- and Intra-Species Replacements in Freshwater Fishes in Japan
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Sequencing
2.2. Sampling Sites and Geomorphological Information
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3.1. H. longirostris
2.3.2. N. temminckii
2.3.3. T. limbata and Its Related Species
2.3.4. Genus Carassius
2.4. Simulation-Based Testing of the Intra-Species Replacements
2.5. Data Availability
2.6. Code Availability
2.7. Ethical Statement
3. Results
3.1. Phylogeography of H. longirostris
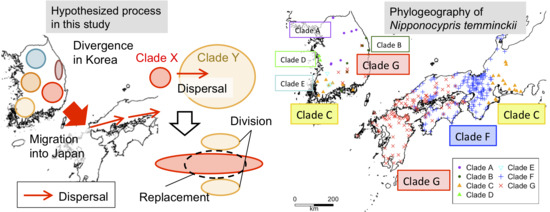
3.2. Phylogeography of N. temminckii
3.3. Significance of Intra-Species Replacement
3.4. T. limbata and Related Species, and C. spp. and C. cuvieri
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pearson, R.G.; Dawson, T.P. Predicting the impacts of climate change on the distribution of species: Are bioclimate envelope models useful? Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2003, 12, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waters, J.M. Competitive exclusion: Phylogeography’s ‘elephant in the room’? Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 4388–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisz, M.S.; Pottier, J.; Kissling, W.D.; Pellissier, L.; Lenoir, J.; Damgaard, C.F.; Dormann, C.F.; Forchhammer, M.C.; Grytnes, J.A.; Guisan, A.; et al. The role of biotic interactions in shaping distributions and realised assemblages of species: Implications for species distribution modelling. Biol. Rev. 2013, 88, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yackulic, C.B. Competitive exclusion over broad spatial extents is a slow process: Evidence and implications for species distribution modeling. Ecography 2017, 40, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, E.E.; Boria, R.A.; Anderson, R.P. Can biotic interactions cause allopatry? Niche models, competition, and distributions of South American mouse opossums. Ecography 2014, 37, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellenthal, G.; Busby, G.B.J.; Band, G.; Wilson, J.F.; Capelli, C.; Falush, D.; Myers, S. A genetic atlas of human admixture history. Science 2014, 343, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, R.; Akey, J.M.; Jakobsson, M.; Pritchard, J.K.; Tishkoff, S.; Willerslev, E. Tracing the peopling of the world through genomics. Nature 2017, 541, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baba, A.K.; Matsuda, T.; Itaya, T.; Wada, Y.; Hori, N.; Yokoyama, M.; Eto, N.; Kamei, R.; Zaman, H.; Kidane, T.; et al. New age constraints on counter-clockwise rotation of NE Japan. Geophys. J. Int. 2007, 171, 1325–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, K.; Tominaga, K.; Nakajima, J.; Kakioka, R.; Tabata, R. Japanese Freshwater Fishes: Biogeography and Cryptic Diversity. In Species Diversity of Animals in Japan; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2017; pp. 183–227. [Google Scholar]
- Shafer, A.B.A.; Cullingham, C.I.; Côté, S.D.; Coltman, D.W. Of glaciers and refugia: A decade of study sheds new light on the phylogeography of northwestern North America. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 4589–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flint, R.F. Glacial and Quaternary Geology; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Otofuji, Y.I. Large tectonic movement of the Japan Arc in late Cenozoic times inferred from paleomagnetism: Review and synthesis. Island Arc 1996, 5, 229–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbanks, R.G. A 17,000-year glacio-eustatic sea level record: Influence of glacial melting rates on the Younger Dryas event and deep-ocean circulation. Nature 1989, 342, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohling, E.J.; Fenton, M.; Jorissen, F.J.; Bertrand, P.; Ganssen, G.; Caulet, J.P. Magnitudes of sea-level lowstands of the past 500,000 years. Nature 1998, 394, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amante, C.; Eakins, B.W. ETOPO1 1 Arc-Minute Global Relief Model: Procedures, Data Sources and Analysis; US Department of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information Service, National Geophysical Data Center, Marine Geology and Geophysics Division Colorado: Denver, CO, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria, 2017. Available online: https://www.r-project.org (accessed on 7 December 2017).
- Pante, E.; Simon-Bouhet, B. marmap: A package for importing, plotting and analyzing bathymetric and topographic data in R. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geospatial Information Authority of Japan. Elevation Chart by Color. 2013. Available online: https://maps.gsi.go.jp/development/ichiran.html (accessed on 15 October 2019).
- Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. National Land Numerical Information Rivers Data. 2011. Available online: http://nlftp.mlit.go.jp/ksj-e/gml/datalist/KsjTmplt-W05.html (accessed on 28 November 2017).
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouckaert, R.; Heled, J.; Kühnert, D.; Vaughan, T.; Wu, C.H.; Xie, D.; Suchard, M.A.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J. BEAST 2: A software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Landis, M.J.; Matzke, N.J.; Moore, B.R.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. Bayesian analysis of biogeography when the number of areas is large. Syst. Biol. 2013, 62, 789–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pagel, M. Detecting correlated evolution on phylogenies: A general method for the comparative analysis of discrete characters. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1994, 255, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, K. Parsimony analysis of the distribution pattern of Japanese primary freshwater fishes, and its application to the distribution of the bagrid catfishes. Ichthyol. Res. 1998, 45, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Phillips, M.J.; Rambaut, A. Relaxed phylogenetics and dating with confidence. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zardoya, R.; Doadrio, I. Molecular evidence on the evolutionary and biogeographical patterns of European Cyprinids. J. Mol. Evol. 1999, 49, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. PAML 4: Phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beaumont, M.A.; Zhang, W.; Balding, D.J. Approximate Bayesian computation in population genetics. Genetics 2002, 162, 2025–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aeschbacher, S.; Beaumont, M.A.; Futschik, A. A novel approach for choosing summary statistics in approximate Bayesian computation. Genetics 2012, 192, 1027–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A.; Templeton, A.R. Nested clade analysis statistics. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 590–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeton, A.R.; Routman, E.; Phillips, C.A. Separating population structure from population history: A cladistic analysis of the geographical distribution of mitochondrial DNA haplotypes in the tiger salamander, Ambystoma tigrinum. Genetics 1995, 140, 767–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeton, A.R. Statistical phylogeography: Methods of evaluating and minimizing inference errors. Mol. Ecol. 2004, 13, 789–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panchal, M.; Beaumont, M.A. Evaluating nested clade phylogeographic analysis under models of restricted gene flow. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 415–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, K. Faunal structure of Japanese freshwater fishes and its artificial disturbance. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2012, 94, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japan Association for Quaternary Research. Japanese Quaternary Map (Nihon Daiyonki Chizu); University of Tokyo Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1987. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Kuwashiro, I. Submarine Topography of Japanese Inlandsea Setonaikai. Geogr. Rev. Japan 1959, 32, 24–35. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, G.; Smith, D.K.; Zhu, H.; Guan, Y.; Lam, T.T.Y. GGTREE: An R package for visualization and annotation of phylogenetic trees with their covariates and other associated data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, T.; Watanabe, M.; Mizuguchi, K.; Hosoya, K. Genetic differentiation between two types of dark chub, Zacco temmincki, in Japan. Jpn. J. Ichthyol. 1991, 38, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, W.K.; Beckenbach, A.T. Variation in salmonid mitochondrial DNA: Evolutioinary constraints and mechanisms of substitution. J. Mol. Evol. 1989, 29, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taruno, H. The stages of land bridge formation between the Japanese Islands and the continent on the basis of faunal succession. Quat. Res. 2010, 49, 309–314. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeon, H.; Anderson, D.; Won, H.; Lim, H.; Young, H. Taxonomic characterization of Tanakia species ( Acheilognathidae ) using DNA barcoding analyses. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2018, 29, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biwako Shizenshi Kenkyukai. Natural History of Lake Biwa (Biwako no Shizen-Shi); Yasaka Shobo: Tokyo, Japan, 1994. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga, K.; Nagata, N.; Kitamura, J.I.; Watanabe, K.; Sota, T. Phylogeography of the bitterling Tanakia lanceolata (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) in Japan inferred from mitochondrial cytochrome b gene sequences. Ichthyol. Res. 2020, 67, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Sanmartín, I. Phylogenetic Methods in Biogeography. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2011, 42, 441–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higuchi, Y. Freshwater fishes of Mie Prefecture. Bull. Mie Prefect. Museum 1980, 2, 69–100. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Sato, J.J. A review of the processes of mammalian faunal assembly in Japan: Insights from molecular phylogenetics. In Species Diversity of Animals in Japan; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2017; pp. 49–116. [Google Scholar]
- Power, G.; Brown, R.S.; Imhof, J.G. Groundwater and fish—Insights from northern North America. Hydrol. Process. 1999, 13, 401–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, T.; Watanabe, M.; Kitagawa, E.; Yoshioka, M.; Kashiwagi, M.; Okazaki, T. Phylogeography and the maternal origin of the tetraploid form of the Japanese spined loach, Cobitis biwae, revealed by mitochondrial DNA analysis. Ichthyol. Res. 2003, 50, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takehana, Y.; Nagai, N.; Matsuda, M.; Tsuchiya, K.; Sakaizumi, M. Geographic variation and diversity of the cytochrome b gene in Japanese wild populations of medaka, Oryzias latipes. Zool. Sci. 2003, 20, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iguchi, Y.; Nakao, R.; Matsuda, M.; Takata, K.; Kitagawa, T. Origin of the widely and discontinuously distributed mitochondrial genotypes of Oryzias latipes: Introduced or native genotypes? Ichthyol. Res. 2018, 66, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, K.; Nakajima, J.; Watanabe, K. Cryptic divergence and phylogeography of the pike gudgeon Pseudogobio esocinus (Teleostei: Cyprinidae): A comprehensive case of freshwater phylogeography in Japan. Ichthyol. Res. 2016, 63, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, H. Revision of the Asian moles of the genus Mogera. J. Mammal. Soc. Japan 1995, 20, 51–68. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, H. Isolated relic populations and their keeping mechanisms in moles. Mammal. Sci. 2001, 41, 35–52. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Abe, H. The northeastern front in the distribution of Mogera wogura in the central Honshu, Japan in 2009, especially the past 50 years’ change in Nagano Prefecture. Mammal. Sci. 2010, 50, 55–66. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura, K.; Ueda, T.; Arai, R.; Nagata, Y.; Saitoh, K.; Ohtaka, H.; Kanoh, Y. Genetic Introgression by the Rose Bitterling, Rhodeus ocellatus ocellatus, into the Japanese Rose Bitterling, R. o. kurumeus (Teleostei: Cyprinidae). Zool. Sci. 2001, 18, 1027–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohta, T. Population Size and Rate of Evolution. J. Mol. Evol. 1972, 1, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, K. Species Diversity of Japanese Amphibians: Recent Progress and Future Prospects of Systematic Studies. In Species Diversity of Animals in Japan; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2017; pp. 165–181. [Google Scholar]
- Imaizumi, Y. Coloured Illustrations of the Mammals of Japan; Hoikusha: Osaka, Japan, 1960. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Shalabi, M.A.; Abramov, A.V.; Kosintsev, P.A.; Lin, L.K.; Han, S.H.; Watanabe, S.; Yamazaki, K.; Kaneko, Y.; Masuda, R. Comparative phylogeography of the endemic Japanese weasel (Mustela itatsi) and the continental Siberian weasel (Mustela sibirica) revealed by complete mitochondrial genome sequences. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2017, 120, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okazaki, T.; Jeon, S.R.; Kitagawa, T. Genetic differentiation of piscivorous chub (genus Opsariichthys) in Japan, Korea and Russia. Zool. Sci. 2002, 19, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, D.; Mano, T.; Abramov, A.V.; Baryshnikov, G.F.; Kosintsev, P.A.; Vorobiev, A.A.; Raichev, E.G.; Tsunoda, H.; Kaneko, Y.; Murata, K.; et al. Molecular phylogeography of the brown bear (Ursus arctos) in Northeastern Asia based on analyses of complete mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1644–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirata, D.; Abramov, A.V.; Baryshnikov, G.F.; Masuda, R. Mitochondrial DNA haplogrouping of the brown bear, Ursus arctos (Carnivora: Ursidae) in Asia, based on a newly developed APLP analysis. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2014, 111, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waits, L.; Talbot, S.; Ward, R.H.; Shields, G. Mitochondrial DNA Phylogeography of the North American Brown Bear and Implications for Conservation. Conserv. Biol. 1998, 12, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, G.; Nunome, M.; Han, S.-H.; Hirakawa, H.; Suzuki, H. Ancient Colonization and Within-Island Vicariance Revealed by Mitochondrial DNA Phylogeography of the Mountain Hare (Lepus timidus) in Hokkaido, Japan. Zool. Sci. 2012, 29, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takehana, Y.; Uchiyama, S.; Matsuda, M.; Jeon, S.; Sakaizumi, M. Geographic variation and diversity of the cytochrome b gene in wild populations of medaka (Oryzias latipes) from Korea and China. Zool. Sci. 2004, 21, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taniguchi, S.; Bertl, J.; Futschik, A.; Kishino, H.; Okazaki, T. Waves Out of the Korean Peninsula and Inter- and Intra-Species Replacements in Freshwater Fishes in Japan. Genes 2021, 12, 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12020303
Taniguchi S, Bertl J, Futschik A, Kishino H, Okazaki T. Waves Out of the Korean Peninsula and Inter- and Intra-Species Replacements in Freshwater Fishes in Japan. Genes. 2021; 12(2):303. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12020303
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaniguchi, Shoji, Johanna Bertl, Andreas Futschik, Hirohisa Kishino, and Toshio Okazaki. 2021. "Waves Out of the Korean Peninsula and Inter- and Intra-Species Replacements in Freshwater Fishes in Japan" Genes 12, no. 2: 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12020303
APA StyleTaniguchi, S., Bertl, J., Futschik, A., Kishino, H., & Okazaki, T. (2021). Waves Out of the Korean Peninsula and Inter- and Intra-Species Replacements in Freshwater Fishes in Japan. Genes, 12(2), 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12020303