Testis Development and Differentiation in Amphibians
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Amphibian Sex Chromosomes and Sex Determination
2.1. Sex Chromosomes
2.2. Sex Determination
3. Gonadal Development and Differentiation in Amphibians
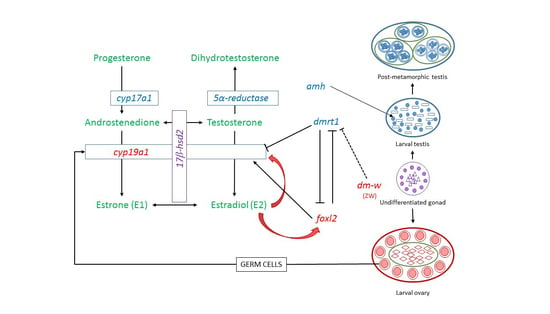
3.1. General Considerations
3.2. Sexually Undifferentiated Gonad
3.2.1. Germ Cell Specification
3.2.2. Initial Gonadal Formation
3.3. Sexual Differentiation of the Testis
3.3.1. Morphological Changes
3.3.2. Cellular Mechanisms Involved in Testis Differentiation
3.3.3. Germ Cell Differentiation: Spermatogenesis
4. Testis Plasticity
5. Genetic Control of Testicular Differentiation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- AmphibiaWeb. Available online: https://amphibiaweb.org (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Schmid, M.; Evans, B.J.; Bogart, J.P. Polyploidy in Amphibia. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2015, 145, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragghianti, M.; Bucci, S.; Marracci, S.; Casola, C.; Mancino, G.; Hotz, H.; Guex, G.-D.; Plötner, J.; Uzzell, T. Gametogenesis of intergroup hybrids of hemiclonal frogs. Genet. Res. 2007, 89, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bogart, J.P.; Bi, K.; Fu, J.; Noble, D.W.A.; Niedzwiecki, J. Unisexual salamanders (genus Ambystoma) present a new reproductive mode for eukaryotes. Genome 2007, 50, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khokha, M.K.; Krylov, V.; Reilly, M.J.; Gall, J.G.; Bhattacharya, D.; Cheung, C.Y.J.; Kaufman, S.; Lam, D.K.; Macha, J.; Ngo, C.; et al. Rapid gynogenetic mapping of Xenopus tropicalis mutations to chromosomes. Dev. Dyn. 2009, 238, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, J.J.; Voss, S.R. Amphibian sex determination: Segregation and linkage analysis using members of the tiger salamander species complex (Ambystoma mexicanum and A. t. tigrinum). Heredity 2009, 102, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stöck, M.; Lamatsch, D.K.; Steinlein, C.; Epplen, J.T.; Grosse, W.-R.; Hock, R.; Klapperstück, T.; Lampert, K.P.; Scheer, U.; Schmid, M.; et al. A bisexually reproducing all-triploid vertebrate. Nat. Genet. 2002, 30, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levis, N.A.; Pfennig, D.W. Phenotypic plasticity, canalization, and the origins of novelty: Evidence and mechanisms from amphibians. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 88, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, C.F.B.; Prado, C.P.A. Reproductive modes in frogs and their unexpected diversity in the Atlantic forest of Brazil. Bioscience 2005, 55, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogielska, M. (Ed.) Reproduction of Amphibians; Science Publishers: Rawalpindi, Pakistan, 2009; ISBN 9783540773405. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffries, D.L.; Lavanchy, G.; Sermier, R.; Sredl, M.J.; Miura, I.; Borzée, A.; Barrow, L.N.; Canestrelli, D.; Crochet, P.-A.; Dufresnes, C.; et al. A rapid rate of sex-chromosome turnover and non-random transitions in true frogs. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, B.L.S.; Evans, B.J. Divergent Evolutionary Trajectories of Two Young, Homomorphic, and Closely Related Sex Chromosome Systems. Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 742–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cauret, C.M.S.; Gansauge, M.T.; Tupper, A.S.; Furman, B.L.S.; Knytl, M.; Song, X.Y.; Greenbaum, E.; Meyer, M.; Evans, B.J.; Wilson, M. Developmental Systems Drift and the Drivers of Sex Chromosome Evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöck, M.; Croll, D.; Dumas, Z.; Biollay, S.; Wang, J.; Perrin, N. A cryptic heterogametic transition revealed by sex-linked DNA markers in Palearctic green toads. J. Evol. Biol. 2011, 24, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Steinlein, C.; Feichtinger, W. Chromosome banding in Amphibia. XVII. First demonstration of multiple sex chromosomes in amphibians: Eleutherodactylus maussi (Anura, leptodactylidae). Chromosoma 1992, 101, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Feichtinger, W.; Steinlein, C.; Visbal García, R.; Fernández Badillo, A. Chromosome banding in Amphibia: XXVIII. Homomorphic XY sex chromosomes and a derived Y-autosome translocation in Eleutherodactylus riveroi (Anura, Leptodactylidae). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2003, 101, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, I.; Shams, F.; Lin, S.; Cioffi, M.D.B.; Liehr, T.; Al-rikabi, A.; Kuwana, C.; Srikulnath, K.; Higaki, Y.; Ezaz, T. Evolution of a Multiple Sex-Chromosome System by Three-Sequential Translocations among Potential Sex-Chromosomes in the Taiwanese Frog Odorrana swinhoana. Cells 2021, 10, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazoni, T.; Haddad, C.F.B.; Narimatsu, H.; Cabral-De-Mello, D.C.; Lyra, M.L.; Parise-Maltempi, P.P. More sex chromosomes than autosomes in the Amazonian frog Leptodactylus pentadactylus. Chromosoma 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Green, D.M. Cytogenetics of the endemic New Zealand frog, Leiopelma hochstetteri: Extraordinary supernumerary chromosome variation and a unique sex-chromosome system. Chromosoma 1988, 97, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillis, D.M.; Green, D.M. Evolutionary changes of heterogametic sex in the phylogenetic history of amphibians. J. Evol. Biol. 1990, 3, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Steinlein, C.; Bogart, J.P.; Feichtinger, W.; León, P.; La Marca, E.; Díaz, L.M.; Sanz, A.; Chen, S.H.; Hedges, S.B. The chromosomes of terraranan frogs: Insights into vertebrate cytogenetics. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2010, 130–131, 1–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, M.; Steinlein, C. Sex chromosomes, sex-linked genes, and sex determination in the vertebrate class amphibia. In Genes and Mechanisms in Vertebrate Sex Determination; Scherer, G., Schmid, M., Eds.; Birkhäuser Verlag: Basel, Switzerland, 2001; pp. 143–176. [Google Scholar]
- Ashman, T.-L.; Bachtrog, D.; Blackmon, H.; Goldberg, E.E.; Hahn, M.W.; Kirkpatrick, M.; Kitano, J.; Mank, J.E.; Mayrose, I.; Ming, R.; et al. Tree of sex: A database of sexual systems. Sci. Data 2014, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dournon, C.; Houillon, C. Démonstration génétique de l’inversion fonctionnelle du phénotype sexuel femelle sous l’action de la température d’élevage chez l’Amphibien Urodèle: Pleurodeles waltlii Michah. Reprod. Nutr. Dévelop. 1984, 24, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.Y.; Witschi, E. Genic Control and Hormonal Reversal of Sex Differentiation in Xenopus. Proc. Soc. Exp. Bioi. Med. 1956, 93, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikamo, K.; Witschi, E. Masculinization and Breeding of the WW Xenopus. Exp. XX 1964, 622–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, I.; Ohtani, H.; Fujitani, T. Unusual sex-ratios and developmental mortality in the rice frog Fejervarya kawamurai. Chromosom. Sci. 2015, 18, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, M.R.; Skelly, D.K.; Ezaz, T. Sex-linked markers in the North American green frog (Rana clamitans) developed using DArTseq provide early insight into sex chromosome evolution. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furman, B.L.S.; Evans, B.J. Sequential Turnovers of Sex Chromosomes in African Clawed Frogs (Xenopus) Suggest Some Genomic Regions are Good at Sex Determination. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2016, 6, 3625–3633. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, J.; Kodama, M.; Oike, A.; Matsuo, Y.; Min, M.-S.; Hasebe, T.; Ishizuya-Oka, A.; Kawakami, K.; Nakamura, M. Involvement of androgen receptor in sex determination in an amphibian species. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, Y.; Nishida, C.; Takagi, C.; Igawa, T.; Ueno, N.; Sumida, M.; Matsuda, Y. Extraordinary Diversity in the Origins of Sex Chromosomes in Anurans Inferred from Comparative Gene Mapping. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2015, 145, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, B.C.; Rodrigues, N.; Jansen van Rensburg, A.; Perrin, N. Phylogeography, more than elevation, accounts for sex chromosome differentiation in Swiss populations of the common frog (Rana temporaria). Evolution 2020, 74, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, N.; Merilä, J.; Patrelle, C.; Perrin, N. Geographic variation in sex-chromosome differentiation in the common frog (Rana temporaria). Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 3409–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, I. Sex Determination and Sex Chromosomes in Amphibia. Sex. Dev. 2017, 8526, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, I. An evolutionary witness: The frog Rana rugosa underwent change of heterogametic sex from XY male to ZW female. Sex. Dev. 2008, 1, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roco, Á.S.; Olmstead, A.W.; Degitz, S.J.; Amano, T.; Zimmerman, L.B.; Bullejos, M. Coexistence of Y, W, and Z sex chromosomes in Xenopus tropicalis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E4752–E4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oike, A.; Watanabe, K.; Min, M.-S.; Tojo, K.; Kumagai, M.; Kimoto, Y.; Yamashiro, T.; Matsuo, T.; Kodama, M.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. Origin of sex chromosomes in six groups of Rana rugosa frogs inferred from a sex-linked DNA marker. J. Exp. Zool. Part A Ecol. Integr. Physiol. 2017, 327, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, M.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, S.; Ohtani, H.; Sekiya, K.; Igarashi, T.; Hasegawa, Y.; Ichikawa, Y.; Miura, I. The prototype of sex chromosomes found in Korean populations of Rana rugosa. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2002, 99, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, M.; Lambert, M.; Ezaz, T.; Miura, I. Reconstruction of female heterogamety from admixture of XX-XY and ZZ-ZW sex-chromosome systems within a frog species. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishioka, M.; Hanada, H.; Miura, I.; Ryuzaki, M. Four kinds of sex chromosomes in Rana rugosa. Sci. Rep. Lab. Amphib. Biol. Hiroshima Univ. 1994, 13, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Uno, Y.; Nishida, C.; Yoshimoto, S.; Ito, M.; Oshima, Y.; Yokoyama, S.; Nakamura, M.; Matsuda, Y. Diversity in the origins of sex chromosomes in anurans inferred from comparative mapping of sexual differentiation genes for three species of the Raninae and Xenopodinae. Chromosom. Res. 2008, 16, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, I.; Ohtani, H.; Ogata, M. Independent degeneration of W and Y sex chromosomes in frog Rana rugosa. Chromosom. Res. 2012, 20, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furman, B.L.S.; Cauret, C.M.S.; Knytl, M.; Song, X.Y.; Premachandra, T.; Ofori-Boateng, C.; Jordan, D.C.; Horb, M.E.; Evans, B.J. A frog with three sex chromosomes that co-mingle together in nature: Xenopus tropicalis has a degenerate W and a Y that evolved from a Z chromosome. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1009121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, I.; Takase, M.; Nakamura, M. Sex determination and differentiation in amphibians. In Reproductive and Developmental Strategies; Kobayashi, K., Kitano, T., Iwao, Y., Kondo, M., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2018; pp. 349–366. ISBN 9784431566090. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, T.B. Sex determination and primary sex differentiation in amphibians: Genetic and developmental mechanisms. J. Exp. Zool. 1998, 281, 373–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M. The mechanism of sex determination in vertebrates-are sex steroids the key-factor? J. Exp. Zool. A Ecol. Genet. Physiol. 2010, 313, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M. Is a sex-determining gene(s) necessary for sex-determination in amphibians? Steroid hormones may be the key factor. Sex. Dev. 2013, 7, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggert, C. Sex determination: The amphibian models. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 2004, 44, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flament, S. Sex Reversal in Amphibians. Sex. Dev. 2016, 10, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, H.; Badawy, G.M.I.; Wallace, B.M.N. Amphibian sex determination and sex reversal. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1999, 55, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dournon, C.; Houillon, C.; Pieau, C. Temperature sex-reversal in amphibians and reptiles. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 1990, 34, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-H.; Zhao, W.-G.; Guo, Y.-M.; Xue, J.-H. Development of Sexual Gland and Influence of Temperature on Sexual Differentiation in Rana chensinensis. Zool. Res. 2001, 22, 351–356. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, Y.; Zheng, R.; Zheng, S.; Yan, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Hong, Y. Gonad differentiation and the effects of temperature on sex determination in Quasipaa spinosa. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 4809–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, L.; Yong-Long, Y.; Jun, L.D. Gonad differentiation and the effects of temperature on sex determination in the rice frog Rana limnocharis. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 54, 271–281. [Google Scholar]
- Kobel, H.R. Allopolyploid speciation. In The Biology of Xenopus; Kobel, H.R., Tinsley, R.C., Eds.; Clarendon Press: Wotton-under-Edge, UK, 1996; pp. 391–401. [Google Scholar]
- Sakata, N.; Tamori, Y.; Wakahara, M. P450 aromatase expression in the temperature-sensitive sexual differentiation of salamander (Hynobius retardatus) gonads. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2005, 49, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dournon, C.; Guillet, F.; Boucher, D.; Lacroix, J.C. Cytogenetic and genetic evidence of male sexual inversion by heat treatment in the newt Pleurodeles poireti. Chromosoma 1984, 90, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, H.; Wallace, B.M.N. Sex reversal of the newt Triturus cristatus reared at extreme temperatures. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2000, 44, 807–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-García, A.; Roco, Á.S.; Bullejos, M. Sex-differentiation in amphibians: Effect of temperature and its influence on sex reversal. Sex. Dev. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, M.R.; Tran, T.; Kilian, A.; Ezaz, T.; Skelly, D.K. Molecular evidence for sex reversal in wild populations of green frogs (Rana clamitans). PeerJ 2019, 2019, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alho, J.S.; Matsuba, C.; Merilä, J. Sex reversal and primary sex ratios in the common frog (Rana temporaria). Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 1763–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schartl, M. Sex chromosome evolution in non-mammalian vertebrates. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2004, 14, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Anderson, J.; Bertho, S.; Herpin, A.; Wilson, C.; Postlethwait, J.H.; Schartl, M.; Guiguen, Y. Vertebrate sex-determining genes play musical chairs. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2016, 339, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herpin, A.; Schartl, M. Plasticity of gene-regulatory networks controlling sex determination: Of masters, slaves, usual suspects, newcomers, and usurpators. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ito, M.; Mawaribuchi, S. Molecular Evolution of Genes Involved in Vertebrate Sex Determination. eLS 2013, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawaribuchi, S.; Yoshimoto, S.; Ohashi, S.; Takamatsu, N.; Ito, M. Molecular evolution of vertebrate sex-determining genes. Chromosom. Res. 2012, 20, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshimoto, S.; Okada, E.; Umemoto, H.; Tamura, K.; Uno, Y.; Nishida-umehara, C.; Matsuda, Y.; Takamatsu, N.; Shiba, T.; Ito, M. A W-linked DM-domain gene, DM-W, participates in primary ovary development in Xenopus laevis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2469–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mikamo, K.; Witschi, E. The mitotic chromosomes in Xenopus laevis (Daudin): Normal, sex reversed and female WW. Cytogenetics 1966, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tymowska, J. Polyploidy and Cytogenetic Variation in Frogs of the Genus Xenopus. In Amphibian Cytogenetics and Evolution; Green, D.M., Sessions, S.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 259–297. [Google Scholar]
- Session, A.M.; Uno, Y.; Kwon, T.; Chapman, J.A.; Toyoda, A.; Takahashi, S.; Fukui, A.; Hikosaka, A.; Suzuki, A.; Kondo, M.; et al. Genome evolution in the allotetraploid frog Xenopus laevis. Nature 2016, 538, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mawaribuchi, S.; Takahashi, S.; Wada, M.; Uno, Y.; Matsuda, Y.; Kondo, M.; Fukui, A.; Takamatsu, N.; Taira, M.; Ito, M. Sex chromosome differentiation and the W- and Z-specific loci in Xenopus laevis. Dev. Biol. 2017, 426, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bewick, A.J.; Anderson, D.W.; Evans, B.J. Evolution of the closely related, sex-related genes DM-W and DMRT1 in African clawed frogs (Xenopus). Evolution 2011, 65, 698–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, S.; Ikeda, N.; Izutsu, Y.; Shiba, T.; Takamatsu, N.; Ito, M. Opposite roles of DMRT1 and its W-linked paralogue, DM-W, in sexual dimorphism of Xenopus laevis: Implications of a ZZ/ZW-type sex-determining system. Development 2010, 137, 2519–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okada, E.; Yoshimoto, S.; Ikeda, N.; Kanda, H.; Tamura, K.; Shiba, T.; Takamatsu, N.; Ito, M. Xenopus W-linked DM-W induces Foxl2 and Cyp19 expression during ovary formation. Sex. Dev. 2009, 3, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobel, H.R.; Pasquier, L.D.; Tinsley, R.C. Natural hybridization and gene introgression between Xenopus gilli and Xenopus laevis laevis (Anura: Pipidae). J. Zool. 1981, 194, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picker, M.D. Hybridization and Habitat Selection in Xenopus gilli and Xenopus laevis in the South-Western Cape Province. Copeia 1985, 1985, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picker, M.D.; Harrison, J.; Wallace, D. Natural hybridization between Xenopus laevis laevis and X. gilli in the south-western Cape province, South Africa. In The Biology of Xenopus; Kobel, H.R., Tinsley, R.R., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1996; pp. 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Kobel, H.R.; Pasquier, L. Du Genetics of polyploid Xenopus. Trends Genet. 1986, 2, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, Y.; Nishida, C.; Oshima, Y.; Yokoyama, S.; Miura, I.; Matsuda, Y.; Nakamura, M. Comparative chromosome mapping of sex-linked genes and identification of sex chromosomal rearrangements in the Japanese wrinkled frog (Rana rugosa, Ranidae) with ZW and XY sex chromosome systems. Chromosom. Res. 2008, 16, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, S.; Oshima, Y.; Tokita, J.; Suda, M.; Shinozuka, T.; Nakamura, M. Androgen receptor of the frog Rana rugosa: Molecular cloning and its characterization. J. Exp. Zool. A Ecol. Genet. Physiol. 2009, 311, 796–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oike, A.; Kodama, M.; Yasumasu, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Ito, E.; Nakamura, M. Participation of androgen and its receptor in sex determination of an amphibian species. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, M.; Hanada, H. Sex of Reciprocal Hybrids between the Hamakita (XX-XY Type) Population and the Murakami (ZW-ZZ Type) Population of Rana rugosa. Sci. Rep. Lab. Amphib. Biol. Hiroshima Univ. 1994, 13, 35–50. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, M.; Ohta, S.; Steinlein, C.; Guttenbach, M. Chromosome banding in Amphibia XIX. Primitive ZW/ZZ sex chromosomes in Buergeria buergeri (Anura, Rhacophoridae). Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1993, 62, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, S.; Sumida, M.; Nishioka, M. Sex-determining mechanism in Buergeria buergeri (Anura, Rhacophoridae). III. Does the ZZW triploid frog become female or male? J. Exp. Zool. 1999, 283, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, N. Random sex determination: When developmental noise tips the sex balance. BioEssays 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witschi, E. Studies on sex differentiation and sex determination in amphibians. III. Rudimentary hermaphroditism and Y chromosome in Rana temporaria. J. Exp. Zool. 1929, 54, 157–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogielska, M.; Kotusz, A. Pattern and Rate of Ovary Differentiation with Reference to Somatic Development in Anuran Amphibians. J. Morphol. 2004, 259, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, J. Gonadal differentiation and development in the snouted treefrog, Scinax fuscovarius (Amphibia, Anura, Hylidae). J. Herpetol. 2015, 49, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramapurohit, N.P.; Shanbhag, B.A.; Saidapur, S.K. Pattern of gonadal sex differentiation, development, and onset of steroidogenesis in the frog, Rana curtipes. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2000, 119, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witschi, E. Studies on sex differentiation and sex determination in amphibians. IV. The geographical distribution of the sex races of the European grass frog (Rana temporaria, L.). A contribution to the problem of the evolution of sex. J. Exp. Zool. 1930, 56, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconi, R.; Dalpiaz, D.; Zaccanti, F. Ultrastructural aspects of gonadal morphogenesis in Bufo bufo (Amphibia Anura) 1. Sex differentiation. J. Exp. Zool. A. Comp. Exp. Biol. 2004, 301, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogielska, M. The Undifferentiated Amphibian Gonad. In Reproduction of Amphibians; Ogielska, M., Ed.; Science Publishers: Rawalpindi, Pakistan, 2009; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Tanimura, A.; Iwasawa, H. Origin of somatic cells and histogenesis in the primordial gonad of the Japanese tree frog Rhacophorus arboreus. Anat. Embryol. 1989, 180, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconi, R.; Petrini, S.; Quaglia, A.; Zaccanti, F. Fine structure of undifferentiated gonads in Rana dalmatina tadpoles. Ital. J. Zool. 2001, 68, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, H. Juvenile Hermaphroditism in the Zebrafish, Brachydanio rerio. Bull. Fac. Fish. Hokkaido Univ. 1977, 28, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzoni, T.S.; Grier, H.J.; Quagio-Grassiotto, I. The Basement Membrane and the Sex Establishment in the Juvenile Hermaphroditism During Gonadal Differentiation of the Gymnocorymbus ternetzi (Teleostei: Characiformes: Characidae). Anat. Rec. 2015, 298, 1984–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, D.; Yamashita, M.; Kitano, T.; Iguchi, T. Oocyte apoptosis during the transition from ovary-like tissue to testes during sex differentiation of juvenile zebrafish. J. Exp. Biol. 2002, 205, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.W.; Pan, Y.J.; Wang, Y.W.; Tong, S.K.; Chung, B. Changes in the morphology and gene expression of developing zebrafish gonads. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2018, 265, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, D.; Yamashita, M.; Kitano, T.; Iguchi, T. An aromatase inhibitor or high water temperature induce oocyte apoptosis and depletion of P450 aromatase activity in the gonads of genetic female zebrafish during sex-reversal. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2004, 137, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.D.; Drum, M.; Bachvarova, R.F.; Masi, T.; White, M.E.; Crother, B.I. Evolution of predetermined germ cells in vertebrate embryos: Implications for macroevolution. Evol. Dev. 2003, 5, 414–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flament, S.A.; Chardard, D.; Chesnel, A.; Dumond, H.G.A. Sex Determination and Sexual Differentiation in Amphibians. Horm. Reprod. Vertebr. 2011, 2, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, D.W.; King, M. Lou Germ plasm and molecular determinants of germ cell fate. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2000, 50, 155–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakahara, M. Primordial germ cell development: Is the urodele pattern closer to mammals than to anurans? Int. J. Dev. Biol. 1996, 40, 653–659. [Google Scholar]
- Dumond, H.; Kuntz, S.; Chesnel, A.; Ko, C.; Wallacides, A.; Chardard, D.; Flament, S. Sexual development of the urodele amphibian Pleurodeles waltl. Sex. Dev. 2008, 2, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjubault, E.; Exbrayat, J. Development of Gonads. In Reproductive Biology and Phylogeny of Gymnophiona (Caecilians); Exbrayat, J.-M., Ed.; Science Publishers: Rawalpindi, Pakistan, 2006; Volume 9, pp. 291–302. [Google Scholar]
- Whittle, C.A.; Extavour, C.G. Causes and evolutionary consequences of primordial germ-cell specification mode in metazoans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 5784–5791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez, K. Sex differentiation and early gonadal development in Bombina orientalis (Anura: Discoglossidae). J. Morphol. 1989, 199, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, C.C.; Heasman, J. The formation of the gonadal ridge in Xenopus laevis I. A light and transmission electron microscope study. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 1976, 35, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Piprek, R.P.; Pecio, A.; Szymura, J.M. Differentiation and development of gonads in the yellow-bellied toad, Bombina variegata L., 1758 (Amphibia: Anura: Bombinatoridae). Zoolog. Sci. 2010, 27, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piprek, R.P.; Pecio, A.; Kubiak, J.Z.; Szymura, J.M. Differential effects of busulfan on gonadal development in five divergent anuran species. Repod. Toxicol. 2012, 34, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wylie, C.C.; Bancroft, M.; Heasman, J. The formation of the gonadal ridge in Xenopus laevis. II. A scanning electron microscope study. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 1976, 35, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roco, Á.S.; Ruiz García, A.; Bullejos, M. Interaction between sex-determining genes from two species: Clues from Xenopus hybrids. Philos. Trans. B 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Asaad, I.; Dumond, H.; Chardard, D.; Chesnel, A.; Flament, S. Busulfan-mediated germ cell depletion does not alter gonad differentiation in the urodele amphibian Pleurodeles waltl. Sex. Dev. 2012, 6, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFalco, T.; Capel, B. Gonad morphogenesis in vertebrates: Divergent means to a convergent end. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2009, 25, 457–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanimura, A.; Iwasawa, H. Ultrastructural Observations on the Origin and Differentiation of Somatic Cells during Gonadal Development in the Frog Rana nigromaculata. Dev. Growth Differ. 1988, 30, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Cruz, E.; Moreno-Mendoza, N.; Zambrano, L.; Villagrán-SantaCruz, M. Development and gonadal sex differentiation in the neotenic urodele: Ambystoma mexicanum. Zoomorphology 2017, 136, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piprek, R.P.; Kloc, M.; Tassan, J.-P.; Kubiak, J.Z. Development of Xenopus laevis bipotential gonads into testis or ovary is driven by sex-specific cell-cell interactions, proliferation rate, cell migration and deposition of extracellular matrix. Dev. Biol. 2017, 432, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haczkiewicz, K.; Ogielska, M. Gonadal sex differentiation in frogs: How testes become shorter than ovaries. Zoolog. Sci. 2013, 30, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawaribuchi, S.; Musashijima, M.; Wada, M.; Izutsu, Y.; Kurakata, E.; Park, M.K.; Takamatsu, N.; Ito, M. Molecular evolution of two distinct dmrt1 promoters for germ and somatic cells in vertebrate gonads. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanimura, A.; Iwasawa, H. Proliferative activity of somatic cells during gonadal development in the Japanese pond frog, Rana nigromaculata. J. Exp. Zool. 1991, 259, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant-Larios, H.; Villalpando, I. Ultrastructural events during early gonadal development in Rana pipiens and Xenopus laevis. Anat. Rec. 1981, 199, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witschi, E. Studies on sex differentiation and sex determination in amphibians. I. Development and sexual differentiation of the gonads of Rana sylvatica. J. Exp. Zool. 1929, 52, 235–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwkoop, P.D.; Faber, J. Normal Table of Xenopus Laevis (Daudin): A Systematical and Chronological Survey of the Development from the Fertilized Egg Till the End of Metamorphosis; Garland Publishing, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Schmahl, J.; Eicher, E.M.; Washburn, L.L.; Capel, B. Sry induces cell proliferation in the mouse gonad. Development 2000, 127, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, C.A.; Joss, J.M.P. Sertoli cell differentiation and gonadogenesis in Alligator mississippiensis. J. Exp. Zool. 1994, 270, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.H.-C.; DiNapoli, L.; Capel, B. Cellular mechanisms of sex determination in the red-eared slider turtle, Trachemys scripta. Mech. Dev. 2004, 121, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmahl, J.; Yao, H.H.; Pierucci-Alves, F.; Capel, B. Colocalization of WT1 and cell proliferation reveals conserved mechanisms in temperature-dependent sex determination. Genesis 2003, 35, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saotome, K.; Isomura, T.; Seki, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Nakamura, M. Structural changes in gonadal basement membranes during sex differentiation in the frog Rana rugosa. J. Exp. Zool. A Ecol. Genet. Physiol. 2010, 313, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dournon, C.; Durand, D.; Demassieux, C.; Lesimple, M. Differential germ cell proliferation in the salamander Pleurodeles waltl: Controls by sexual genotype and by thermal epigenetic factor before differentiation of sexual phenotype of gonads. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 1990, 34, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilmann, C.; Capel, B. Mesonephric cell migration induces testis cord formation and Sertoli cell differentiation in the mammalian gonad. Development 1999, 126, 2883–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Combes, A.N.; Wilhelm, D.; Davidson, T.; Dejana, E.; Harley, V.R.; Sinclair, A.; Koopman, P.A. Endothelial cell migration directs testis cord formation. Dev. Biol. 2009, 326, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno-Mendoza, N.; Harley, V.R.; Merchant-Larios, H. Temperature regulates SOX9 expression in cultured gonads of Lepidochelys olivacea, a species with temperature sex determination. Dev. Biol. 2001, 229, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, C.A.; McClive, P.J.; Hudson, Q.; Sinclair, A.H. Male-specific cell migration into the developing gonad is a conserved process involving PDGF signalling. Dev. Biol. 2005, 284, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, C.A.; Sinclair, A.H. Sex determination: Insights from the chicken. BioEssays 2004, 26, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallacides, A.; Chesnel, A.; Chardard, D.; Flament, S.; Dumond, H. Evidence for a conserved role of retinoic acid in urodele amphibian meiosis onset. Dev. Dyn. 2009, 238, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, J.; Barrasso, D.A.; Agostini, M.G.; Quinzio, S. Vocal sac development and accelerated sexual maturity in the lesser swimming frog, Pseudis minuta (Anura, Hylidae). Zoology 2016, 119, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downie, J.R.; Sams, K.; Walsh, P.T. The paradoxical frog Pseudis paradoxa: Larval anatomical characteristics, including gonadal maturation. Herpetol. J. 2009, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Griswold, M.D. The central role of Sertoli cells in spermatogenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 1998, 9, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.Y.; Seddon, A.P.; Meister, A.; Risley, M.S. Spermatogenic cell-somatic cell interactions are required for maintenance of spermatogenic cell glutathione. Biol. Reprod. 1989, 40, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouma, J.; Harbor, B. Sertoli Cell Biology in Fishes and Amphibians. In Sertoli Cell Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- França, L.R.; Hess, R.A.; Dufour, J.M.; Hofmann, M.C.; Griswold, M.D. The Sertoli cell: One hundred fifty years of beauty and plasticity. Andrology 2016, 4, 189–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castañeda Cortés, D.C.; Langlois, V.S.; Fernandino, J.I. Crossover of the hypothalamic pituitary-adrenal/interrenal, -thyroid, and -gonadal axes in testicular development. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rozenblut-Kościsty, B.; Piprek, R.P.; Pecio, A.; Bartmańska, J.; Szymura, J.M.; Ogielska, M. The structure of spermatogenic cysts and number of Sertoli cells in the testes of Bombina bombina and Bombina variegata (Bombinatoridae, Anura, Amphibia). Zoomorphology 2017, 136, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haczkiewicz, K.; Rozenblut-Kościsty, B.; Ogielska, M. Prespermatogenesis and early spermatogenesis in frogs. Zoology 2017, 122, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holstein, A.-F.; Schulze, W.; Davidoff, M. Understanding spermatogenesis is a prerequisite for treatment. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2003, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Culty, M. Gonocytes, from the fifties to the present: Is there a reason to change the name? Biol. Reprod. 2013, 89, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akat, E. Characterization of testicular histology and spermatogenesis in the Levantine frog, Pelophylax bedriagae (Amphibia: Anura: Ranidae). Ann. Limnol. 2020, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogielska, M.; Bartmańska, J. Development of testes and differentiation of germ cells in water frogs of the Rana esculenta—Complex (Amphibia, Anura). Amphib. Reptil. 1999, 20, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelmeiser, J.; Greven, H.; Bergmann, M. The Immature Part of the Testis in Salamandra salamandra (L.) (Amphibia, Urodela). Arch. Histol. Jpn. 1983, 46, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Báo, S.N.; Dalton, G.C.; de Oliveira, S.F. Spermiogenesis in Odontophrynus cultripes (Amphibia, Anura, Leptodactylidae): Ultrastructural and cytochemical studies of proteins using E-PTA. J. Morphol. 1991, 207, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, M.C.; Gracia-Fernández, S. Sequence of Germ Cells Differentiation during Spermiogenesis of the Amphibian Urodele Ambystoma dumerilii. Spermatozoa Facts Perspect. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pierantoni, R.; Cobellis, G.; Meccariello, R.; Palmiero, C.; Fienga, G.; Minucci, S.; Fasano, S. The amphibian testis as model to study germ cell progression during spermatogenesis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 132, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudney, J. Spermatogenesis in nonmammalian vertebrates. Microsc. Res. Tech. 1995, 32, 459–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, A.F.A.; França, L.R.; Hess, R.A.; Costa, G.M.J. Sertoli cells are capable of proliferation into adulthood in the transition region between the seminiferous tubules and the rete testis in Wistar rats. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 2486–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- França, L.R.; Nóbrega, R.H.; Morais, R.D.V.S.; De Castro Assis, L.H.; Schulz, R.W. Sertoli cell structure and function in anamniote vertebrates. In Sertoli Cell Biology; Griswold, M.D., Ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 385–407. ISBN 9780124170476. [Google Scholar]
- Matta, S.L.P.; Vilela, D.A.R.; Godinho, H.P.; França, L.R. The goitrogen 6-n-propyl-2-thiouracil (PTU) given during testis development increases Sertoli and germ cell numbers per cyst in fish: The tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) model. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, D.A.R.; Silva, S.G.B.; Peixoto, M.T.D.; Godinho, H.P.; França, L.R. Spermatogenesis in teleost: Insights from the Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) model. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2003, 28, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, R.W.; Menting, S.; Bogerd, J.; França, L.R.; Vilela, D.A.R.; Godinho, H.P. Sertoli cell proliferation in the adult testis—Evidence from two fish species belonging to different orders. Biol. Reprod. 2005, 73, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leal, M.C.; Cardoso, E.R.; Nóbrega, R.H.; Batlouni, S.R.; Bogerd, J.; França, L.R.; Schulz, R.W. Histological and stereological evaluation of zebrafish (Danio rerio) spermatogenesis with an emphasis on spermatogonial generations. Biol. Reprod. 2009, 81, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flament, S.; Dumond, H.; Chardard, D.; Chesnel, A. Lifelong testicular differentiation in Pleurodeles waltl (Amphibia, Caudata). Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2009, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falconi, R.; Dalpiaz, D.; Zaccanti, F. Morphological aspects of gonadal morphogenesis in Bufo bufo (Amphibia Anura): Bidder’s organ differentiation. Anat. Rec. 2007, 290, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piprek, R.P.; Kloc, M.; Kubiak, J.Z. Bidder’s organ—Structure, development and function. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2014, 58, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abramyan, J.; Wilhelm, D.; Koopman, P.A. Molecular characterization of the Bidder’s organ in the cane toad (Bufo marinus). J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2010, 314, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, C.F.; Carvalho-e-Silva, S.P.; De Brito-Gitirana, L. Bidder’s organ of Bufo ictericus: A light and electron microscopy analysis. Micron 2002, 33, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancak-Roessler, M.K.; Norris, D.O. The effects of orchidectomy and gonadotropins on steroidogenesis and oogenesis in Bidder’s organs of the toad Bufo woodhousii. J. Exp. Zool. 1991, 260, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silberschmidt Freitas, J.; Franco-Belussi, L.; De Oliveira, C. Morphological and histochemical studies of Bidder’s organ in Rhinella schneideri (Amphibia: Anura) males. Ital. J. Zool. 2015, 82, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, F.D.; Del Pino, E.M.; Krohne, G. Bidder’s organ in the toad Bufo marinus: Effects of orchidectomy on the morphology and expression of lamina-associated polypeptide 2. Dev. Growth Differ. 2002, 44, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaccanti, F.; Tognato, G. Effects of different doses of diethylstilbestrol dipropionate on the bidder’s organ of intact or orchiectomized adult males of Bufo bufo (L). Monit. Zool. Ital. Ital. J. Zool. 1976, 10, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrini, S.; Zaccanti, F. The Effects of Aromatase and 5 a-Reductase Inhibitors, Antiandrogen, and Sex Steroids on Bidder’s Organs Development and Gonadal Differentiation in Bufo bufo Tadpoles. J. Exp. Zool. 1998, 259, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms-Marburg, W. Untersuchungen über das Biddersche Organ der männlichen und weiblichen Kröten. I. Mitteilung: Die Morphologie des Bidderschen Organes. Zeitschrift Anatomie Entwicklungsgeschichte 1921, 62, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piprek, R.P.; Pecio, A.; Laskowska-Kaszub, K.; Kloc, M.; Kubiak, J.Z.; Szymura, J.M. Retinoic acid homeostasis regulates meiotic entry in developing anuran gonads and in Bidder’s organ through Raldh2 and Cyp26b1 proteins. Mech. Dev. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaia, M.F.; Regueira, E.; Sassone, A.G.; Volonteri, M.C.; Ceballos, N.R. The Bidder’s organ of the toad Rhinella arenarum (Amphibia, Anura). Presence of steroidogenic enzymes. J. Exp. Zool. Part A Ecol. Genet. Physiol. 2011, 315A, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stévant, I.; Papaioannou, M.D.; Nef, S. A brief history of sex determination. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 468, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estermann, M.A.; Williams, S.; Hirst, C.E.; Roly, Z.Y.; Serralbo, O.; Adhikari, D.; Powell, D.; Major, A.T.; Smith, C.A. Insights into Gonadal Sex Differentiation Provided by Single-Cell Transcriptomics in the Chicken Embryo. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwinski, M.; Natarajan, A.; Barske, L.; Looger, L.L.; Capel, B. A timecourse analysis of systemic and gonadal effects of temperature on sexual development of the red-eared slider turtle Trachemys scripta elegans. Dev. Biol. 2016, 420, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsu, R.; Miyagawa, S.; Kohno, S.; Parrott, B.B.; Yamaguchi, K.; Ogino, Y.; Miyakawa, H.; Lowers, R.H.; Shigenobu, S.; Guillette, L.J.; et al. RNA-seq analysis of the gonadal transcriptome during Alligator mississippiensis temperature-dependent sex determination and differentiation. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piprek, R.P.; Damulewicz, M.; Tassan, J.P.; Kloc, M.; Kubiak, J.Z. Transcriptome profiling reveals male- and female-specific gene expression pattern and novel gene candidates for the control of sex determination and gonad development in Xenopus laevis. Dev. Genes Evol. 2019, 229, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tao, W.; Chen, J.; Tan, D.; Yang, J.; Sun, L.; Wei, J.; Conte, M.A.; Kocher, T.D.; Wang, D. Transcriptome display during tilapia sex determination and differentiation as revealed by RNA-Seq analysis. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Capel, B. Vertebrate sex determination: Evolutionary plasticity of a fundamental switch. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.H.C.; Capel, B. Temperature, genes, and sex: A comparative view of sex determination in Trachemys scripta and Mus musculus. J. Biochem. 2005, 138, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biscotti, M.A.; Carducci, F.; Barucca, M.; Gerdol, M.; Pallavicini, A.; Schartl, M.; Canapa, A.; Adolfi, M.C. The transcriptome of the newt Cynops orientalis provides new insights into evolution and function of sexual gene networks in sarcopterygians. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, D.; Bull, J.J. Mode and tempo in environmental sex determination in vertebrates. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2009, 20, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujitani, K.; Otomo, A.; Wada, M.; Takamatsu, N.; Ito, M. Sexually dimorphic expression of Dmrt1 and γH2AX in germ stem cells during gonadal development in Xenopus laevis. FEBS Open Bio 2016, 6, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piprek, R.P.; Damulewicz, M.; Kloc, M.; Kubiak, J.Z. Transcriptome analysis identifies genes involved in sex determination and development of Xenopus laevis gonads. Differentiation 2018, 100, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, I.; Ohtani, H.; Ogata, M.; Ezaz, T. Evolutionary Changes in Sensitivity to Hormonally Induced Gonadal Sex Reversal in a Frog Species. Sex. Dev. 2016, 10, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piprek, R.P.; Kolasa, M.; Podkowa, D.; Kloc, M.; Kubiak, J.Z. Transcriptional profiling validates involvement of extracellular matrix and proteinases genes in mouse gonad development. Mech. Dev. 2018, 149, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haselman, J.T.; Olmstead, A.W.; Degitz, S.J. Global gene expression during early differentiation of Xenopus (Silurana) tropicalis gonad tissues. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2016, 214, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piprek, R.P.; Pecio, A.; Laskowska-Kaszub, K.; Kubiak, J.Z.; Szymura, J.M. Sexual dimorphism of AMH, DMRT1 and RSPO1 localization in the developing gonads of six anuran species. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2013, 57, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Jamil, A.; Kanhoush, R.; Magre, S.; Boizet-Bonhoure, B.; Penrad-Mobayed, M. Sex-specific expression of SOX9 during gonadogenesis in the amphibian Xenopus tropicalis. Dev. Dyn. 2008, 237, 2996–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumond, H.; Al-Asaad, I.; Chesnel, A.; Chardard, D.; Boizet-Bonhoure, B.; Flament, S.; Kuntz, S. Temporal and spatial SOX9 expression patterns in the course of gonad development of the caudate amphibian Pleurodeles waltl. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2011, 316B, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Asaad, I.; Chardard, D.; Di Clemente, N.; Picard, J.Y.; Dumond, H.; Chesnel, A.; Flament, S. Müllerian inhibiting substance in the caudate amphibian Pleurodeles waltl. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 3931–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuntz, S.; Chesnel, A.; Duterque-Coquillaud, M.; Grillier-Vuissoz, I.; Callier, M.; Dournon, C.; Flament, S.; Chardard, D. Differential expression of P450 aromatase during gonadal sex differentiation and sex reversal of the newt Pleurodeles waltl. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 84, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osawa, N.; Oshima, Y.; Nakamura, M. Molecular cloning of Dmrt1 and its expression in the gonad of Xenopus. Zoolog. Sci. 2005, 22, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, K.; Takase, M.; Nakamura, M. The Dmrt1 expression in sex-reversed gonads of amphibians. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2002, 127, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sakata, N.; Miyazaki, K.; Wakahara, M. Up-regulation of P450arom and down-regulation of Dmrt-1 genes in the temperature-dependent sex reversal from genetic males to phenotypic females in a salamander. Dev. Genes Evol. 2006, 216, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mawaribuchi, S.; Ikeda, N.; Fujitani, K.; Ito, Y.; Onuma, Y.; Komiya, T.; Takamatsu, N.; Ito, M. Cell-mass structures expressing the aromatase gene Cyp19a1 lead to ovarian cavities in Xenopus laevis. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 3996–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruo, K.; Suda, M.; Yokoyama, S.; Oshima, Y.; Nakamura, M. Steroidogenic gene expression during sex determination in the frog Rana rugosa. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2008, 158, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, I.; Kitamoto, H.; Koizumi, Y.; Ogata, M.; Sasaki, K. An X-linked body color gene of the frog Rana rugosa and its application to the molecular analysis of gonadal sex differentiation. Sex. Dev. 2011, 5, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, N.; Maruo, K.; Haraguchi, S.; Uno, Y.; Oshima, Y.; Tsutsui, K.; Matsuda, Y.; Do Rego, J.L.; Pelletier, G.; Vaudry, H.; et al. Immunohistochemical detection and biological activities of CYP17 (P450c17) in the indifferent gonad of the frog Rana rugosa. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 112, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwade, R.; Maruo, K.; Okada, G.; Nakamura, M. Elevated expression of P450c17 (CYP17) during testicular formation in the frog. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2008, 155, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, D.B. Sexual differentiation in Xenopus laevis. In The Biology of Xenopus; Tiinsely, R., Kobel, H.R., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1996; pp. 143–176. [Google Scholar]
- Oshima, Y.; Uno, Y.; Matsuda, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Nakamura, M. Molecular cloning and gene expression of Foxl2 in the frog Rana rugosa. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2008, 159, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Oatley, J.; Bardwell, V.J.; Zarkower, D. DMRT1 Is Required for Mouse Spermatogonial Stem Cell Maintenance and Replenishment. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dranow, D.B.; Tucker, R.P.; Draper, B.W. Germ cells are required to maintain a stable sexual phenotype in adult zebrafish. Dev. Biol. 2013, 376, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dranow, D.B.; Hu, K.; Bird, A.M.; Lawry, S.T.; Adams, M.T.; Sanchez, A.; Amatruda, J.F.; Draper, B.W. Bmp15 Is an Oocyte-Produced Signal Required for Maintenance of the Adult Female Sexual Phenotype in Zebrafish. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bögi, C.; Levy, G.; Lutz, I.; Kloas, W. Functional genomics and sexual differentiation in amphibians. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 133, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrish, B.C.; Sinclair, A.H. Vertebrate sex determination: Many means to an end. Reproduction 2002, 124, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takase, M.; Noguchi, S.; Nakamura, M. Two Sox9 messenger RNA isoforms: Isolation of cDNAs and their expression during gonadal development in the frog Rana rugosa. FEBS Lett. 2000, 466, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abramyan, J.; Feng, C.W.; Koopman, P.A. Cloning and expression of candidate sexual development genes in the cane toad (Bufo marinus). Dev. Dyn. 2009, 238, 2430–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Watakabe, I.; Nishimura, T.; Toyoda, A.; Taniguchi, Y.; Tanaka, M. Analysis of medaka sox9 orthologue reveals a conserved role in germ cell maintenance. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santa Barbara, P.; Bonneaud, N.; Boizet, B.; Desclozeaux, M.; Moniot, B.; Sudbeck, P.; Scherer, G.; Poulat, F.; Berta, P. Direct interaction of SRY-related protein SOX9 and steroidogenic factor 1 regulates transcription of the human anti-Müllerian hormone gene. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 6653–6665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oreal, E.; Pieau, C.; Mattei, M.G.; Josso, N.; Picard, J.-Y.; Carré-Eusèbe, D.; Magre, S. Early expression of AMH in chicken embryonic gonads precedes testicular SOX9 expression. Dev. Dyn. 1998, 212, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, E.; Mattsson, A.; Goldstone, J.; Berg, C. Sex-dependent expression of anti-Müllerian hormone (amh) and amh receptor 2 during sex organ differentiation and characterization of the Müllerian duct development in Xenopus tropicalis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2016, 229, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, M.; Suda, M.; Sakamoto, D.; Iwasaki, T.; Matsuo, Y.; Uno, Y.; Matsuda, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Maekawa, S.; Katsu, Y.; et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) from the Japanese wrinkled frog, Rana rugosa. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 1914–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morinaga, C.; Saito, D.; Nakamura, S.; Sasaki, T.; Asakawa, S.; Shimizu, N. The hotei mutation of medaka in the anti-Müllerian hormone receptor causes the dysregulation of germ cell and sexual development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 9691–9696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shiraishi, E.; Yoshinaga, N.; Miura, T.; Yokoi, H.; Wakamatsu, Y.; Abe, S.I.; Kitano, T. Müllerian inhibiting substance is required for germ cell proliferation during early gonadal differentiation in medaka (Oryzias latipes). Endocrinology 2008, 149, 1813–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, S.; Watakabe, I.; Nishimura, T.; Picard, J.Y.; Toyoda, A.; Taniguchi, Y.; di Clemente, N.; Tanaka, M. Hyperproliferation of mitotically active germ cells due to defective anti-Müllerian hormone signaling mediates sex reversal in medaka. Development 2012, 139, 2283–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dumond, H.; Maufroid, J.-P.; Ko, C.-I.; Chardard, D.; Chesnel, A.; Flament, S.A. Freemartin in the Amphibian Pleurodeles waltl: Parabiosis Between Individuals From Opposite Sex Triggers Both Germ and Somatic Cells Alterations During Female Gonad Development. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2008, 75, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolfi, M.C.; Nakajima, R.T.; Nóbrega, R.H.; Schartl, M. Intersex, Hermaphroditism, and Gonadal Plasticity in Vertebrates: Evolution of the Müllerian Duct and Amh/Amhr2 Signaling. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2019, 7, 149–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roco, Á.S.; Ruiz-García, A.; Bullejos, M. Testis Development and Differentiation in Amphibians. Genes 2021, 12, 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12040578
Roco ÁS, Ruiz-García A, Bullejos M. Testis Development and Differentiation in Amphibians. Genes. 2021; 12(4):578. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12040578
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoco, Álvaro S., Adrián Ruiz-García, and Mónica Bullejos. 2021. "Testis Development and Differentiation in Amphibians" Genes 12, no. 4: 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12040578
APA StyleRoco, Á. S., Ruiz-García, A., & Bullejos, M. (2021). Testis Development and Differentiation in Amphibians. Genes, 12(4), 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12040578